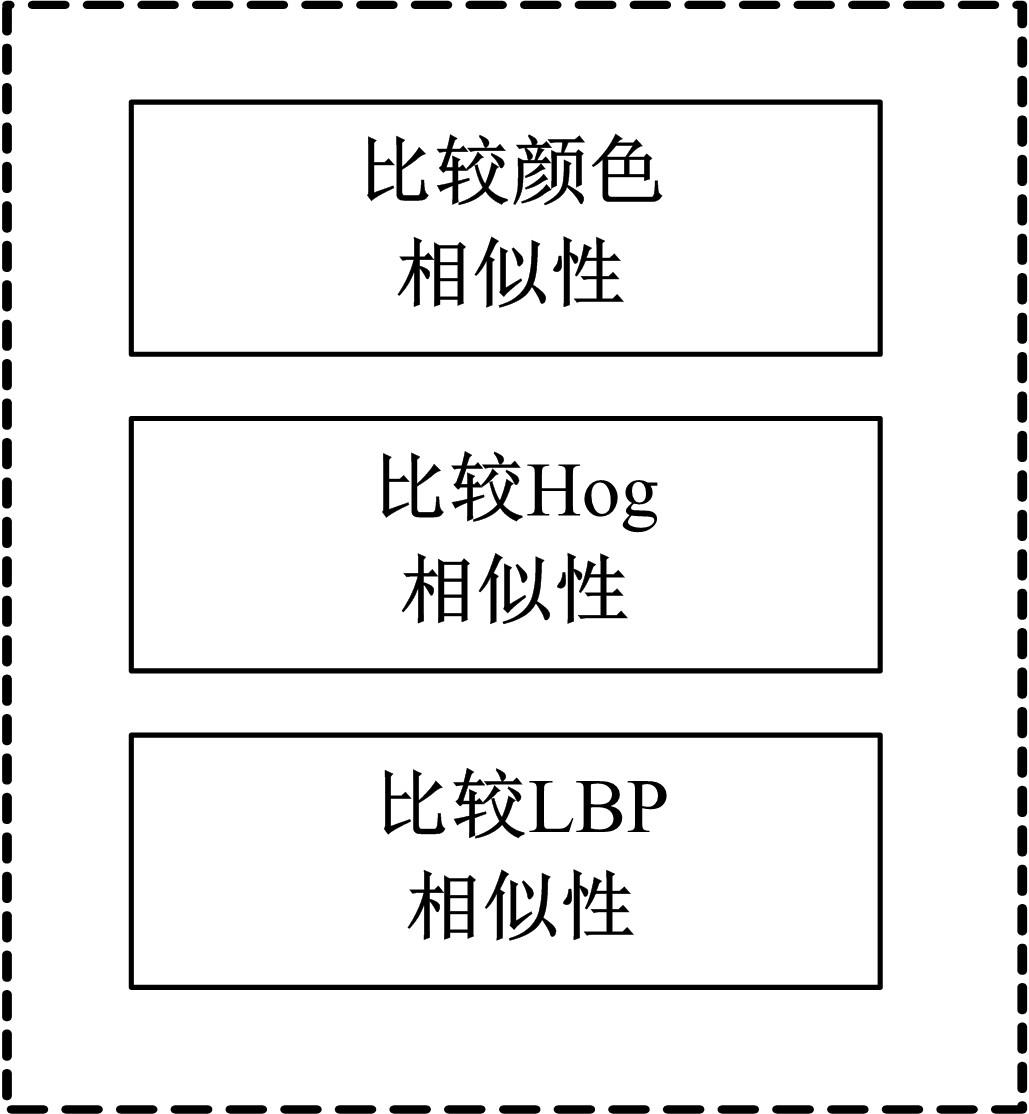
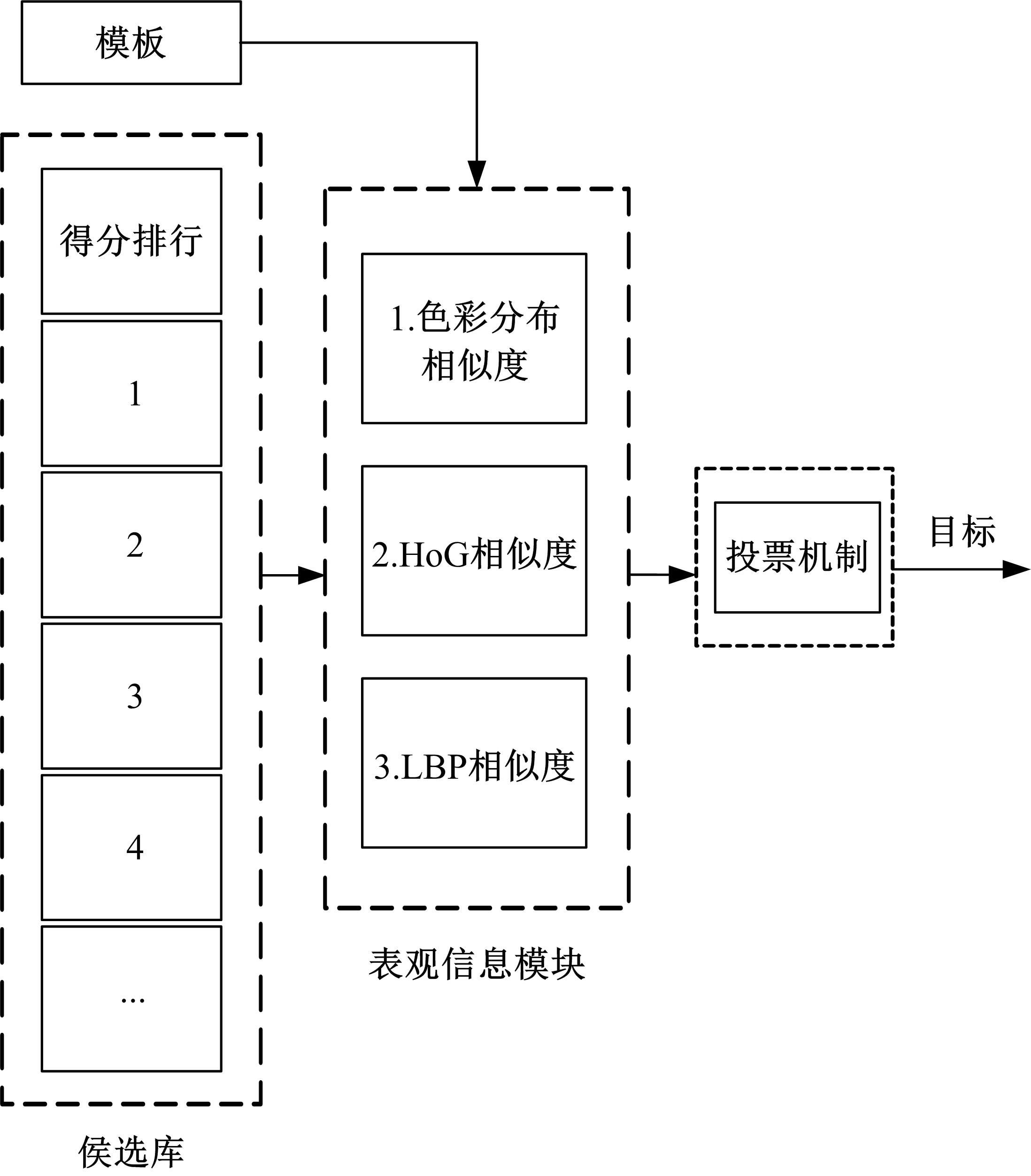
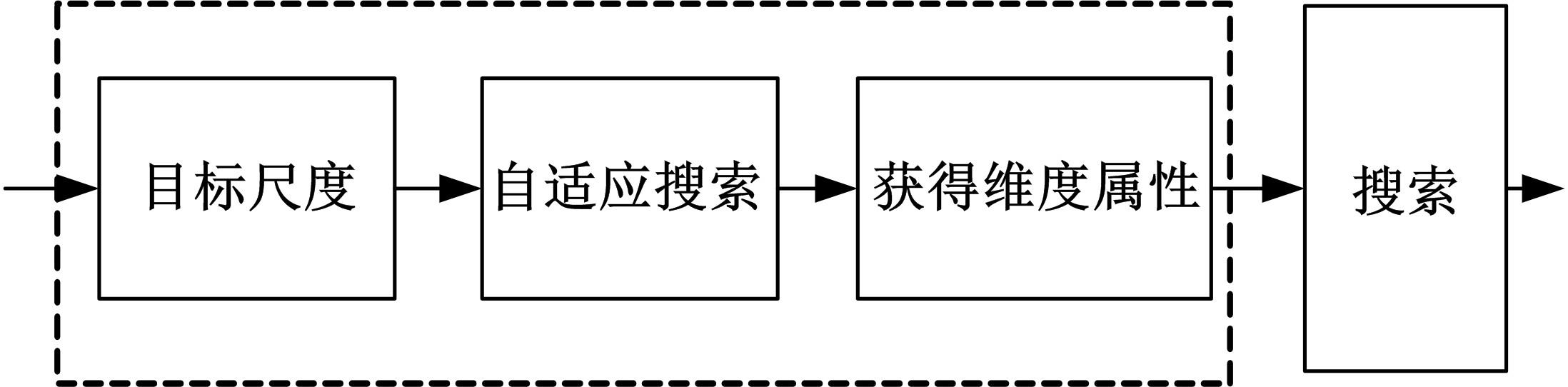
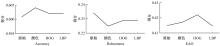
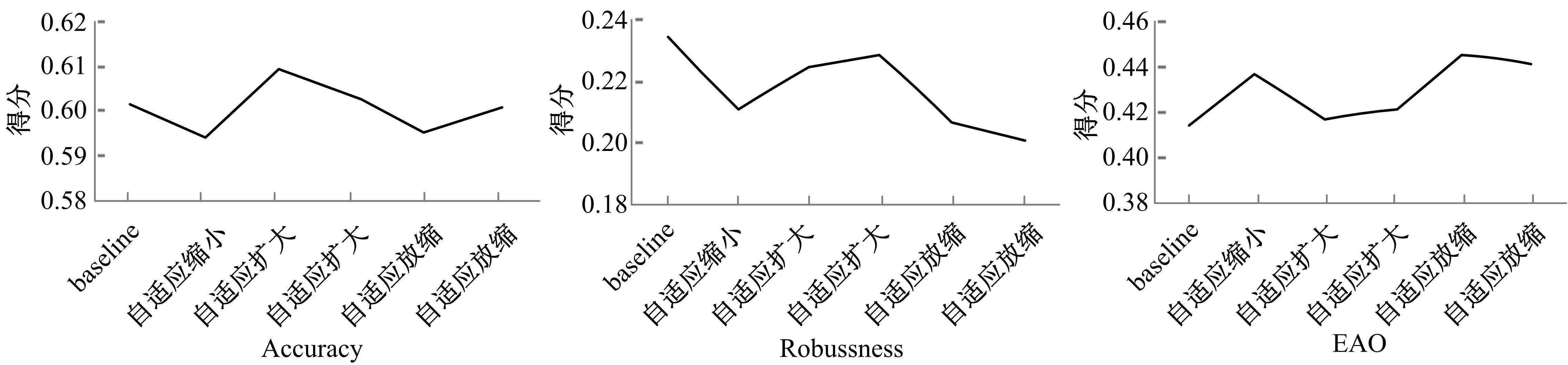
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2676-2684.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210367
Deep target tracking using augmented apparent information
Kan WANG1( ),Hang SU2,Hao ZENG2,Jian QIN2(
),Hang SU2,Hao ZENG2,Jian QIN2( )
)
- 1.Institute of Southwest Electronic Technology,Chengdu 610036,China
2.Microelectronic and Communication College,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400030,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| 1 | 徐谦,李颖,王刚.基于深度学习的行人和车辆检测[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| Xu Qian, Li Ying, Wang Gang, Pedestrian-vehicle detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. | |
| 2 | Li B, Yan J, Wu W, et al. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Utah, USA, 2018: 8971-8980. |
| 3 | Matej K, Ales L, Jiri M, et al. The sixth visual object tracking VOT2018 challenge results[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-53. |
| 4 | Wang Q, Li B. SiamRPN++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4277-4286. |
| 5 | Zhang Z P, Peng H W. Deeper and wider siamese networks for real-time visual tracking[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4586-4595. |
| 6 | 徐涛, 马克, 刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| Xu Tao, Ma Ke, Liu Cai-hua. Multi object pedestrian tracking based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. | |
