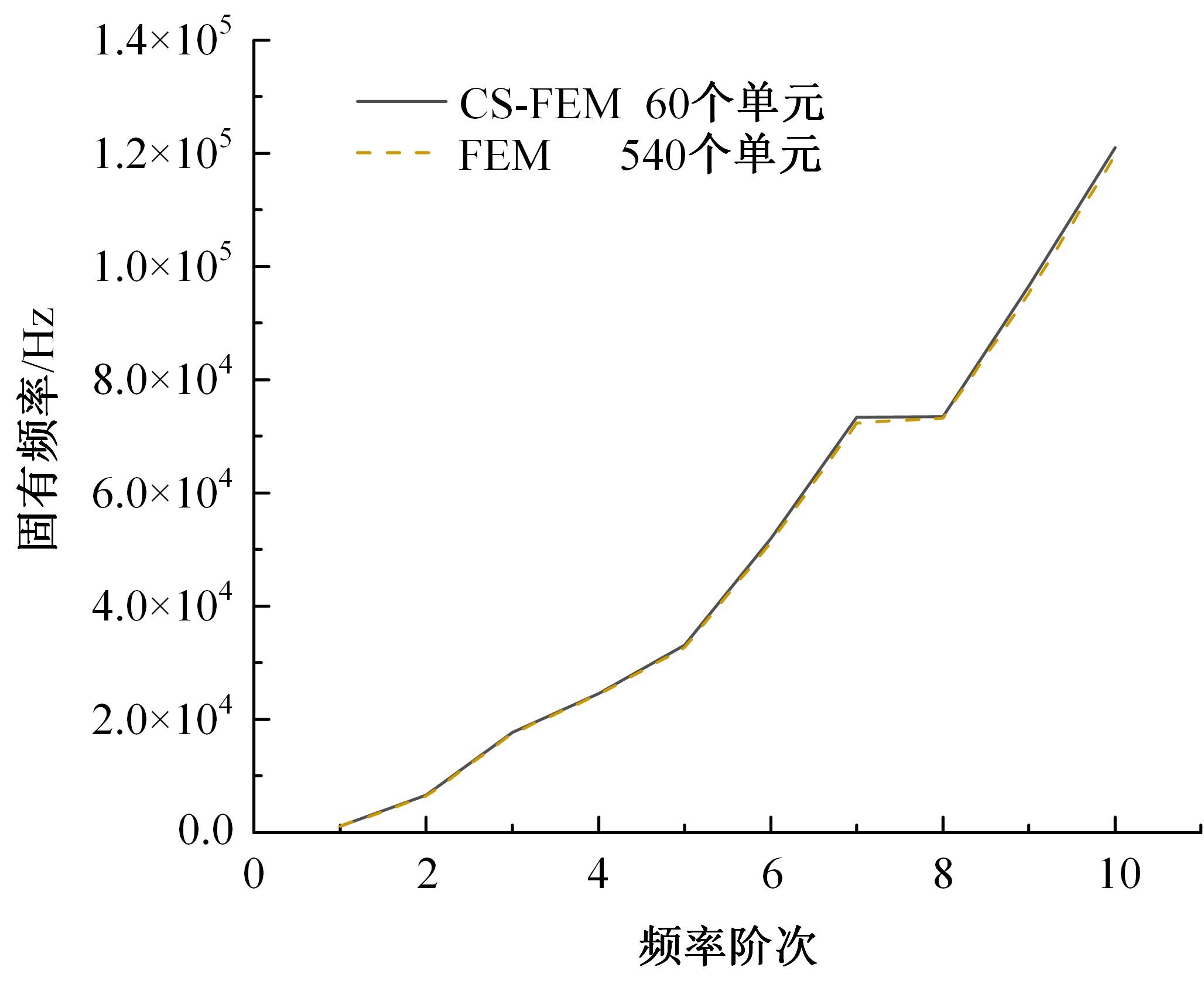
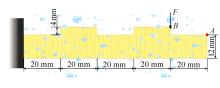
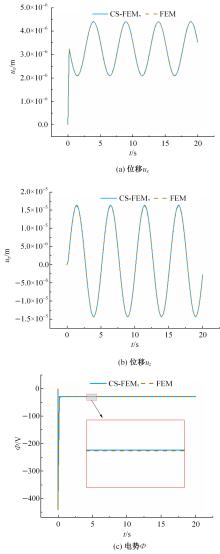
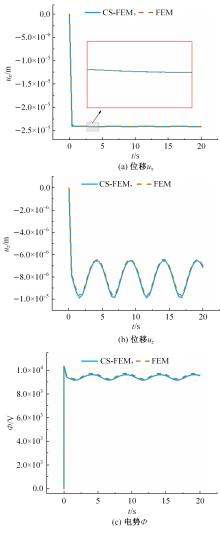
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 1876-1886.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230414
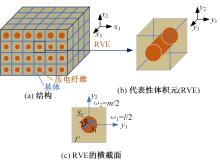
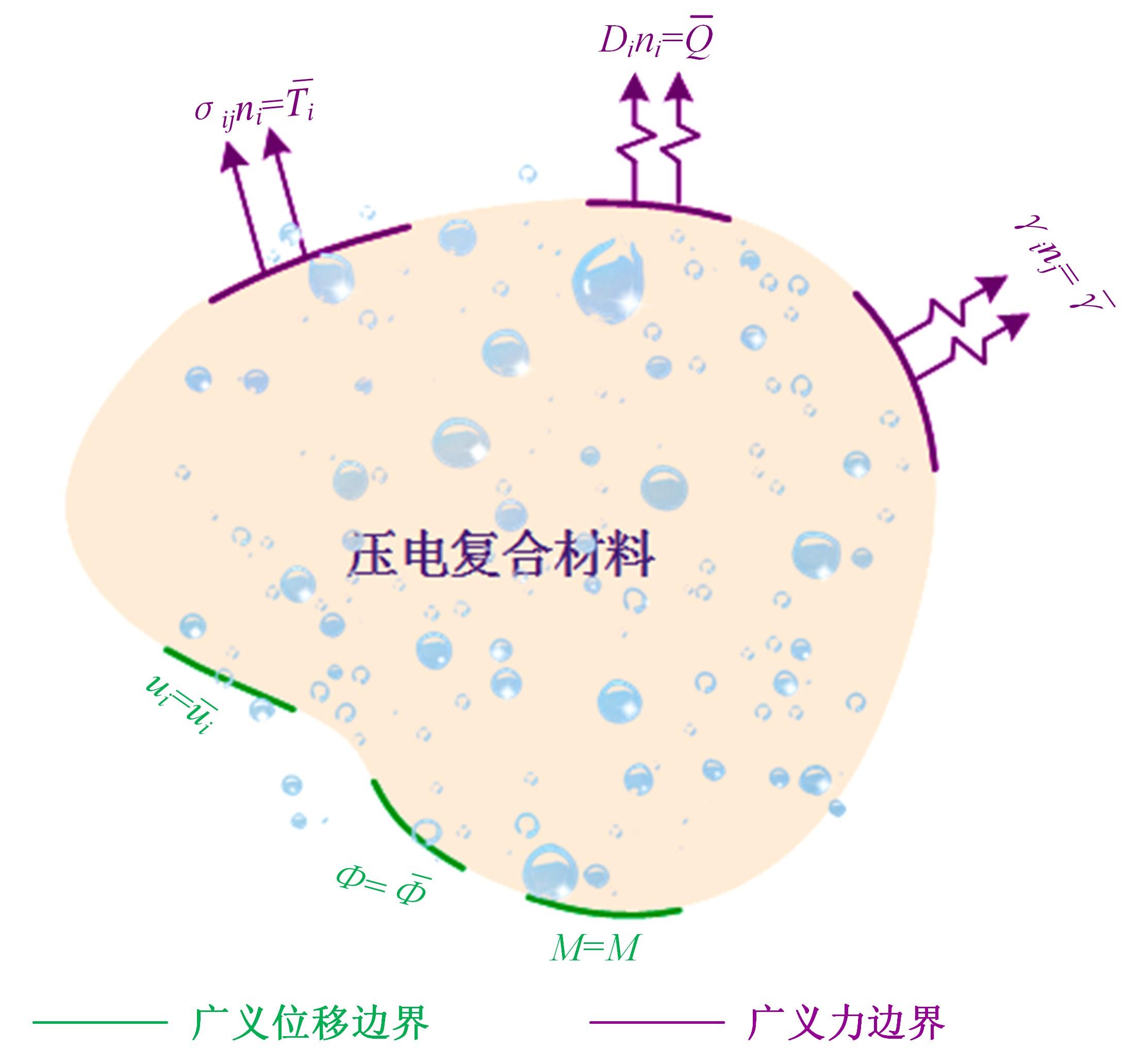
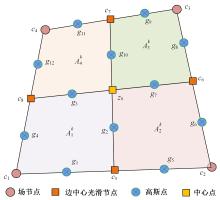
Moisture-electro-mechanical coupling smoothed finite element method based on asymptotic homogenization
Jian-xiao ZHENG1,2( ),Wen-bo WANG1,Jin-song LIU1(
),Wen-bo WANG1,Jin-song LIU1( ),Li-ming ZHOU3,Yu LI4
),Li-ming ZHOU3,Yu LI4
- 1.School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology,Xi′an 710055,China
2.Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Technology,Xi′an 710055,China
3.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
4.Shanghai Baoye Group Corp. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201999,China
CLC Number:
- TB115
| 1 | Dagdeviren C, Joe P, Tuzman O L, et al. Recent progress in flexible and stretchable piezoelectric devices for mechanical energy harvesting, sensing and actuation[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2016, 9:269-281. |
| 2 | Sappati K K, Bhadra S. Piezoelectric polymer and paper substrates: a review[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18:No.3605. |
| 3 | Akdogan E K, Allahverdi M, Safari A. Piezoelectric composites for sensor and actuator applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2005, 52(5): 746-775. |
| 4 | Bie Y H, Cui X Y, Li Z C. A coupling approach of state-based peridynamics with node-based smoothed finite element method[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 331: 675-700. |
| 5 | Zeng Y, Jiang L, Sun Y,et al. 3D-printing piezoelectric composite with honeycomb structure for ultrasonic devices[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(8):No.E713. |
