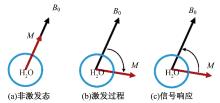
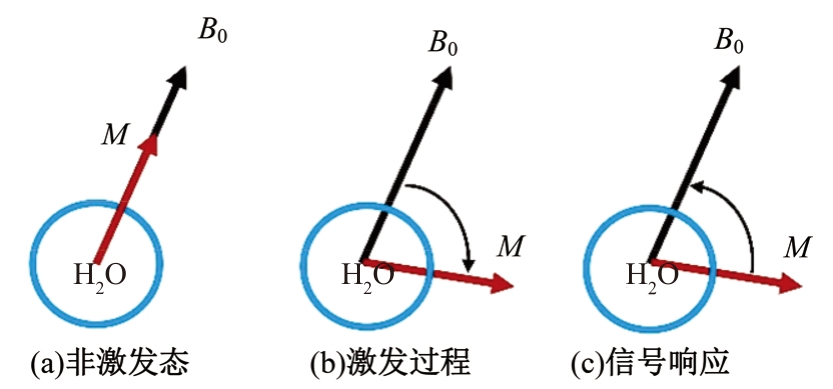
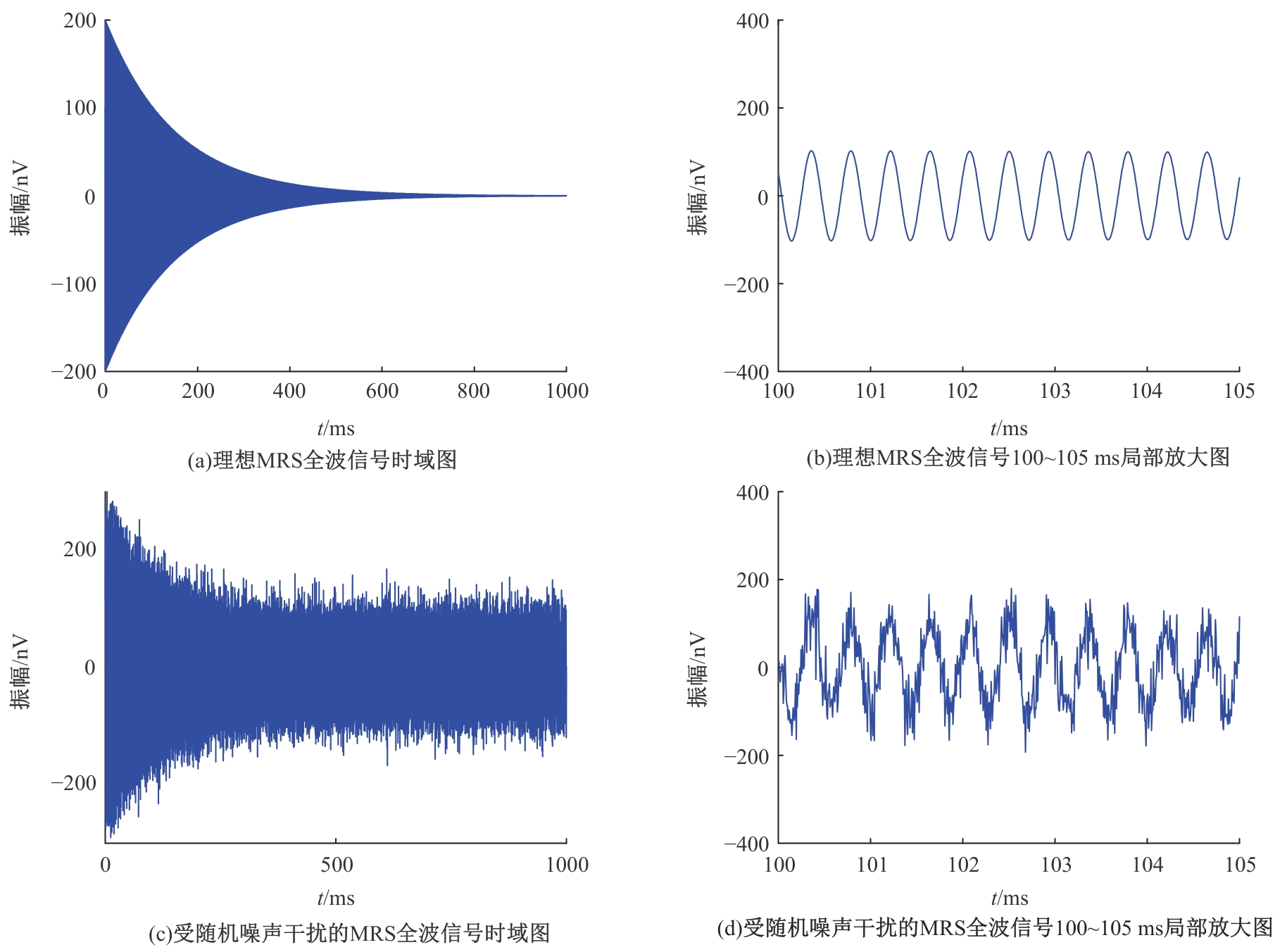
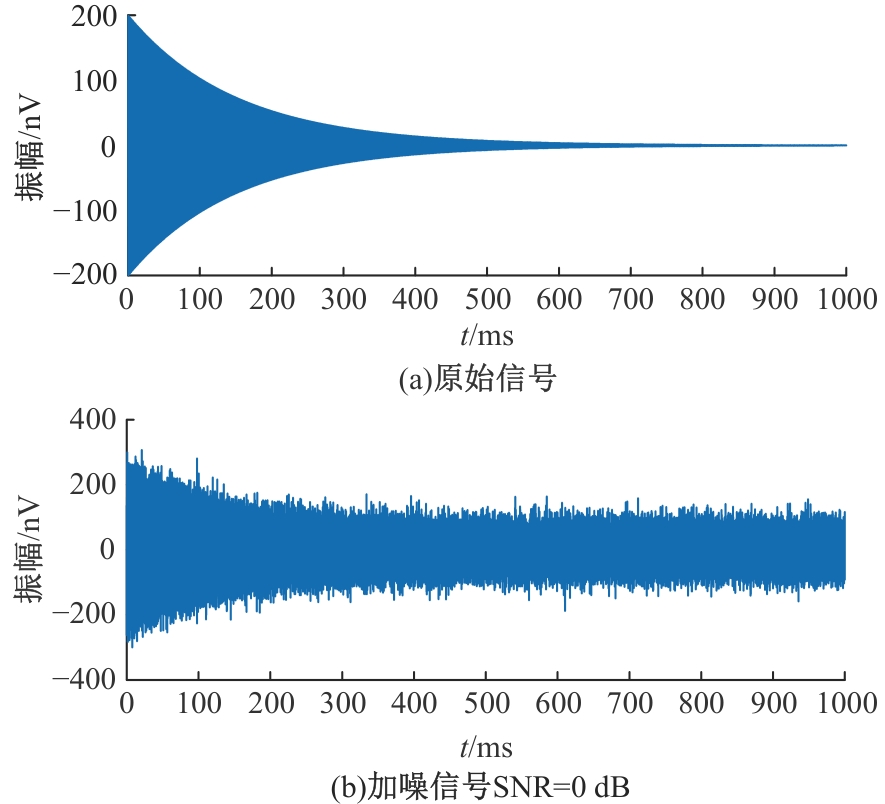
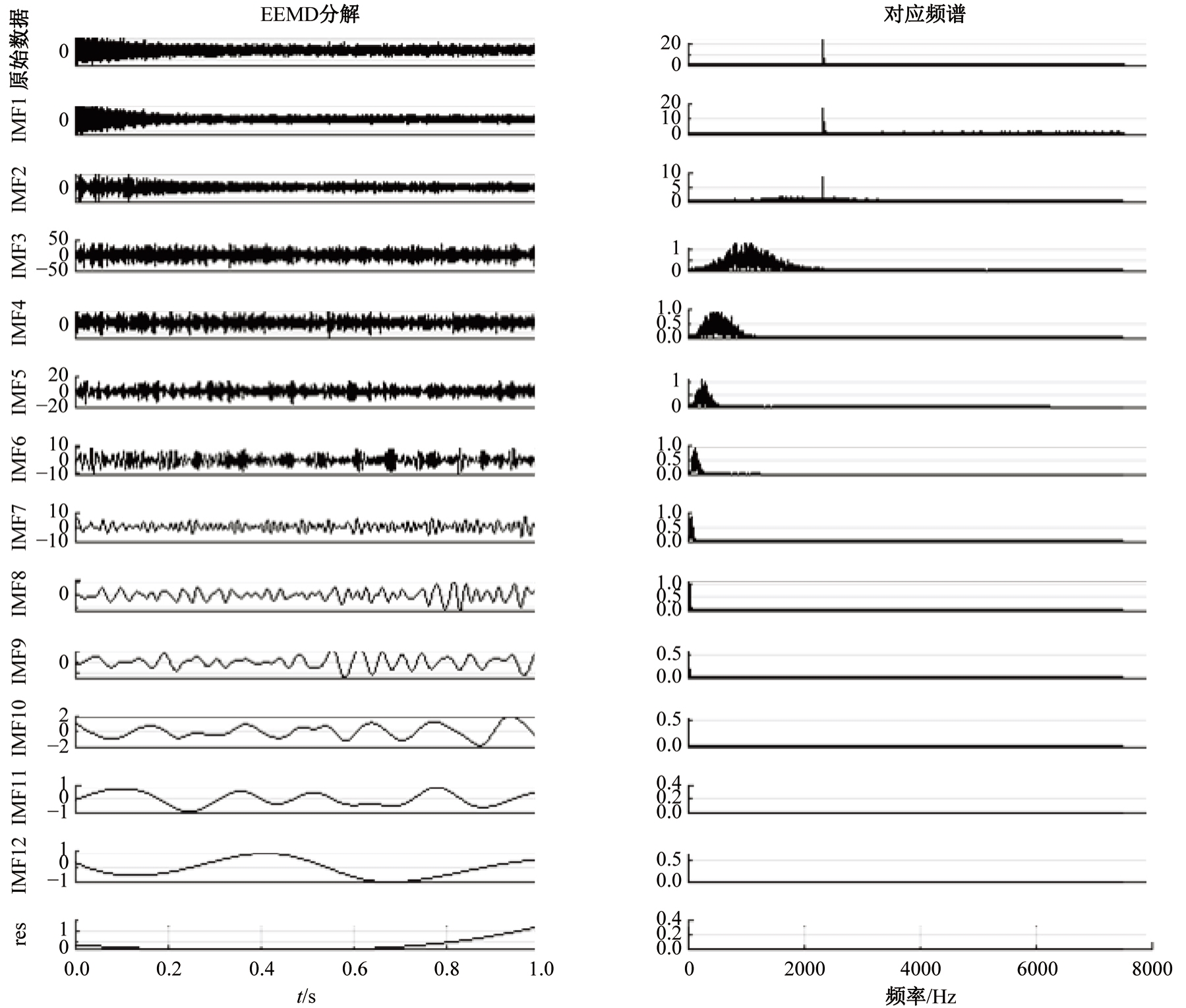
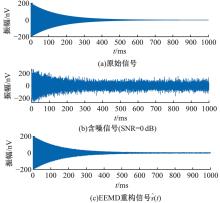
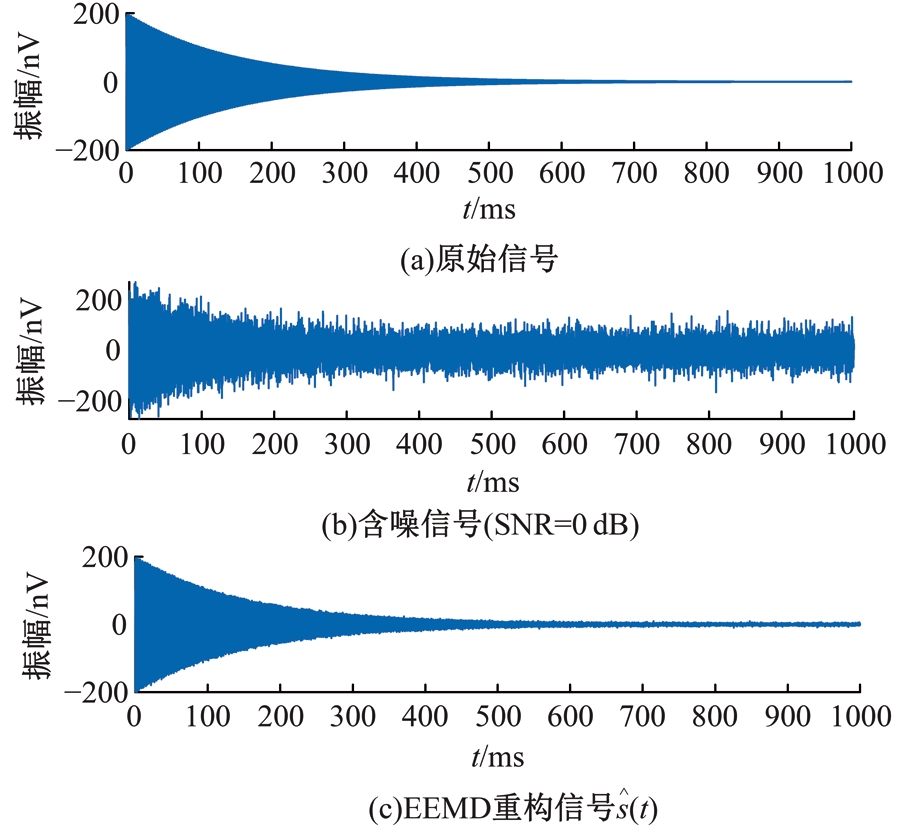
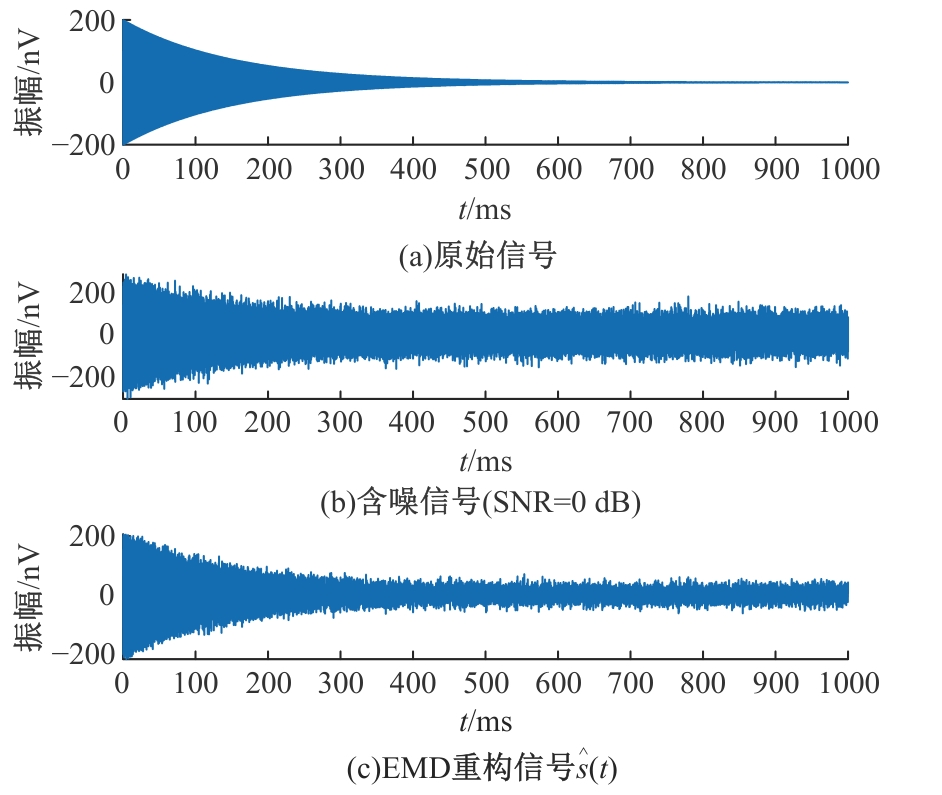
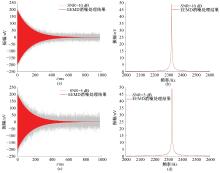
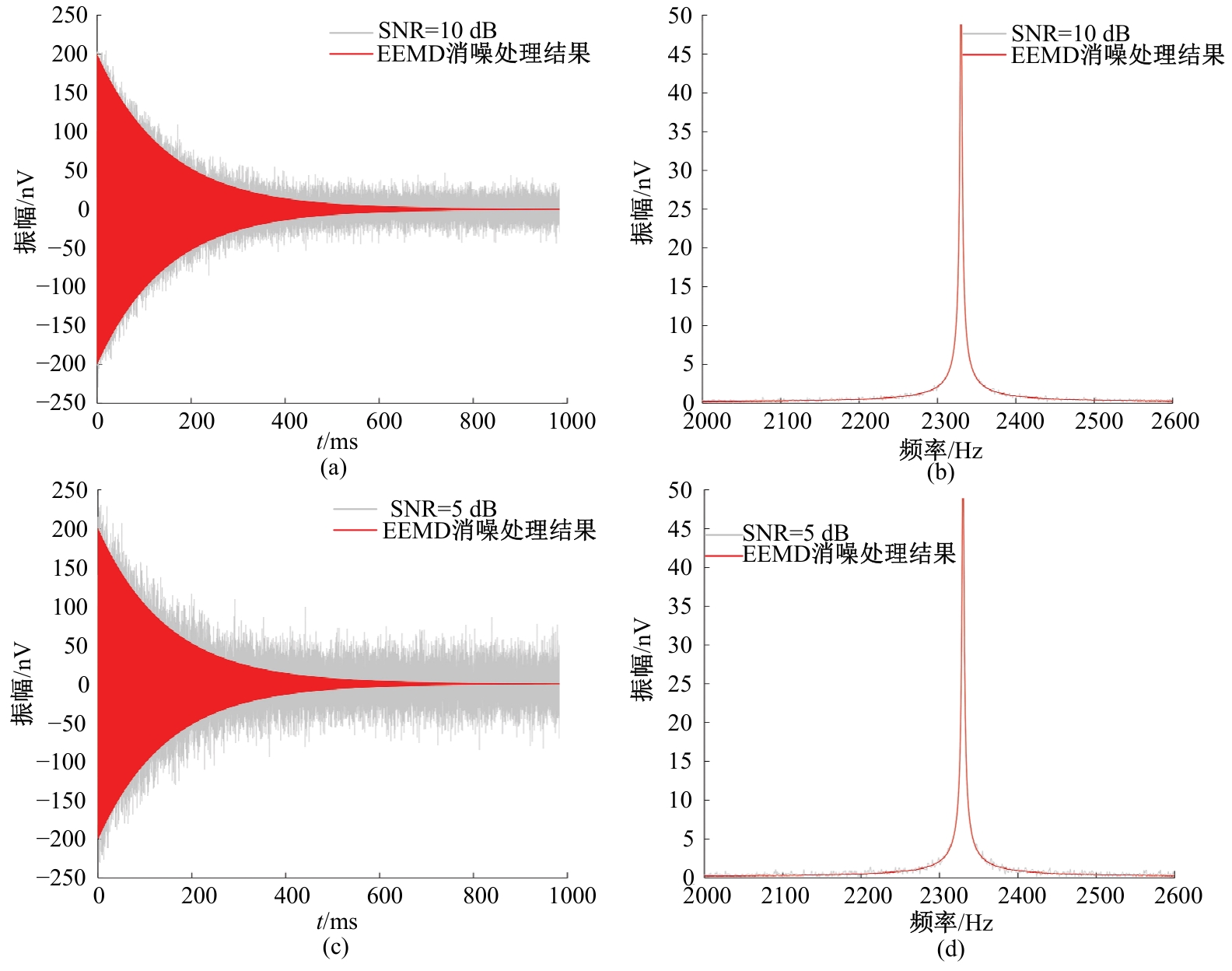
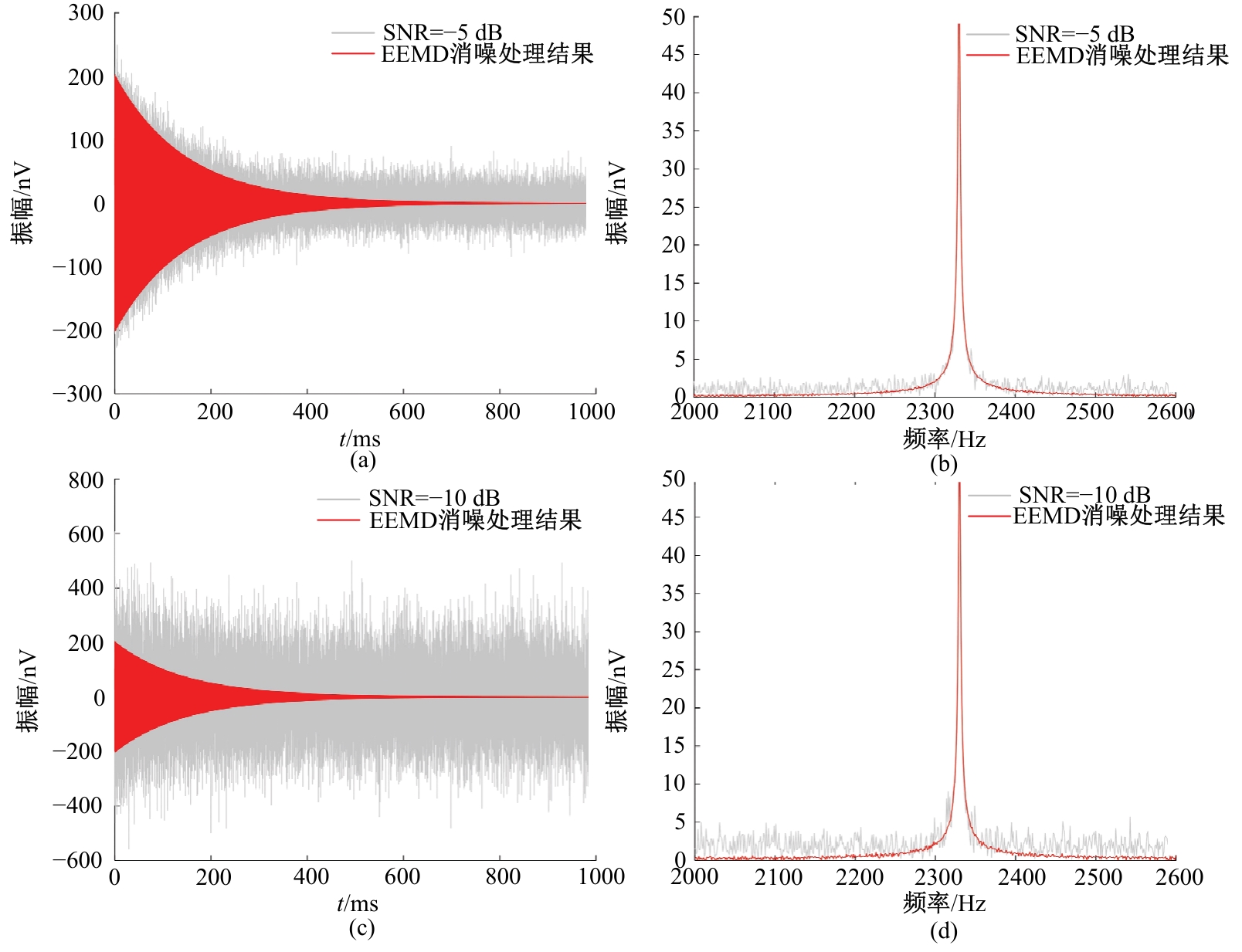
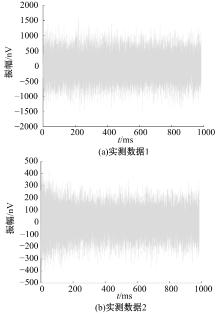
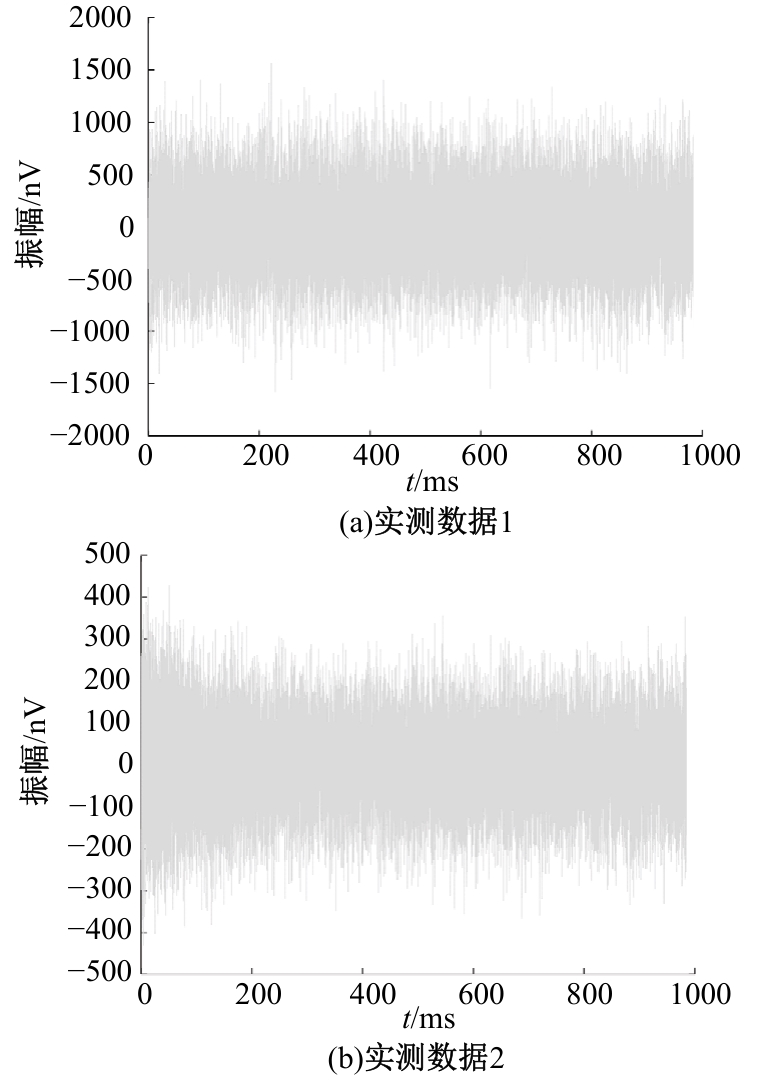
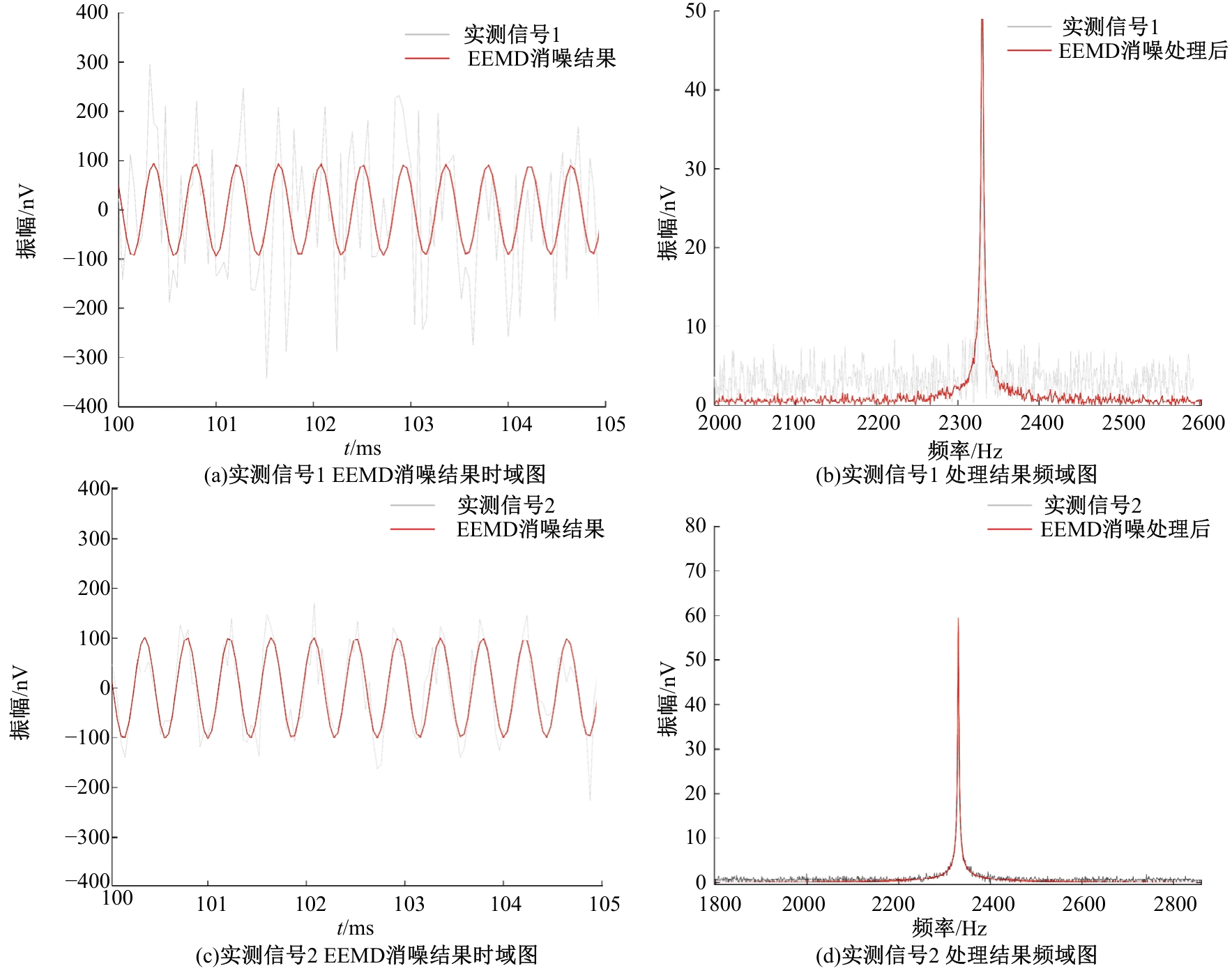
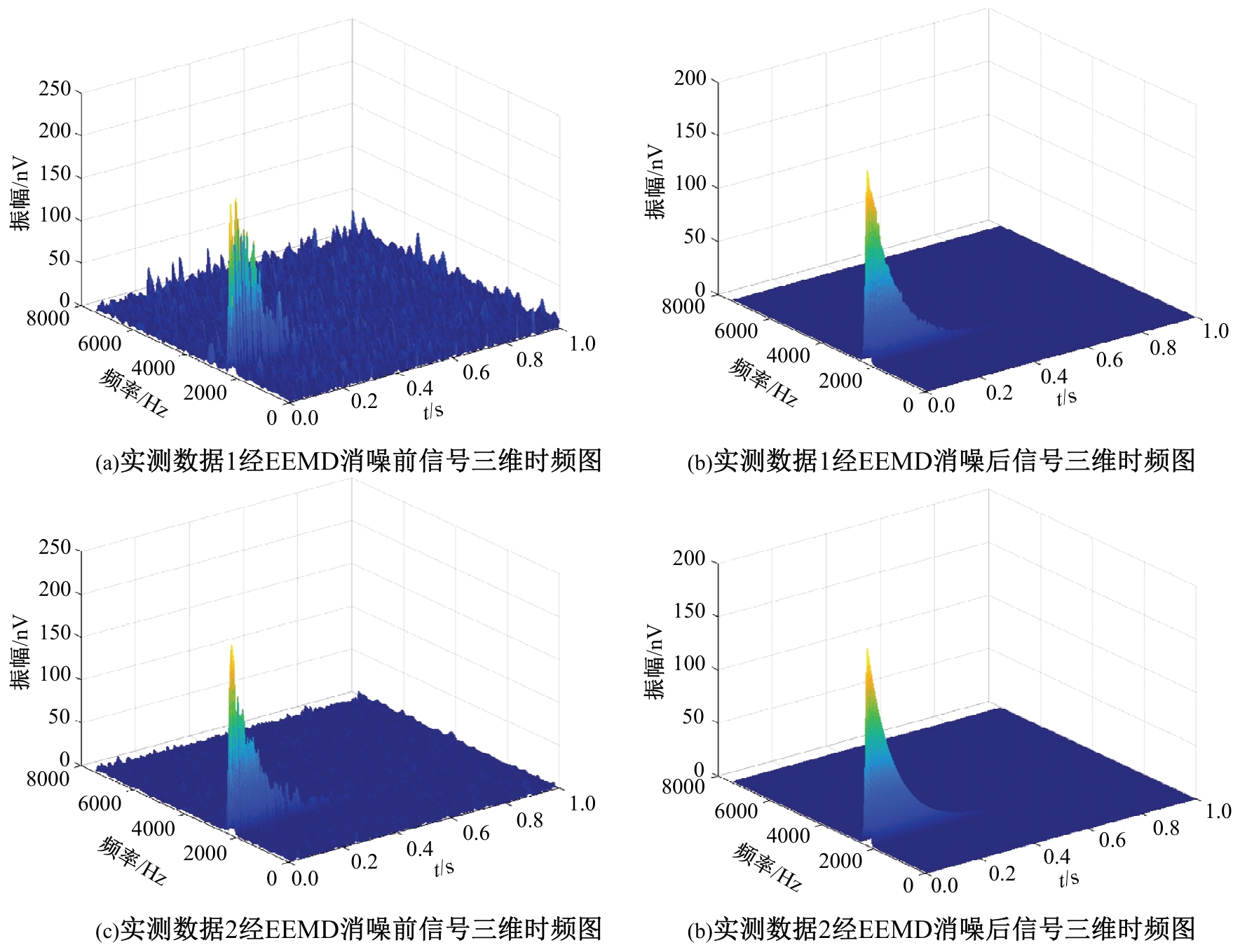
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 2771-2781.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231282
Random noise suppression method for magnetic resonance full-wave signal with ensemble empirical mode decomposition