| 7 | Voigtlaender P, Luiten J, Torr P H S, et al. Siam R-CNN: visual tracking by re-detection[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6577-6587. |
| 8 | Xu Y D, Wang Z Y, Li Z, et al. SiamFC++: towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines[C]// Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12549-12556. |
| 9 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 10 | Kristan M, Leonardis A, Matas J, et al. The visual object tracking VOT2016 challenge results[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 607-628. |
| 11 | Kristan M, Leonardis A, Matas J, et al.The seventh visual object tracking VOT2019 challenge results[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 2206-2241. |
| 12 | Martin D, Goutam B, Fahad S K, et al. ATOM: accurate tracking by overlap maximization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4660-4669. |
| 13 | Wang Q, Zhang L, Luca B, et al. Fast online object tracking and segmentation: a unifying approach[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1328-1338. |
| 14 | Anelljan M, Robinson A, Khan F S, et al. Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 472-488. |
| 15 | Xu T, Feng Z H, Wu X J, et al. Learning adaptive discriminative correlation filters via temporal consistency preserving spatial feature selection for robust visual object tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(11): 5596-5609. |
| 16 | Goutam B, Martin D, Luc V G, et al. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 6182-6191. |
| 17 | 薛英杰,韩威,周松斌,等.基于生成对抗单分类网络的异常声音检测[J].吉林大学学报:理学版,2021,59(6):1517-1524. |