| 6 | Zhou L, Ren S, Meng G,et al. A multi-physics node-based smoothed radial point interpolation method for transient responses of magneto-electro-elastic structures[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Element, 2019, 101: 371-384. |
| 7 | 郑建校, 段志善, 周立明. 基于渐近均匀化的力-电-热耦合光滑有限元法研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 54(4): 1325-1335. |
| Zheng Jian-xiao, Duan Zhi-shan, Zhou Li-ming. Research on thermo-electro-mechanical coupling smoothed finite element method based on asymptotic homogenization[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2023, 54(4):1325-1335. | |
| 8 | Chan H L W, Unsworth J. Simple model for piezoelectric ceramic/polymer 1-3 composites used in ultrasonic transducer applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 1989, 36(4): 434-441. |
| 9 | Hagood N, Bent A. Development of piezoelectric fiber composites for structural actuation[C]//The 34th Conference on Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials of AIAA, La Jolla, USA, 1993: No.1717. |
| 10 | Safari A, Janas V, Panda R K. Fabrication of fine-scale 1-3 Pb(Zr x,Ti1- x )O3/ceramic/polymer composites using a modified lost mold method[J]. Int Soc Opt Eng, 1996, 2721: 251-262. |
| 11 | Bisegna P, Luciano R. Variational bounds for the overall properties of piezoelectric composites[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1996, 44(4): 583-602. |
| 12 | Meng G, Wang L, Zhang Q,et al. Coupled thermal-electrical-mechanical inhomogeneous cell-based smoothed finite element method for transient responses of functionally graded piezoelectric structures to dynamic loadings[J]. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2020, 17(6): No.1950012. |
| 13 | Zheng J, Duan Z, Zhou L. A coupling electromechanical cell-based smoothed finite element method based on micromechanics for dynamic characteristics of piezoelectric composite materials[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, No.4913784. |
| 14 | Yang H, Cui X Y, Li S, et al. A stable node-based smoothed finite element method for metal forming analysis[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2019, 63:1147-1164. |
