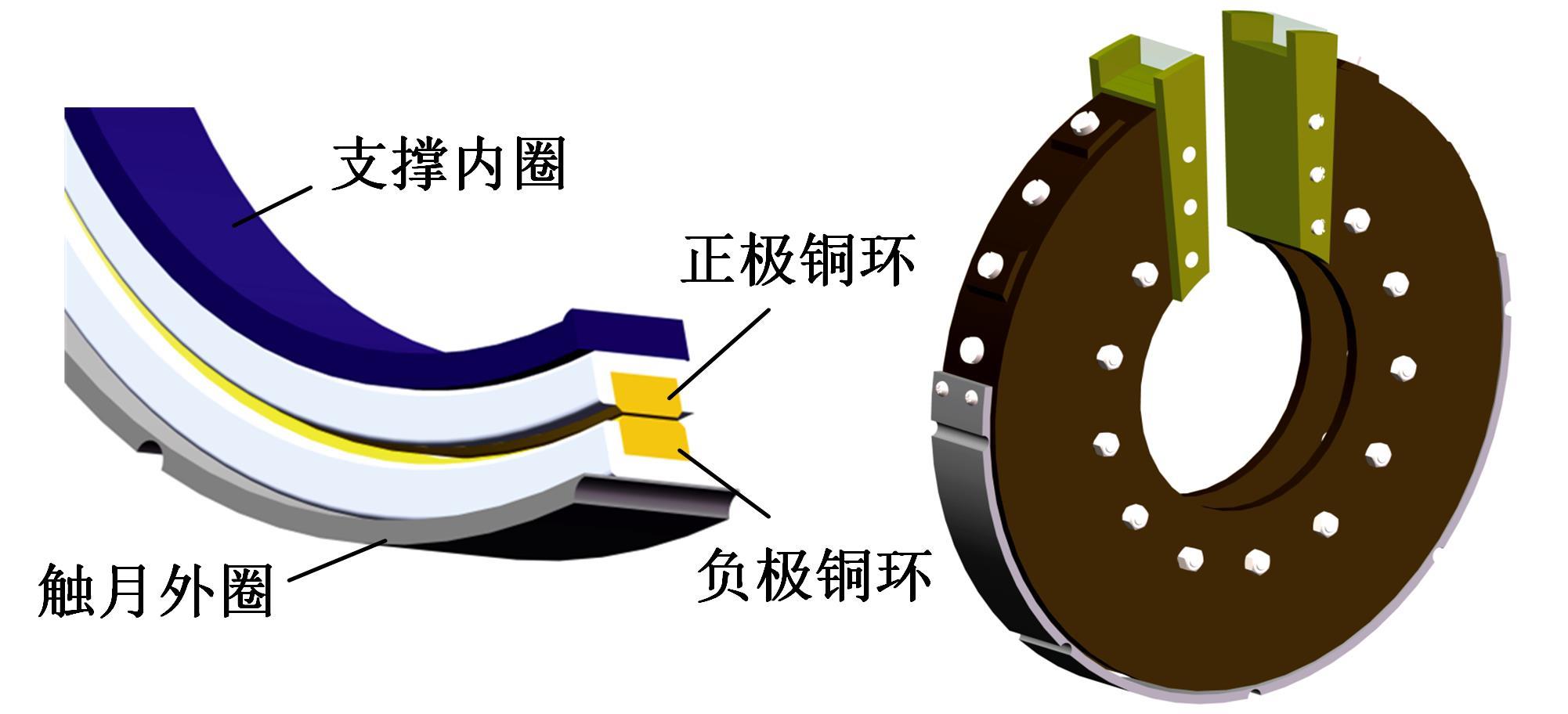
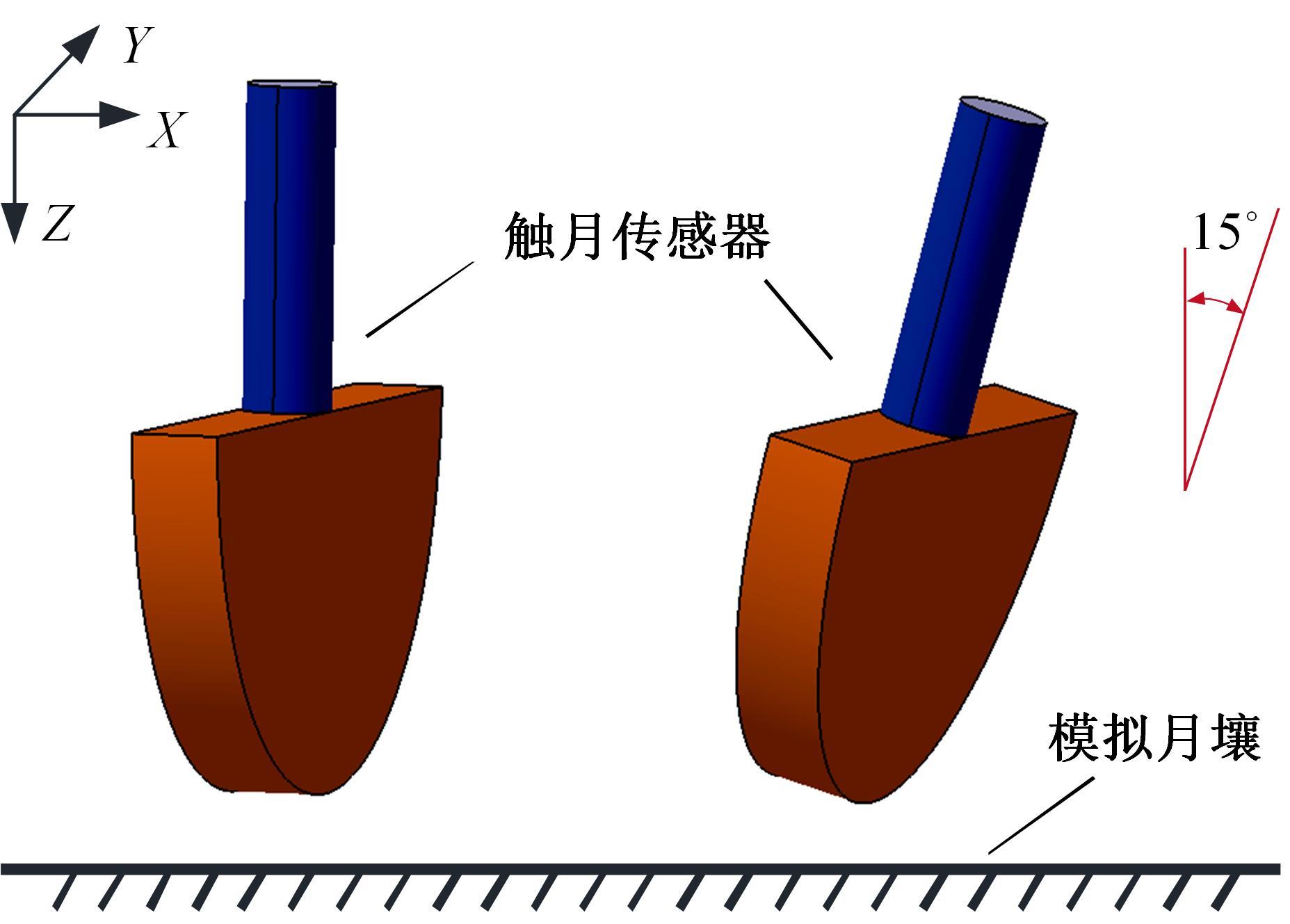
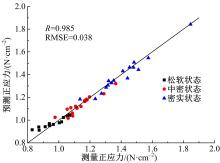
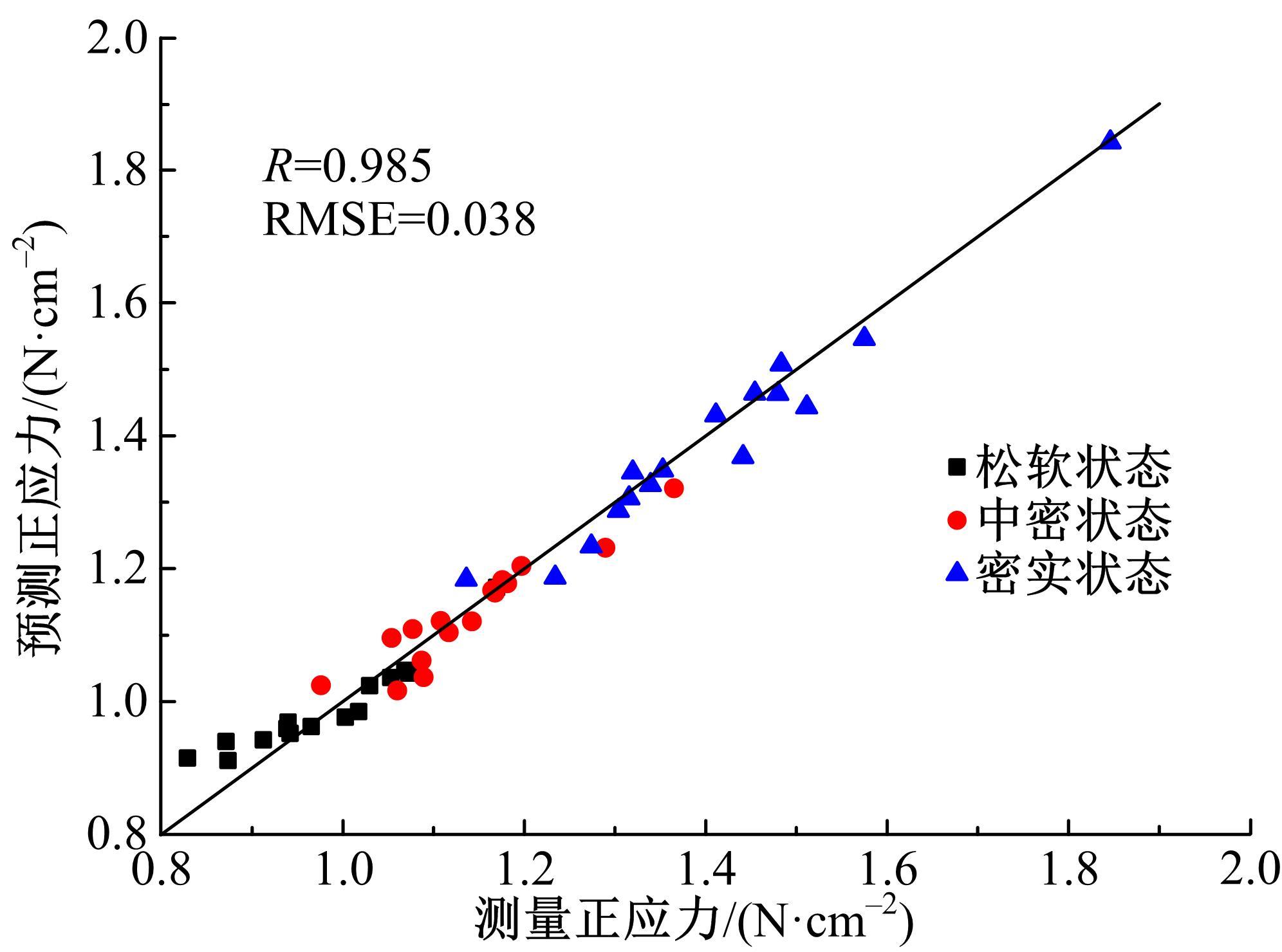
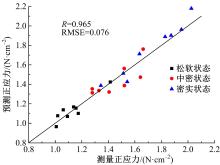
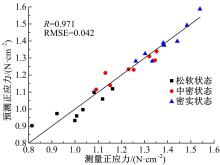
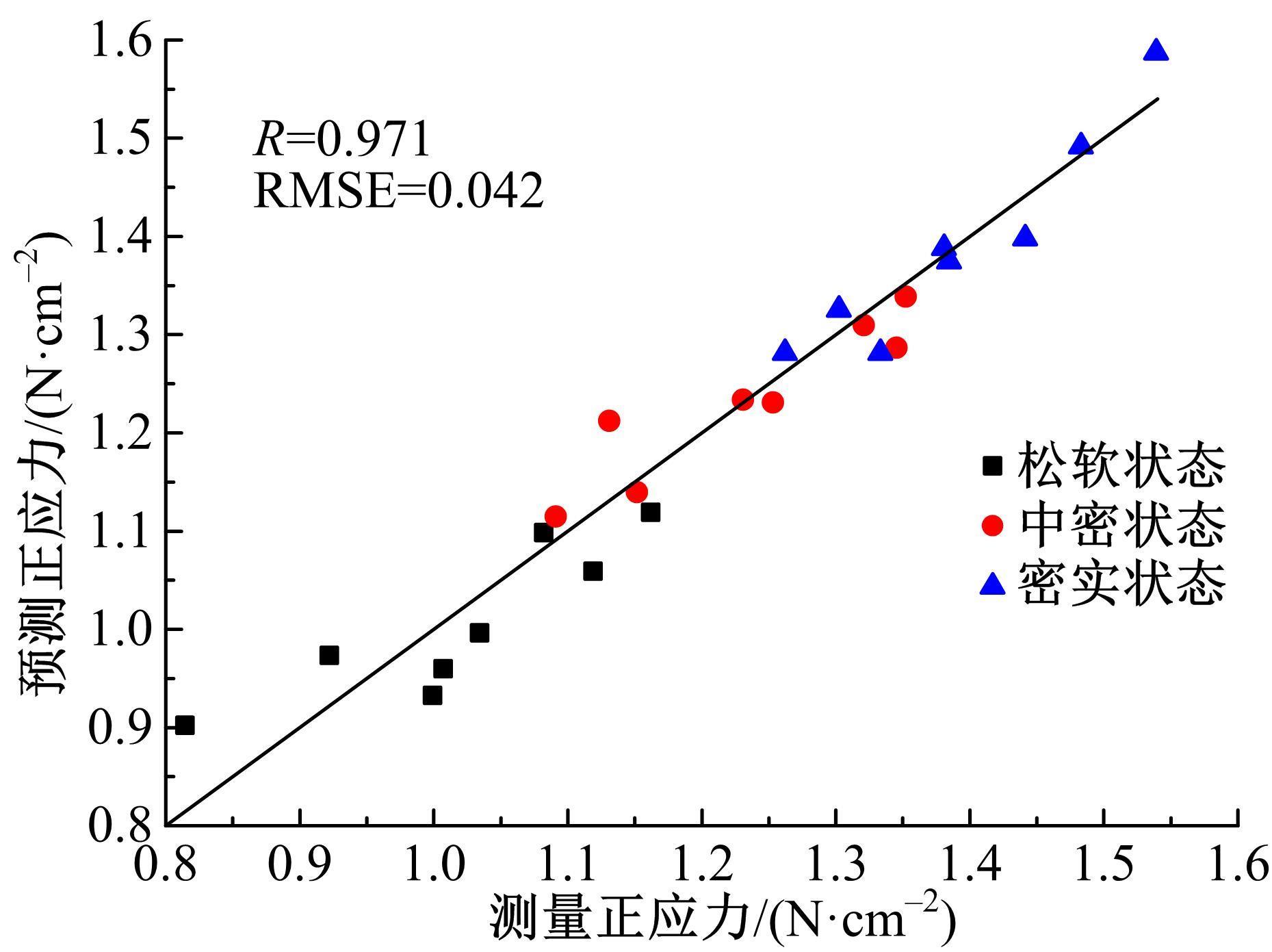
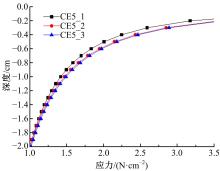
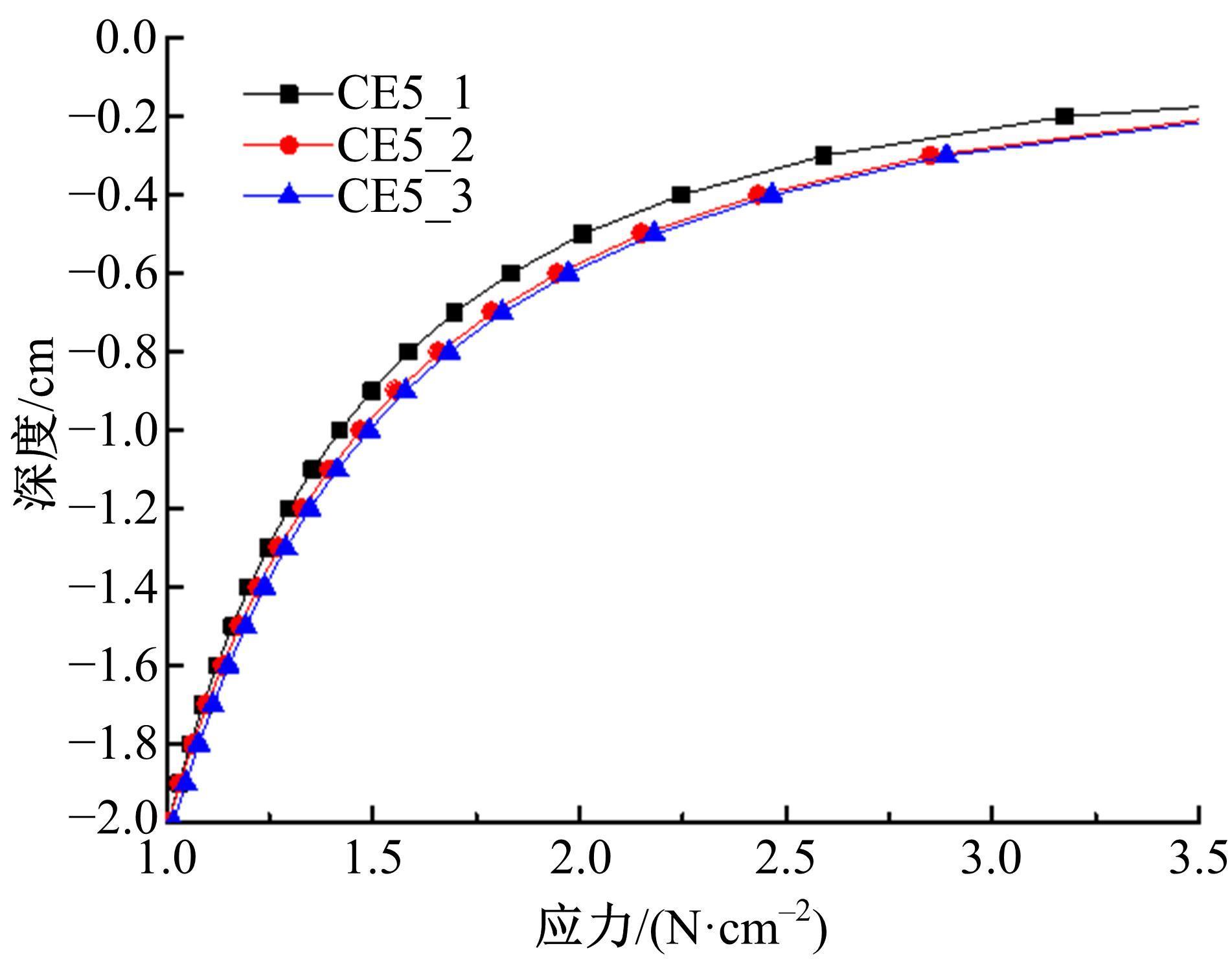
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 497-503.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200800
Experimental analysis of mechanical properties of surface lunar soil based on lunar indentation
Long XUE1( ),Meng YAO2,Li-ben LI3,Yin-wu LI3,Xiang-jin DENG2,Jian-qiao LI3,Meng ZOU3(
),Meng YAO2,Li-ben LI3,Yin-wu LI3,Xiang-jin DENG2,Jian-qiao LI3,Meng ZOU3( )
)
- 1.Key Lab of Modern Agricultural Equipment,Jiangxi Agricultural University,Nanchang 330045,China
2.Beijing Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering,China Academy of Space Technology,Beijing 100094,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TB17
