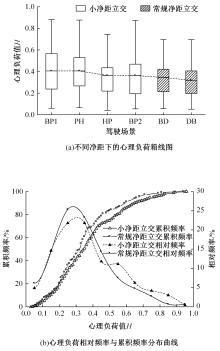
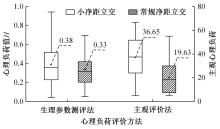
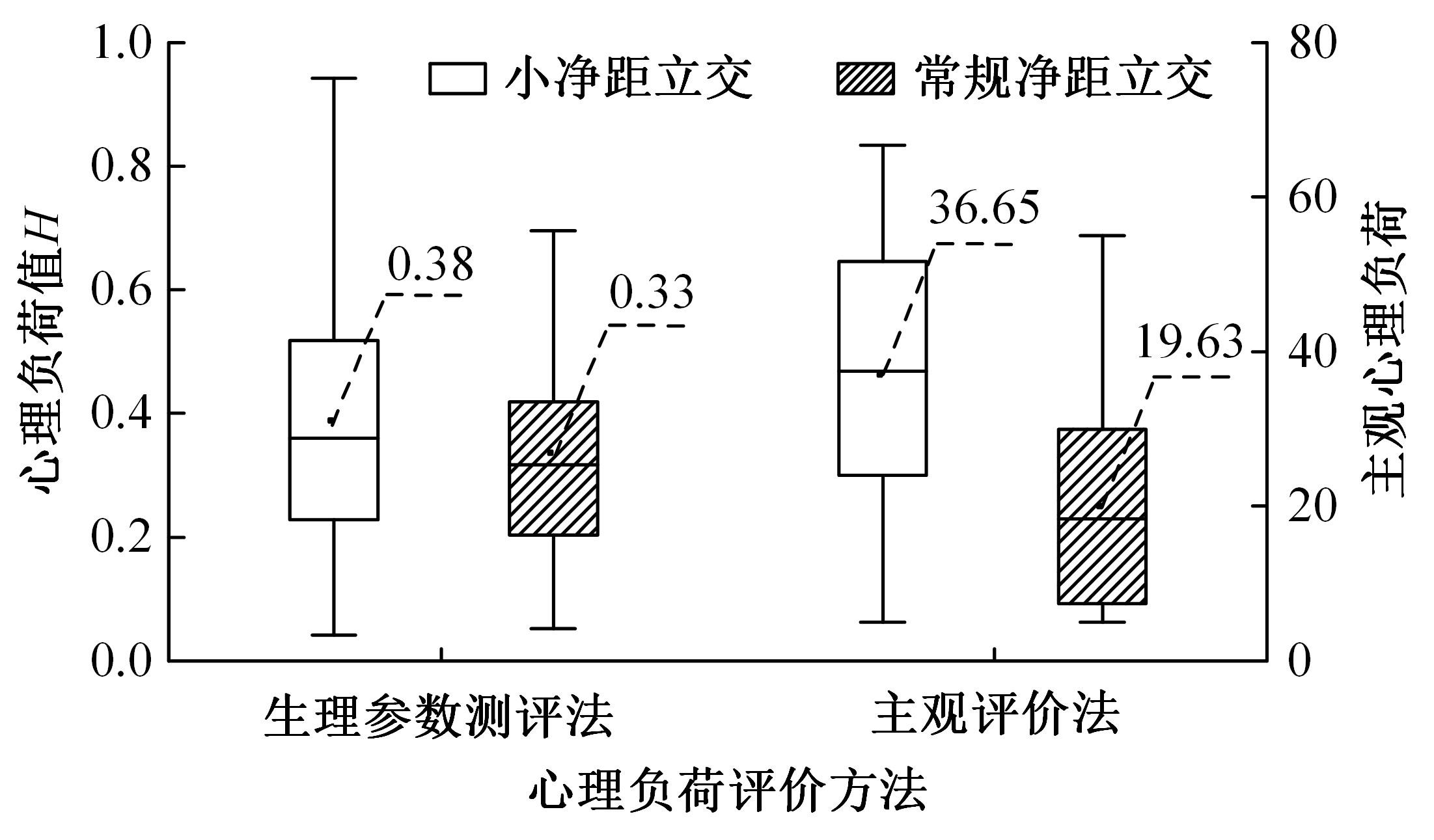
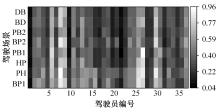
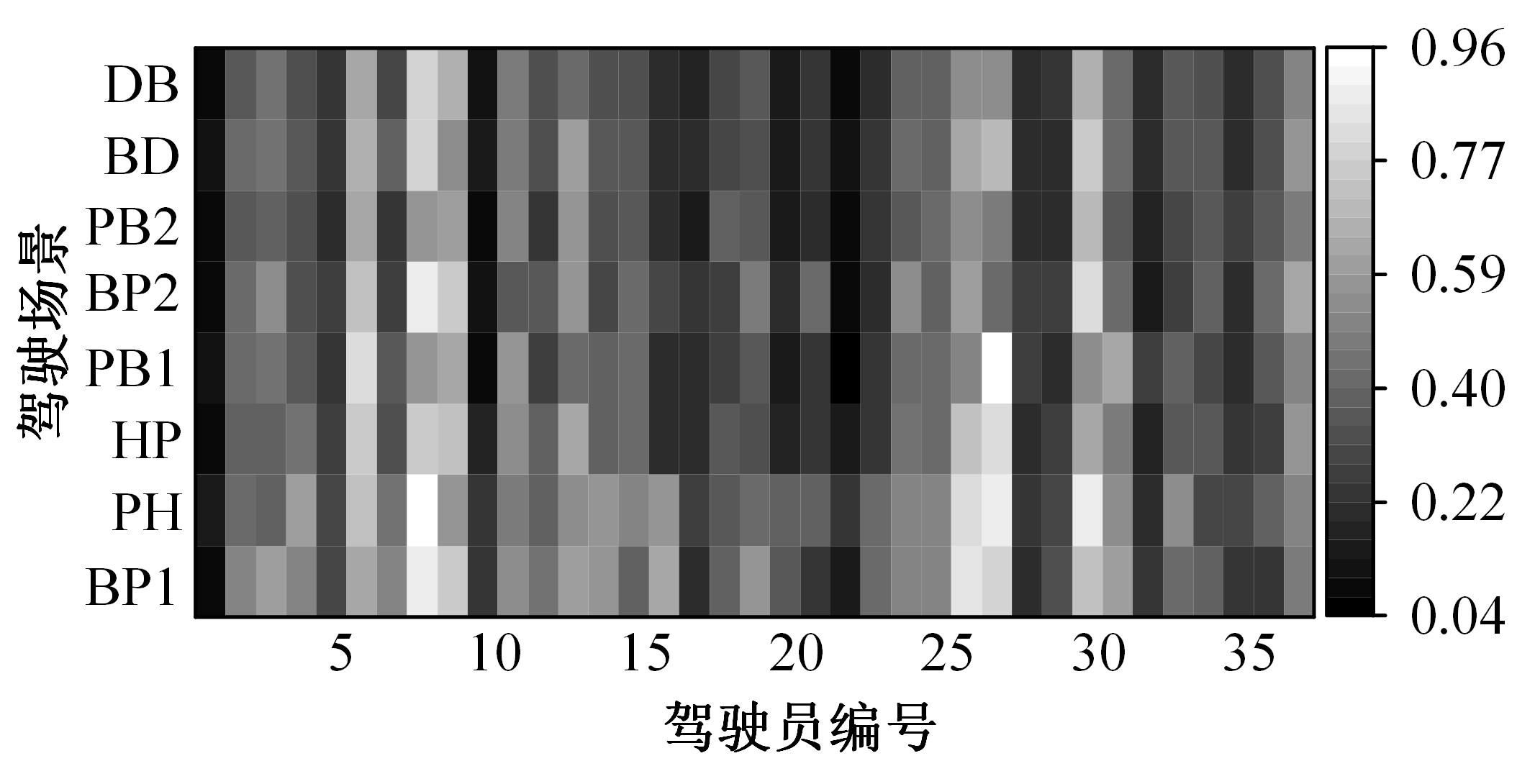
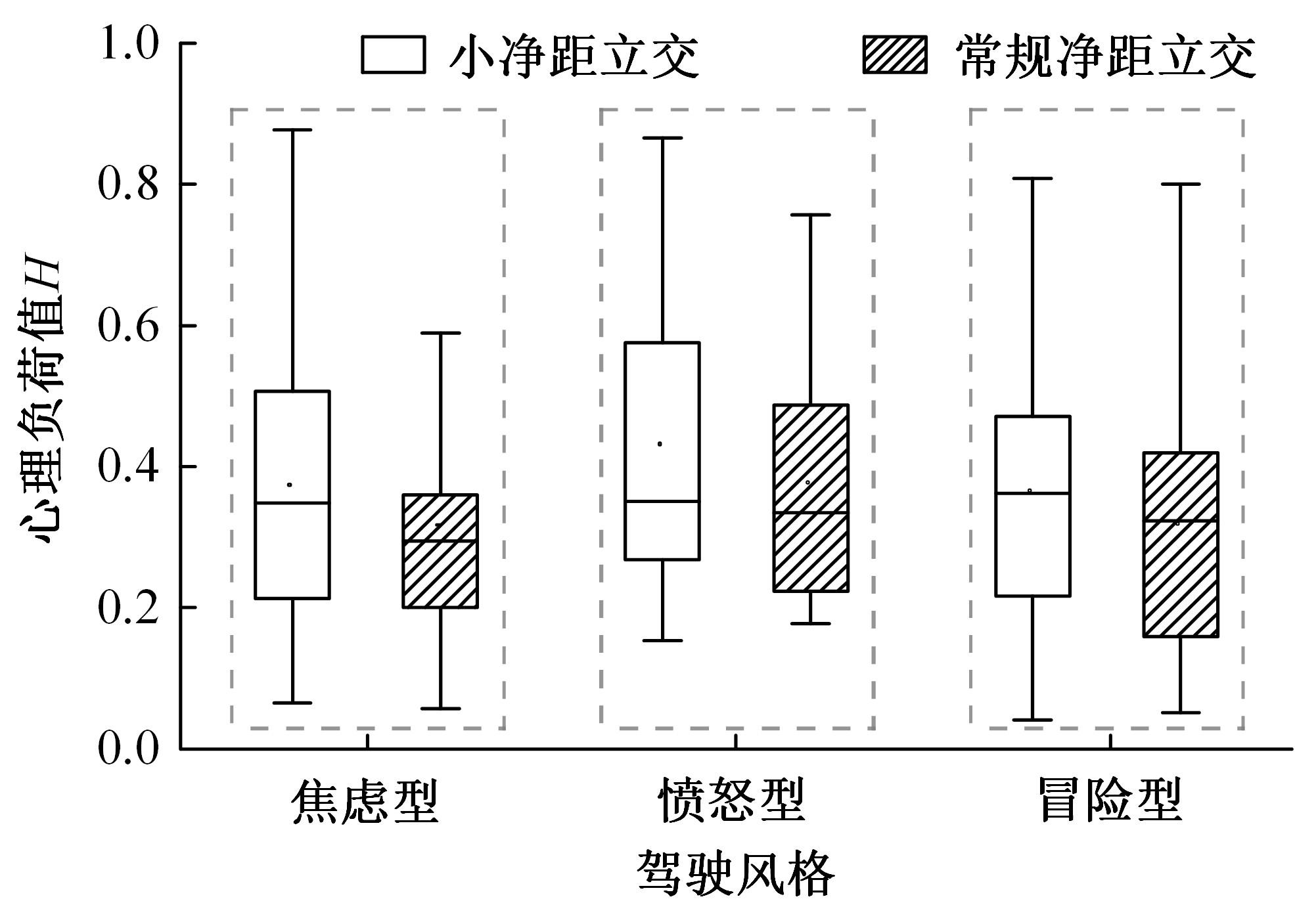
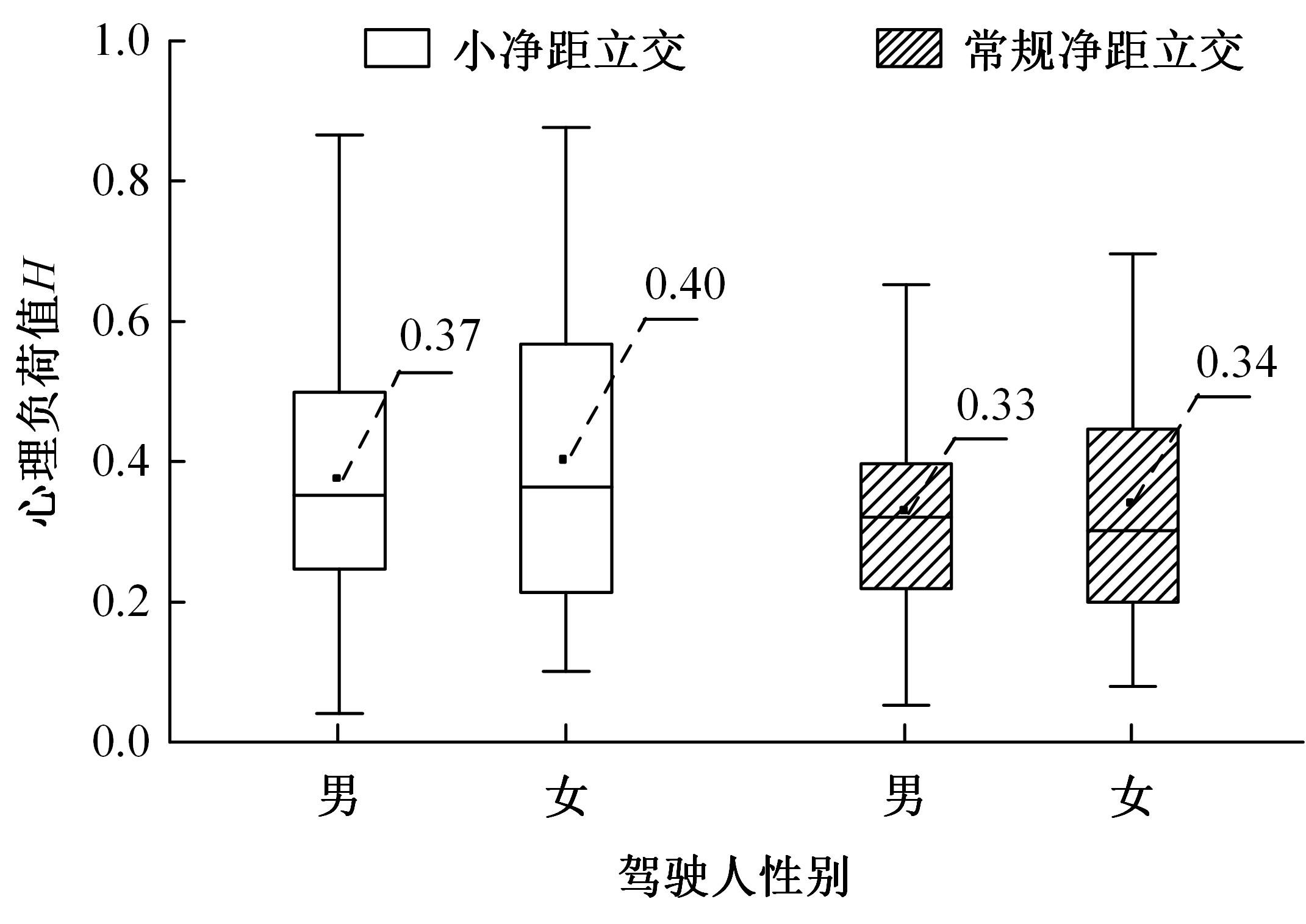
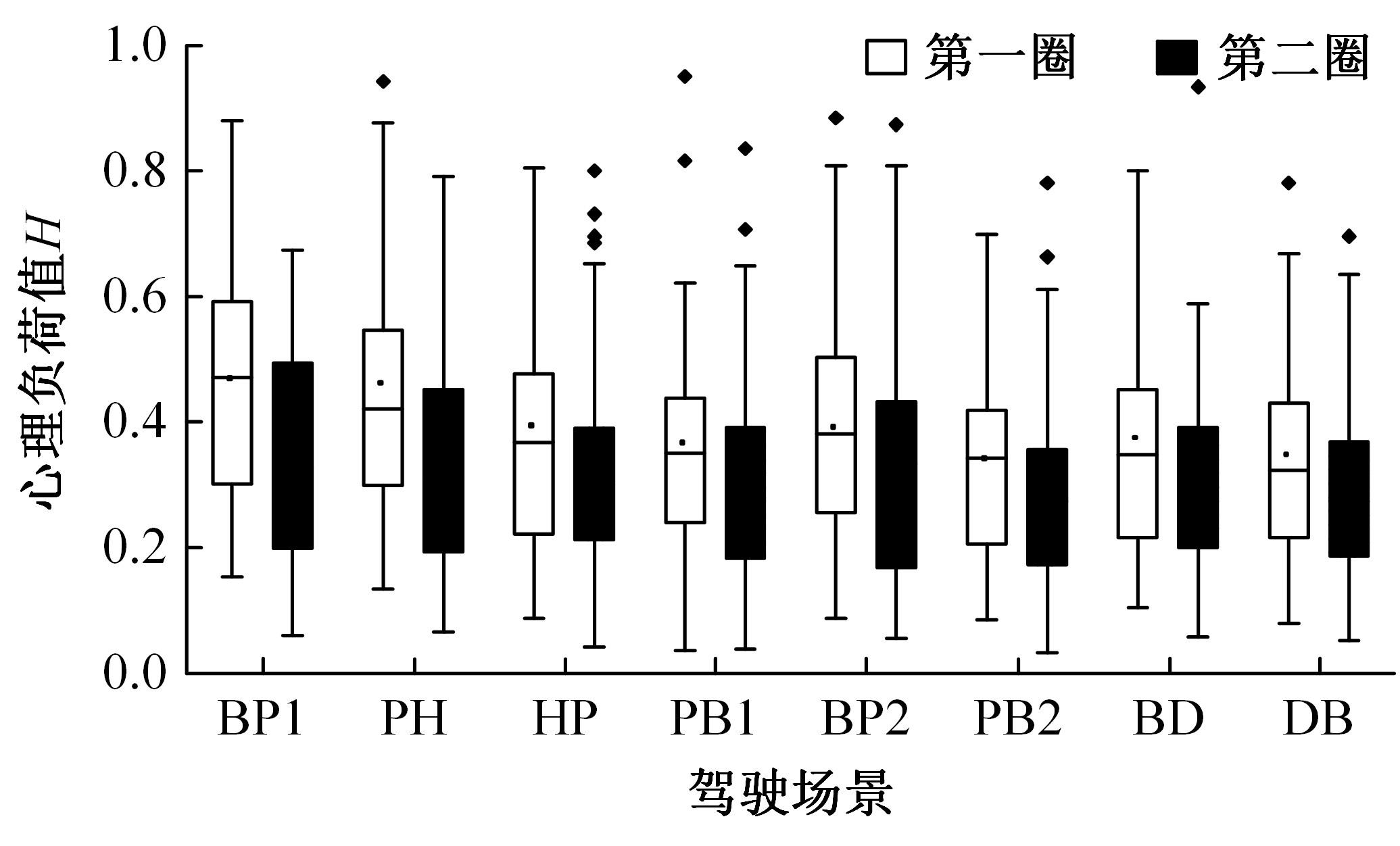
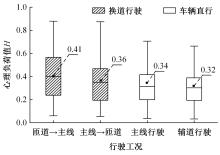
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2807-2818.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221522
Mental workload of drivers at high-density interchanges of freeways based on ECG data
Jin XU1,2( ),Zheng-huan CHEN1,Qi-shuo LIAO3,Zhan-ji ZHENG1,He-shan ZHANG1
),Zheng-huan CHEN1,Qi-shuo LIAO3,Zhan-ji ZHENG1,He-shan ZHANG1
- 1.School of Traffic & Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.Chongqing Key Laboratory of "Human-Vehicle-Road" Cooperation and Safety for Mountain Complex Environment,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
3.Chongqing City Transportation Development & Investment Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Chongqing 401121,China
CLC Number:
- U491.2
| 1 | 吕能超, 旷权, 吴萌. 基于HRV量化的高速公路出口匝道区域驾驶负荷特性研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(4): 143-148. |