| 15 | Aliqué M, Simão C D, Murillo G, et al. Fully-printed piezoelectric devices for flexible electronics applications[J]. Advances Materials Technologies, 2021, 6(3): No. 2001020. |
| 16 | Pettermann H E, Suresh S. A comprehensive unit cell model: a study of coupled effects in piezoelectric 1-3 composites[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2000, 37(39): 5447-5464. |
| 17 | Berger H, Kari S, Gabbert U, et al. An analytical and numerical approach for calculating effective material coefficients of piezoelectric fiber composites[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2005, 42(21/22): 5692-5714. |
| 18 | Poizat C, Sester M. Effective properties of composites with embedded piezoelectric fibres[J]. Computational Materials Science, 1999, 16(1/4): 89-97. |
| 19 | Zhang F, Feng P, Wang T,et al. Mechanical-electric response characteristics of 1—3 cement based piezoelectric composite under impact loading[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 228: No.116781. |
| [1] | Zhong-hua SHI,Quan-wei SONG,Zhen-hang KANG,Qiang XIE,Ji-feng ZHANG. Numerical simulation and experiment on ultrasonic deicing system of airfoil structure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1561-1573. |
| [2] | Xiao⁃qin ZHOU,Lu YANG,Lei ZHANG,Li⁃jun CHEN. Finite element analysis of hinging octahedron structure withnegative compressibility [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 865-871. |
| [3] | SUN Rong-jun, GU Shuan-cheng, JU Pei, GAO Ke. Optimal design of new arc angle PDC drill bit for coal mining based on finite element method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1991-1998. |
| [4] | MENG Guang-wei,LI Xiao-lin,LI Feng,ZHOU Li-ming,WANG Hui. Smoothed multiscale finite element method for flow in fractured media [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 481-486. |
