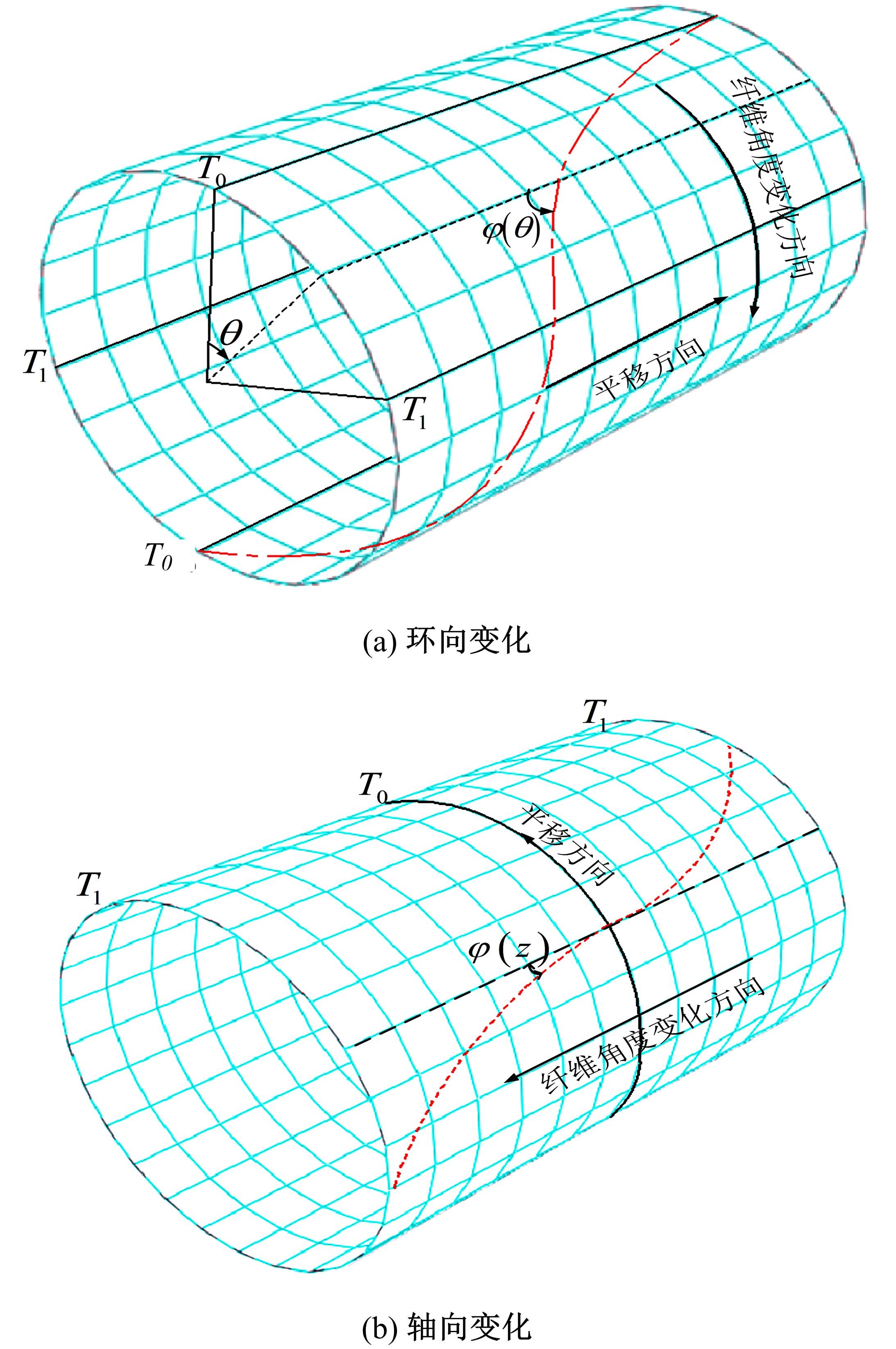
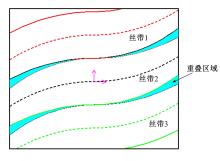
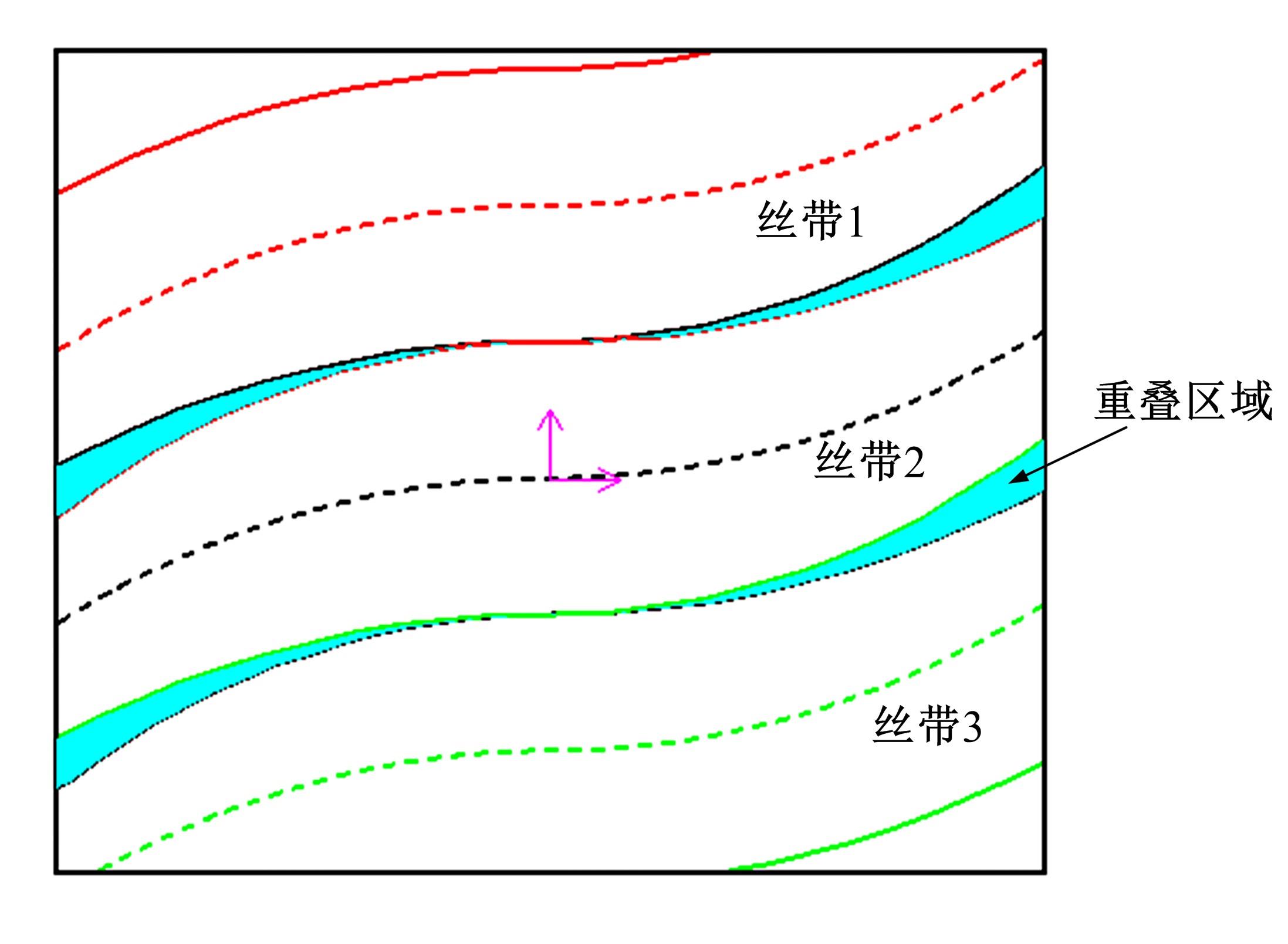
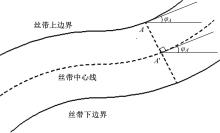
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 91-100.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200715
Previous Articles Next Articles
Buckling performance of variable stiffness composite cylindrical shells based on mode imperfections
Yu-xuan WEI1( ),Ming ZHANG2(
),Ming ZHANG2( ),Jia LIU1,Shuo LIU1,Ming-yu LU1,Hong-yu WANG1
),Jia LIU1,Shuo LIU1,Ming-yu LU1,Hong-yu WANG1
- 1.Beijing Satellite Manufacturing Factory Co. ,Ltd,Beijing 100094,China
2.China Academy of Space Technology,Beijing 100094,China
CLC Number:
- TB332
| 1 | 刘书田, 陈秀华, 曹先凡,等. 夹芯圆柱壳稳定性优化[J]. 工程力学, 2005, 22(1): 135-140. |
| Liu Shu-tian, Chen Xiu-hua, Cao Xian-fan, et al. Optimization of buckling-prone cylindrical shells with porous material core[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2005, 22(1): 135-140. | |
| 2 | 文立伟, 肖军, 王显峰, 等. 中国复合材料自动铺放技术研究进展[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 47(5): 637-649. |
| Wen Li-wei, Xiao Jun, Wang Xian-feng, et al. Process of automated placement technology for composites in china[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2015, 47(5): 637-649. | |
| 3 | 周晓芹, 曹正华. 复合材料自动铺放技术的发展及应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2009, 42(s1): 1-3, 7. |
| Zhou Xiao-qin, Cao Zheng-hua. Development and application of automated placement technology for composites[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 42(s1): 1-3, 7. | |
| 4 | Shirinzadeh B, Cassidy G, Oetomo D, et al. Trajectory generation for open-contoured structures in robotic fibre placement[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2007, 23(4): 380-394. |
| 5 | Abdalla M M, Setoodeh S, Gürdal Z. Design of variable stiffness composite panels for maximum fundamental frequency using lamination parameters[J]. Composite Structures, 2007, 81(2): 283-291. |
| 6 | Hyer M W, Charette R F. Use of curvilinear fiber format in composite structure design[J]. AIAA Journal, 1991, 29(6): 1011-1015. |