| Neng-chao Lyu, Kuang Quan, Wu Meng. Study on the specific driving workload features of highway off-ramp area based on the HRV index quantization[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(4): 143-148. | |
| 2 | 孙雨斐. 高速公路互通式立交路段对驾驶员工作负荷的影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2021. |
| Sun Yu-fei. Study on the impact of freeway interchange sections on driving workload[D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2021. | |
| 3 | Hu J B, He L C, Wang R H. Safety evaluation of freeway interchange merging areas based on driver workload theory[J]. Science Progress, 2020, 103(3): 1-16. |
| 4 | Hu J B, Wang R H. Classification of driving workload affected by highway alignment conditions based on classification and regression tree algorithm[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2018, 19(2): 214-218. |
| 5 | Shakouri M, Ikuma L H, Aghazadeh F, et al. Analysis of the sensitivity of heart rate variability and subjective workload measures in a driving simulator: the case of highway work zones[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2018, 66: 136-145. |
| 6 | 乔建刚, 杨程, 陈彦欣. 基于驾驶员心率和速度差的高速公路纵坡度研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022,18(5): 216-221. |
| Qiao Jian-gang, Yang Cheng, Chen Yan-xin. Research on longitudinal slope of expressway based on driver's heart rate and speed difference[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(5): 216-221. | |
| 7 | Di Flumeri G, Borghini G, Aricò P, et al. EEG-based mental workload neurometric to evaluate the impact of different traffic and road conditions in real driving settings[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2018, 12: 509. |
| 8 | Deng T M, Fu J H, Shao Y M, et al. Pedal operation characteristics and driving workload on slopes of mountainous road based on naturalistic driving tests[J]. Safety Science, 2019, 119: 40-49. |
| 9 | 徐进, 陈薇, 周佳, 等. 汽车转向盘操作与驾驶负荷的相关性[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(2): 438-445. |
| Xu Jin, Chen Wei, Zhou Jia, et al. Correlation between steering and driver's workload[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 438-445. | |
| 10 | 朱可宁, 龚波. 高速公路特长隧道出口段驾驶人心理负荷变化规律[J]. 交通科技与经济, 2017, 19(3): 6-9. |
| Zhu Ke-ning, Gong Bo. Research on driver mental load in exit of super long tunnel[J]. Technology & Economy in Areas of Communications, 2017, 19(3): 6-9. | |
| 11 | 朱彤, 吴玲, 胡月琦, 等. 基于因子模型的高速公路特长隧道驾驶人心理负荷特性研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(11): 165-175. |
