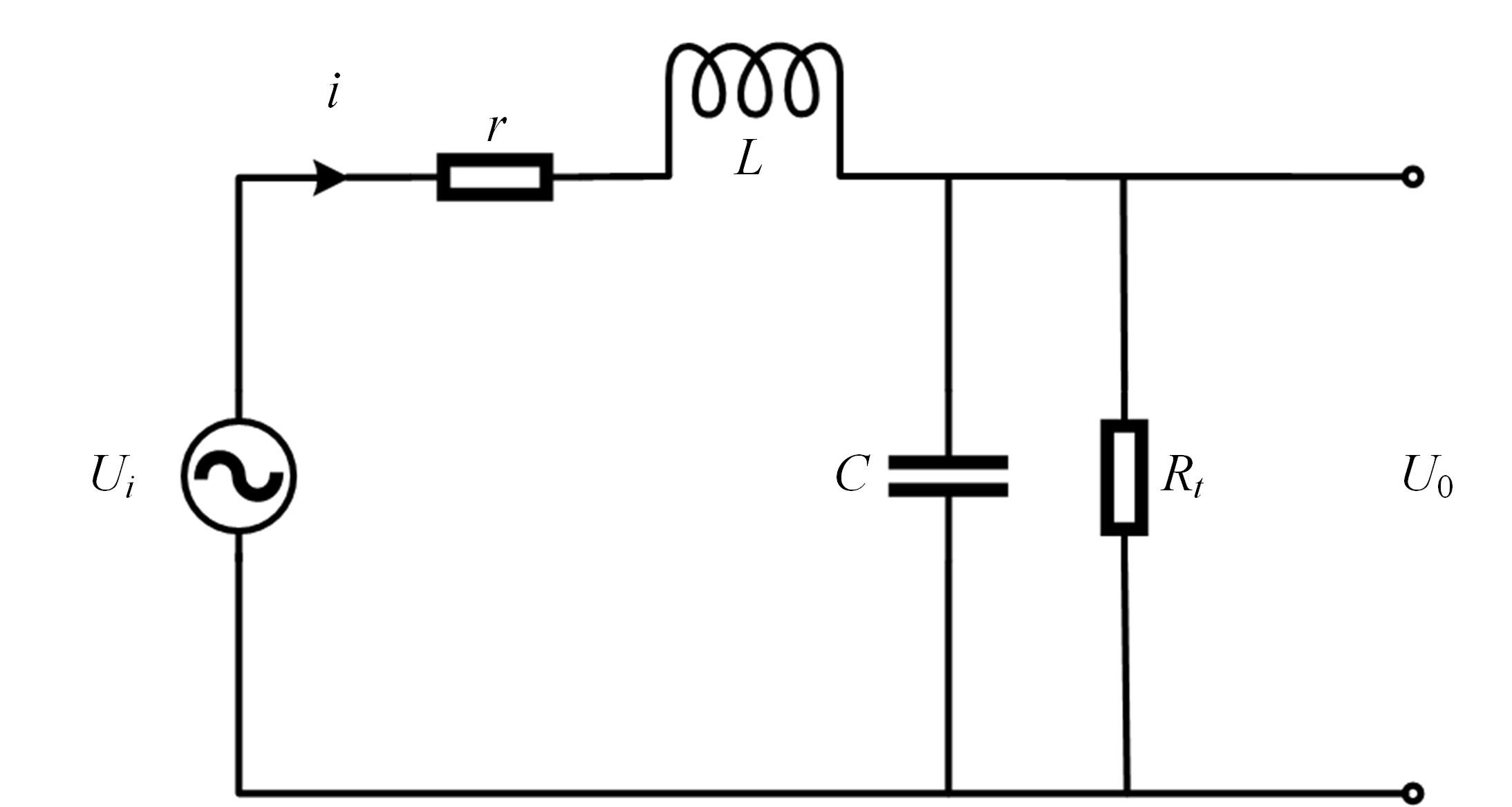
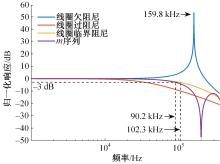
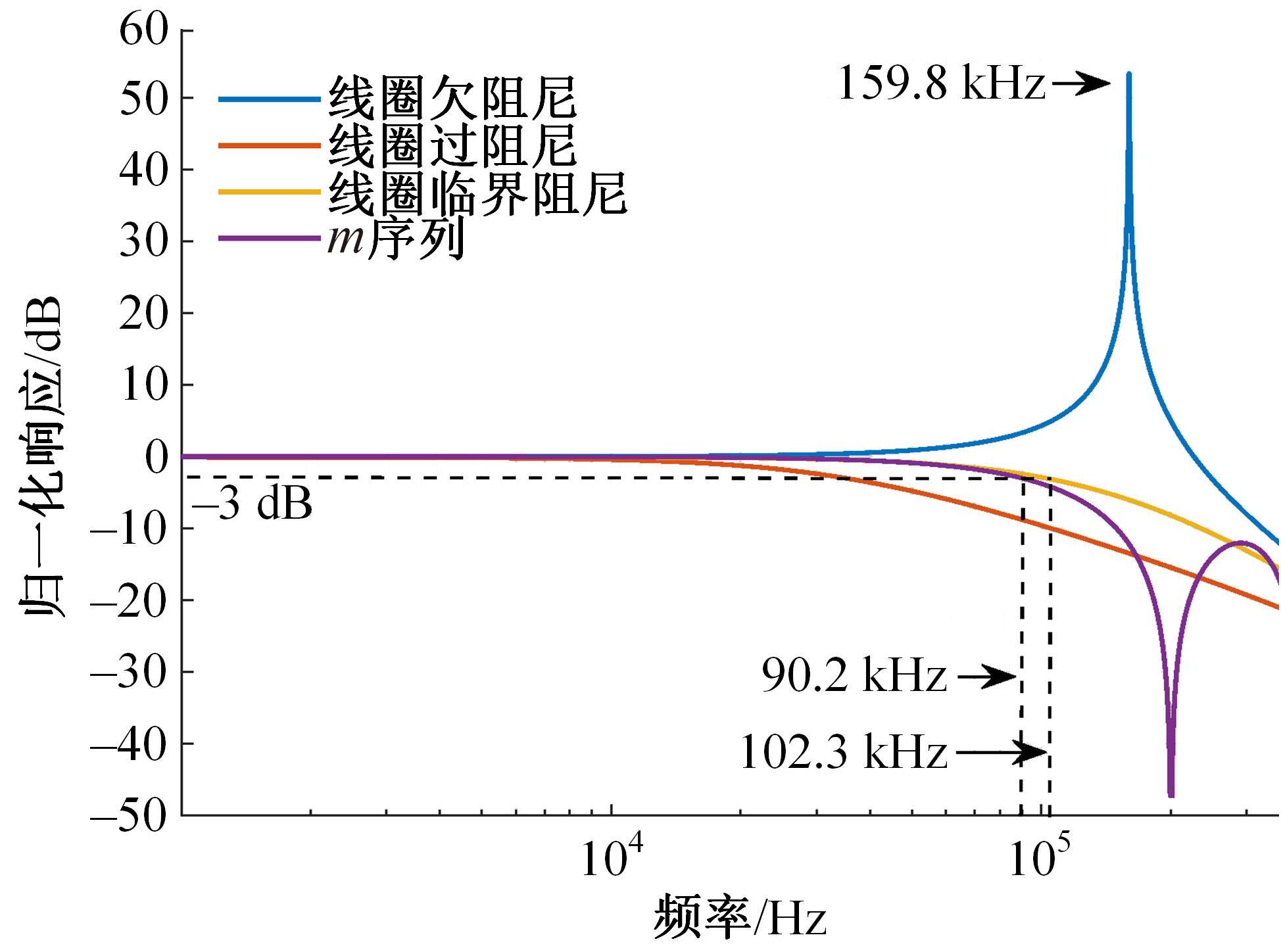
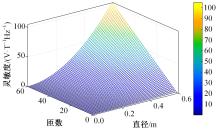
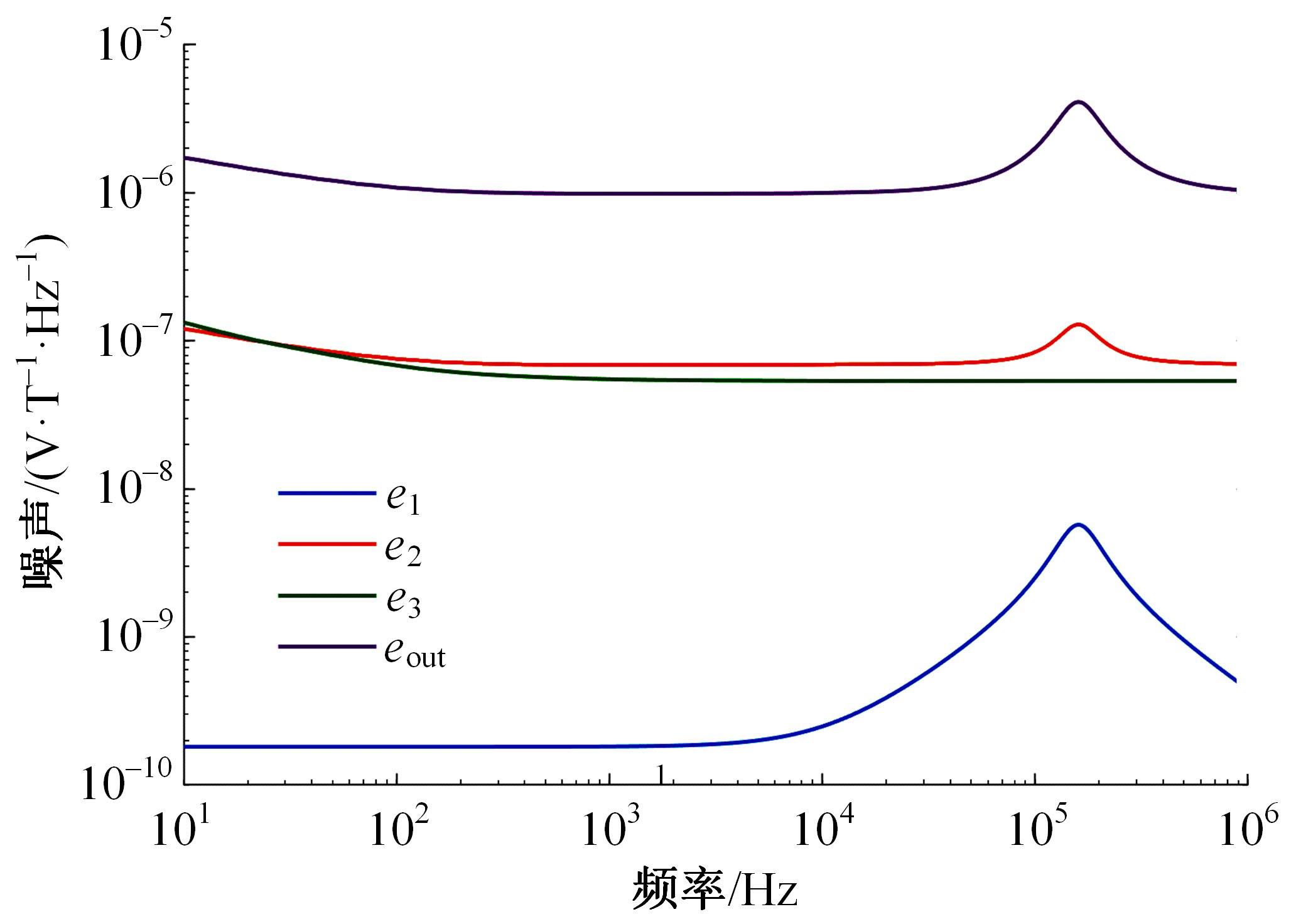
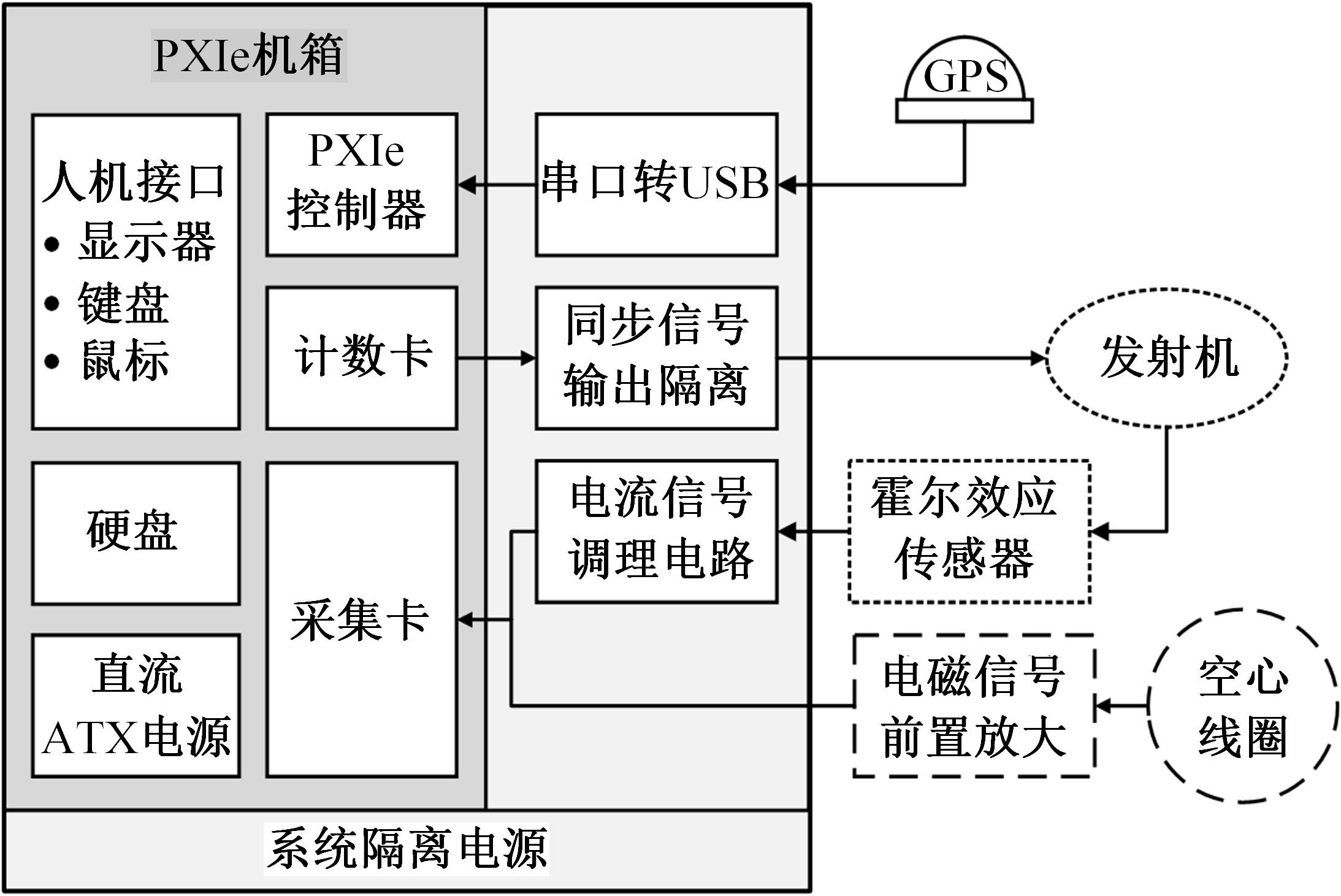
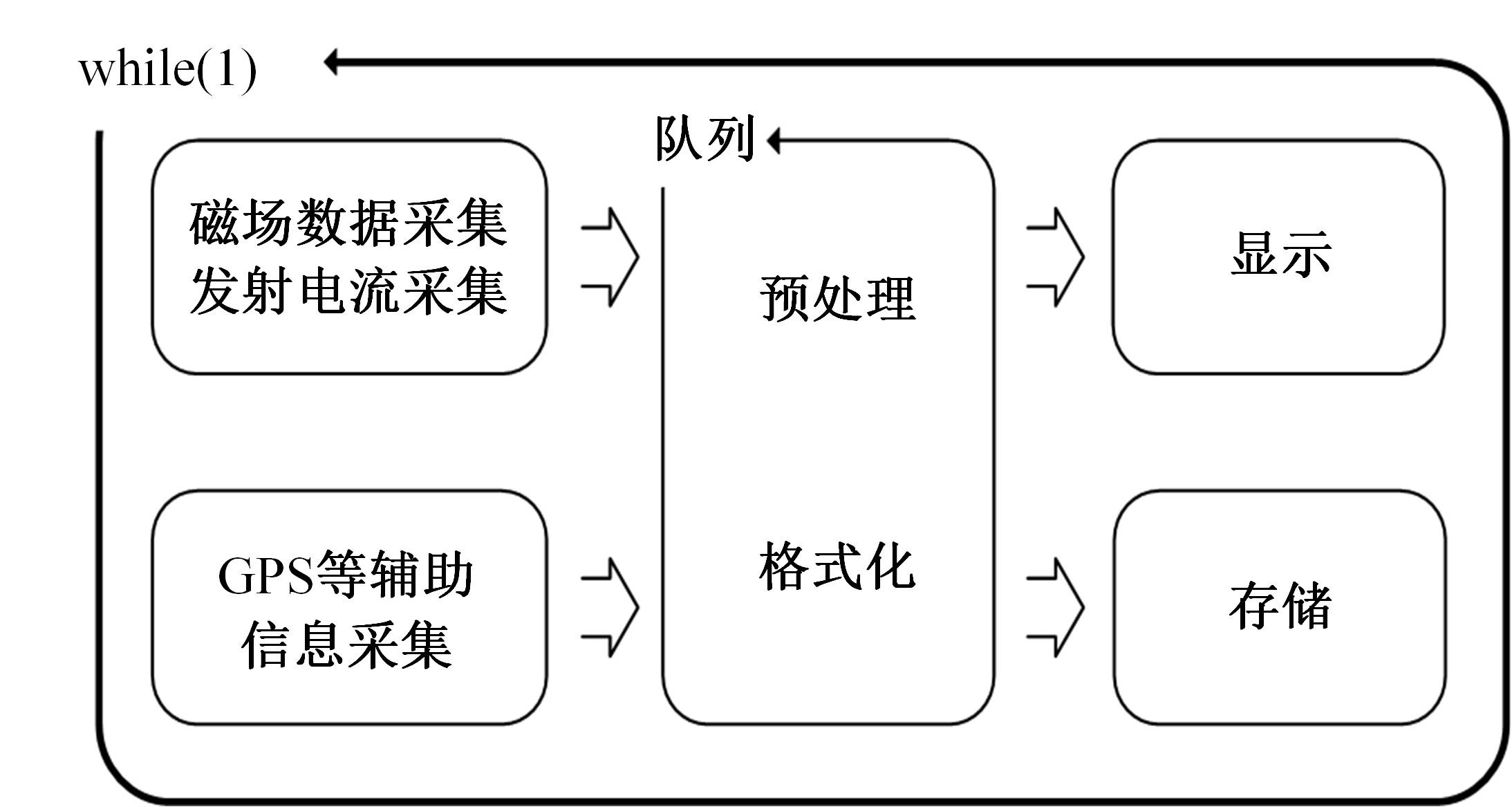
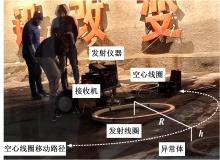
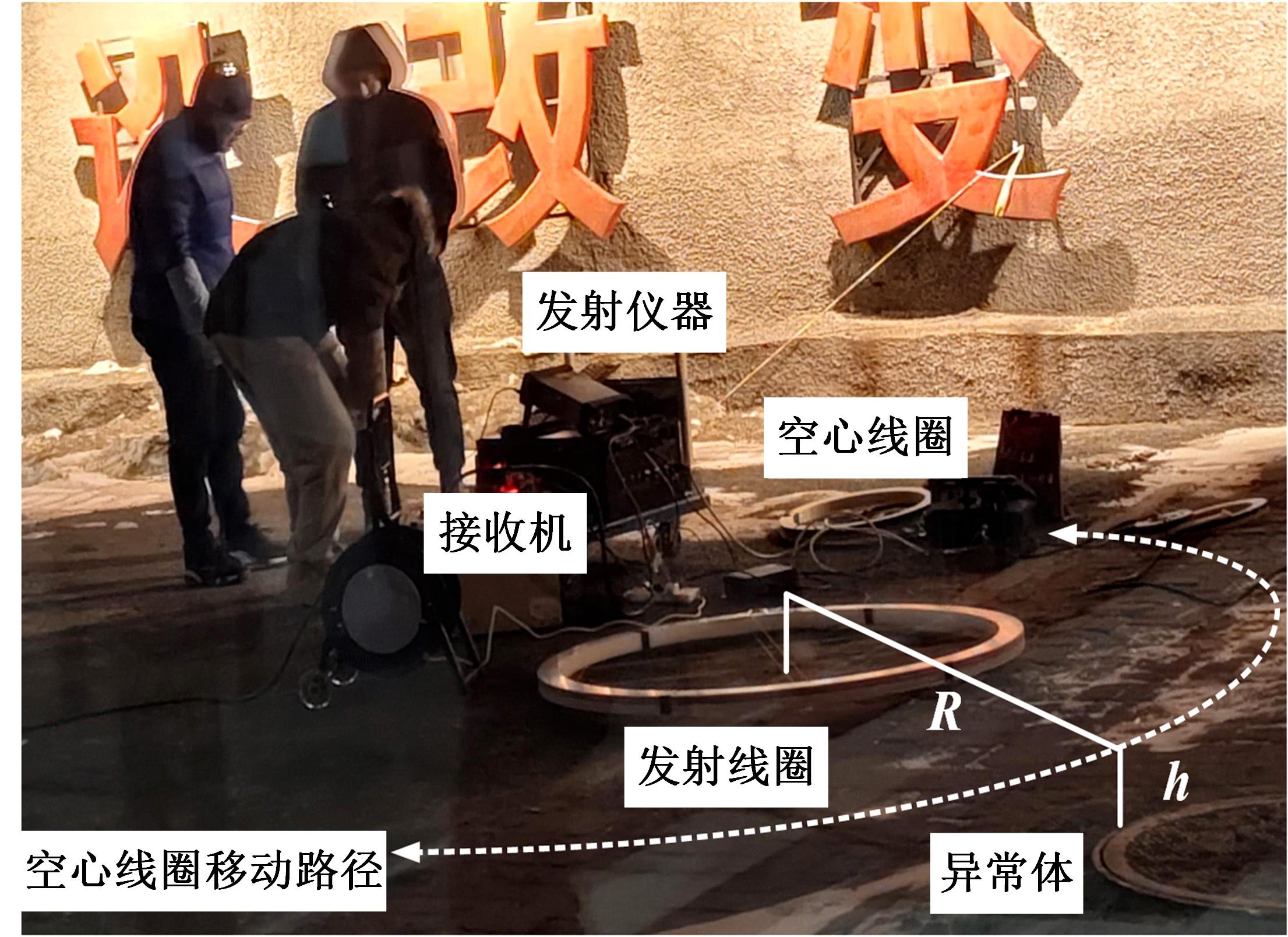
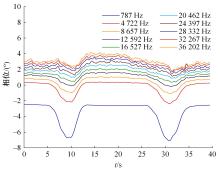
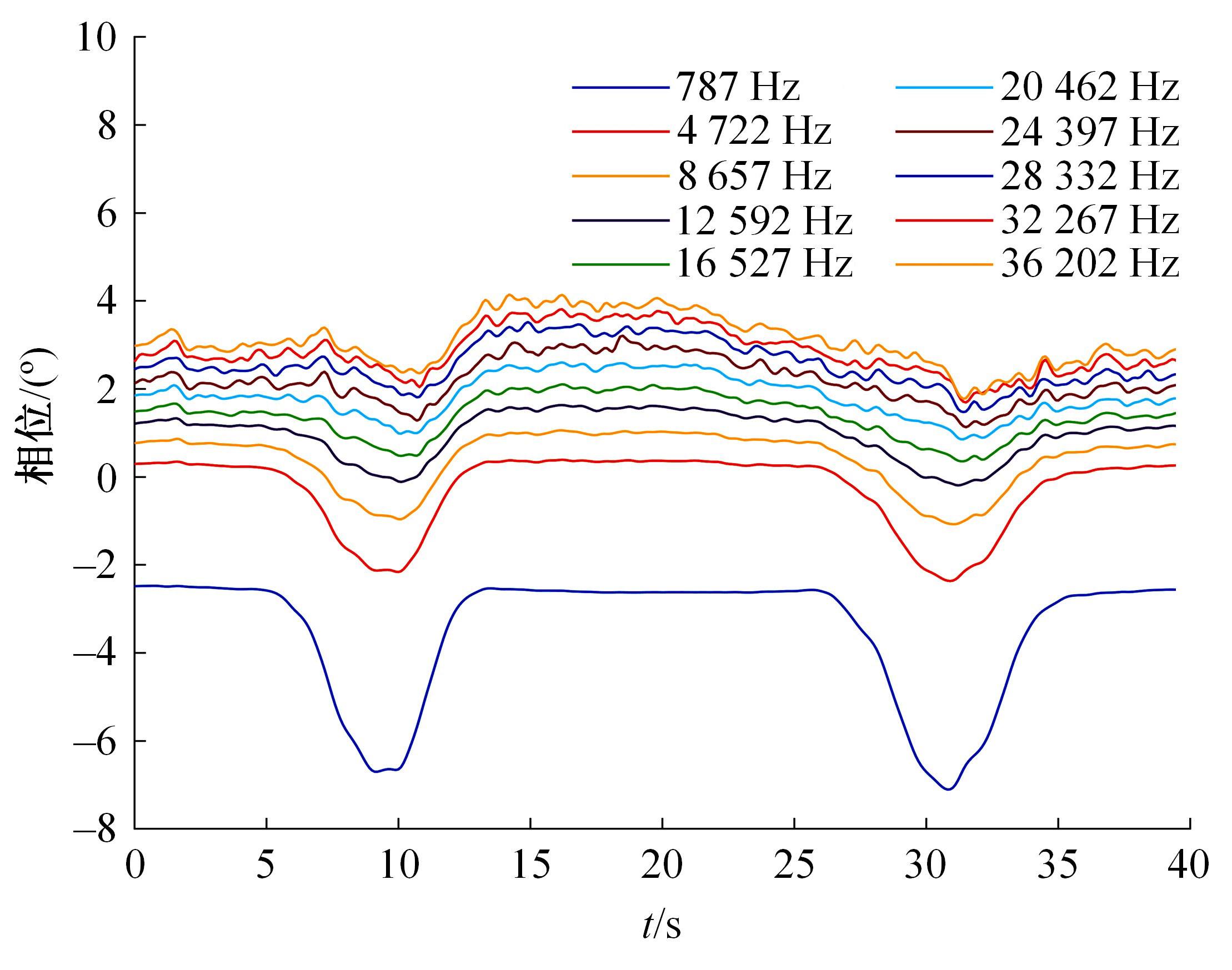
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2982-2993.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211364
Previous Articles Next Articles
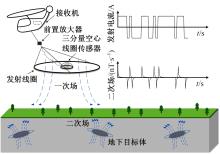
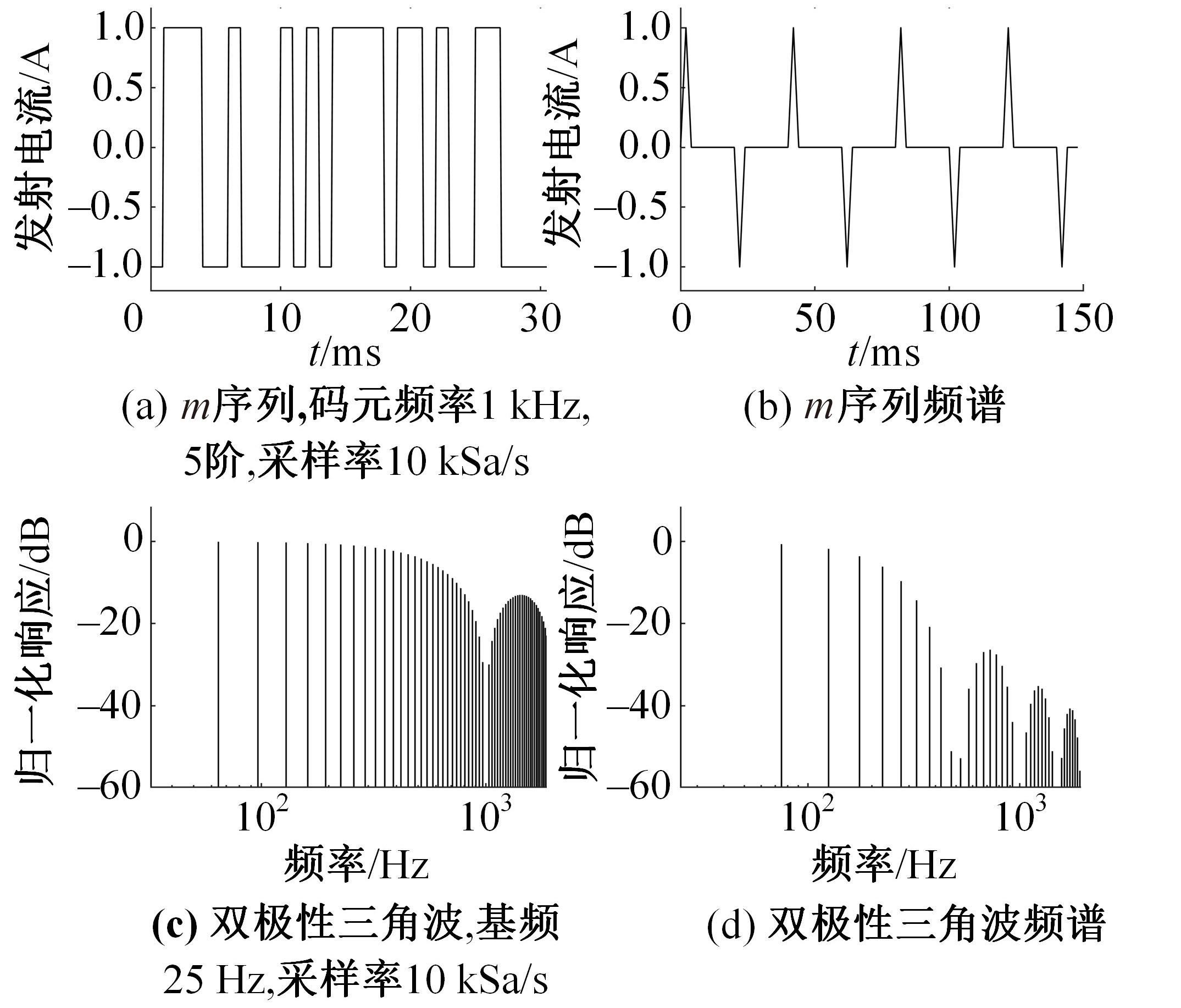
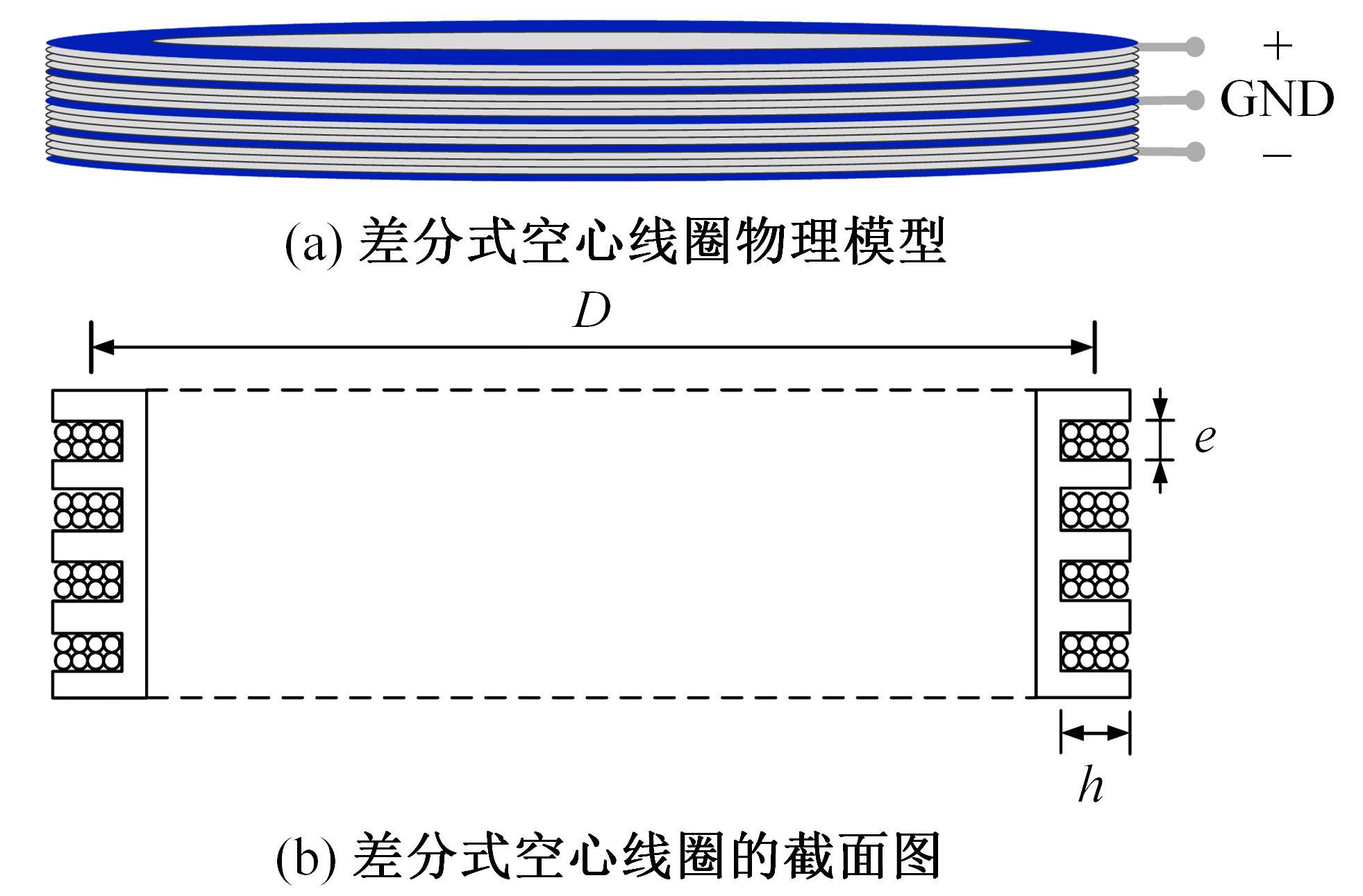
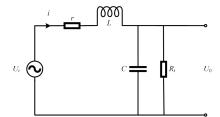
Optimization design of broadband and low noise receiving for helicopter⁃borne electromagnetic method with pseudo⁃random coded waveforms
Yan-zhang WANG1,2( ),Ming LIU1,2,Jia-lin ZHANG1,2,Kai-guang ZHU1,2,Shou-peng DENG1,2,Shi-long WANG1,2(
