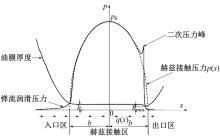
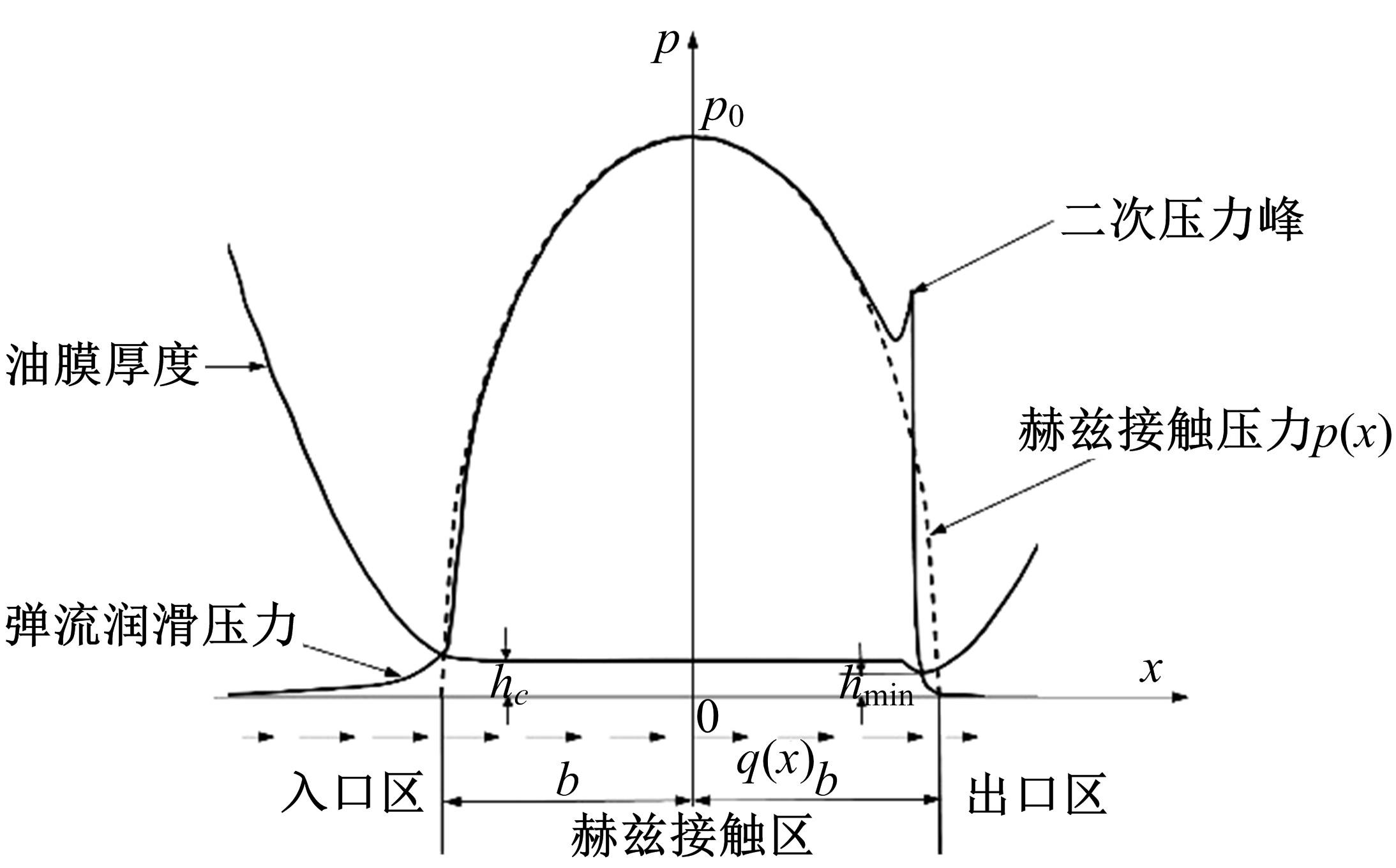
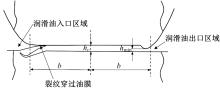
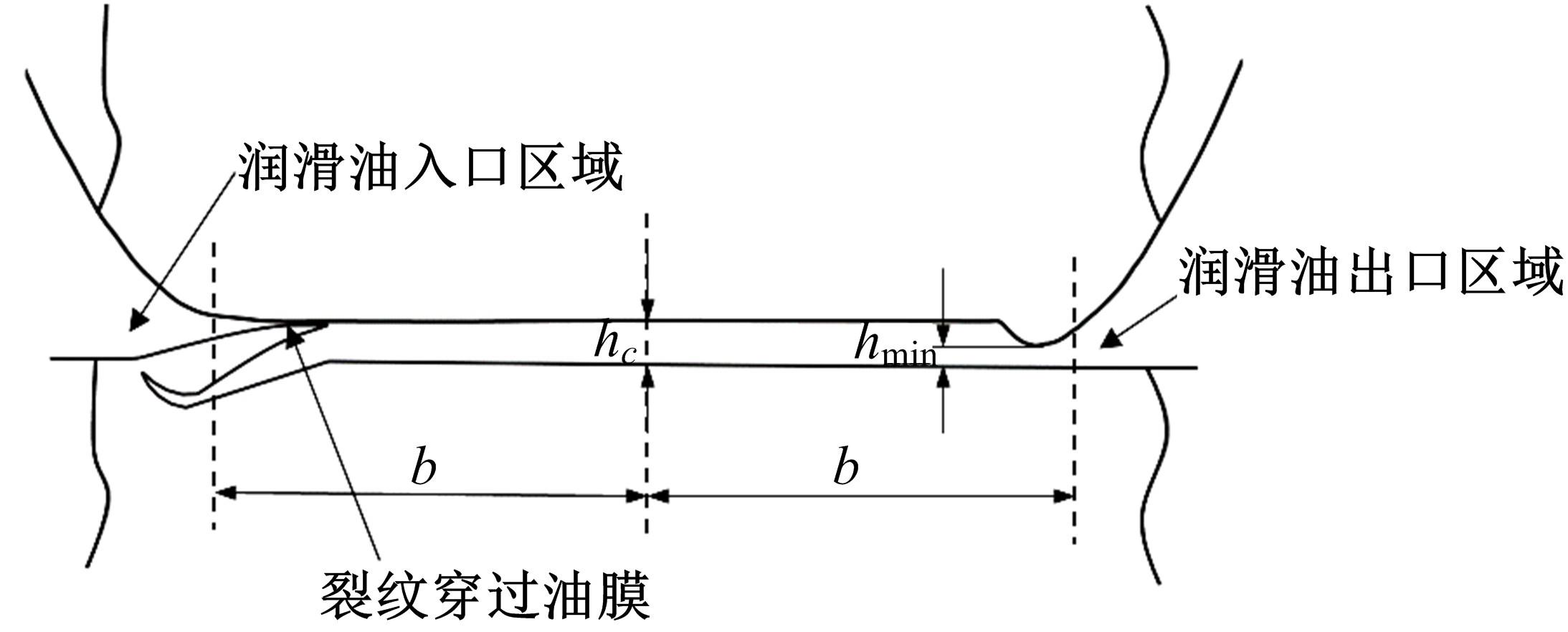
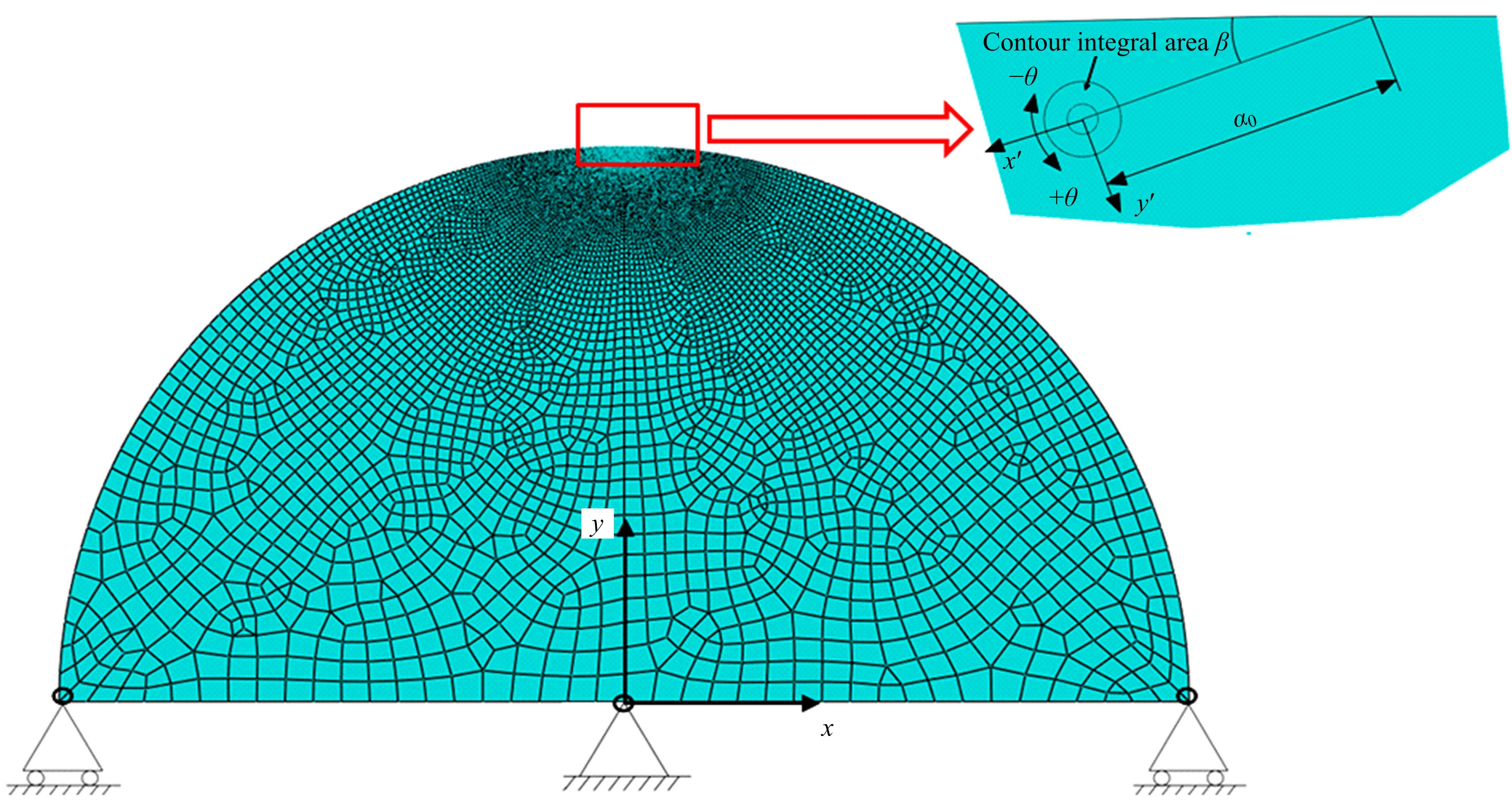
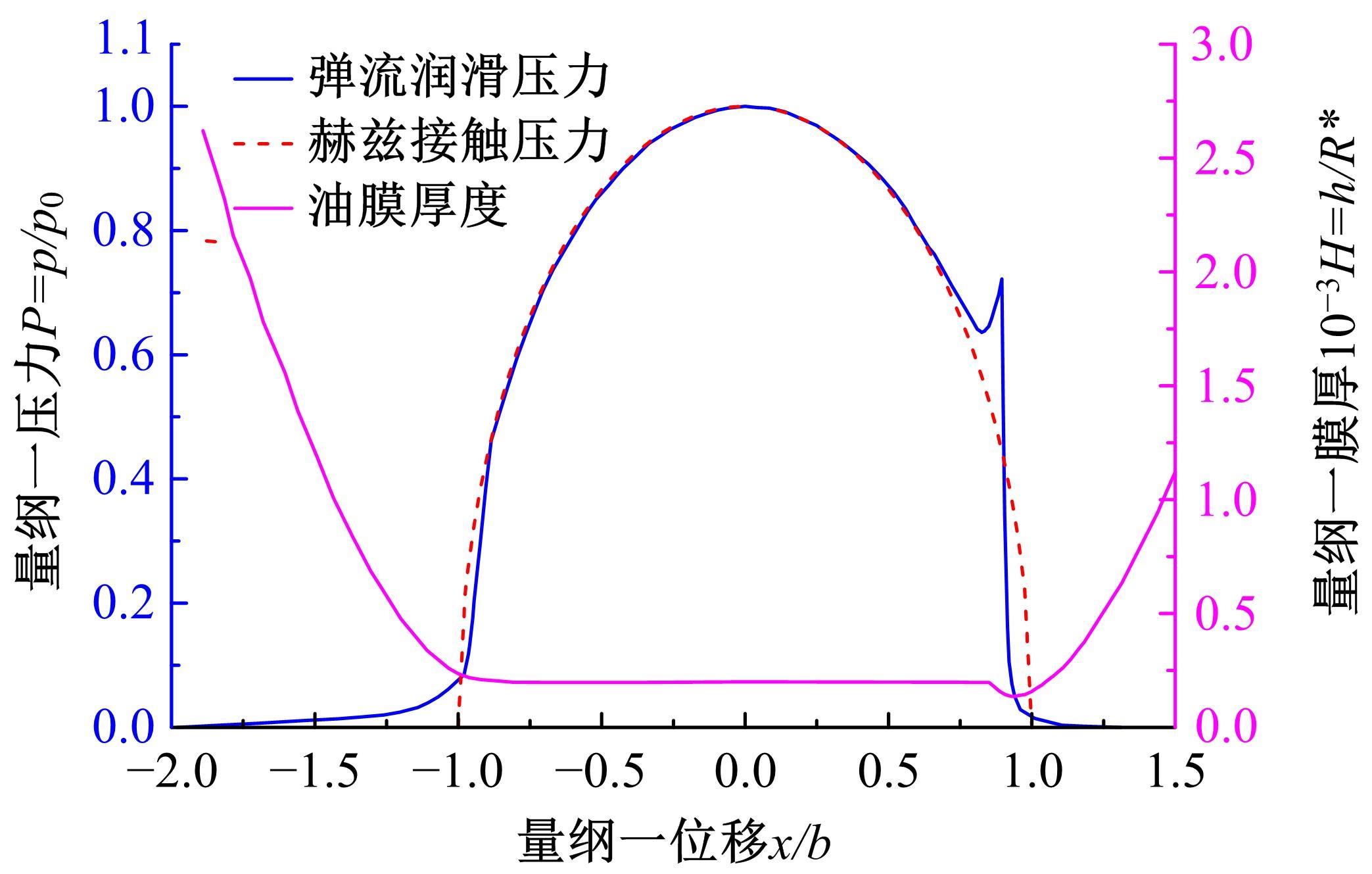
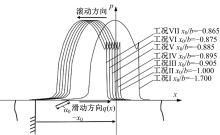
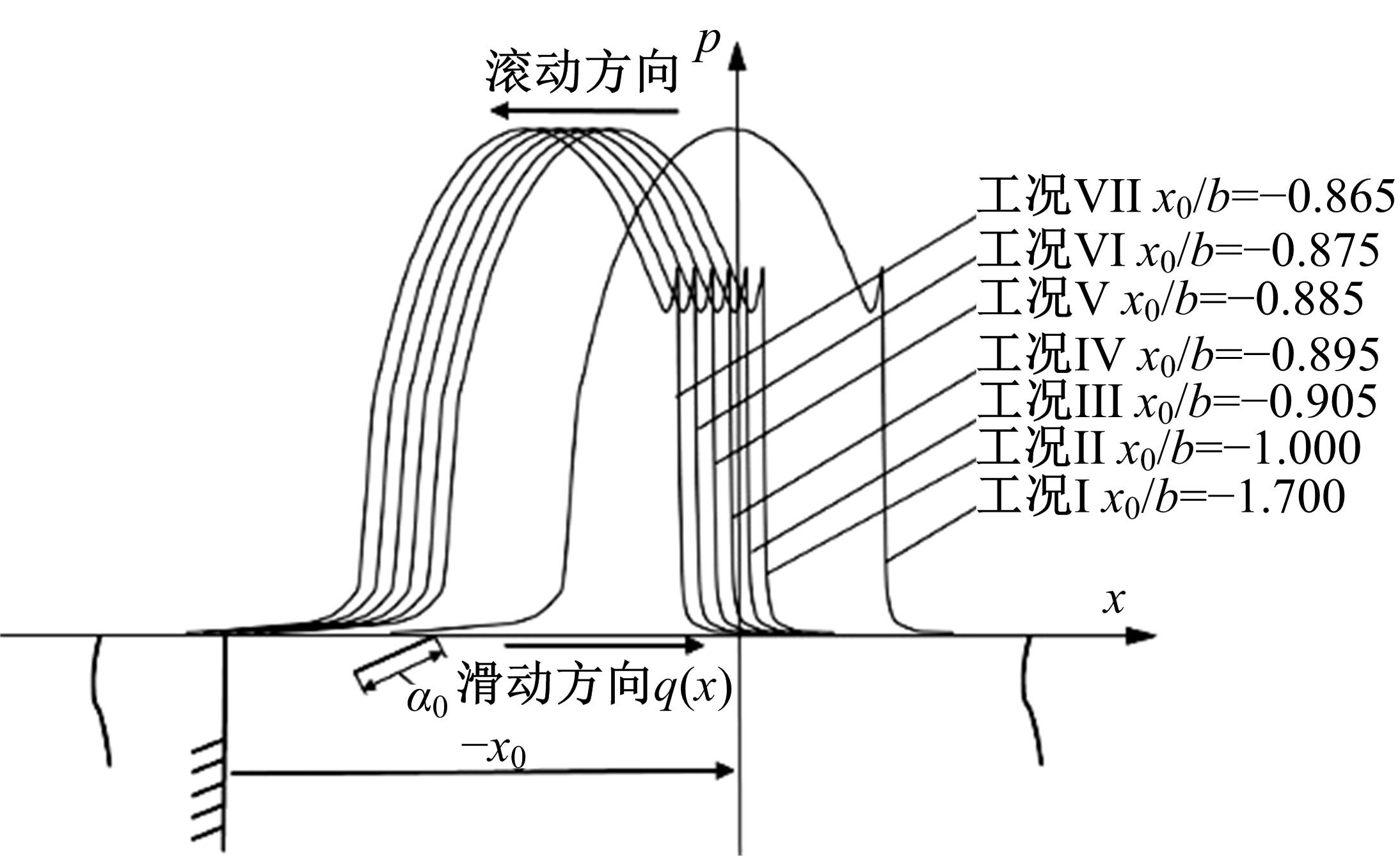
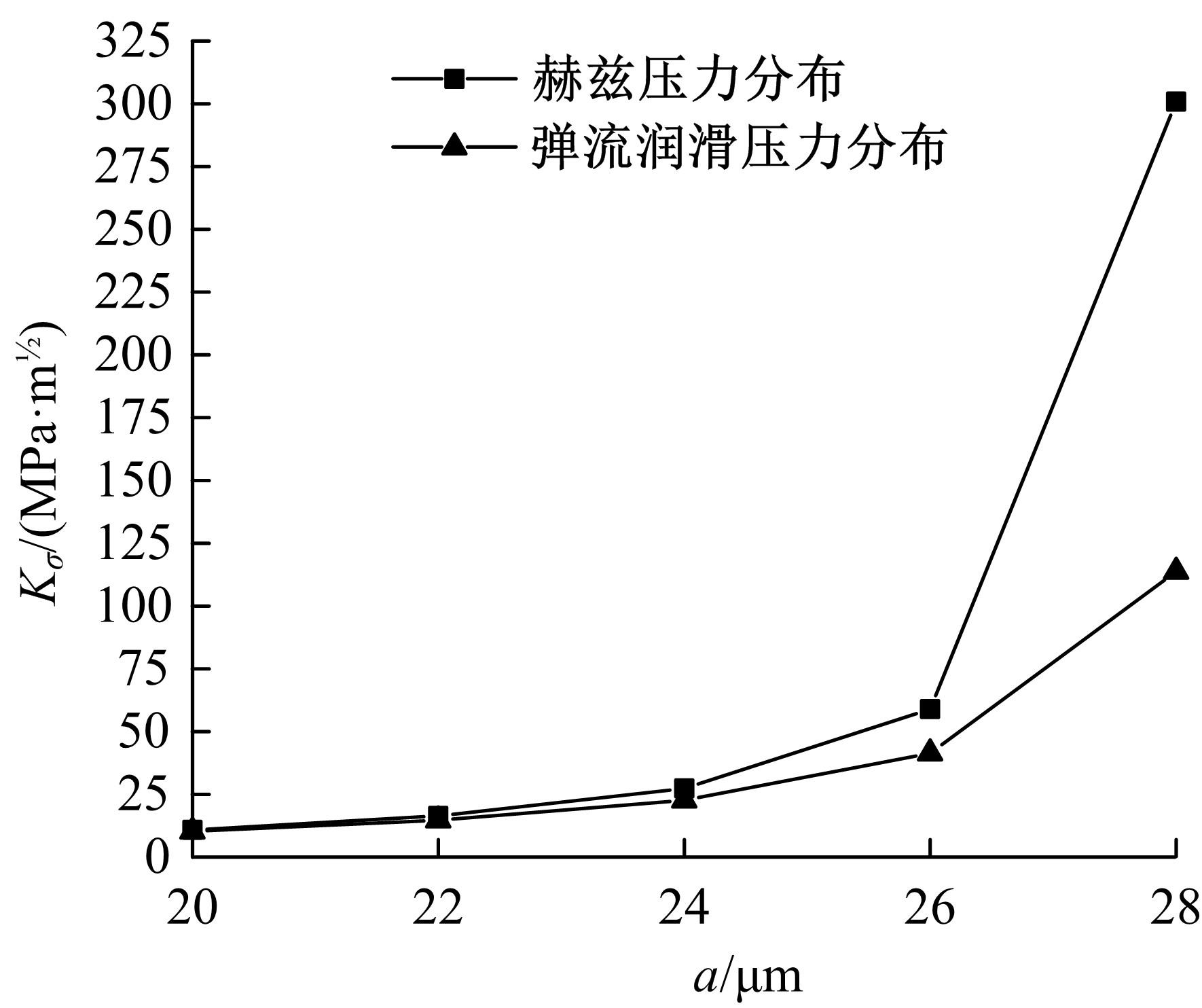
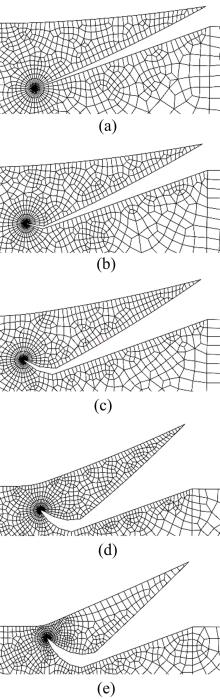
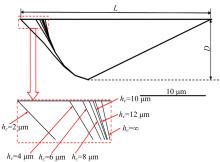
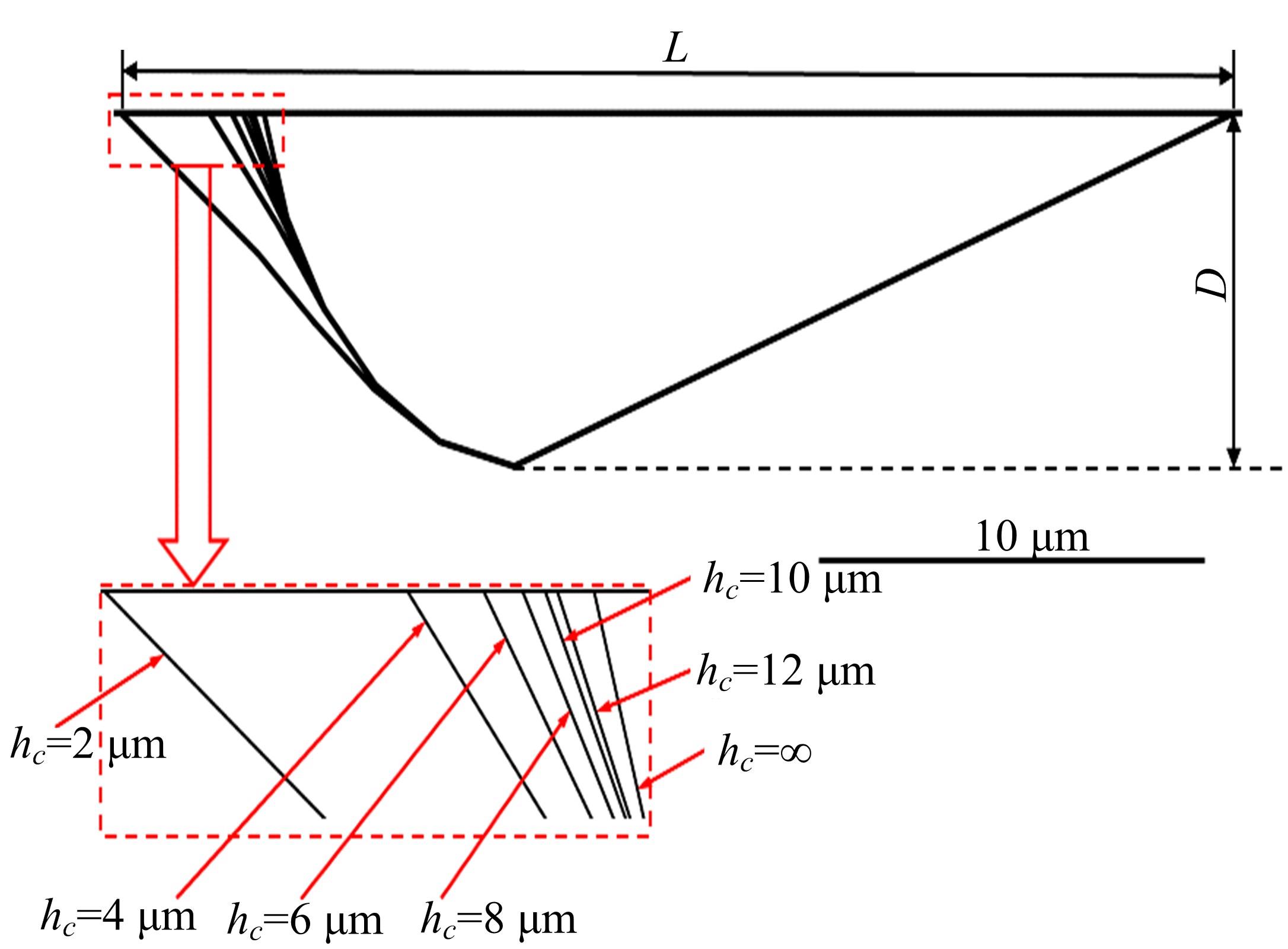
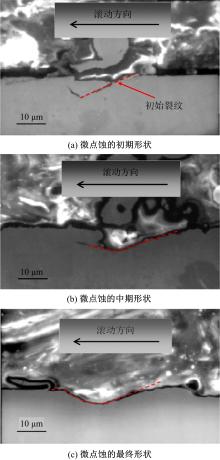
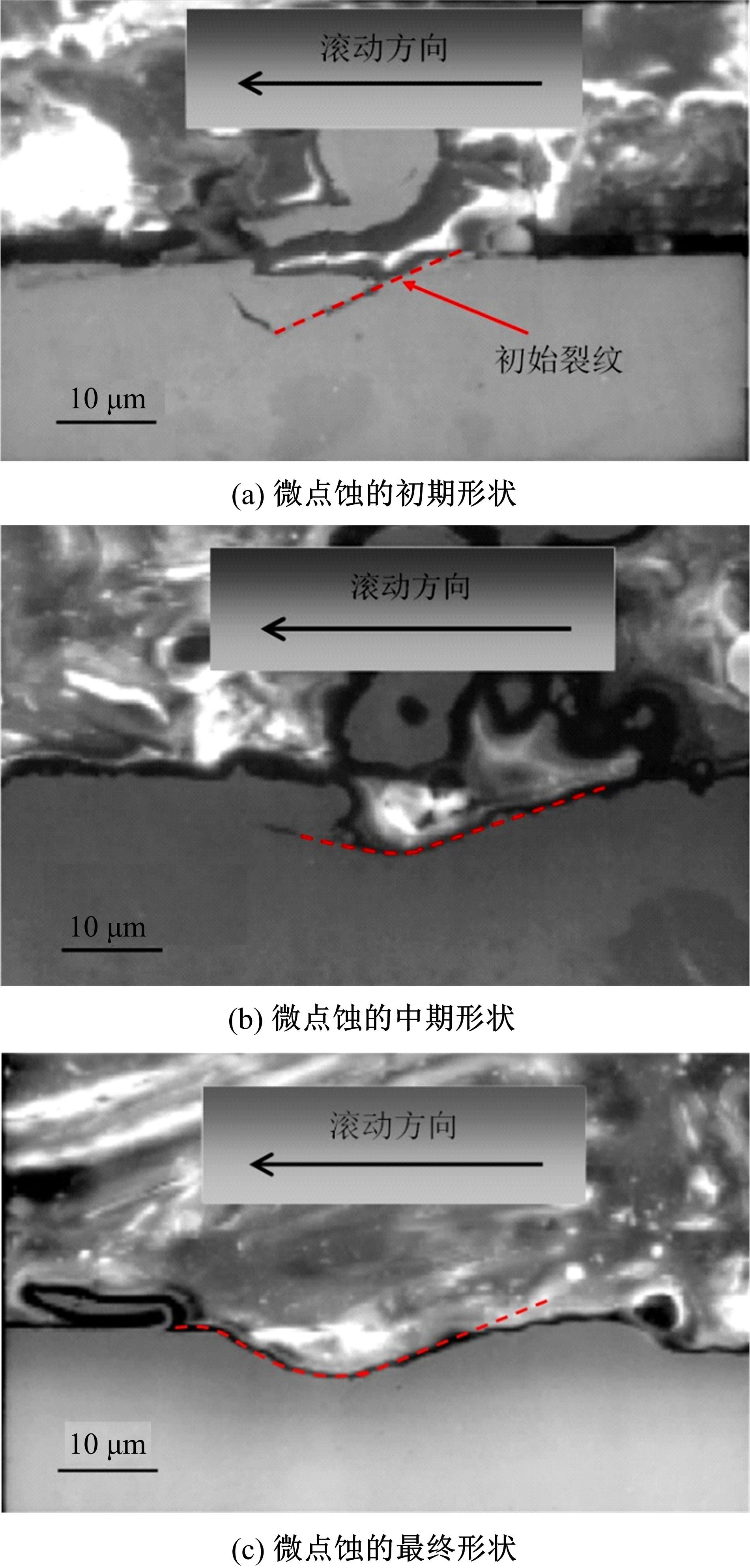
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 799-810.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200903
Numerical simulation of micro pitting damage characteristics of lubricated contact gears based on contour integral
Yang ZHAO1,2,3( ),Yang XIAO2,Hao SUN4,Wen-hao HUO4,Song FENG2,Yong LIAO1(
),Yang XIAO2,Hao SUN4,Wen-hao HUO4,Song FENG2,Yong LIAO1( )
)
- 1.School of Electrical Engineering,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