| 7 | Rouhi M, Ghayoor H, Fortin-Simpson J, et al. Design, manufacturing, and testing of a variable stiffness composite cylinder[J]. Composite Structures, 2018, 184: 146-152. |
| 8 | 叶辉, 李清原, 闫康康. 变刚度复合材料层合板的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(3):920-928. |
| Ye Hui, Li Qing-yuan, Yan Kang-kang. Mechanical properties of variable⁃stiffness carbon fiber composite laminates[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3):920-928. | |
| 9 | Gürdal Z, Tatting B F, Wu C K. Variable stiffness composite panels: effects of stiffness variation on the in-plane and buckling response[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2008, 39(5): 911-922. |
| 10 | Setoodeh S, Abdalla M M, Ijsselmuiden S T, et al. Design of variable-stiffness composite panels for maximum buckling load[J]. Composite Structures, 2009, 87(1): 109-117. |
| 11 | Blom A W, Stickler P B, Gürdal Z. Optimization of a composite cylinder under bending by tailoring stiffness properties in circumferential direction[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2010, 41(2): 157-165. |
| 12 | Rouhi M, Ghayoor H, Hoa S V, et al. Multi-objective design optimization of variable stiffness composite cylinders[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2015, 69: 249-255. |
| 13 | Nopour H, Kabiri A A, Shokrieh M M. Fiber path optimization in a variable-stifness cylinder to maximize its buckling load under external hydrostatic pressure[J]. Mechanics of Composite Materials, 2019, 54(6): 765-774. |
| 14 | Khani A, Abdalla M M, Gürdal Z. Optimum tailoring of fibre-steered longitudinally stiffened cylinders[J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 122: 343-351. |
| 15 | 孙士平, 张冰, 邓同强, 等. 复合载荷作用变刚度复合材料回转壳屈曲优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(4): 1052-1061. |
| Sun Shi-ping, Zhang Bing, Deng Tong-qiang, et al. Buckling optimization of variable stiffness composite rotary shell under combined loads[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(4): 1052-1061. | |
