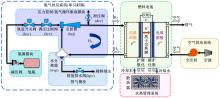
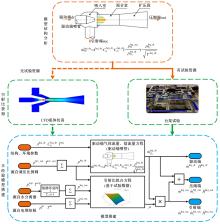
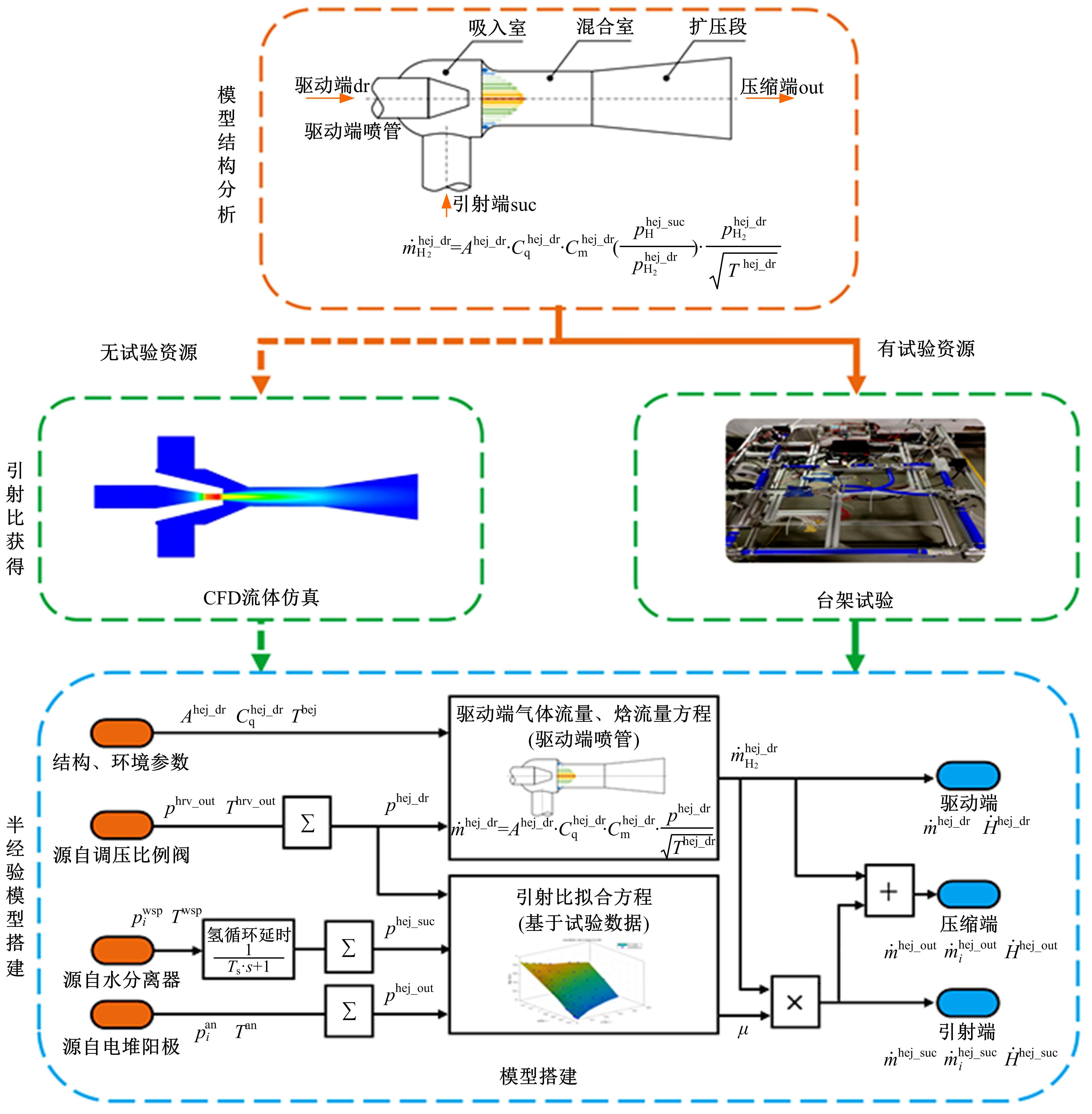
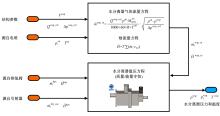
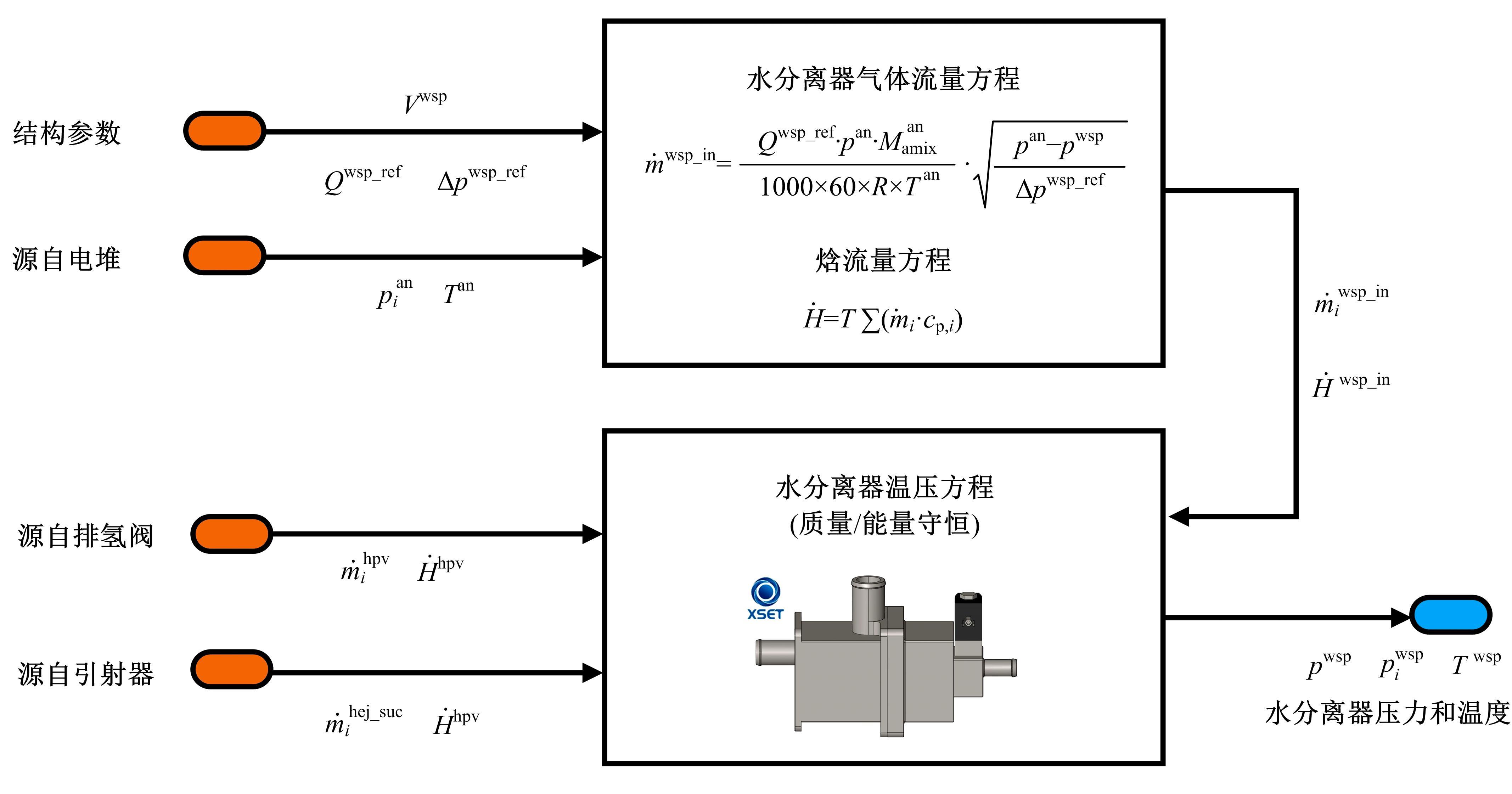
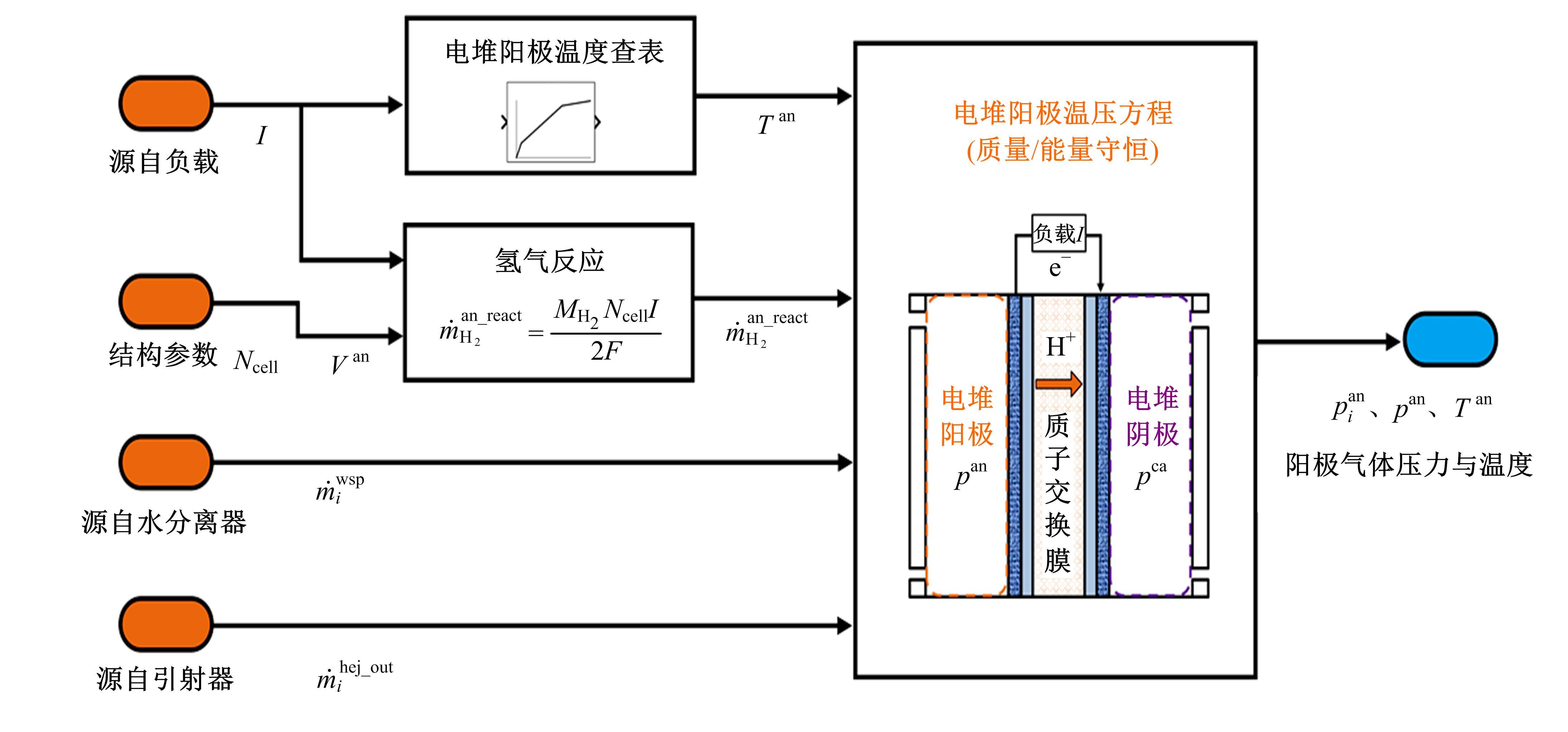
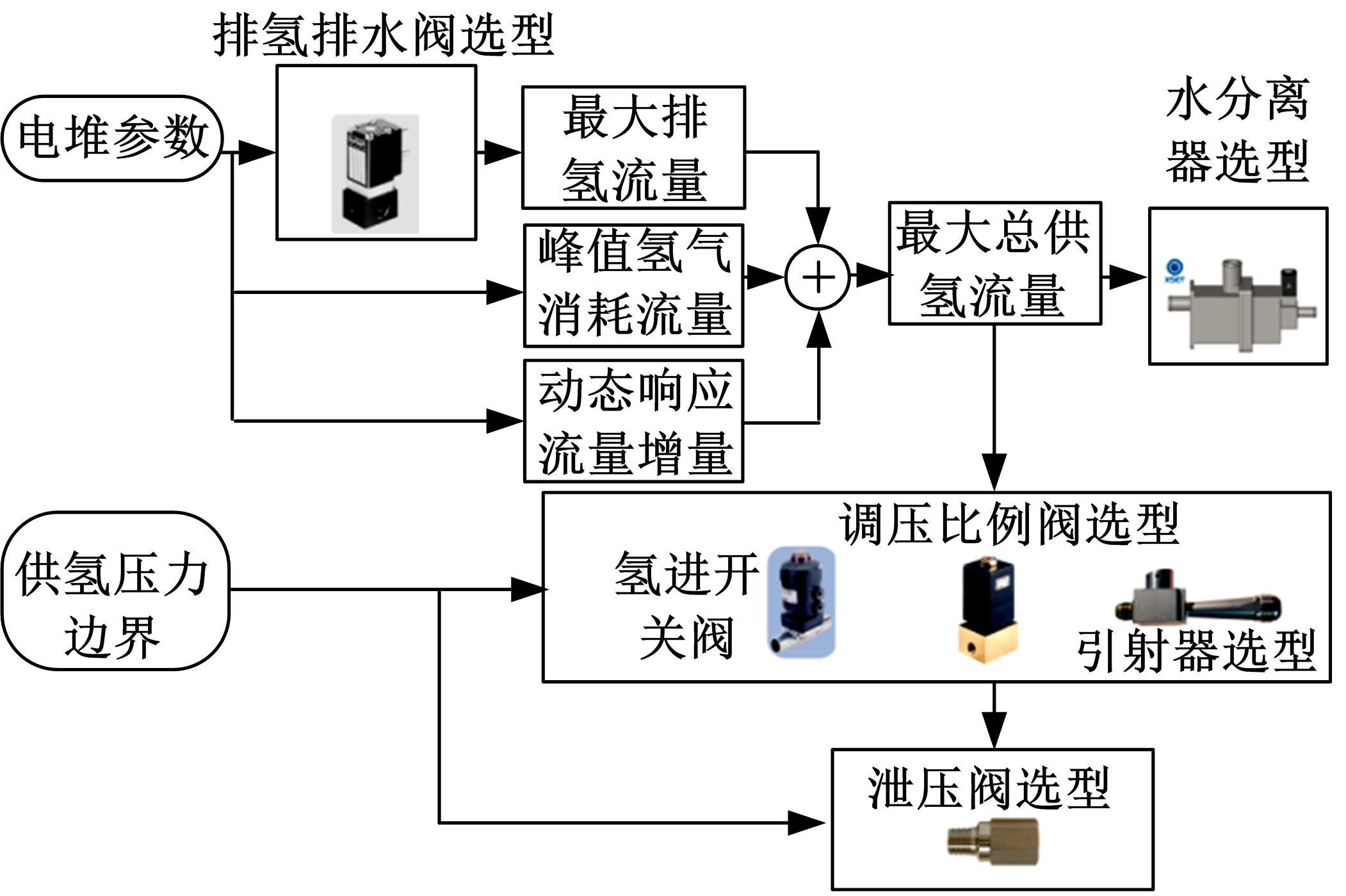
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 1982-1995.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220344
Modeling and selection scheme of proton exchange membrane fuel cell hydrogen supply system
Feng-xiang CHEN1( ),Jun-yu ZHANG1,Feng-lai PEI2,Ming-tao HOU1,Qi-peng LI3,Pei-qing LI3,Yang-yang WANG4,Wei-dong ZHANG5
),Jun-yu ZHANG1,Feng-lai PEI2,Ming-tao HOU1,Qi-peng LI3,Pei-qing LI3,Yang-yang WANG4,Wei-dong ZHANG5
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Shanghai Motor Vehicle Inspection Certification and Technology Innovation Center,Shanghai 201805,China
3.School of Mechanical and Energy Engineering,Zhejiang University of Science and Technology,Hangzhou 310023,China
4.Shaoxing Xuesheng Energy Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Shaoxing 312000,China
5.School of Information and Communication Engineering,Hainan University,Haikou 570228,China
CLC Number:
- U469.72
| 1 | Ryan O'Hayre Whitney Colella. 燃料电池基础[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2007. |
