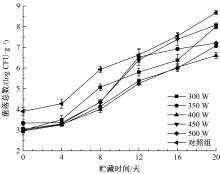
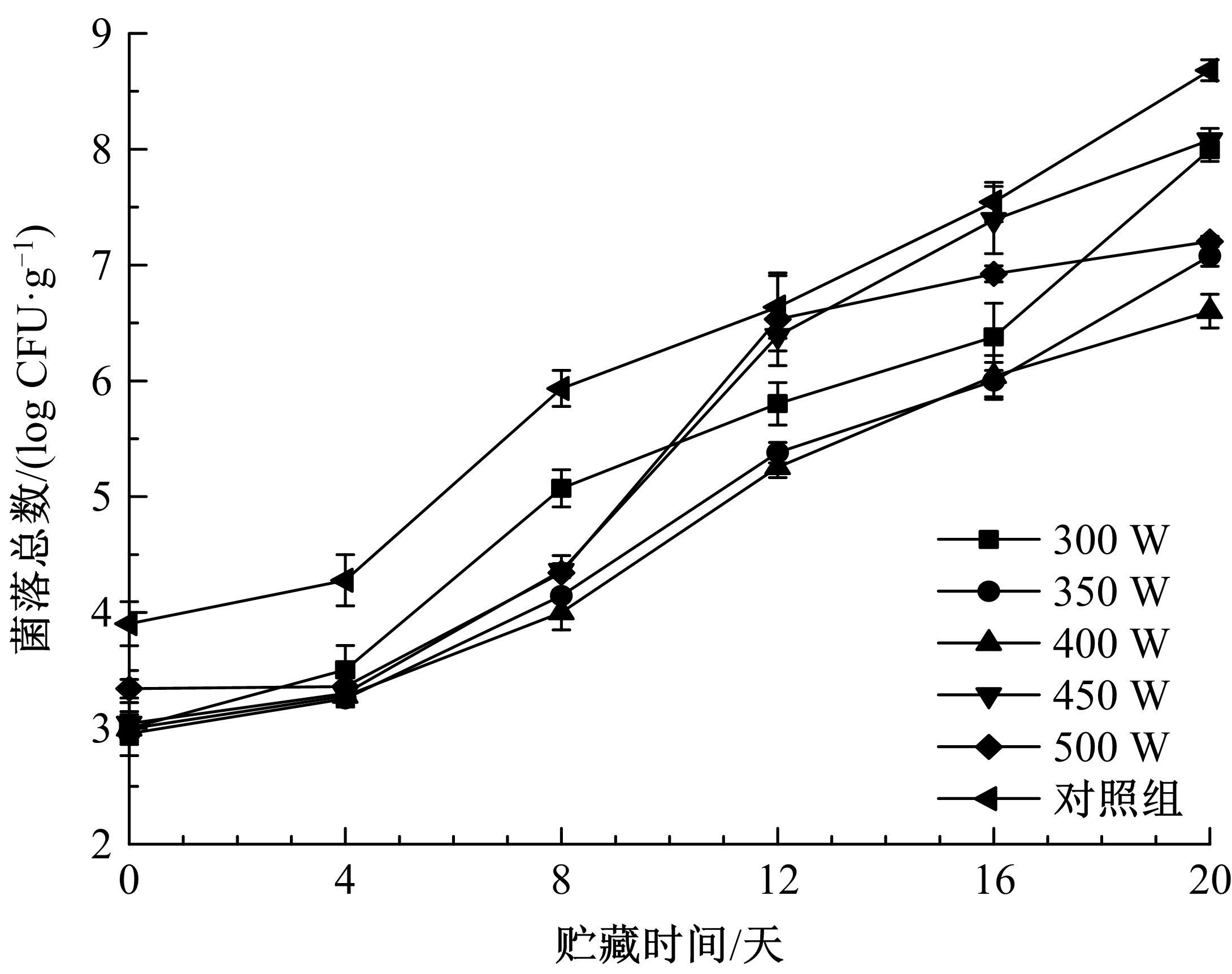
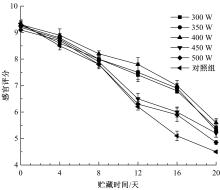
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1934-1940.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20191072
Effect of low⁃temperature plasma treatment power on storage quality of spiced beef
Xin-xin LI1( ),Da-yu LI1,Zi-rui ZHAO2,Ya-jun ZHOU1(
),Da-yu LI1,Zi-rui ZHAO2,Ya-jun ZHOU1( )
)
- 1.College of Food Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130062, China
2.College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
CLC Number:
- TS251.61
| 1 | 李素, 周慧敏, 张顺亮, 等. 不同加水量腌制酱牛肉中挥发性风味物质变化[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(10): 199-205. |
| Li Su, Zhou Hui-min, Zhang Shun-liang, et al. Changes of volatile flavor compounds in spiced beef marinated with different water contents[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(10): 199-205. | |
| 2 | Attri P, Kim Y H, Park D H, et al. Generation mechanism of hydroxyl radical species and its lifetime prediction during the plasma-initiated ultraviolet(UV) photolysis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015(5): 1-8. |
| 3 | Dasan B G, Boyaci I H, Mutlu M. Nonthermal plasma treatment of Aspergillus spp. spores on hazelnuts in an atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma system: impact of process parameters and surveillance of the residual viability of spores[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2017, 196: 139-149. |
| 4 | Zhu F. Plasma modification of starch[J]. Food Chemistry, 2017, 232: 476-486. |
| 5 | Toyokawa Y, Yagyu Y, Yamashiro R, et al. Roller conveyer system for the reduction of pesticides using non-thermal gas plasma—a potential food safety control measure?[J]. Food Control, 2018, 87: 211-217. |
| 6 | Bauer A, Ni Y, Bauer S, et al. The effects of atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment on micro-biological, physical-chemical and sensory characteristics of vacuum packaged beef loin[J]. Meat Science, 2017, 128: 77-87. |
| 7 | 黄现青, 宋莲军, 赵秋艳, 等. 300W低温等离子体处理对真空包装酱卤鸭腿货架期的影响[J]. 肉类工业, 2017(10): 31-33, 36. |
| Huang Xian-qing, Song Lian-jun, Zhao Qiu-yan, et al. Effect of 300W low temperature plasma treatment on the shelf life of vacuum packaged sauced stewed duck leg[J]. Meat Industry, 2017(10): 31-33, 36. | |
| 8 | 张建友, 赵瑜亮, 张梦雨, 等. 不同贮藏温度酱鸭品质变化及其货架期预测[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(5): 250-257. |