| Zhu Tong, Wu Ling, Hu Yue-qi, et al. Research on characteristics of drivers mental workload in extra-long expressway tunnels based on the factor model[J]. China Journal of Highway Transport, 2018, 31(11): 165-175. | |
| 12 | 郭玉洁, 郭唐仪, 吴军. 基于因子分析的城市隧道驾驶人心理负荷变化规律[J]. 交通运输研究, 2021, 7(2): 91-99. |
| Guo Yu-jie, Guo Tang-yi, Wu Jun. Change regularity of drivers' psychological load in urban tunnels based on factor analysis[J]. Transport Research, 2021, 7(2): 91-99. | |
| 13 | 乔建刚, 谢一丹. 基于心生理反应的高速公路隧道入口安全[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(23): 10074-10079. |
| Qiao Jian-gang, Xie Yi-dan. Safety of expressway tunnel entrance based on psychophysiological response[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(23): 10074-10079. | |
| 14 | Feng Z X, Yang M M, Zhang W H, et al. Effect of longitudinal slope of urban underpass tunnels on drivers' heart rate and speed: a study based on a real vehicle experiment[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 81: 525-533. |
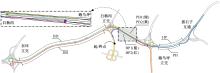
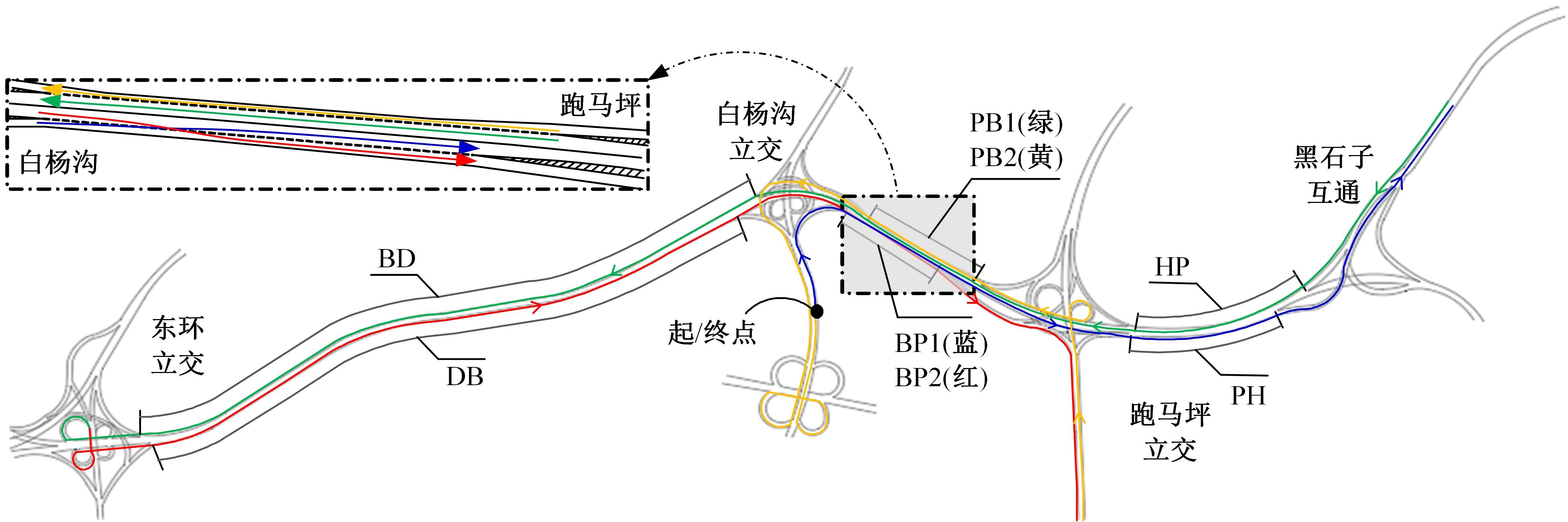
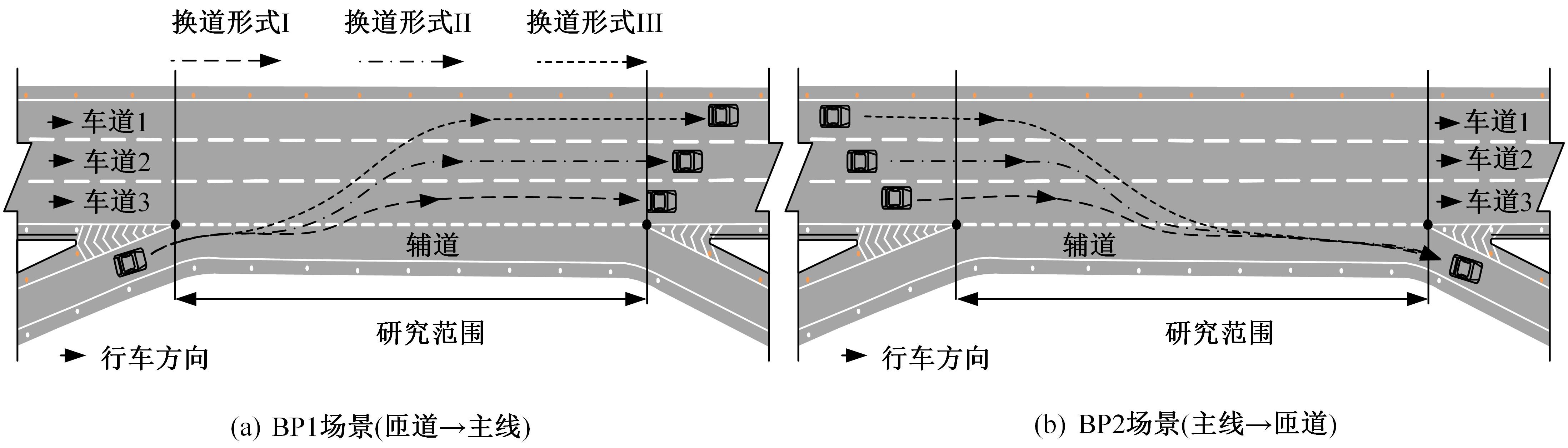
