Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 437-444.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190766
Shoveling trajectory planning method for wheel loader based on kriging and particle swarm optimization
Xiang-jun YU1( ),Yuan-hui HUAI2,Xue-fei LI3,De-wu WANG1,An YU1(
),Yuan-hui HUAI2,Xue-fei LI3,De-wu WANG1,An YU1( )
)
- 1.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Kunming University, Kunming 650214, China
2.Kunming Motor Vehicle Inspection and Supervision Service Center, Kunming 650200, China
3.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
CLC Number:
- TH243
| 1 | Filla R. Evaluating the efficiency of wheel loader bucket designs and bucket filling strategies with non-coupled DEM simulations and simple performance indicators[C]∥Fachtagung Baumaschinentechnik, Dresden, Germany, September, 2015: 16-17. |
| 2 | Frank B, Kleinert J, Filla R. Optimal control of wheel loader actuators in gravel applications[J]. Automation in Construction, 2018, 91: 1-14. |
| 3 | 龚捷,崔玉鑫. 装载机铲掘作业的轨迹规划[J]. 机械工程学报, 2009, 45(7): 29-34. |
| Gong Jie, Cui Yu-xin. Track planning for a wheel loader in a digging [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(7): 29-34. | |
| 4 | 赵腾云,秦四成,曾庆强,等. 轮式装载机铲斗铲掘与路径轨迹研究[J]. 建筑机械, 2011(3): 80-82. |
| Zhao Teng-yun, Qin Si-cheng, Zeng Qing-qiang, et al. Research of bucket digging and path trajectory of wheel loader [J]. Construction Machinery, 2011(3): 80-82. | |
| 5 | 宁俏俏. 装载机铲掘作业轨迹的自适应控制仿真研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学机械科学与工程学院, 2008. |
| Ning Qiao-qiao. Research on adaptive control of loaders in dingging[D]. Changchun: School of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Jilin University, 2008. | |
| 6 | 张大庆,何清华,郝鹏,等. 液压挖掘机铲斗轨迹跟踪的鲁棒控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2006, 36(6): 934-938. |
| Zhang Da-qing, He Qing-hua, Hao Peng, et al. Robust trajectory tracking control of hydraulic excavator bucket[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2006, 36(6): 934-938. | |
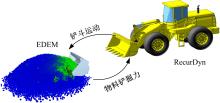
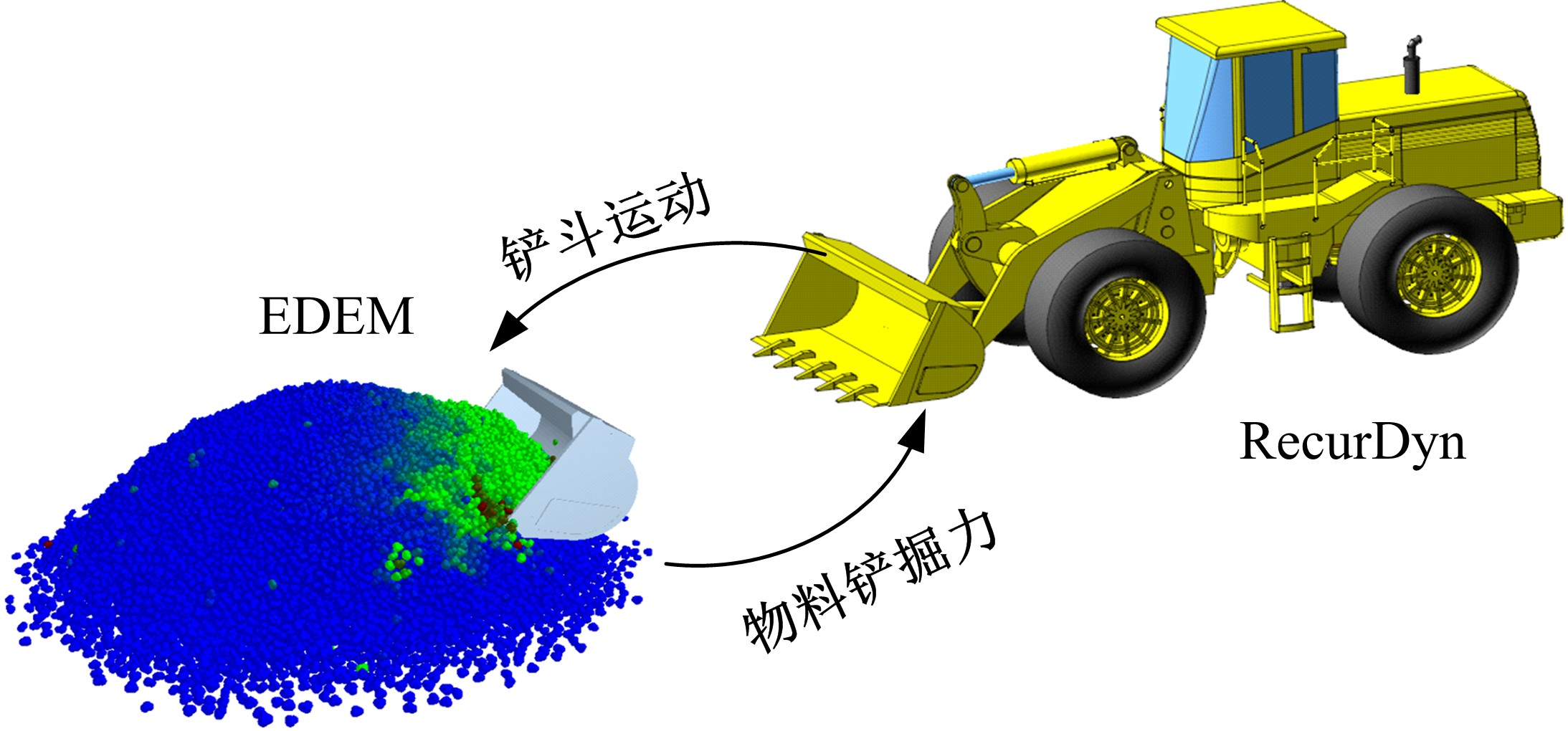
| 7 | 毕秋实,王国强,陈立军,等.基于离散元-多体动力学联合仿真的机械式挖掘机挖掘阻力仿真与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 106-116. |
| Bi Qiu-shi, Wang Guo-qiang, Chen Li-jun, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment on excavation resistance of mechanical excavator based on DEM-MBD co-simulation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 106-116. | |
| 8 | Alshaer B, Darabseh T, Alhanouti M. Path planning, modeling and simulation of an autonomous articulated heavy construction machine performing a loading cycle[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2013, 37: 5315-5325. |
| 9 | Engelbrecht A P. Particle swarm optimization with crossover: a review and empirical analysis[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2016, 45(2): 131-165. |
| [1] | Shun-fu JIN,Xiu-chen QIE,Hai-xing WU,Zhan-qiang HUO. Clustered virtual machine allocation strategy in cloud computing based on new type of sleep-mode and performance optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 237-246. |