2.School of Advanced Manufacturing Engineering,Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Chongqing 400065,China
3.State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures,Xi'an Jiaotong University,Xi’an 710039,China
4.Chongqing General Industry (Group) Co. ,Ltd. ,Chongqing 401336,China
CLC Number:
- TH117.1
| 1 | 程功, 肖科, 王家序, 等. 混合润滑状态下齿轮接触刚度[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 494-503. |
| Cheng Gong, Xiao Ke, Wang Jia-xu, et al. Gear contact stiffness under mixed lubrication status[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 494-503. | |
| 2 | 张俊, 卞世元, 鲁庆, 等. 准静态工况下渐开线直齿轮齿面磨损建模与分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(5): 136-145. |
| Zhang Jun, Bian Shi-yuan, Lu Qing, et al. Quasi-static-model-based wear analysis of spur gears[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(5): 136-145. | |
| 3 | Webster M, Norbart C. An experimental investigation of micro-pitting using a roller disk machine[J]. Tribology Transactions, 1995, 38(4): 883-893. |
| 4 | Höhn B R, Michaelis K. Influence of oil temperature on gear failures[J]. Tribology International, 2004, 37(2): 103-109. |
| 5 | 朱有利, 王燕礼, 边飞龙, 等. 渐开线直齿圆柱齿轮接触疲劳失效成因再分析[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2014, 34(6): 722-728. |
| Zhu You-li, Wang Yan-li, Bian Fei-long, et al. Re-examining the origins of contact fatigue failure of involute cylindrical spur gears[J]. Tribology, 2014, 34(6): 722-728. | |
| 6 | Chue C H, Chung H H. Pitting formation under rolling contact[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2000, 34(1): 1-9. |
| 7 | Flašker J, Fajdiga G, Glodež S, et al. Numerical simulation of surface pitting due to contact loading[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2001, 23(7): 599-605. |
| 8 | Aslantas K, Tasgetiren S. A study of spur gear pitting formation and life prediction[J]. Wear, 2004, 257(11): 1167-1175. |
| 9 | Fajdiga G, Flašker J, Glodež S. Numerical modelling of micro-pitting of gear teeth flanks[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2003, 26(12): 1135-1143. |