),Ming LIU1,2,Jia-lin ZHANG1,2,Kai-guang ZHU1,2,Shou-peng DENG1,2,Shi-long WANG1,2( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Geo-exploration Instruments,Ministry of Education of China,Changchun 130061,China
2.College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
CLC Number:
- TH763
| 1 | Liu G. Effect of transmitter current waveform on airborne TEM response[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 1998, 29: 35-41 |
| 2 | 陈曙东, 林君, 张爽. 发射电流波形对瞬变电磁响应的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(2): 709-716. |
| Chen Shu-dong, Lin Jun, Zhang Shuang. Effect of transmitter current waveform on TEM response[J], Chinese J Geophys,2012, 55(2): 709-716. | |
| 3 | Ziolkowski A, Wright D, Mattsson J. Comparison of pseudo-random binary sequence and square-wave transient controlled-source electromagnetic data over the Peon gas discovery, Norway[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 59(6): 1114-1131. |
| 4 | Ziolkowski A, Parr R, Wright D, et al. Multi-transient electromagnetic repeatability experiment over the North Sea Harding field[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58: 1159-1176. |
| 5 | Ziolkowski A, Hobbs B A, Wright D. Multitransient electromagnetic demonstration survey in France[J]. Geophysics, 2007, 72(4): 197-209. |
| 6 | Sorensen K I, Auken E. New developments in high resolution airborne TEM instrumentation[J]. ASEG Extended Abstracts, 2003(2): 1-4. |
| 7 | Eadie T, Legault J M, Plastow G, et al. VTEM ET: an improved helicopter time-domain EM system for near surface applications[J]. ASEG Extended Abstracts, 2018(1): 1-5. |
| 8 | 武欣, 薛国强, 方广有. 中国直升机航空瞬变电磁探测技术进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(4): 1679-1686. |
| Wu Xin, Xue Guo-qiang, Fang Guang-you. Development of helicopter-borne transient electromagnetic in China[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(4): 1679-1686. | |
