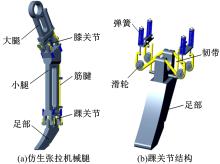
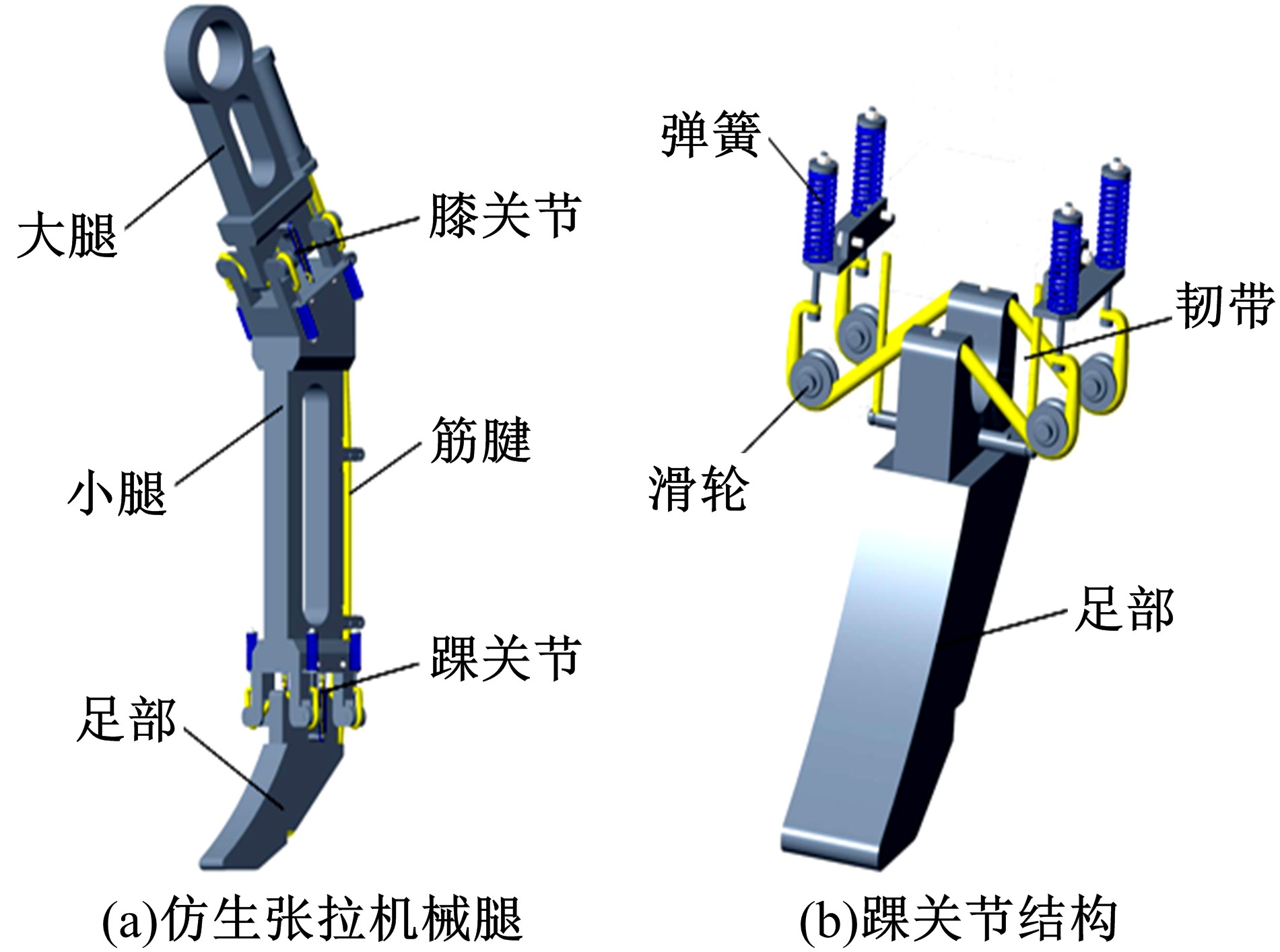
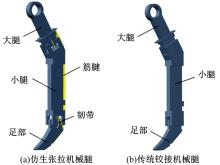
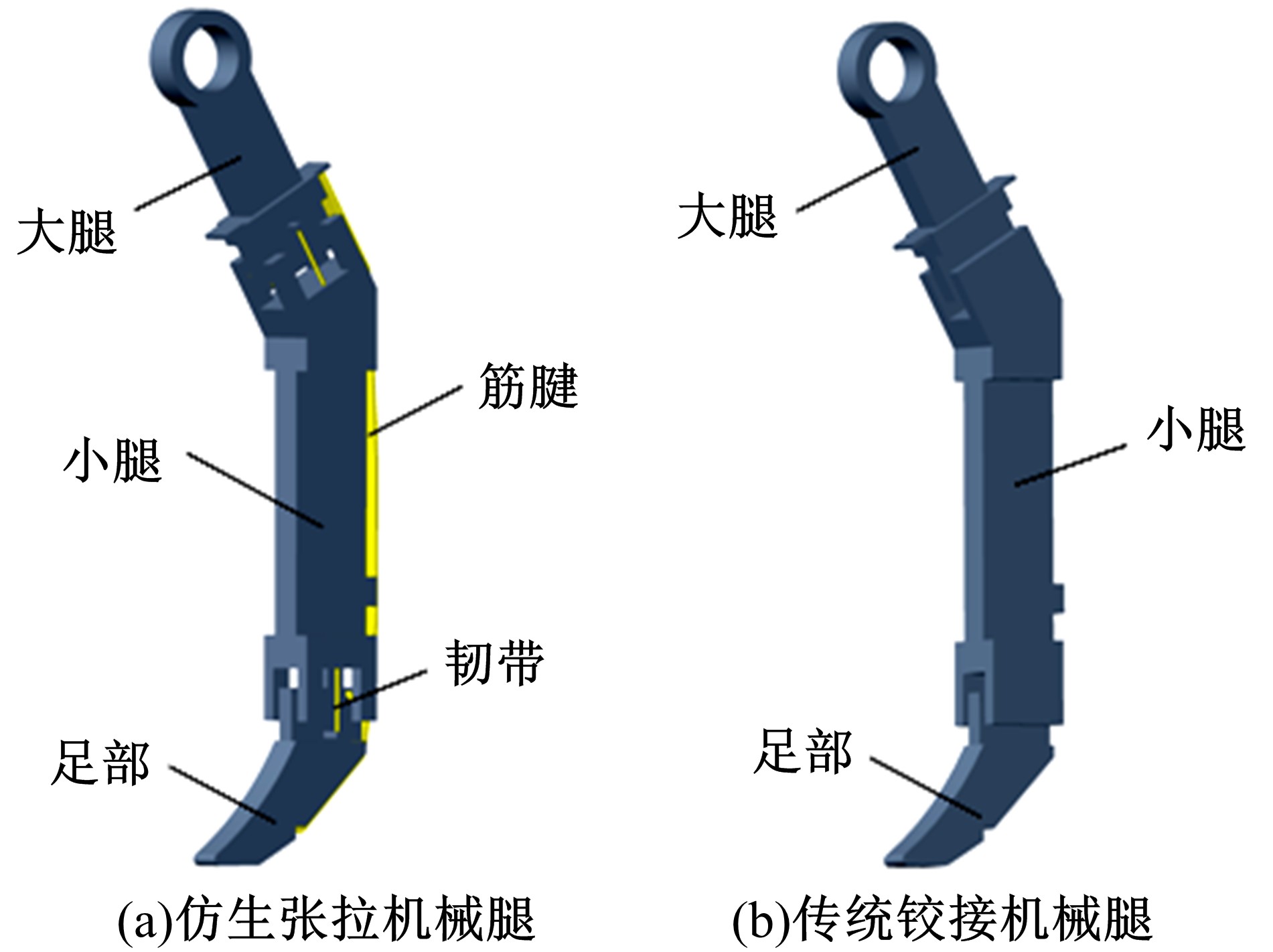
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 758-764.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190265
Design of bionic tensegrity leg and simulation analysis of its impact resistance
Zhi-hui QIAN1( ),Si-jie WU1,2,Qiang WANG1,Xin-yan ZHOU1,Jia-nan WU1,Lei REN1(
),Si-jie WU1,2,Qiang WANG1,Xin-yan ZHOU1,Jia-nan WU1,Lei REN1( ),Lu-quan REN1
),Lu-quan REN1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
2.College of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150006, China
CLC Number:
- TB17
| 1 | 高峰. 机构学研究现状与发展趋势的思考[J]. 机械工程学报, 2005, 41( 8): 3- 17. |
| Gao Feng. Thoughts on the status quo and development trend of institutional research[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41( 8): 3- 17. | |
| 2 | 陈学东, 郭鸿勋, 渡边桂吾. 四足步行机器人爬行步态的正运动学分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2003, 39( 2): 8- 12. |
| Chen Xue-dong, Guo Hong-xun, Duan Gui-wu. Direct kinematics analysis of crawling gait of four-legged walking robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 39( 2): 8- 12. | |
| 3 | Pongas D, Mistry M, Schaal S. A robust quadruped walking gait for traversing rough terrain[C]∥ IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, 2007: 1474- 1479. |
| 4 | Raibert M, Blankespoor K, Nelson G, et al. Bigdog, the rough-terrain quadruped robot[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2008, 41( 2): 10823- 10825. |
| 5 | Dynamics Boston. Cheetah[EB/OL].[ 2018-12-18]. |
| 6 | Unitree. Laikago[EB/OL].[ 2018-12-30]. |
| 7 | 熊蓉. 仿生腿足式机器人的发展[J]. 机器人技术与应用, 2017( 2): 29- 36. |
| Xiong Rong. Development of bionic leg-foot robot[J]. Robotics and Applications, 2017( 2): 29- 36. | |
| 8 | 钱志辉, 苗怀彬, 任雷, 等. 基于多种步态的德国牧羊犬下肢关节角[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45( 6): 1857- 1862. |