| 15 | 徐进, 孙子秋, 王思棋, 等. 高密度互通立交出口匝道驾驶人视觉搜索行为特征[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 52(6): 1189-1198. |
| Xu Jin, Sun Zi-qiu, Wang Si-qi, et al. Characteristics of driver's visual search behavior in exit ramp of high-density interchanges[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1189-1198. | |
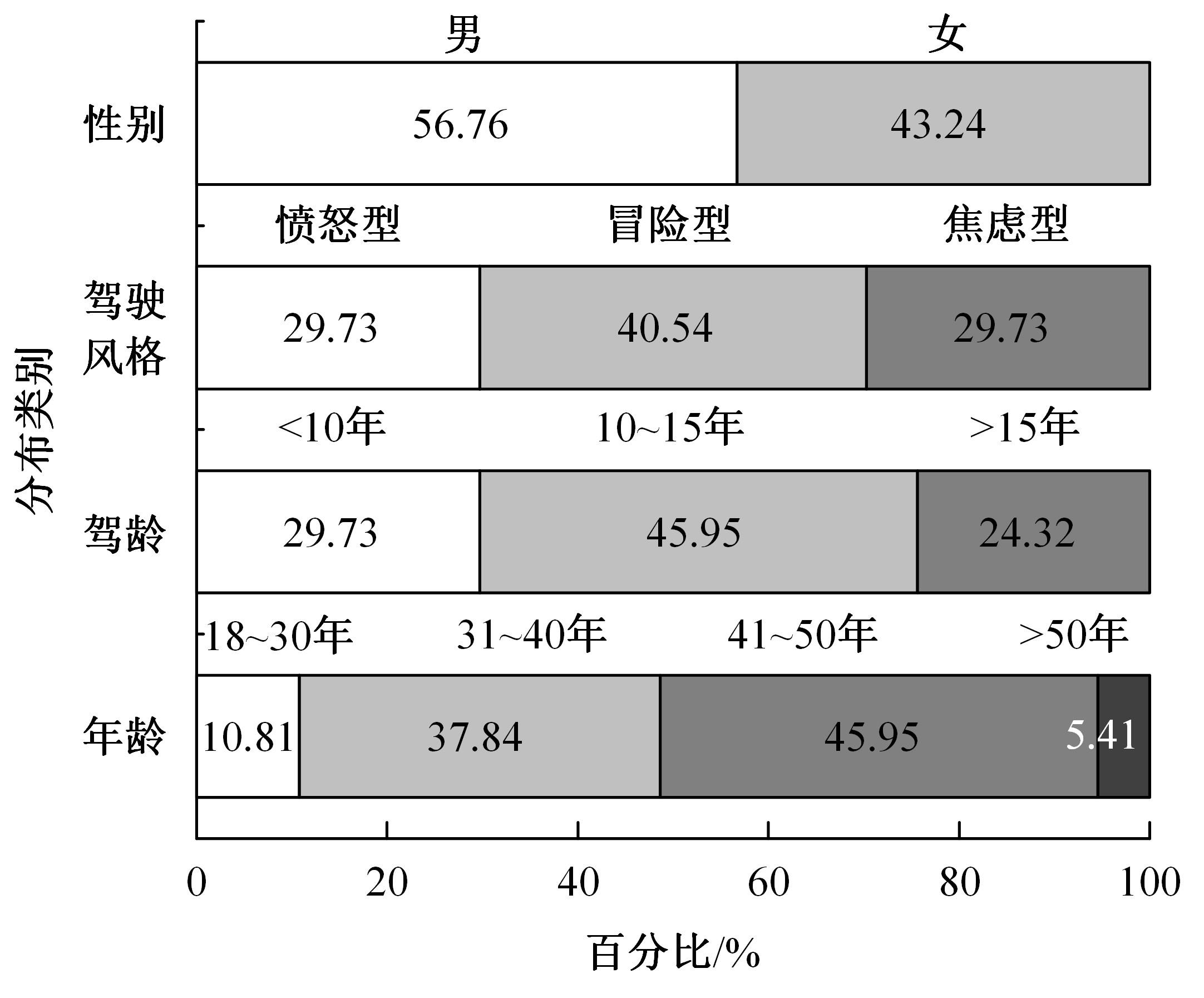
| 16 | 孙龙, 杨程程, 常若松. 多维度驾驶风格量表的修订及初步应用[J]. 人类工效学, 2014, 20(2): 6-9. |
| Sun Long, Yang Cheng-cheng, Chang Ruo-song. Revision and pre-liminary application of multidimensional driving style inventory[J]. Chinese Journal of Ergonomics, 2014, 20(2): 6-9. | |
| 17 | 王海玮, 温惠英, 刘敏. 夜间环境驾驶员精神负荷的生理特性评估与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(2): 420-428. |
| Wang Hai-wei, Wen Hui-ying, Liu Min. Experimental evaluation of nighttime driver's physiological characteristics in driving simulator[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 420-428. | |
| 18 | Fallahi M, Motamedzade M, Heidarimoghadam R, et al. Effects of mental workload on physiological and subjective responses during traffic density monitoring: a field study[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2016, 52: 95-103. |