| 2 | 衣宝廉. 燃料电池原理、技术、应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2003. |
| 3 | Pukrushpan J T. Modeling and control of fuel cell systems and fuel processors[D]. Michigan: Department of Mechanical Engineering the University of Michigan, 2003. |
| 4 | Hu M, Cao G. Research on the long-term stability of a PEMFC stack: analysis of pinhole evolution[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(15): 7940-7954. |
| 5 | Bao C, Ouyang M, Yi B. Modeling and control of air stream and hydrogen flow with recirculation in a PEM fuel cell system—I. Control-oriented modeling[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2006, 31(13): 1879-1896. |
| 6 | 董凯瑞, 刘广彬, 高志成. 燃料电池氢气循环系统综述[J]. 电源技术, 2021, 45(4): 545-551. |
| Dong Kai-rui, Liu Guang-bin, Gao Zhi-cheng. Review of fuel cell hydrogen circulation system[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 45(4): 545-551. | |
| 7 | 南泽群, 许思传, 章道彪, 等. 车用PEMFC系统氢气供应系统发展现状及展望[J]. 电源技术, 2016, 40(8): 1726-1730. |
| Ze-qun Nan, Xu Si-chuan, Zhang Dao-biao, et al. Development and prospect of hydrogen supply system in vehicle PEMFC[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 40(8): 1726-1730. | |
| 8 | 索科洛夫, 津格尔.喷射器[M].黄秋云译.北京:科学出版社, 1977. |