| Qian Zhi-hui, Miao Huai-bin, Ren Lei, et al. Lower limb joint angles of German shepherd dog during foot-ground contact in different gait patterns[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45( 6): 1857- 1862. | |
| 9 | 钱志辉, 苗怀彬, 商震, 等. 基于多种步态的德国牧羊犬足-地接触分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44( 6): 1692- 1697. |
| Qian Zhi-hui, Miao Huai-bin, Shang Zheng, et al. Foot-ground contact analysis of German shepherd dog in walking, trotting and jumping gaits[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44( 6): 1692- 1697. | |
| 10 | Auke J I. Biorobotics: using robots to emulate and investigate agile locomotion[J]. Science, 2014, 346( 6206): 196- 203. |
| 11 | Seok S, Wang A, Meng C Y, et al. Design principles for energy-efficient legged locomotion and implementation on the MIT cheetah robot[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2015, 20( 3): 1117- 1129. |
| 12 | 丁良宏. Bigdog四足机器人关键技术分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51( 7): 1- 23. |
| Ding Liang-hong. Key technologies of bigdog quadruped robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51( 7): 1- 23. | |
| 13 | Wolf S, Hirzinger G. A new variable stiffness design: Matching requirements of the next robot generation[C]∥ IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, 2008: 1741- 1746. |
| 14 | Seok S, Wang A, Meng C M Y, et al. Design principles for highly efficient quadrupeds and implementation on the MIT Cheetah robot[C]∥ IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Germany, 2013: 3307- 3312. |
| 15 | Hutter M, Gehring C, Bloesch M, et al. “Starleth”: a compliant quadrupedal robot for fast, efficient and versatile locomotion[C]∥ 15th International Conference on Climbing Walking Robots and the Support Technologies for Mobile Machines, Baltimore, 2012: 483- 490. |