| 10 | Fajdiga G, Flašker J, Glodež S. The influence of different parameters on surface pitting of contacting mechanical elements[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2004, 71(4-6): 747-758. |
| 11 | Glodež S, Aberšek B, Flašker J, et al. Evaluation of the service life of gears in regard to surface pitting[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2004, 71(4-6): 429-438. |
| 12 | Fajdiga G, Glodež S, Kramar J. Pitting formation due to surface and subsurface initiated fatigue crack growth in contacting mechanical elements[J]. Wear, 2007, 262(9/10): 1217-1224. |
| 13 | Zafošnik B, Glodež S, Ulbin M, et al. A fracture mechanics model for the analysis of micro-pitting in regard to lubricated rolling-sliding contact problems[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2007, 29(9-11): 1950-1958. |
| 14 | Glodež S, Potočnik R, Flašker J, et al. Numerical modelling of crack path in the lubricated rolling–sliding contact problems[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75(3/4): 880-891. |
| 15 | Ding Y, Gear J A. Spalling depth prediction model[J]. Wear, 2009, 267(5-8): 1181-1190. |
| 16 | 熊永强, 孙义忠, 张合超. 采用热弹流润滑理论数值计算的风电齿轮微点蚀承载能力分析[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2015, 38(1): 126-132. |
| Xiong Yong-qiang, Sun Yi-zhong, Zhang He-chao. Calculation of micro-pitting load capacity of gears for wind power based on elastohydrodynamic lubrication contact theory[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2015, 38(1): 126-132. | |
| 17 | 程俊, 王硕, 武通海, 等. 基于拓展有限元的齿轮点蚀磨粒形态学特征模拟[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(15): 99-105. |
| Cheng Jun, Wang Shuo, Wu Tong-hai, et al. Morphological feature simulation of gear pitting debris based on the extended finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(15): 99-105. | |
| 18 | 李旭平. 基于扩展有限元的风电齿轮箱齿轮微点蚀模拟[D]. 浙江: 浙江理工大学机电产品可靠性分析与测试国家地方联合工程研究中心, 2018. |
| Li Xu-ping. Gear Micro-Pitting Simulation of wind turbine gearbox based on extended finite element method[D]. Zhejiang: Reliability Analysis and Testing of Mechanical and Electrical Products of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center, 2018. | |