| 9 | Wu Xin, Fang Guang-you, Xue Guo-qiang, et al. The development and applications of the helicopter-borne transient electromagnetic system CAS-HTEM[J]. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 24(4): 653-663. |
| 10 | 王麒. 基于PC104架构的时间域航空电磁多信息流数据收录系统研制[D]. 长春: 吉林大学仪器科学与电气工程学院, 2021. |
| Wang Qi. Research on multi-stream data recording system of time domain airborne electromagnetic based on PC104 architecture[D]. Changchun: College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering, Jilin University, 2021 | |
| 11 | 齐彦福, 殷长春, 王若, 等. 多通道瞬变电磁m序列全时正演模拟与反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(7): 2566-2577. |
| Qi Yan-fu, Yin Chang-chun, Wang Ruo, et al. Multi-transient EM full-time forward modeling and inversion of m-sequence[J]. Chinese J Geophys, 2015, 58(7): 2566-2577. | |
| 12 | 景春阳. 伪随机源浅层航空电磁探测的时域辨识方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学仪器科学与电气工程学院, 2021. |
| Jing Chun-yang. Research on time domain identification method for shallow airborne electromagnetic exploration using pseudo-random current[D]. Changchun: College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering, Jilin University, 2021 | |
| 13 | 汤井田, 李飞, 罗维斌. 基于逆重复m序列的精细探测电法发送机设计[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(3): 994-1000. |
| Tang Jing-tian, Li Fei, Luo Wei-bin. Electrical fine-exploration transmitter design based on invert-repeated m-sequence[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(3): 994-1000. | |
| 14 | Jing Chun-yang, Zhu Kai-guang, Peng Cong, et al. Early time data processing in shallow AEM exploration[C]∥Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Princeton, USA, 2020: 837-842. |
| 15 | 陈曙东. 瞬变电磁收录系统的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学电子学院, 2009. |
| Chen Shu-dong. Research of receiving system of transient electromagnetic[D]. Changchun: College of Electronics, Jilin University, 2009. | |
| 16 | 符磊. 感应式空心线圈传感器关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学仪器科学与电气工程学院, 2013. |