| 19 | Feng D S, Chen F, Pan X D. Research on driver physiological load at the lowest point of city river-crossing tunnels[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2017, 25: 1494-1502. |
| 20 | Dey A, Mann D D. Sensitivity and diagnosticity of NASA-TLX and simplified SWAT to assess the mental workload associated with operating an agricultural sprayer[J]. Ergonomics, 2010, 53(7): 848-857. |
| [1] | Ya-ning CUI,Chun-di SI,Tao-tao FAN,Fei WANG. Analysis on crack propagation of asphalt bridge deck pavement under water-force coupling action [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1988-1996. |
| [2] | Ying-li GAO,Xiao-lei GU,Mei-jie LIAO,Xin-lang HU,Yu-tong XIE. Rheological properties and modification mechanism of SiO2 aerogel/reactive elastomer terpolymer/Polyphosphoric acid composite modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1978-1987. |
| [3] | Yong-li XU,Xu-lan YANG,Ji-sen ZHOU,Song-han YANG,Ming-gang SUN. Asphalt fume composition of warm mix asphalt and smoke suppression performance of warm mix agent [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1701-1707. |
| [4] | Xiao-kang ZHAO,Zhe HU,Zhen-xing NIU,Jiu-peng ZHANG,Jian-zhong PEI,Yong WEN. Meso-cracking behavior of cement-stabilized macadam materials based on heterogeneous model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1258-1266. |
