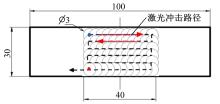
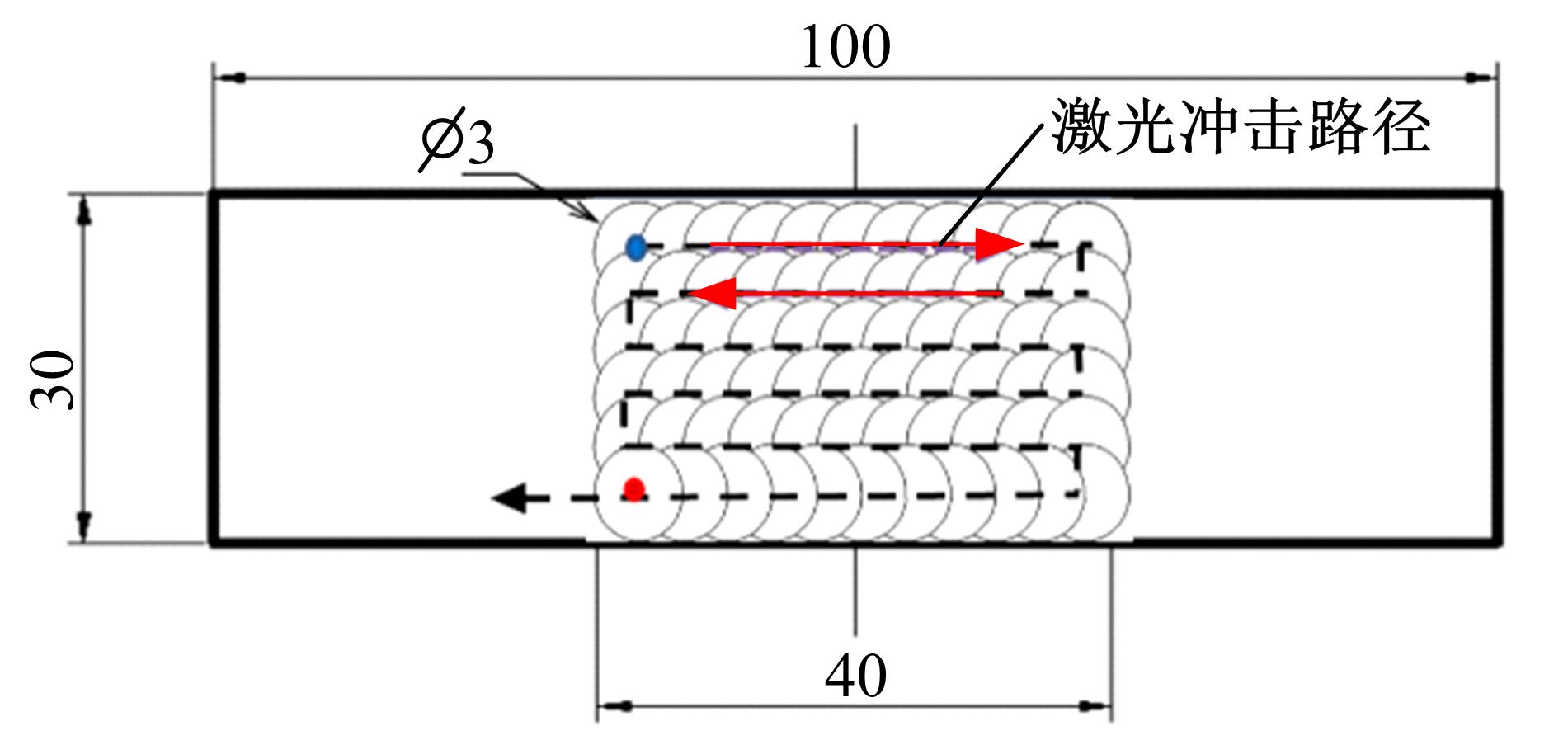
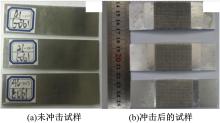
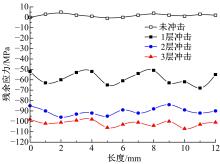
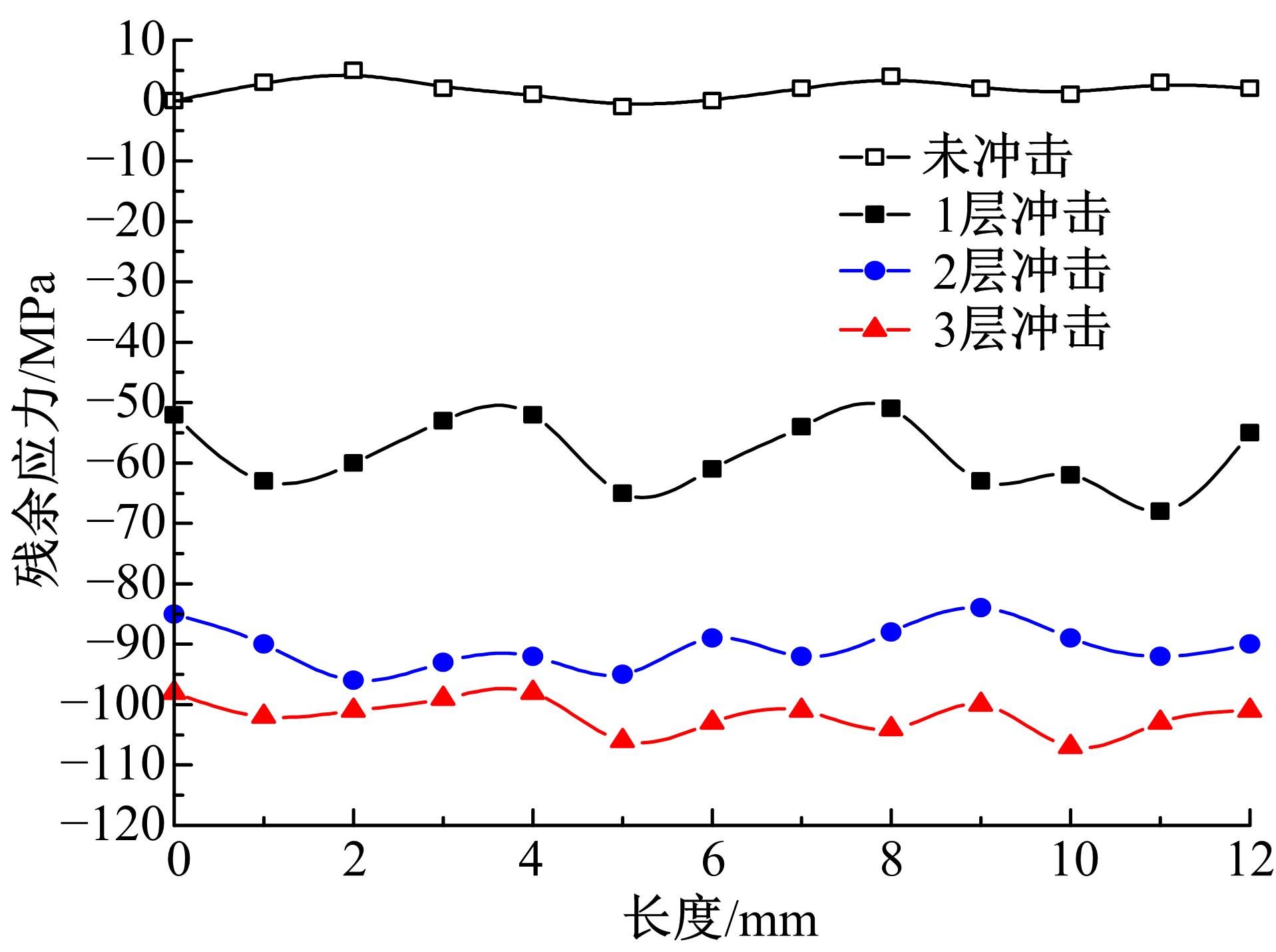
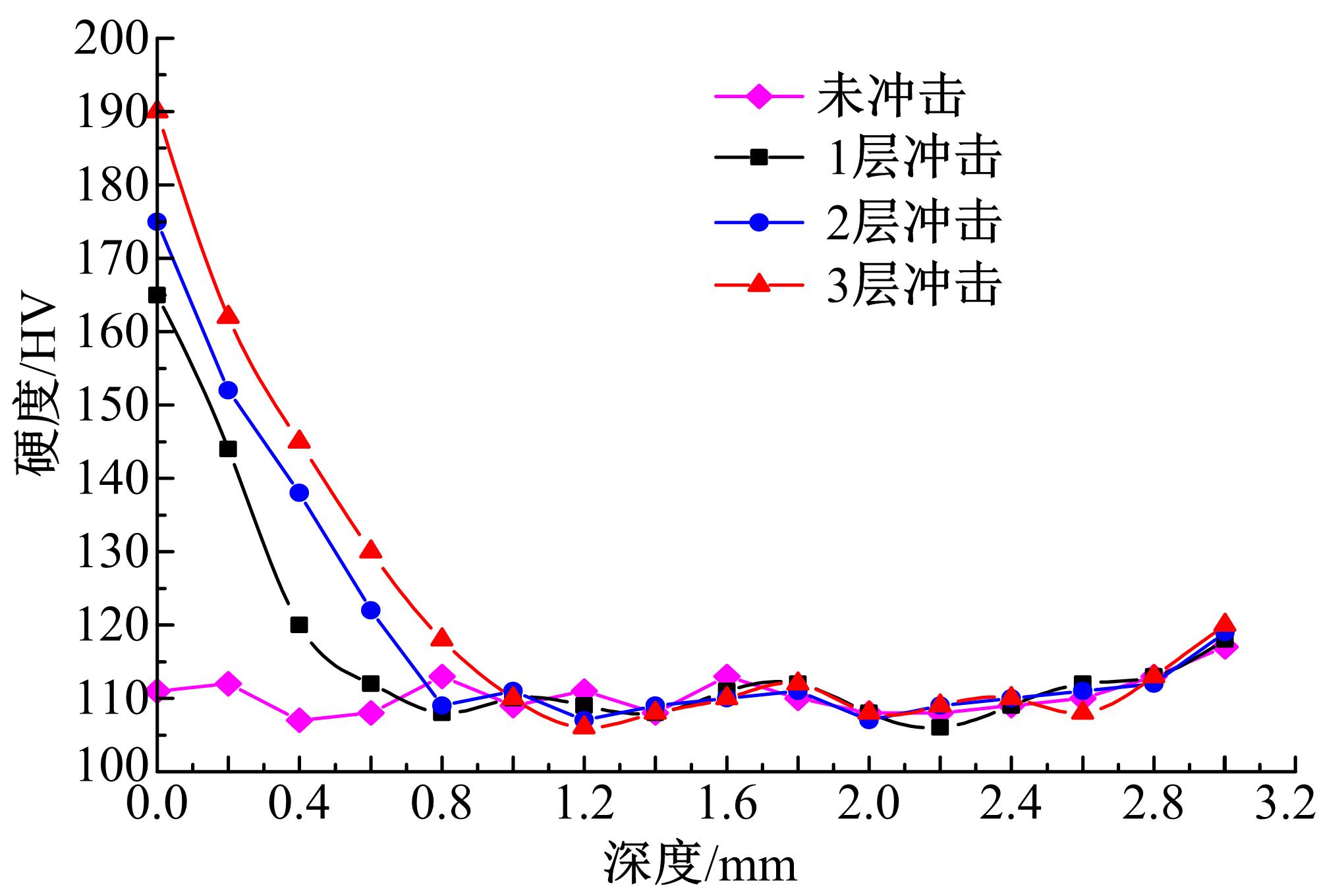
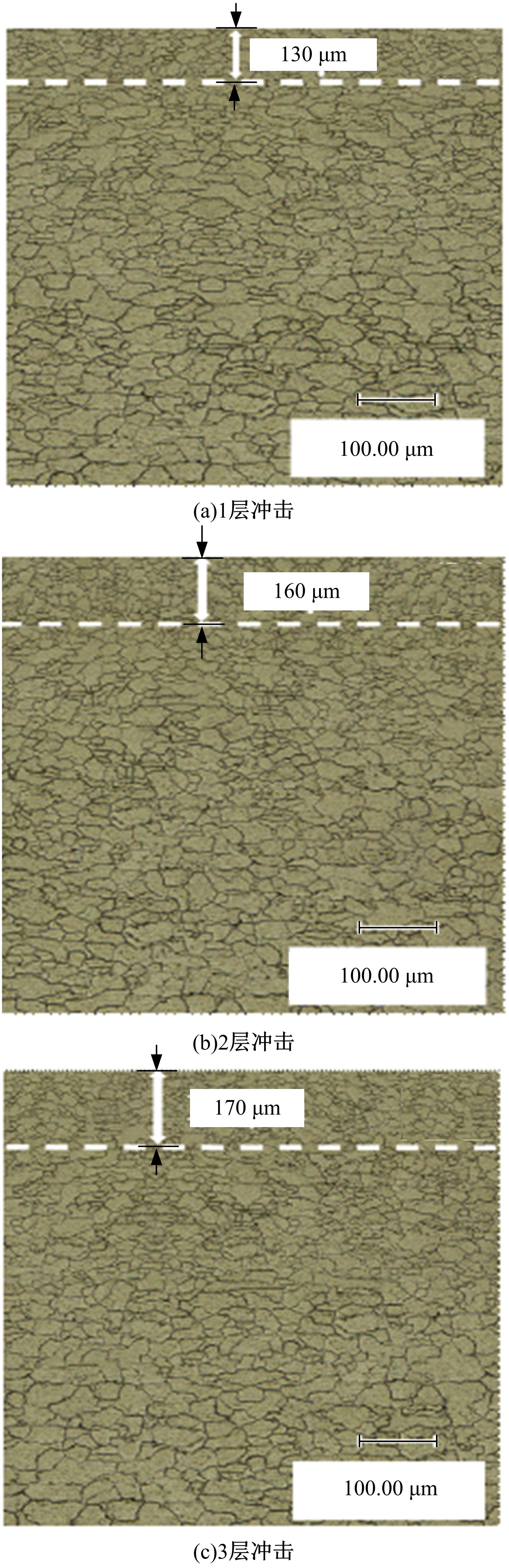
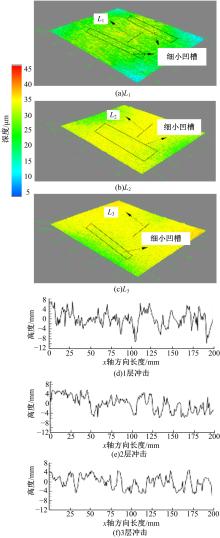
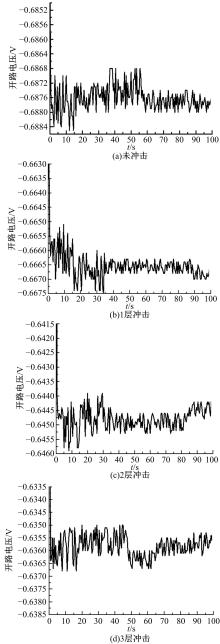
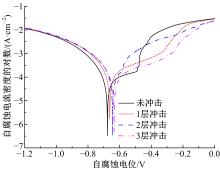
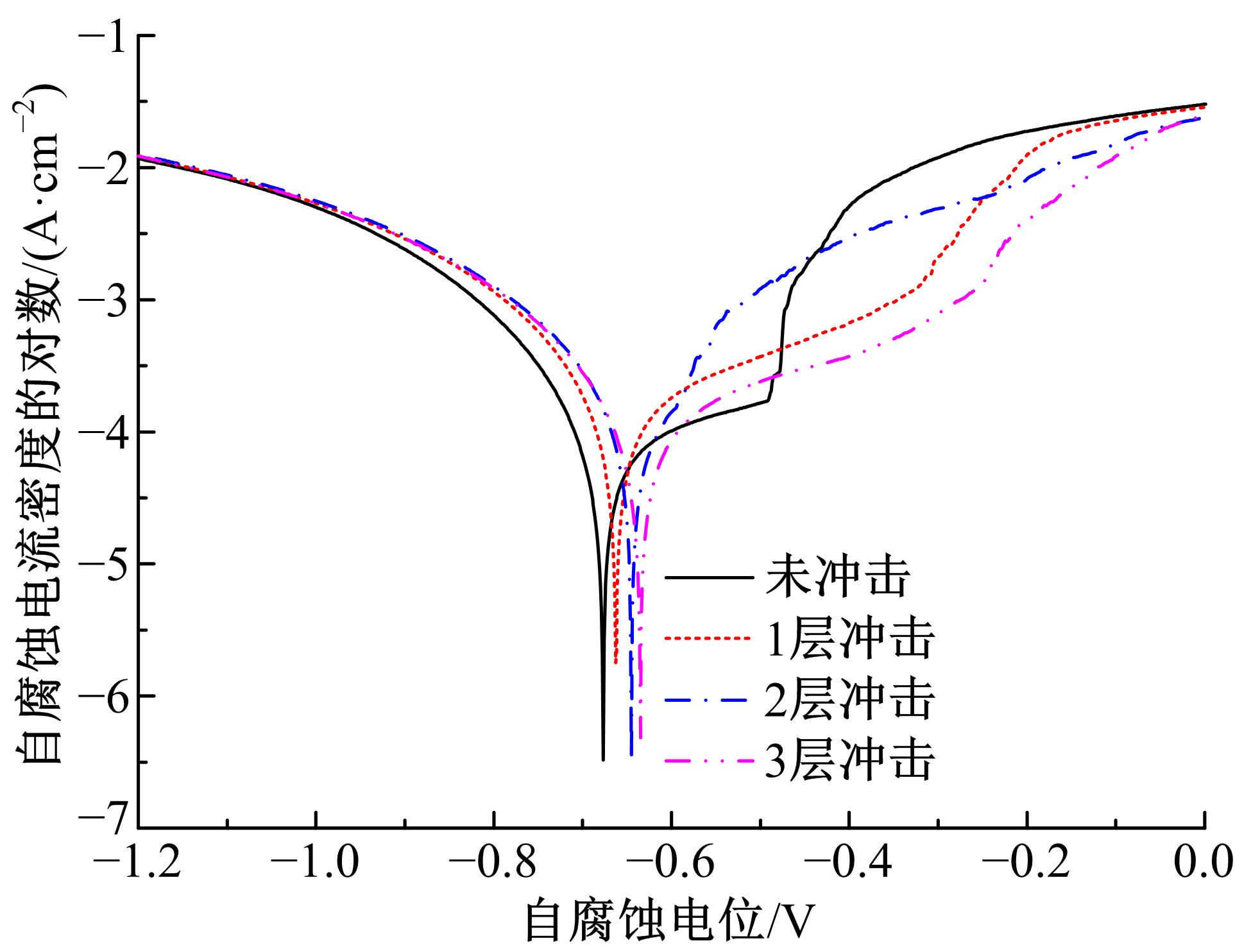
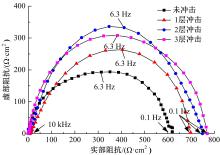
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 842-849.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180112
Previous Articles Next Articles
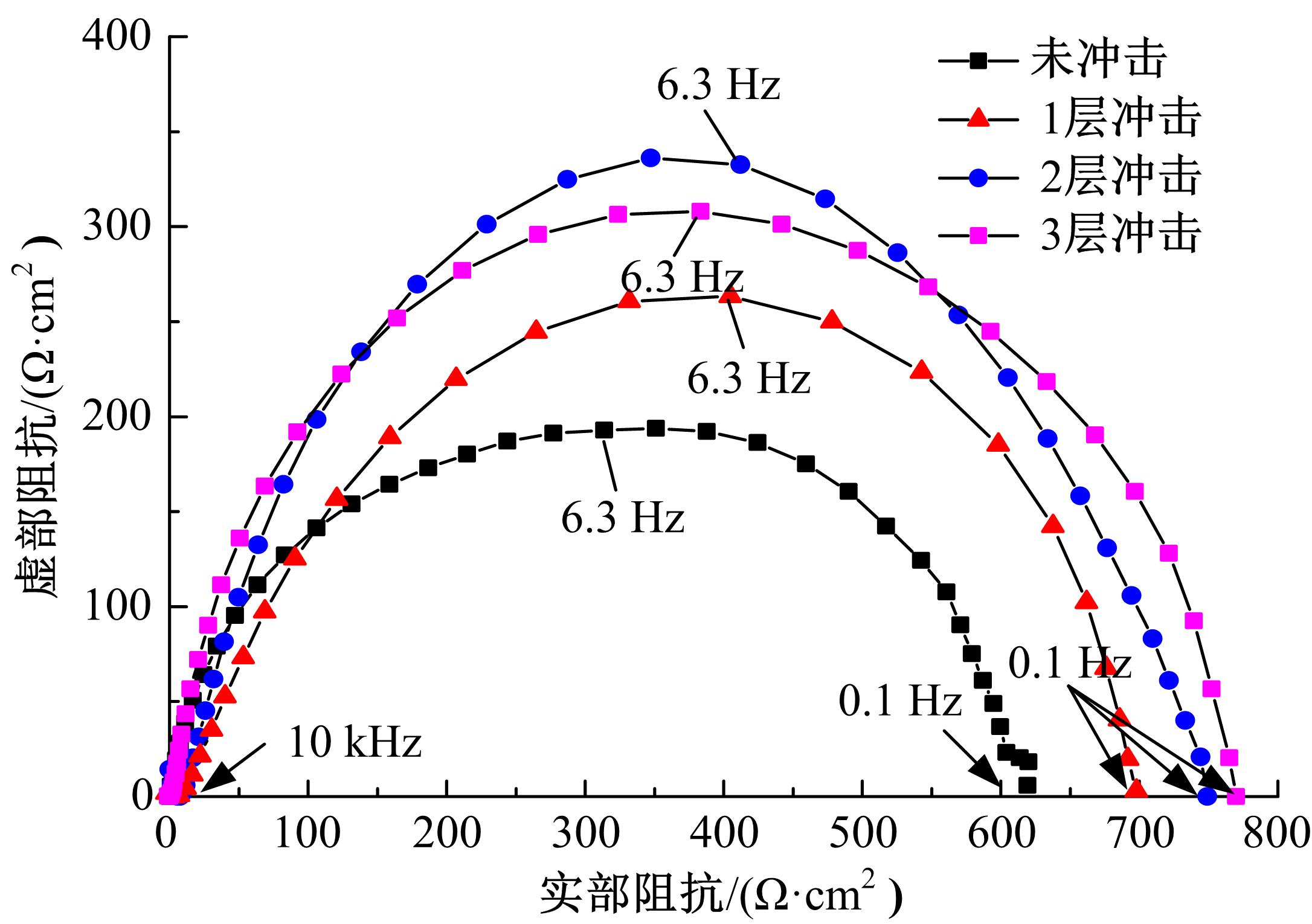
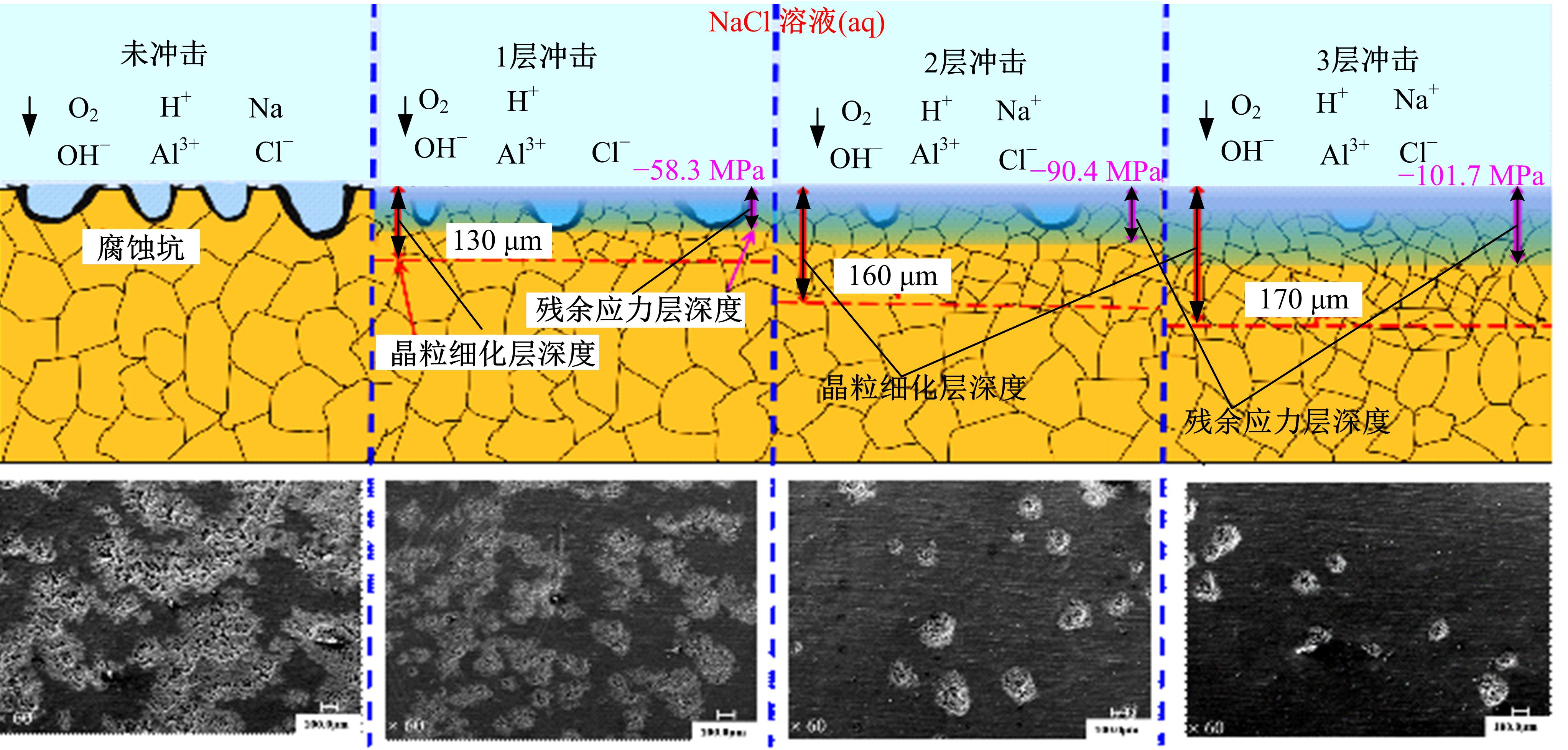
Effect of coverage layer on corrosion resistance of 6061⁃T6 aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening
Jin⁃zhong LU( ),Wan⁃ting ZHOU,Sheng⁃yang ZHANG,Yi⁃kai SHAO,Chang⁃yu WANG,Kai⁃yu LUO
),Wan⁃ting ZHOU,Sheng⁃yang ZHANG,Yi⁃kai SHAO,Chang⁃yu WANG,Kai⁃yu LUO
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
CLC Number:
- TH16,TN249