| Fu Lei. Key technology research of inductive air-core coil sensor[D]. Changchun: College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering, Jilin University, 2013. | |
| 17 | Chen C, Fei L, Jun L, et al. An optimized air-core coil sensor with a magnetic flux compensation structure suitable to the helicopter TEM system[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(4): 508. |
| 18 | 刘飞. 直升机时间域电磁探测系统动态噪声产生机理及抑制方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学仪器科学与电气工程学院, 2019. |
| Liu Fei. Research on generation mechanism and suppression method of motion induced noise in helicopter time domain electromagnetic system[D]. Changchun: College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering, Jilin University, 2019 | |
| 19 | 武欣, 薛国强, 底青云, 等. 伪随机编码源电磁响应的精细辨识[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8): 2792-2802. |
| Wu Xin, Xue Guo-qiang, Di Qing-yun, et al. Accurate identification for the electromagnetic impulse response og the earth with pseudo random coded waveforms[J]. Chinese J Geophys, 2015, 58(8): 2792-2802. | |
| 20 | 王世隆, 林君, 王言章, 等. 直升机式航空时间域电磁法全波收录[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(3): 776-781. |
| Wang Shi-long, Lin Jun, Wang Yan-zhang, et al. Helicopter-borne TEM full-wave recording[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(3): 776-781. |
| [1] | Xiao-hui WENG,You-hong SUN,Shu-jun ZHANG,Jun XIE,Zhi-yong CHANG. Oil and gas detection method and experimental new technology based on bionic nasal chamber optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 382-388. |
| [2] | ZHOU Feng-dao, WANG Shuang, HAN Si-yu, XU Fei, LIAN Shi-bo, SUN Cai-tang. Improved quadrature detection algorithm for controlled source electromagnetic detection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2128-2136. |
| [3] | YU Sheng-bao, SU Fa, ZHENG Jian-bo, ZHU Zhan-shan. Design of transient electromagnetic receiving system based on LabVIEW [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1725-1731. |
| [4] | ZHOU Feng-dao, DING Kai-lai, ZENG Xin-sen, XUE Kai-chang, SUN Cai-tang. Improved orthogonal lock-in amplification based on step wave reference signal [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 996-1003. |
| [5] | TIAN Bao-feng, WANG Yue, ZHANG Jian, WU Pei-lin, ZHOU Yuan-yuan. Design and implementation of an electromagnetic noise test system in nuclear magnetic resonance sounding environment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2034-2042. |
| [6] | ZHOU Feng-dao, TANG Hong-zhong, GUO Xin, WANG Jin-yu. Current overshoot produce principle and inhibition of transmitter of time domain electromagnetic detection system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 1023-1028. |
| [7] | ZHOU Feng-dao, WANG Jin-yu, TANG Hong-zhong, ZHANG He, ZHOU Ji-yu. Multi-frequency digital drive signal generation technology in near surface electromagnetic detection domain [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(03): 682-687. |
|
||