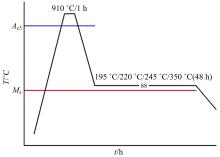
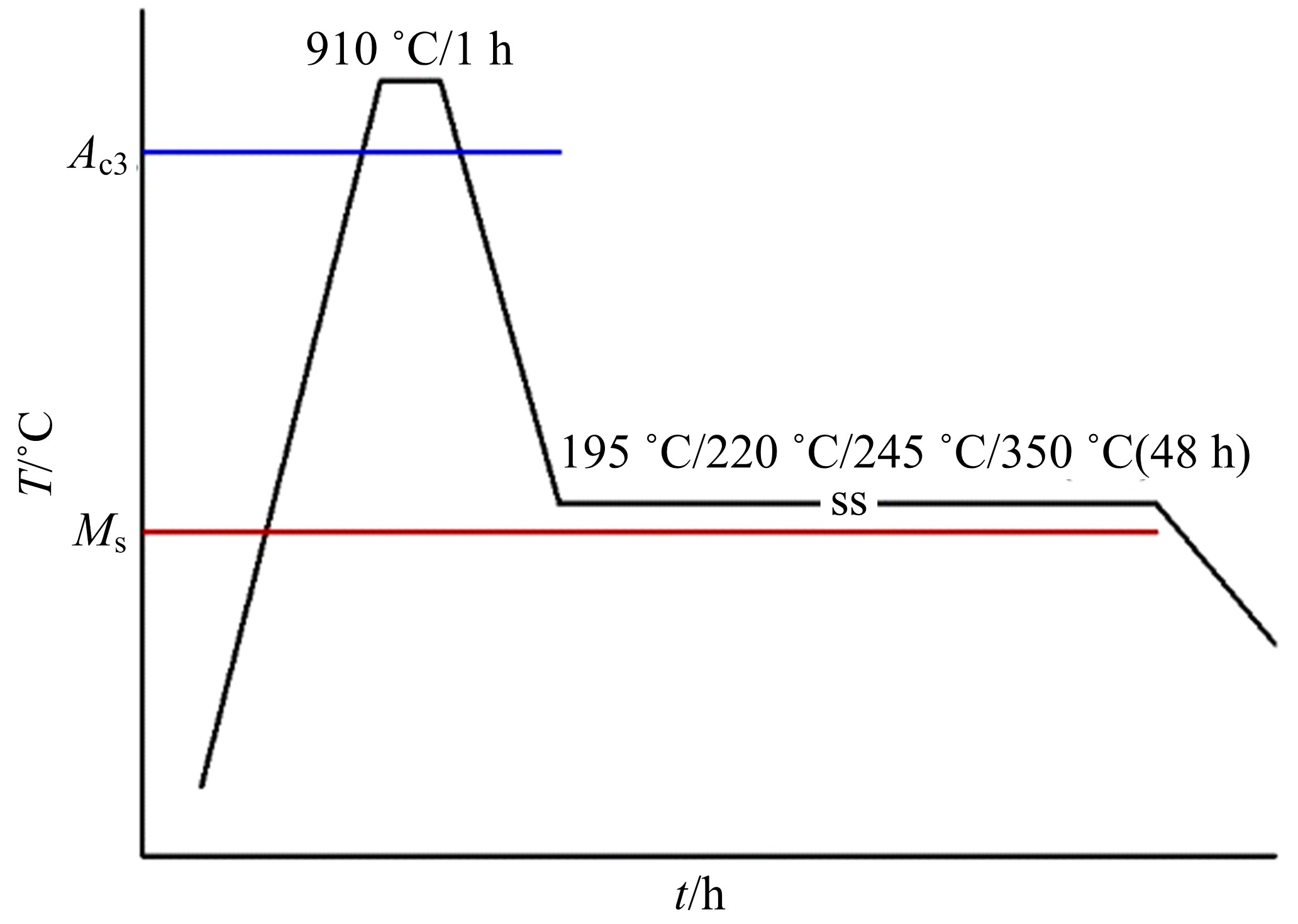
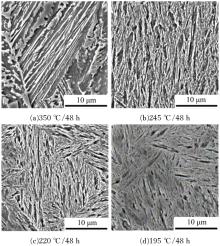
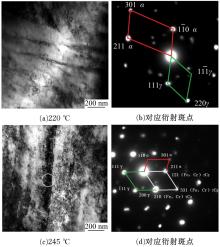
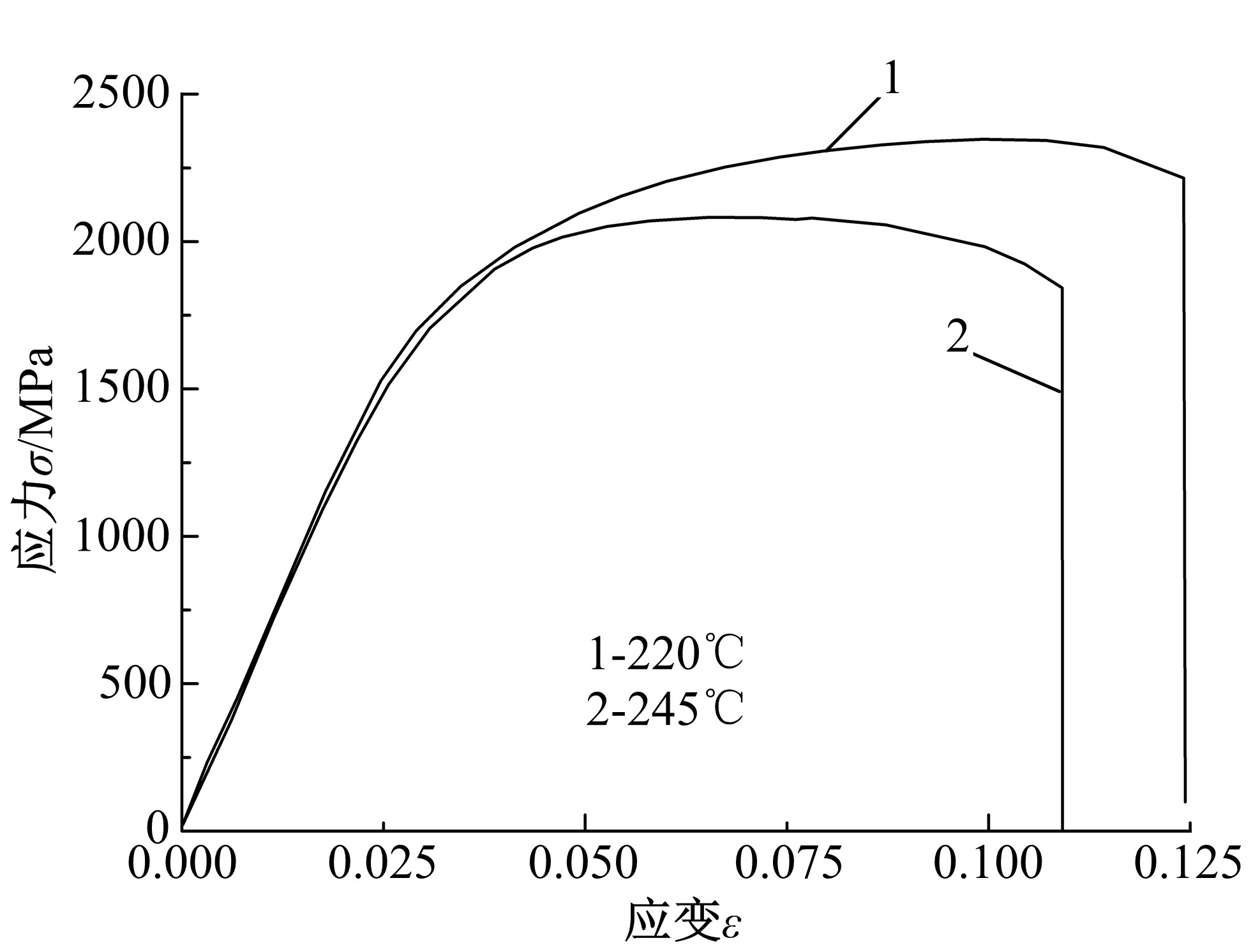
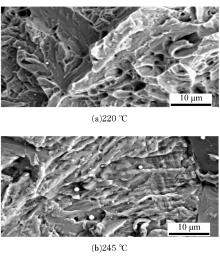
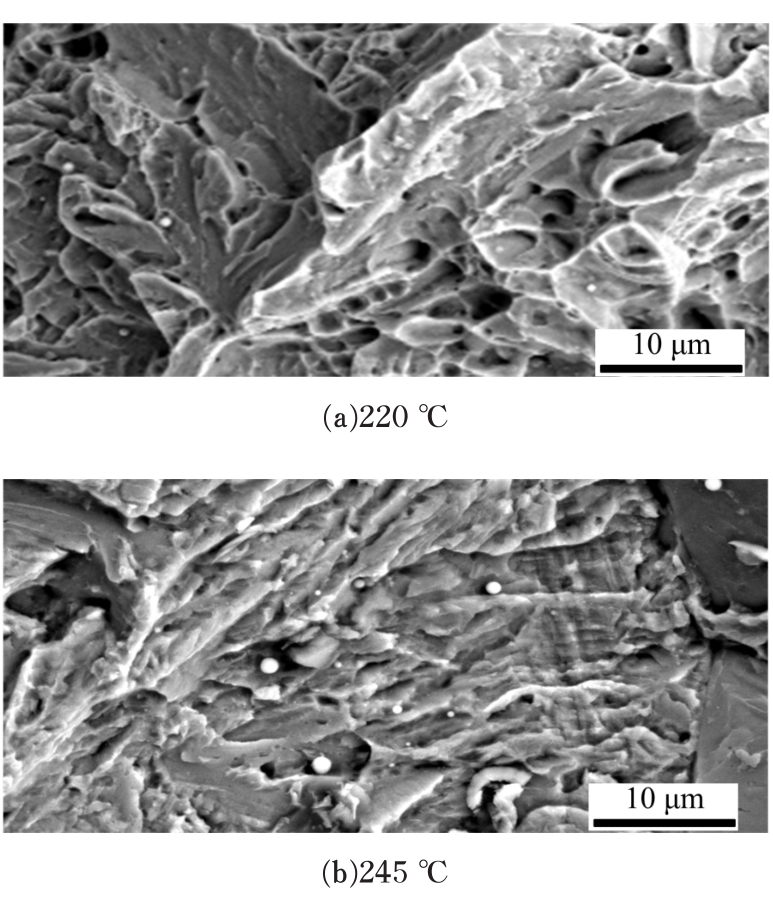
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 520-525.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190012
Effect of isothermal heat treatment temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of super bainite
Wen-cui XIU1,2( ),Hua WU1(
),Hua WU1( ),Ying HAN1,Yun-xu LIU1
),Ying HAN1,Yun-xu LIU1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials of Ministry of Education,Changchun University of Technology,Changchun 130012, China
2.School of Mechanical and Civil Engineering,Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology University, Jilin 132101, China
CLC Number:
- TG142.1
| 1 | Caballero F G, Bhadeshia H K D H. Very strong bainite[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2004, 8(3): 251-257. |
| 2 | Hase K, Garcia-Mateo C, Bhadeshia H K D H. Bimodal size-distribution of bainite plates[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2006, 438-440: 145-148. |
| 3 | Luzginova N V, Zhao L, Sietsma J. Bainite formation kinetics in high carbon alloyed steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2008, 481: 766-769. |
| 4 | Han Y, Wu H, Liu C, et al. Microstructures and mechanical characteristics of a medium carbon super-bainitic steel after isothermal transformation[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2014, 23(12): 4230-4236. |
| 5 | Podder A S, Bhadeshia H K D H. Thermal stability of austenite retained in bainitic steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2010, 527(7/8): 2121-2128. |
| 6 | Wu H, Liu C, Zhao Z B, et al. Design of air-cooled bainitic microalloyed steel for a heavy truck front axle beam[J]. Materials and Design, 2006, 27(8): 651-656. |
