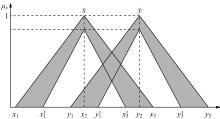
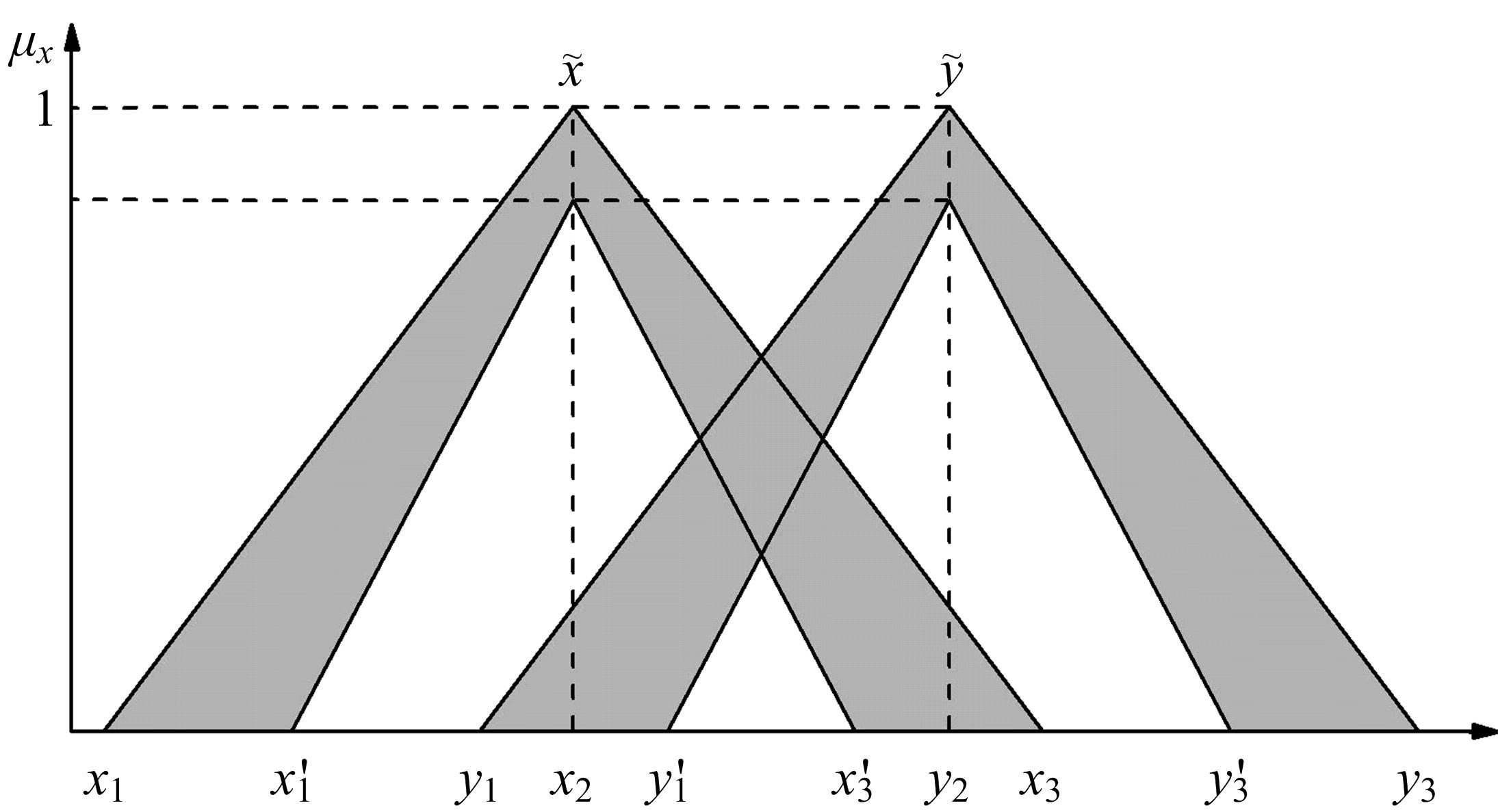
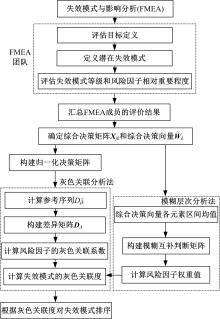
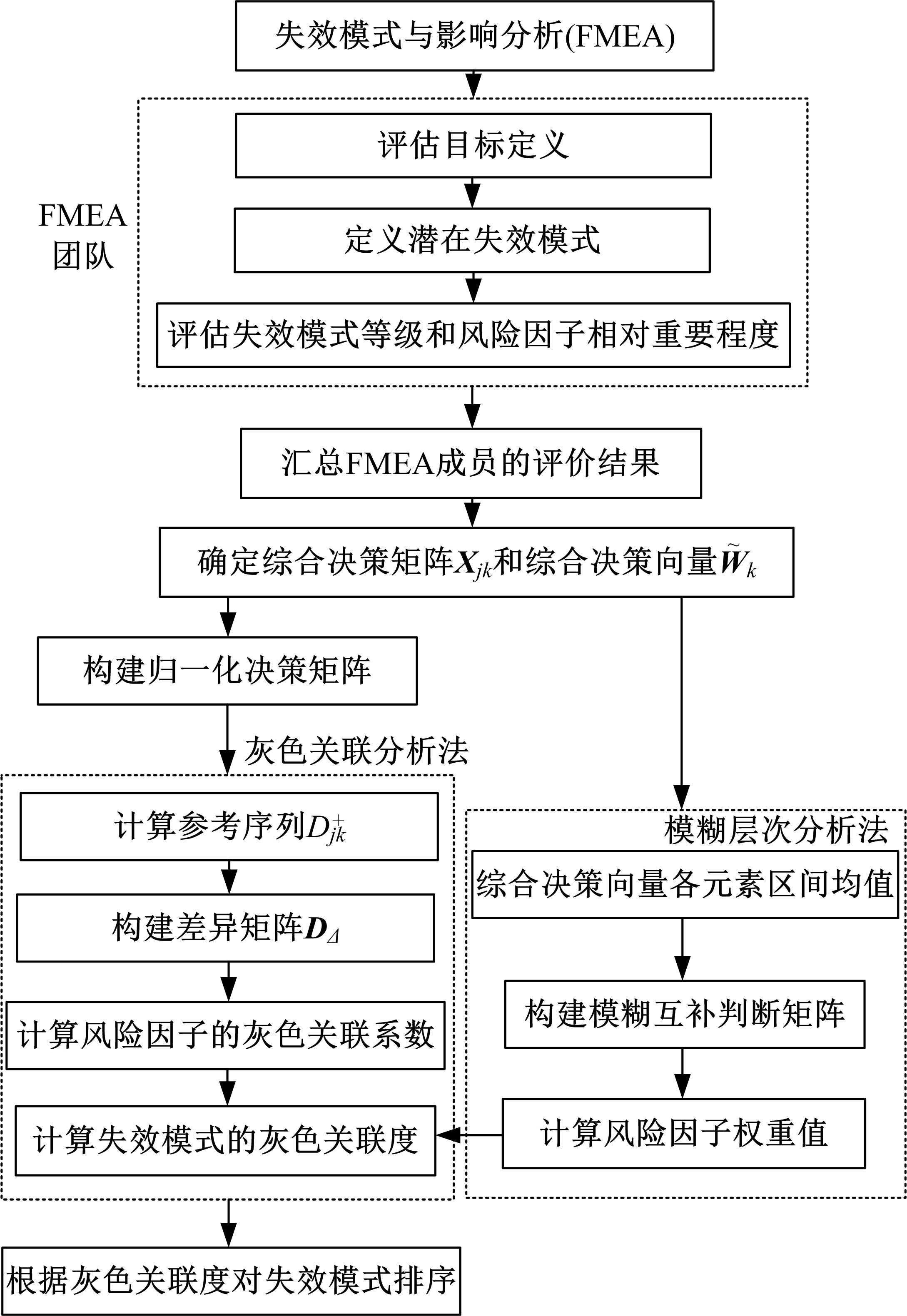
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 345-352.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211101
Application of improved failure mode and effect analysis method in risk analysis of spindle system of machining center
Hai-ji YANG1,2( ),Jia-long HE1,2,Guo-fa LI1,2(
),Jia-long HE1,2,Guo-fa LI1,2( ),Li-ding WANG1,2,Si-yuan WANG3
),Li-ding WANG1,2,Si-yuan WANG3
- 1.Key Laboratory of CNC Equipment Reliability,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Ansteel Mining Blasting Co. ,Ltd. ,Anshan 114051,China
CLC Number:
- TG659
| 1 | Schneider H. Failure mode and effect analysis: FMEA from theory to execution[J]. Technometrics, 1996, 38(1): 80. |
| 2 | Yang Z, Guo J, Tian H, et al. Weakness ranking method for subsystems of heavy-duty machine tools based on FMECA information[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 34(1): 1-12. |
| 3 | Yang H, Li G, He J, et al. Improved FMEA based on IVF and fuzzy VIKOR method: a case study of workpiece box system of CNC gear milling machine[J]. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2021, 37(6): 2478-2498. |
| 4 | 孟书, 申桂香, 陈炳锟, 等. 基于灰关联的加工中心可用性需求重要度研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(24): 187-193. |
| Meng Shu, Shen Gui-xiang, Chen Bing-kun, et al. Analysis on requirement importance rating for availability of machining center based on grey relation method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(24): 187-93. | |
| 5 | Li G, Wang Y, He J, et al. Tool wear state recognition based on gradient boosting decision tree and hybrid classification RBM[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 110(18): 511-522. |
| 6 | Liu H, You J, You X, et al. A novel approach for failure mode and effects analysis using combination weighting and fuzzy VIKOR method[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 28: 579-588. |
| 7 | Li G F, Li Y, Chen C H, et al. Advanced FMEA method based on interval 2-tuple linguistic variables and TOPSIS[J]. Quality Engineering, 2020, 32(4): 653-662. |
| 8 | Liu H, Liu L, Liu N. Risk evaluation approaches in failure mode and effects analysis: a literature review[J]. Expert Systems with Application, 2013, 40(2): 828-838. |
| 9 | 陈传海, 杨兆军, 陈菲, 等. 基于模糊数据包络分析的数控机床故障模式分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(6): 1523-1528. |