| 16 | Folkertsma S K G, Stramigioli S. Parallel stiffness in a bounding quadruped with flexible spine[C]∥ IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Portugal, 2012: 2210- 2215. |
| 17 | Haberland M, Karssen J, Kim S, et al. The effect of swing leg retraction on running energy efficiency[C]∥ IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, 2011: 3957- 3962. |
| 18 | Ren L, Qian Z, Ren L. Biomechanics of musculoskeletal system and its biomimetic implications: a review[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2014, 11( 2): 159- 175. |
| 19 | Levin S M. The tensegrity-truss as a model for spine mechanics: biotensegrity[J]. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 2012, 2( 3/4): 375- 378. |
| 20 | Bai R X, Jiang H, Lei Z K, et al. Virtual field method for identifying elastic-plastic constitutive parameters of aluminum alloy laser welding considering kinematic hardening[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 110: 122- 131. |
| 21 | Ristaniemi A, Stenroth L, Mikkonen S, et al. Comparison of elastic, viscoelastic and failure tensile material properties of knee ligaments and patellar tendon[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2018, 79: 31- 38. |
| 22 | 梁基照. 微珠填充LDPE复合物拉伸弹性模量的预测[J]. 塑料, 1997, 26( 6): 17- 20. |
| Liang Ji-zhao. Prediction of tensile elastic modulus of LDPE complex filled with microbeads[J]. Plastics, 1997, 26( 6): 17- 20. |
| [1] | TIAN Wei-jun, WANG Ji-yue, LI Ming, ZHANG Xing-wang, ZHANG Yong, CONG Qian. Observation of locomotion of water strider towards water strider robot [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 812-820. |
| [2] | CHEN Dong-hui, LIU Wei, LYU Jian-hua, CHANG Zhi-yong, WU Ting, MU Hai-feng. Bionic design of corn stubble collector based on surface structure of Patinopecten yessoensis [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1185-1193. |