| 1 | GencaldI S, SaklakogluN, AkmanE, et al. Pulsed Nd:YAG laser shock processing effects on mechanical properties of 6061⁃T6 alloy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2014,56(1):273⁃277. |
| 2 | ZhangX C, ZhangY K, LuJ Z, et al. Improvement of fatigue life of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by laser shock peening[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A,2010,527(15):3411⁃3415. |
| 3 | 葛茂忠,张永康,项建云.AZ31B镁合金激光冲击强化及抗应力腐蚀研究[J].中国激光,2010,37(11):2925⁃2930. |
| GeMao⁃zhong, ZhangYong⁃kang, XiangJian⁃yun. Research on laser shock strengthening and stress corrosion cracking resistance of AZ31B magnesium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal Lasers, 2010, 37(11): 2925⁃2930. | |
| 4 | YangJ M, HerY C, HanN, et al. Laser shock peening on fatigue behavior of 2024⁃T3 Al alloy with fastener holes and stopholes[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A,2001,298(1/2):296⁃299. |
| 5 | 邢清蒲,张凌峰,李少哲,等. 激光冲击强化对2A02铝合金电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术,2013,25(5):402⁃405. |
| XingQing⁃pu, ZhangLing⁃feng, LiShao⁃zhe, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 2A02 aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion Science & Protection Technology, 2013,25(5):402⁃405. | |
| 6 | 王江涛,张永康,陈菊芳,等. 强激光冲击对7075铝合金等离子弧焊接头电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2015,42(12):106⁃115. |
| WangJiang⁃tao, ZhangYong⁃kang, ChenJu⁃fang, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy plasma arc weldments[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(12):106⁃115. | |
| 7 | 汪诚,赖志林,何卫锋,等. 激光冲击次数对1Cr11Ni2W2MoV不锈钢高周疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(1):46⁃51. |
| WangCheng, LaiZhi⁃lin, HeWei⁃feng, et al. Effect of multi⁃impact on high cycle fatigue properties of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV stainless steel subject to laser shock processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2014,41(1):46⁃51. | |
| 8 | DiS A, KennyJ M. Grain size dependence of the fatigue behaviour of a ultrafine⁃grained AISI 304 stainless steel[J]. Materials Letters,2003,57(21):3182⁃3185. |
| 9 | ZhenL, HuH, WangX Y, et al. Distribution characterization of boundary misorientation angle of 7050 aluminum alloy after high⁃temperature compression[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2009,209(2):754⁃761. |