| Xue Ying-jie, Han Wei, Zhou Song-bin,et al. Abnormal sound detection based on generative adversarial single classification network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Science Edition),2021,59(6):1517-1524. | |
| 18 | 朱新丽,才华,寇婷婷,等.行人多目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:理学版,2021,59(5):1161-1170. |
| Zhu Xin-li, Cai Hua, Kou Ting-ting, et al. Pedestrian multi-target tracking algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Science Edition),2021,59(5):1161-1170. | |
| 19 | 龙年.基于轨迹提取算法的视频关联动作跟踪仿真[J].吉林大学学报:理学版,2022,60(3):641-646. |
| Long Nian. Simulation of video association motion tracking based on trajectory extraction algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Science Edition),2022,60(3):641-646. |
| [1] | Yong LIU,Lei XU,Chu-han ZHANG. Deep reinforcement learning model for text games [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [2] | Jie CAO,Xue QU,Xiao-xu LI. Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [3] | Tao XU,Ke MA,Cai-hua LIU. Multi object pedestrian tracking based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [4] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhao LI,Jing LIU,Huang-shui HU,Dan WANG,Xue-bai ZANG. Scene classification based on degree of naturalness and visual feature channels [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1668-1675. |
| [5] | CHE Xiang-jiu, WANG Li, GUO Xiao-xin. Improved boundary detection based on multi-scale cues fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [6] | WANG Yi-yuan, OUYANG Dan-tong, ZHANG Li-ming. Min-length hitting set GRASP algorithm based on dynamic degree of components [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 930-936. |