| Chen Chuan-hai, Yang Zhao-jun, Chen Fei, et al. Failure mode analysis of computer numerical control machine tools based on fuzzy-DEA[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(6): 1523-1528. | |
| 10 | Liu H, Liu L, Liu N, et al. Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis with extended VIKOR method under fuzzy environment[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2012, 39(17): 12926-12934. |
| 11 | Kutlu A C, Ekmekçioğlu M. Fuzzy failure modes and effects analysis by using fuzzy TOPSIS-based fuzzy AHP[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2012, 39(1): 61-67. |
| 12 | Chang K, Cheng C. Evaluating the risk of failure using the fuzzy OWA and DEMATEL method[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2011, 22(2): 113-129. |
| 13 | Geum Y, Cho Y, Park Y. A systematic approach for diagnosing service failure: service-specific FMEA and grey relational analysis approach[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2011, 54(11/12): 3126-3142. |
| 14 | Bian T, Zheng H, Yin L, et al. Failure mode and effects analysis based on D numbers and TOPSIS[J]. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2018, 34(4): 501-515. |
| 15 | Liu H, You J, Fan X, et al. Failure mode and effects analysis using D numbers and grey relational projection method[J]. Expert Systems with Application, 2014, 41(10): 4670-4679. |
| 16 | Zadeh L A. Fuzzy sets[J]. Information & Control, 1965, 8(3): 338-353. |
| 17 | Zadeh L A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I[J]. Information Sciences, 1975, 8(3): 199-249. |
| 18 | Zhang S, Liu S, Zhai R. An extended GRA method for MCDM with interval-valued triangular fuzzy assessments and unknown weights[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2011, 61(4): 1336-1341. |
| 19 | Ashtiani B, Haghighirad F, Makui A, et al. Extension of fuzzy TOPSIS method based on interval-valued fuzzy sets[J]. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 2009, 9(2): 457-461. |
| 20 | Li Z, Chen L. A novel evidential FMEA method by integrating fuzzy belief structure and grey relational projection method[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 77: 136-147. |
| 21 | 张吉军. 模糊层次分析法(FAHP)[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2000, 14(2): 80-88. |
| Zhang Ji-jun. Fuzzy analytical hierarchy process[J]. Fuzzy Systems and Mathematics, 2000, 14(2): 80-88. | |