| [2] | Hong⁃zhi WANG,Fang⁃da JIANG,Ming⁃yue ZHOU. Power allocation of cognitive radio system based on genetic particle swarm optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1363-1368. |
| [3] | Yuan-ning LIU,Shuai LIU,Xiao-dong ZHU,Guang HUO,Tong DING,Kuo ZHANG,Xue JIANG,Shu-jun GUO,Qi-xian ZHANG. Iris secondary recognition based on decision particle swarm optimization and stable texture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1329-1338. |
| [4] | Kai XU,Zhi⁃gang CHEN,Jing⁃hua ZHAO,Lu DAI,Feng LI. Layout design method of star sensor based on particle swarm optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 972-978. |
| [5] | ZHAO Dong,SUN Ming-yu,ZHU Jin-long,YU Fan-hua,LIU Guang-jie,CHEN Hui-ling. Improved moth-flame optimization method based on combination of particle swarm optimization and simplex method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1867-1872. |
| [6] | LIU Yuan-ning, LIU Shuai, ZHU Xiao-dong, CHEN Yi-hao, ZHENG Shao-ge, SHEN Chun-zhuang. LOG operator and adaptive optimization Gabor filtering for iris recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1606-1613. |
| [7] | ZANG Guo-shuai, SUN Li-jun. Method based on inertial point for setting depth to rigid layer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [8] | HUANG Hui, FENG Xi-an, WEI Yan, XU Chi, CHEN Hui-ling. An intelligent system based on enhanced kernel extreme learning machine for choosing the second major [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1224-1230. |
| [9] | HU Man-jiang, LUO Yu-gong, CHEN Long, LI Ke-qiang. Vehicle mass estimation based on longitudinal frequency response characteristics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 977-983. |
| [10] | JIN Li-qiang, SUN Zhi-xiang, ZHENG Ying. Coordinated anti-lock braking control of compound regenerative braking system in electric-wheel vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1344-1351. |
| [11] | LIU Ying, ZHANG Kai, YU Xiang-jun. Multi-objective optimization of hydrostatic bearing of hollow shaft based on surrogate model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1130-1137. |
| [12] | HUANG Xuan, GUO Li-hong, LI Jiang, YU Yang. Target threat assessment based on BP neural network optimized by modified particle swarm optimization [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 996-1002. |
| [13] | SUN Liang, XU Hai-lang, GE Hong-wei. Novel global convergence stochastic particle swarm optimizers [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 615-623. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jia-xu, LI Jing. Parameter identification for UniTire model based on hybrid optimization method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 15-20. |
| [15] | LU Ying, WANG Hui-qin, QIN Li-ke. Accurate fire location method in high and large-span space buildings [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2067-2073. |
|
||