| 1 | 郑燕红, 邓湘金, 庞勇, 等. 月球风化层钻取采样过程密实度分类研究[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(4):No.223391. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Deng Xiang-jin, Peng Yong, et al. Research on classification of relative density in lunar regolith drilling[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(4):No.223391. | |
| 2 | 姚猛,郑燕红,赵志晖,等. 一种月表采样器合理铲挖深度的研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 26(3):50-56. |
| Yao Meng, Zheng Yan-hong, Zhao Zhi-hui, et al. Research on reasonable excavation depth for lunar regolith sampler[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(3):50-56. | |
| 3 | 姜水清,刘荣凯,林云成,等. 铲挖式表层月壤采样器设计与试验[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2019, 39(1):49-58. |
| Jiang Shui-qing, Liu Rong-kai, Lin Yun-cheng,et al. Design and test of a sampler for lunar surface regolith[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2019, 39(1):49-58. | |
| 4 | Shaw A, Arvidson R E, Bonitz R, et al. Phoenix soil physical properties investigation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2009, 114(E1):No.E00E05. |
| 5 | Tsuchiya K, Ishigami G. Vision-based measurement of spatio-temporal deformation of excavated soil for the estimation of bucket resistive force[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2020, 90:11-21. |
| 6 | Jiang Xiao-hu, Tong Jin, Ma Yun-hai, et al. Development and verification of a mathematical model for the specific resistance of a curved subsoiler[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 190:107-119. |
| 7 | Malaguti F. Soil machine interaction in digging and earthmoving automation[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th ISARC, Brighton, United Kingdom, 1994:187-191. |
| 8 | Blouin S, Hemami A, Lipsett M. Review of resistive force models for earthmoving processes[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2001, 14(3):102-111. |
| 9 | Swick W C, Perumpral J V. A model for predicting soil-tool interaction[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 1988, 25(1):43-56. |
| 10 | Xi Bang-lu, Jiang Ming-jing, Cui Liang, et al. Experimental verification on analytical models of lunar excavation[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2019, 83:1-13. |