| Zhang Jian-you, Zhao Yu-liang, Zhang Meng-yu, et al. Quality changes and predictive modeling of shelf life of sauced duck stored at different temperatures[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(5): 250-257. | |
| 9 | GB 4789.2—2016. 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. |
| 10 | GB/T16860. 感官分析方法质地剖面检验[S]. |
| 11 | Kim H J, Yong H I, Park S, et al. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on pathogen inactivation and the physicochemical and sensory characteristics of pork loin[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2013, 13(7): 1420-1425. |
| 12 | Stoffels E, Sakiyama Y, Grave D B. Cold atmospheric plasma: charged species and their interactions with cells and tissues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2008, 36(4): 1441-1457. |
| 13 | Yadav B, Spinelli A C, Govindan B N, et al. Cold plasma treatment of ready-to-eat ham: influence of process conditions and storage on inactivation of Listeria innocua[J]. Food Research International, 2019, 123: 276-285. |
| 14 | Shintani H, Sakudo A, Burke P, et al. Gas plasma sterilization of microorganisms and mechanisms of action[J]. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 2010, 1(5): 731-738. |
| 15 | Thirumdas R, Sarangapani C, Annapure U S. Cold plasma: a novel non-thermal technology for food processing[J]. Food Biophysics, 2015, 10(1): 1-11. |
| 16 | GB 2726—2016. 食品安全国家标准 熟肉制品[S]. |
| 17 | Jayasena D D, Kim H J, Yong H I, et al. Flexible thin-layer dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment of pork butt and beef loin: effects on pathogen inactivation and meat-quality attributes[J]. Food Microbiology, 2015, 46: 51-57. |
| [1] | XU Meng-lei, GAO Yu, LIU Jing-bo, XIONG Jin-feng, ZHAO Song-ning, HUANG Yan-jun. Neuroprotective effects of soy isoflavones on PC12 cells based on antioxidation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 332-336. |
| [2] | ZHANG Tie-hua, JIANG Nan, LIU Di-ru, HAO Jin-feng, MAO Chun-ling, GUO Ming-ruo. Preparation of whey protein based fat replacer and application in low fat milk [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 1024-1028. |
| [3] | YUAN Yuan,ZHANG Huan-jie, MIAO Yu-tian,WU Si-jia, LIN Song-yi,LIU Jing-bo. Contribution of the frying condition of potato slices to the formation of acrylamide [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1525-1530. |
| [4] | ZHAO Mou-ming,LONG Zhao,ZHAO Qiang-zhong,XU Ju-cai. Effects of protein content and composition on the physicochemical properties of whipping cream [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1531-1536. |