| [3] | TIAN Li-mei, WANG Yang-jun, LI Zi-yuan, SHANG Yan-geng. Development of drag-reduction test system of bionic functional surfaces with internal flow [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1179-1184. |
| [4] | WANG Ying, LI Jian-qiao, ZHANG Guang-quan, HUANG Han, ZOU Meng. Mechanical characteristics of bionic walking foot in different media [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 546-551. |
| [5] | ZHANG Rui, YANG Ming-ming, LIU Hai-bao, ZENG Gui-yin, PAN Run-duo, LI Jian-qiao. Numerical simulation of sand flow fixation characteristics of plantar surface of ostrich didactyl foot [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 508-515. |
| [6] | TIAN Li-mei, SHANG Zhen, HU Guo-liang, LI Nan. Numerical simulation of the lift and drag characteristics of passenger car based on morphological bionics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1283-1289. |
| [7] | ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Si-hua, LIU Fang, LI Jian-qiao. Structure design and performance analysis of bionic desert hiking stick [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 976-982. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yan, HUANG He, REN Lu-quan. Drag reduction experiment of bionic excvavtor bucket teeth [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 126-130. |
| [9] | CHANG Zhi-yong, CHEN Dong-hui, TONG Jin, TONG Yue-ying, XIE Jun. Human olfactory feature based bionic electronic nose technology for pork freshness detection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 131-134. |
| [10] | SHI Lei, ZHANG Cheng-chun, WANG Jing, WANG Yong-hua,ZHANG Xue-peng, REN Lu-quan. Reduction of aerodynamic noise from NACA0018 airfoil model using bionic methods [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1664-1668. |
| [11] |
Cheng Ping,Zhang Hai-tao,Gao Yan,Li Jun-feng,Wang Hong-yan .
Application of ANN in property prediction of polyacrylate emulsion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(02): 362-0366. |
|
||