Ling WAN1,2( ),Jia-lin ZHANG1,Shi-he LI1,Qing-yu PING1
),Jia-lin ZHANG1,Shi-he LI1,Qing-yu PING1
- 1.College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130026,China
2.Key Laboratory of Geo-Information Detection Instruments,Ministry of Education,Changchun 130026,China
CLC Number:
- TH763
| [1] | Price W S. Spin dynamics: basics of nuclear magnetic resonance, 2nd edition[J]. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance Part A, 2009, 34A(1): 60-61. |
| [2] | Dalgaard E, Christiansen P, Larsen J J, et al. A temporal and spatial analysis of anthropogenic noise sources affecting SNMR[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2014, 110: 34-42. |
| [3] | Grunewald E, Grombacher D, Walsh D. Adiabatic pulses enhance surface nuclear magnetic resonance measurement and survey speed for groundwater investigations[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(4): 85-96. |
| [4] | Lin T T, Zhang Y, Müller-Petke M. Random noise suppression of magnetic resonance sounding oscillating signal by combining empirical mode decomposition and time-frequency peak filtering[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 79917-79926. |
| [5] | Li F, Li K T, Lu K, et al. Random noise suppression and parameter estimation for Magnetic Resonance Sounding signal based on maximum likelihood estimation[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2020, 176: No.104007. |
| [6] | Lin T T, Yu S J, Wang P F, et al. Removal of a series of spikes from magnetic resonance sounding signal by combining empirical mode decomposition and wavelet thresholding[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2022, 93(2): No.024502. |