| 7 | Soliman M, Mostafa H, El-Sabbagh A S, et al. Low temperature bainite in steel with 0.26 wt% C[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2010, 527(29/30): 7706-7713. |
| 8 | 吴化. 低合金高强度高塑性复相钢材的成分设计[D]. 上海: 东华大学材料科学与工程学院, 2007. |
| Wu Hua. Composition design of low alloy high strength and plasticity complex phases steels[D]. Shanghai: College of Materials Science and Engineering, Donghua University, 2007. | |
| 9 | 陈连生, 张健杨, 田亚强, 等. 预先Mn配分处理对Q&P钢中C配分及残余奥氏体的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(5): 527-536. |
| Chen Lian-sheng, Zhang Jian-yang, Tian Ya-qiang, et al. Effect of Mn pre-partitioning on C partitioning and retained qustenite of Q&P steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinice, 2015, 51(5): 527-536. | |
| 10 | Misra A, Sharma S, Sangal S, et al. Critical isothermal temperature and optimum mechanical behaviour of high Si-containing bainitic steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2012, 558: 725-729. |
| 11 | 康沫狂, 朱明, 陈大明, 等. 硅合金钢淬火组织中残留奥氏体的力学稳定性与力学性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2005, 30(1): 14-19. |
| Kang Mo-kuang, Zhu Ming, Chen Da-ming, et al. Mechanical property and mechanical stability of retained austenite in quenching microstructure of an alloy steel containing Si[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2005, 30(1): 14-19. | |
| 12 | Sourmail T, Smanio V. Low temperature kinetics of bainite formation in high carbon steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(7): 2639-2648. |
| 13 | 刘宗昌, 王海燕, 王玉峰, 等. 贝氏体碳化物的形貌及形成机制[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2008, 29(1): 32-37, 46. |
| Liu Zong-chang, Wang Hai-yan,Wang Yu-feng, et al. Morphology and formation mechanism of bainitic carbide[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2008, 29(1): 32-37, 46. | |
| 14 | 蔡珣. 材料科学与工程基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2010. |
| 15 | Bhadeshia H K D H. High performance bainitic steels[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 500/501: 63-74. |