| [5] | JIN Sheng-lang, WANG Ying, YIN Yong-guang. Effect of high intensity pulsed electric field pretreatment on elasticity of starch-myofibril protein mixed gelatin [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 573-578. |
| [6] | WANG Li-min, XIAO Zhi-gang, LIU Yu-xin, LI Jie, SUN Xu, SHEN Xun-ye, LI Jia-dong. Optimization of extrusion process parameters of nutritious rice rich in chestnut by response surface method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 550-556. |
| [7] | LIU Jing-bo, CHANG Hao, WANG Er-lei, GONG Xin-tong, JIANG Yi-qun. Phosphatidylcholine of egg yolk lecithin detection using high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC) [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 449-453. |
| [8] | LIU Jing-bo, TAO Xu, JIANG Wei, DING Long, WANG Er-lei. Technology optimization of Sialic acid isolation from hen eggshell membrane by quadric regression orthogonal rotary tests [J]. , 2012, 42(04): 1071-1076. |
| [9] | SUN Zhong-lei, SUN Yong-hai, LI Yu, LIU Jing-jing. Establishment and validation of the food fracture mechanical model based on the bionic indenter [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(02): 510-514. |
| [10] | LIU Jing-bo, WANG Fei, WANG Cui-na, LIU Jun, WANG Zuo-zhao, WANG Er-lei, ZHANG Yan, LIN Song-yi. Optimization of preparation for anticoagulant peptide from egg white powder by Alcalase [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 250-255. |
| [11] | ZHUANG Hong, CHEN Le-qun, ZHANG Ting, ZHU Yuan-yuan, TANG Ning, YUAN Yuan. Property of compound protective agents on ferrous iron of heme-iron enriched polypeptide [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 256-260. |
| [12] | WANG Xin-wei, LIU Huan, MA Zhong-su. The properties of chitosan/corn starch/gelatin/carrot edible films [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 887-892. |
| [13] | ZHANG Tie-hua,WANG Shao-jun,LIU Di-ru,YUAN Yuan,YU Ya-li,YIN Yong-guang. Optimization of exopolysaccharide extraction process from Tibetan spiritual mushroom by pulsed electric fields [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 882-886. |
| [14] | ZHUANG Hong,ZHU Yuan-yuan,ZHANG Ting,CHEN Le-qun,LIU Jing-bo. Enzymatic preparation and protection technology of heme [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 869-875. |
| [15] | XU Cai-na,YIN Yong-guang,WANG Er-lei,LIU Jing-bo,LIN Song-yi,ZHANG Gang. Optimized process of extracting phosvitin from hen egg yolk based on genetic algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 876-881. |
|
||