| 11 | Yang Qin-sen, Sun Shu-ren. A soil-tool interaction model for bulldozer blades[J]. Journal of Terramechanics,1994,31(2):55-65. |
| 12 | Luth H J, Wismer R D. Performance of plane soil cutting blades in sand[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1971, 14(2):255-259. |
| 13 | 薛龙, 邹猛, 李建桥,等. 基于轮地作用参数和PLSDA方法的月壤力学性能评估[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(11):3751-3758. |
| Xue Long, Zou Meng, Li Jian-qiao, et al. Mechanical performance estimation of lunar soil using wheel-soil interaction parameter and PLSDA[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(11):3751-3758. | |
| 14 | 郑燕红, 姚猛, 金晟毅,等. 月面复杂地形表层采样可采点确定方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术,2019,39(2):41-48. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Yao Meng, Jin Sheng-yi, et al. Lunar surface sampling point selection for uneven terrain[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2019, 39(2):41-48. | |
| 15 | 郑燕红, 邓湘金, 彭兢,等. 基于人工势场法的月球表层采样装置避障规划[J]. 中国空间科学技术. 2015(6):66-74. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Deng Xiang-jin, Peng Jing,et al. Lunar surface sampling device collision avoidance planning based on artificial potential field methon[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2015(6):66-74. | |
| 16 | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,等. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2021,51(3):1146-1152. |
| Wang Kang, Yao Meng, Li Li-ben, et al. Mechanical performance identification for lunar soil in lunar surface sampling[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3):1146-1152. | |
| 17 | 王康, 张沛, 林云成,等. 采样机械臂关节月表环境适应性设计[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2017, 34(5):482-489. |
| Wang Kang, Zhang Pei, Lin Yun-cheng, et al. Environmental adaptive design of joint for a lunar surface sampling arm[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2017, 34(5):482-489. |
| [1] | Kang WANG,Meng YAO,Li-ben LI,Jian-qiao LI,Xiang-jin DENG,Meng ZOU,Long XUE. Mechanical performance identification for lunar soil in lunar surface sampling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [2] | ZHAO De-ming, JIANG Sheng-yuan, TANG De-wei, HOU Xu-yan, DENG Zong-quan. Structure design of lunar subsurface sampling drill [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1149-1158. |
| [3] | CUI Jin-sheng, HOU Xu-yan, DENG Zong-quan, PAN Wan-jing, JIANG Sheng-yuan. Measurement system and experiment study of the effective thermal conductivity of granular system in a vacuum [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 457-464. |
| [4] | ZHANG Peng,DENG Zong-quan,HU Ming,GAO Hai-bo. Mobility performance analysis of lunar rover with center of mass varied based on the theory of terramechanics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(06): 1573-1578. |
| [5] | Zou Meng,Li Jian-qiao,Jia Yang,Ren Lu-quan,Li Yin-wu . Statics characteristics of lunar soil by DEM simulation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(02): 383-0387. |
| [6] | Li Wen, Gao Feng, Sun Peng. Design of composite material wheel of planetary rover [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(04): 502-505. |
|
||