| 16 | 范雄. 金属X射线学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1981. |
| 17 | 吴万国, 阮玉忠, 黄清明. 残余奥氏体定量分析的特殊方法[J]. 福州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 30(3): 385-386. |
| Wu Wan-guo, Ruan Yu-zhong, Huang Qing-ming. A special method on quantitative analysis of remnant austenite[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 30(3): 385-386. | |
| 18 | Mandal D, Ghosh M, Pal J, et al. Effect of austempering treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-Si steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(4): 1069-1075 |
| 19 | Xiu W C, Han Y, Liu C, et al. Cyclic stress induced phase transformation in super-bainitic microstructure[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2017, 26(3): 545-549. |
| [1] | Wu⁃jiao XU,Cheng⁃shang LIU,Xin⁃yao LU. Simulation and prediction of surface roughness of 6061 aluminum alloy workpiece after shot peening [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1280-1287. |
| [2] | ZHUNG Wei-min, ZHAO Wen-zeng, XIE Dong-xuan, LI Bing. Joint performance analysis on connection of ultrahigh-strength steel and aluminum alloy with hot riveting [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1016-1022. |
| [3] | LIU Xiao-bo, ZHOU De-kun, ZHAO Yu-guang. Microstructure and mechanical property of Mg2Si/Al composites fabricated by semi-solid extrusion under different isothermal heat treatments [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1577-1582. |
| [4] | LI Chun-ling, FAN Ding, WANG Bin, YU Shu-rong. 5A06 aluminum alloy and galvanized steel butt welding-brazing by laser with preset filler powder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 516-521. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhi-qiang, JIA Xiao-fei, YUAN Qiu-ju. Springback analysis of trip high strength steel based on Yoshida-Uemori model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1852-1856. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhi-qiang, JIA Xiao-fei, ZHAO Yong, LI Xiang-ji. Experiment and simulation on quenching interface heat transfer coefficient of high-strength boron steel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1195-1199. |