| [7] | XU Yan-yan, CHEN Hui, LIU Jia-ju, YUAN Jin-zhao. Cell processor stereo matching parallel computation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 952-958. |
| [8] | ZHANG Bao-hua, HUANG Wen-qian, LI Jiang-bo, ZHAO Chun-jiang, LIU Cheng-liang, HUANG Dan-feng. Online sorting of irregular potatoes based on I-RELIEF and SVM method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1811-1817. |
| [9] | YANG Yan, LIU Sa, LIAN Shi-bin, ZHU Xiao-dong. Analysis of fruit tree pests morphological characteristics based on computer vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 235-238. |
| [10] | SHANG Fei, MA Jun-Xiao, YAO Li, TIAN Di, QIU Chun-Ling. Multifeature fusion based method for monitoring working status of instruments [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 545-0548. |
| [11] | GE Liang, ZHU Qing-sheng, FU Si-si, LUO Da-jiang, LIU Jin-feng. Improved image dense stereo matching algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(01): 212-0217. |
| [12] |
GUAN Xin, JIA Xin, GAO Zhen-hai .
Adaptive threshold algorithm based on contrast-regional homogeneity analysis of lane image [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(04): 758-763. |
| [13] | Wan Peng,Sun Yu,Sun Yong-hai . Recognition method of rice kernel shape based on computer vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(02): 489-0492. |
| [14] | Tian Jian, Li Jiang, Li Yaqiao. Calibration technique of photogrammetry of traffic accident scene [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊1): 136-0139. |
| [15] | GUAN Xin, DONG Yin-ping, GAO Zhen-hai. LMedSquare based road curve fitting algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (2): 194-197. |
|
||