| [5] | CAI Bin,MENG Guang-wei, DONG Xin,LI Feng. Reliability analysis for transverse crack in concrete structure based on fuzzy invalidation criterion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(4): 1029-1033. |
| [6] | PENG Hui-fen, MENG Guang-wei, ZHOU Li-ming, LI Feng. Virtual crack closure technique based on wavelet finite element method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1364-1368. |
| [7] | MENG Guang-Wei, ZHOU Li-Ming, LI Feng. Fuzzy elementfree Galerkin method for the plane with crack [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 287-0292. |
| [8] | MENG Guang-Wei, CA Bin, LI Feng, DONG Xin. New method for structural reliability analysis by combining curve fitting with Monte Carlo simulation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 293-0296. |
| [9] | MENG Guang-Wei, ZHOU Li-Ming, LI Feng, SHA Li-Rong. Perturbation stochastic local orthogonal elementfree Galerkin method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1556-1561. |
| [10] | WU Deng-feng,XU Tao,SUN Rui-heng,YANG Rong,XUAN Wei-qi,Tatsuo Yoshino. Meshless method based on wavelet basis function [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 740-0744. |
| [11] | MA Liang,CHEN Su-huan,MENG Guang-wei . Eigenvalue analysis of structures with large variations of interval parameters [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(01): 98-102. |
| [12] | Li Cheng, Liu Zhi-hua, Zhang Ping . Analysis on stress and displacement of a composite flywheel composed of twolayer rotor with pre-displacement [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(04): 828-832. |
| [13] | Cao Zong-jie,Wang Ming-wei,Quan Ji-cheng,Hu Jin-hai . Electroelastic fracture analysis of piezoelectric materials with cracks [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊2): 157-160. |
| [14] | DONG Jin-kun, LIU Bin, ZHANG Yan-nian, YE Ye. Stability Against Coupled BendingTorsional Galloping Oscillation by Beam Wind in Tall Building 3-Dimensional Structure [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2005, 35(05): 562-0566. |
|
||