| [7] | Lin T T, Li Y, Lin Y S, et al. Magnetic resonance sounding signal extraction using the shaping-regularized Prony method[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2022, 231(3): 2127-2143. |
| [8] | 李丹丹. 基于集合经验模态分析的滚动轴承故障特征提取 [D].合肥: 安徽农业大学工学院, 2014. |
| Li Dan-dan. Rolling bearing fault feature extraction based on set empirical modal analysis[D]. Hefei: College of Engineering, Anhui Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| [9] | Behroozmand A A, Keating K, Auken E. A review of the principles and applications of the NMR technique for near-surface characterization[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2015, 36(1): 27-85. |
| [10] | Chen L, Li X, Li X B, et al. Signal extraction using ensemble empirical mode decomposition and sparsity in pipeline magnetic flux leakage nondestructive evaluation[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2009, 80(2): No.025105. |
| [11] | Larsen J J. Model-based subtraction of spikes from surface nuclear magnetic resonance data[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(4): 1-8. |
| [12] | Zheng J, Cheng J, Yang Y. Partly ensemble empirical mode decomposition: An improved noise-assisted method for eliminating mode mixing[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 96: 362-374. |
| [13] | Du S C, Liu T, Huang D L, et al. An optimal ensemble empirical mode decomposition method for vibration signal decomposition[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics-Transactions of the Asme, 2017, 139(3): No.031003. |