| 22 | 方春明, 孔繁森, 隽志才. 基于模糊综合评判与灰色关联分析的汽车工业第三方物流服务商评价指标体系[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(): 133-137. |
| Fang Chun-ming, Kong Fan-sen, Zhi-cai Juan. Evaluation index system on 3PL in automotive industry based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and grey correlation analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(Sup.1): 133-137. | |
| 23 | Mokhtarian M N. A note on "extension of fuzzy TOPSIS method based on interval-valued fuzzy sets"[J]. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 2015, 26: 513-514. |
| 24 | 申桂香, 戚晓艳, 张英芝, 等. 基于等效样本法的系统组件运行可靠性建模[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(3): 914-919. |
| Shen Gui-xiang, Qi Xiao-yan, Zhang Ying-zhi, et al. Operational reliability modeling of system components based on equivalent sample method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 914-919. | |
| 25 | 郑玉彬, 杨斌, 王晓峰, 等. 基于威布尔分布的电主轴加速寿命试验时间设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(3): 767-772. |
| Zheng Yu-bin, Yang Bin, Wang Xiao-feng, et al. Test time design of motorized spindle accelerated life test based on weibull distribution[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(3): 767-772. |
| [1] | Gui-xiang SHEN,Lan LUAN,Ying-zhi ZHANG,Li-ming MU,Shu-bin LIANG. Fault propagation impact assessment of machining center components [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 63-69. |
| [2] | YANG Zhao-jun, YANG Chuan-gui, CHEN Fei, HAO Qing-bo, ZHENG Zhi-tong, WANG Song. Parameter estimation of reliability model of machining center based on particle swarm optimization and support vector regression [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 829-836. |
| [3] | WANG Xiao-feng, SHEN Gui-xiang, ZHANG Ying-zhi, GU Dong-wei, LI Huai-yang, LIU Wei. Prioritizing failures of abc-axis feeding systems based on improved criticality and DEMATEL method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(01): 122-127. |
| [4] | WANG Xiao-feng, SHEN Gui-xiang, ZHANG Ying-zhi, ZHANG Li-min, WANG Zhi-qiong, LIU Wei. Simulation of reliability and maintainability influence of machining center [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊1): 160-163. |
| [5] | WANG Xiao-feng,SHEN Gui-xiang,ZHANG Ying-zhi,CHEN Bing-kun,LI Huai-yang. Analysis on risk priority number of critical component of machining center based on group decision-making and various assignment ways [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1630-1635. |
|
||