| 10 | LiQ, XuY B, LaiZ H, et al. Dynamic recrystallization induced by plastic deformation at high strain rate in a Monel alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2000,276(1/2):250⁃256. |
| 11 | MazurinaI, SakaiT, MiuraH, et al. Grain refinement in aluminum alloy 2219 during ECAP at 250 ℃[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008,473(1/2):297⁃305. |
| 12 | LuJ Z, HanB, CuiC Y, et al. Electrochemical and pitting corrosion resistance of AISI 4145 steel subjected to massive laser shock peening treatment with different coverage layers[J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2017,88:250⁃262. |
| 13 | 李少哲,张凌峰,邢清蒲.激光冲击强化对AZ91镁合金的电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(5):74⁃78. |
| LiShao⁃zhe, ZhangLing⁃feng, XingQing⁃pu. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2013,40(5):74⁃78. | |
| 14 | AmarH, VignalV, KrawiecH, et al. Influence of the microstructure and laser shock processing(LSP) on the corrosion behavior of the AA2050⁃T8 aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011,53(10):3215⁃3221. |
| 15 | 陈菊芳, 张永康, 许仁军. AM50镁合金表面激光熔凝层的组织与耐蚀性能[J]. 中国激光, 2008,35(2):307⁃310. |
| ChenJu⁃fang, ZhangYong⁃kang, XuRen⁃jun. Microstructure and corrosion resistant property of laser surface melting layer of AM50 magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2008,35(2):307⁃310. | |
| 16 | 罗新民,张静文,赵广志,等. 激光冲击强化对2A02铝合金疲劳行为的影响[J]. 中国激光,2009,36(12):3323⁃3328. |
| LuoXin⁃min, ZhangJing⁃wen, ZhaoGuang⁃zhi, et al. Effect of laser shock strengthening on fatigue behaviors of 2A02 aluminum alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009,36(12):3323⁃3328. | |
| 17 | 洪晰,王声波,郭大浩,等. 激光冲击波在铝靶中衰减特性的研究[J].量子电子学报,1998,15(5):474⁃478. |
| HongXi, WangSheng⁃bo, GuoDa⁃hao, et al. Rsesearch on the attenuation property of the laser induced shock wave propagating in aluminum[J]. Chinese Joural of Quantum Electronics,1998,15(5):474⁃478. | |
| 18 | 叶作彦. 新型铝合金的腐蚀行为及表面改性的影响[D]. 西安:西北工业大学材料学院,2015. |
| YeZuo⁃yan. Corrosion behavior of new aluminum alloy and the effect of surface modification[D]. Xi’an:College of Materials, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2015. |