| 9 | Chen F X, Yu Y, Liu Y, et al. Control system design for proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on a common rail (I): Control strategy and performance analysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(7): 4285-4293. |
| 10 | Chen F X, Yu Y, Liu Y. Control system design for proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on a common rail (II): optimization and schedule scheme for the common rail[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(7): 4294-4301. |
| 11 | 张家明, 马天才, 丛铭, 等. 大功率燃料电池氢气系统建模与控制[J]. 汽车技术, 2021, 51(2): 23-27. |
| Zhang Jia-ming, Ma Tian-cai, Cong Ming, et al. Hydrogen system modelling & control for high-power fuel cell system[J]. Automobile Technology, 2021, 51(2): 23-27. | |
| 12 | Brunner D A, Marcks S, Bajpai M, et al. Design and characterization of an electronically controlled variable flow rate ejector for fuel cell applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(5): 4457-4466. |
| 13 | Zhang Q Q, Feng J M, Zhang Q Q, et al. Performance prediction and evaluation of the scroll-type hydrogen pump for FCVs based on CFD–Taguchi method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(29): 15333-15343. |
| 14 | Macedo-Valencia J, Sierra J M, Figueroa-Ramírez S J, et al. 3D CFD modeling of a PEM fuel cell stack[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(48): 23425-23433. |
| 15 | Nanadegani F S, Lay E N, Iranzo A, et al. On neural network modeling to maximize the power output of PEMFCs[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 348: NO. 136345. |
| 16 | Zheng L, Hou Y, Zhang T, et al. Performance prediction of fuel cells using long short‐term memory recurrent neural network[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(6): 9141-9161. |
| 17 | Ma T C, Zhang Z L, Lin W K, et al. Impedance prediction model based on convolutional neural networks methodology for proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(35): 18534-18545. |
| 18 | 郭爱, 陈维荣, 李奇, 等. 车用燃料电池氢气供应系统的预测控制[J]. 太阳能学报, 2013, 34(8): 1484-1491. |
| Guo Ai, Chen Wei-rong, Li Qi, et al. Predictive control of hydrogen supplying system for fuel cells for vehicle[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2013, 34(8): 1484-1491. | |
| 19 | 裴冯来, 侯明涛, 贺继龙, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池空压机建模[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2019, 8(6): 1247-1252. |
| Pei Feng-lai, Hou Ming-tao, He Ji-long, et al. Modeling of air compressors for proton exchange membrane fuel cell [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2019, 8(6):1247-1252. | |