| 16 | 钟继凡. 基于代理模型的变刚度复合材料结构优化设计[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学航空航天学院, 2018. |
| Zhong Ji-fan. Optimization design of variable stiffness composite structurres based on meta-models[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of science and Technology School of Aerospace Engineering, 2018. | |
| 17 | 闫光, 韩小进, 闫楚良,等. 含口盖复合材料圆柱壳轴压屈曲性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2015, 45(1): 187-192. |
| Yan Guang, Han Xiao-jin, Yan Chu-liang, et al. Buckling analysis of composite cylindrical shell with cover under axial compressive load[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(1): 187-192. | |
| 18 | Arbelo M A, Degenhardt R, Castro S G P, et al. Numerical characterization of imperfection sensitive composite structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 108: 295-303. |
| 19 | Zimmermann R. Buckling research for imperfection tolerant fiber composite structures[C]∥Conference on Spacecraft Structures Materials & Mechanical Testing Noordwijk,Niederlande, 1996:27-29. |
| 20 | Kim B C, Hazra K, Weaver P M, et al. Limitations of fibre placement techniques for variable angle tow composites and their process-induced defects[C]∥The 18th International Conference on Composite Materials, Jeju, Korea, 2011: 109-117. |
| 21 | Acar E, Guler M A, Gereker B, et al. Multi-objective crashworthiness optimization of tapered thin-walled tubes with axisymmetric indentations[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2011, 49(1): 94-105. |
| 22 | 卫宇璇, 张明, 刘佳, 等. 基于自动铺放技术的高精度变刚度复合材料层合板屈曲性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11):2807-2815. |
| Wei Yu-xuan, Zhang Ming, Liu Jia, et al. Buckling performance of high-precision variable stiffness composites laminate based on automatic placement technology[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(11):2807-2815. | |
| 23 | EN1993-1-1. Eurocode 3-Design of Steel Structures[S]. |
| [1] | Fan YANG,Xu-dong ZHANG,Meng ZHAO,Bo SHE,Jun-kai DENG. Deformation behavior of shape memory alloy-metallic glass matrix composites based on finite element calculations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 172-180. |