| [1] | JIANG Qiu-yue,YANG Hai-feng,TAN Cai-wang. Strengthening properties of welded joints of 22MnB5 super high strength steel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1806-1810. |
| [2] | ZHAO Shuang,SHEN Ji-hong,ZHANG Liu,ZHAO Han,CHEN Ke-fan. Evaluation of surface roughness of micro electrical discharge machining based-on fast Gauss algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1838-1843. |
| [3] | ZHENG Xiao-yi, SUN Da-qian, LI Xin, DU Gui-gang, XIN Wei-da, REN Zhen-an. Microstructure and properties of cladded Al-Nb layers reinforced by NbAl3 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1531-1536. |
| [4] | GUAN Qing-feng, DONG Shu-heng, ZHENG Huan-huan, LI Chen, ZHANG Cong-lin, LV-Peng. Cr surface alloying of 45# steel by high-current pulsed electron beam treatment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1161-1168. |
| [5] | REN Qing-lei, WEI Xin, XIE Xiao-zhu, HU Wei. Micro contact mechanism based on force in self rotation grinding of silicon wafer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 796-802. |
| [6] | LIU Zi-wu, LI Jian-feng. Erosion damage and evaluation of remanufacturing cladding layer for impeller metals FV520B [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 835-844. |
| [7] | ZHAO Yu-guang, YANG Xue-hui, XU Xiao-feng, ZHANG Yang-yang, NING Yu-heng. Effects of Al-10Sr modifiers with different states, modification temperature and holding time on microstructure of ZL114A alloy [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 212-220. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zhi-qiang, LIU Cong-hao, HE Dong-ye, LI Xiang-ji, LI Ji-xuan. Effect of hot stamping process of boron steel on shape precision based on performance gradient distribution [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1829-1833. |
| [9] | GUAN Qing-feng, ZHANG Yuan-wang, SUN Xiao, ZHANG Chao-ren, LYU Peng, ZHANG Cong-lin. Surface alloying of Al-W alloy by high current pulsed electron beam treatment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1171-1178. |
| [10] | CUI Ya-nan, HAN Ji-wei, FENG Lei, LI Jia-di, WANG Le. Microstructure of asphalt under salt freezing cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 452-458. |
| [11] | YANG Yue, ZHOU Lei-lei. Effect of micro-arc oxidation treatment on corrosion resistance of aluminum friction stir welding welds [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 511-515. |
| [12] | GUAN Qing-feng, LI Yan, HOU Xiu-li, YANG Sheng-zhi, WANG Xiao-tong. Modification of solid solution Mg-Gd-Y-Nd alloy irradiated by high current pulsed electron beam [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1200-1205. |
| [13] | ZHAO Jia-xin,MA Biao,LI He-yan,ZHU Li,HAN Ming,ZHU Li-an. Thermoelastic stability of wet clutches during engaging process [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 22-28. |
| [14] | XU Jing-bo,YUAN Yi-bao, CUI Xiao-meng, GUO Xin, WANG Sheng. Rational approximation implementation approach to determine Gaussian filtering mean line in surface roughness measurement [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1347-1352. |
| [15] | MA Yao, DONG Xiao-long, LI Ze-jun, SHEN Lin, ZHAO Hong-wei. Finite element simulation of the effect of different initial contact on nano-indentation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1366-1370. |
|
||