| 19 | He H F, Liu H J, Zhu C C, et al. Study on the gear fatigue behavior considering the effect of residual stress based on the continuum damage approach[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 104: 531-544. |
| 20 | Xu X Y, Lai J B, Christoph L, et al. A model to predict initiation and propagation of micro-pitting on tooth flanks of spur gears[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2019, 122(4): 106-115. |
| 21 | Max W B, Leonard G, Peter T. Simulation of fatigue failure on tooth flanks in consideration of pitting initiation and growth[J]. Tribology International, 2019, 131: 299-307. |
| 22 | 王晓鹏, 刘世军. 微点蚀齿轮法向接触刚度分形预估模型[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(1): 68-76. |
| Wang Xiao-peng, Liu Shi-jun. Fractal prediction model of normal contact stiffness of micro-pitting gear[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(1): 68-76. | |
| 23 | Morales-Espejel G E, Gabelli A. A model for gear life with surface and subsurface survival: tribological effects[J]. Wear, 2018, 404-405:133-142. |
| 24 | Evans H P, Snidle R W, Sharif K J, et al. Analysis of micro-elastohydrodynamic lubrication and prediction of surface fatigue damage in micropitting tests on helical gears[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2013, 135(1): No. 011501. |
| 25 | 刘明勇.基于有限长线接触斜齿轮热弹性流体动力润滑研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学机械传动国家重点试验室, 2013. |
| Liu Ming-yong. Research on thermal finite line contact ehl for helical gears[D]. Chongqing: National Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission of Chongqing University, 2013. | |
| 26 | 李群, 亓秀梅, 高创宽. 粗糙齿面接触应力与油膜比厚关系[J]. 润滑与密封, 2013, 38(8): 57-61. |
| Li Qun, Qi Xiu-mei, Gao Chuang-kuan. Analysis on relationship between rough tooth surface contact stress and film ratio[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2013, 38(8): 57-61. | |
| 27 | 黄平. 弹性流体动压润滑数值计算方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013. |
| 28 | 薛虎, 汪久根, 洪玉芳. 线接触脂润滑弹流润滑分析[J].润滑与密封, 2017, 42(9): 12-16, 33. |
| Xue Hu, Wang Jiu-gen, Hong Yu-fang. Elastohydrodynamic lubrication analysis on line contact lubricated with grease[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2017, 42(9): 12-16, 33. | |
| 29 | 黄平.温诗铸,黄平. 摩擦学原理(第4版)[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012. |
| [1] | Wei ZHENG,Jian-jun SUN,Chen-bo MA,Qiu-ping YU,Yu-yan ZHANG,Tao NIU. Research status and prospect of automobile wheel hub machining fixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 25-36. |
| [2] | Wei CHEN,Yu-long LEI,Xing-zhong LI,Yao FU,Jian-long HU,Li-guo HOU. Calculation of adhesive wear of involute cylindrical spur gear under low⁃speed conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1628-1634. |
| [3] | Zhen GUO,Hong-ying YU,Zhong-xin HUA,Di ZHAO. Kinematic analysis and simulation of folding process for rigid origami mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 66-76. |
| [4] | ZHU Wei,WANG Chuan-wei,GU Kai-rong,SHEN Hui-ping,XU Ke,WANG Yuan. Stiffness and dynamics analysis of a new type of tensegrity parallel mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1777-1786. |
|
||