| [2] | HU Zhi-qing, ZHENG Hui-hui, XU Ya-nan, ZHANG Chun-ling, DANG Ting-ting. Effect of Al surface with micro/macro grooves on Al/CFRP adhesive-bonded joints [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 229-235. |
| [3] | WANG Jun-nian, YE Tao, SUN Wen, WANG Qing-nian. Vibration isolation performance of energy-regenerative semi-active suspension with variable stiffness and damping [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 701-708. |
| [4] | LIU Li-ping, LIU Yong-bing, JI Lian-feng, CAO Zhan-yi, YANG Xiao-hong. Flow stress behavior of in situ particulate reinforced titanium atrix composite at elevated temperature [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1197-1201. |
| [5] | YAN Guang, HAN Xiao-jin, YAN Chu-liang,ZHU Lian-qing. Buckling analysis of composite cylindrical shell with cover under axial compressive load [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 187-192. |
| [6] | LU Guang-lin, QIU Xiao-ming, BAI Yang, LUN Xin-jie|DENG Bao-qing,REN Lu-qu. Microstructure and performance of c-BN bionic wearresistant composites [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(01): 73-0077. |
| [7] | SUN Liang,WANG Jun,HAN Ping-chou . Electrospinned PCL nanofiber and its diameter measurement correction [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(06): 1305-1309. |
| [8] |
ZHANG Xiao-ming, WANG Hong-yan, LI Jun-feng .
Preparation of bone repair material of modified-MWNTs/nano-HA/PLA [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(04): 844-847. |
| [9] | Li Hong-ji, He Ran, Zhang Wan-xi, Sun Guo-en, Zhang Li, Niu Yong-sheng . Preparation and properties of nanoTiO2/EVA composites [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(05): 710-0714. |
| [10] | SUN Guoen, ZHANG Li, LI Hongji, ZHANG Chunling, LIANG Jicai, ZHANG Wanxi. Structure and Properties of EVA/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Materials [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2005, 35(06): 577-0581. |
|
||