| 20 | Amphlett J C, Baumert R M, Mann R F, et al. Performance modeling of the Ballard Mark IV solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell II. Empirical model development[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1995, 142(1): 9-15. |
| 21 | Mann R F, Amphlett J C, Hooper M, et al. Development and application of a generalized steady-state electrochemical model for a PEM fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2000, 86(1-2): 173-180. |
| 22 | 卢兰光, 欧阳明高. 车用低压质子交换膜燃料电池电堆的半经验模型[J]. 机械工程学报, 2007, 43(2): 110-114. |
| Lu Lan-guang, Ouyang Ming-gao. Performance modeling for low pressure vehicle proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 43(2): 110-114. | |
| 23 | Chen F X, Hou M T, Li J H, et al. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell ejector test platform design and ejector test analysis[J]. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2021, 12(3): No.103. |
| 24 | Yuan H, Dai H F, Wu W, et al. A fuzzy logic PI control with feedforward compensation for hydrogen pressure in vehicular fuel cell system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(7): 5714-5728. |
| 25 | 张浩琛. 质子交换膜燃料电池供气系统控制策略研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学电气工程与信息工程学院, 2013. |
| Zhang Hao-chen. The research on control strategy of air supply system in proton exchange membrane fuel cell[D]. Lanzhou: College of Electrical and Information Engineering, Lanzhou University of Technology,2013. | |
| 26 | Quan S W, Wang Y X, Xiao X L, et al. Feedback linearization-based MIMO model predictive control with defined pseudo-reference for hydrogen regulation of automotive fuel cells[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 293: No. 116919. |
| 27 | 唐紫英. 控制阀流量系数Kv设计计算中的修正[J]. 抚顺石油学院学报, 1997, 16(3): 59-65. |
| Tang Zi-ying. The correction for design calculation of flow coefficient Kv on the control valve[J]. Journal of Fushun Petroleum Institute, 1997, 16(3): 59-65. | |
| 28 | Zhu Y H, Li Y Z. New theoretical model for convergent nozzle ejector in the proton exchange membrane fuel cell system[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 191(2): 510-519. |
| [1] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [2] | GAN Xin, YIN Kun, HE Jiang-fu, YIN Qi-lei. Development and test of a large diameter hollow-through DTH air hammer and drill bit used in rescue well [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1844-1851. |
|
||