| [5] | Tong-tong WAN,Hai-nian WANG,Wen-hua ZHENG,Po-nan FENG,Yu CHEN,Chen ZHANG. Thermal contraction deformation behavior of asphalt mixture overlay with coordination of unbound aggregate layer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1045-1057. |
| [6] | Jun CHEN,Zhen-hao SUN,Cheng ZHAO,Xin-yi WU,Jun-peng WANG. Laboratory investigation on cooling effect of multi-layer phase change asphalt concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 180-187. |
| [7] | Nai-peng TANG,Chen-yang XUE,Shao-peng LIU,Hong-zhou ZHU,Rui LI. Review on aging mechanism, characterization and evaluation of crumb rubber modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 22-43. |
| [8] | Zhuang WANG,Zhen-gang FENG,Dong-dong YAO,Qi CUI,Ruo-ting SHEN,Xin-jun LI. Research progress of conductive asphalt concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 1-21. |
| [9] | Sheng-qian ZHAO,Zhuo-hong CONG,Qing-long YOU,Yuan LI. Adhesion and raveling property between asphalt and aggregate: a review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2437-2464. |
| [10] | Tao MA,Yuan MA,Xiao-ming HUANG. Optimal combination of key parameters of intelligent compaction based on multiple nonlinear regression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [11] | Liu YANG,Chuang-ye WANG,Meng-yan WANG,Yang CHENG. Traffic flow characteristics of six⁃lane freeways with a dedicated lane for automatic cars [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [12] | Zheng-feng ZHOU,Xiao-tao YU,Ya-le TAO,Mao ZHENG,Chuan-qi YAN. High-temperature performance evaluation of resin and elastomer high viscosity asphalt based on grey correlation analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [13] | Qing-xia ZHANG,Ji-lin HOU,Xin-hao AN,Xiao-yang HU,Zhong-dong DUAN. Road roughness identification method based on vehicle impulse response [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1765-1772. |
| [14] | Ping JIANG,Ye-wen CHEN,Xian-hua CHEN,Wei-qing ZHANG,Na LI,Wei WANG. Unconfined compression behavior of modified lime stabilized soil under dry wet and freeze⁃thaw cycles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1809-1818. |
| [15] | Chun-di SI,Ya-ning CUI,Zhong-yin XU,Tao-tao FAN. Meso⁃mechanical behavior analysis of asphalt bridge deck pavement after interlayer bonding failure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1719-1728. |
|
||