| [7] | YING Liang, DAI Ming-hua, HU Ping, FAN Zheng-shuai, SHEN Guo-zhe, SHI Dong-yong. Strength and hardness prediction based on cooling rate for hot forming high strength steel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1716-1722. |
| [8] | LI Xin,WANG Gang,LU Guan-han,GU Zheng-wei,XU Hong. Weldability of 22MnB5 after hot stamping by TIG welding processes [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 708-711. |
| [9] | LI Zhi-jie, PENG Yan, LIU Hong-min, WANG Su-fen, XIAO Li-zi. Flow stress of medium carbon steel under warm compression deformation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1320-1324. |
| [10] | SUN Ji-yu, WANG Yue-ming, PAN Chun-xiang, CONG Xian-ling. Static and dynamic nano-mechanical properties of the keratinous of cattle horns [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 475-478. |
| [11] | BAI Zhi-fan, LI Gui-zhong, WANG Chao, WANG Liang, ZHANG Zhi-min. Microstructure and mechanical property of the welded joints for high-speed train bogie [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 207-211. |
| [12] | GU Zheng-wei, YU Si-bin, HAN Li-jun, MENG Jia, XU Hong. Laser lap-welding performance of ultra-high strength steel and micro-alloy steel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(02): 349-353. |
| [13] | BAI Zhi-fan, LI Gui-zhong, WANG Chao. Microstructure and mechanical property of the welded joints of S355J2W+N steel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 202-204. |
| [14] | JIANG Ri-hua, BAI Shuang, DAI Yue, ZHAO Mei-sheng. Biomechanical characteristics of keloids [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1675-1677. |
| [15] | GUAN Qing-feng,QIU Dong-hua,LI Yan,CHEN Kang-min,AN Chun-xiang,LONG He-sun. The formation behavior of aging precipitates on 17-4PH stainless steel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 654-658. |
|
||