| [14] | Wang X X, Qi Y, Li Z, et al. A comparative study of DWT and EEMD methods for validation and correction of pyroshock data[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2022, 35(5): No.0001458. |
| [15] | Jiang Y, Tang C, Zhang X, et al. A novel rolling bearing defect detection method based on bispectrum analysis and cloud model-improved EEMD[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24323-24333. |
| [16] | 薛嫚. 总体平均经验模式分解法的理论研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学水声工程学院, 2007. |
| Xue Man. Theoretical research on the decomposition method of overall average empirical mode[D]. Harbin: College of Underwater Acoustic Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, 2007. | |
| [17] | 李文志, 屈晓旭. 基于EEMD和共振峰的自适应语音去噪[J]. 现代电子技术, 2021, 44(23): 52-56. |
| Li Wen-zhi, Qu Xiao-xu. Adaptive speech denoising based on EEMD and resonance peaks[J]. Modern Electronic Technology, 2021, 44 (23): 52-56. | |
| [18] | 连雄飞. 基于改进经验模态分解的轴承故障诊断研究 [D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学机械与装备工程学院, 2022. |
| Lian Xiong-fei. Research on bearing fault diagnosis based on improved empirical mode decomposition [D]. Handan: School of Mechanical and Equipment Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, 2022. | |
| [19] | Kong Y L, Meng Y, Li W, et al. Satellite image time series decomposition based on EEMD[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(11): 15583-15604. |
| [20] | Chang K M, Liu S H. Gaussian noise filtering from ECG by wiener filter and ensemble empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Signal Processing Systems for Signal Image and Video Technology, 2011, 64(2): 249-264. |
| [21] | 林婷婷, 李玥, 刘大震, 等. 基于频域对称法的磁共振数据残余噪声消除方法[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 52(10): 3494-3504. |
| Lin Ting-ting, Li Yue, Liu Da-zhen, et al. Residual noise elimination method for magnetic resonance data based on frequency domain symmetry method[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 52 (10): 3494-3504. |
| [1] | Wen-li JI,Zhong TIAN,Jing CHAI,Ding-ding ZHANG,Bin WANG. Prediction of water⁃flowing height in fractured zone based on distributed optical fiber and multi⁃attribute fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1200-1210. |
| [2] | Li-na LI,Xiao-hui WEI,Lin-lin HAO,Xing-wang WANG,Chu WANG. Cost⁃effective elastic resource allocation strategy in large⁃scale streaming data processing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1832-1843. |
| [3] | Bo-xin WANG,Hai-tao YANG,Qing WANG,Xin GAO,Xiao-xu CHEN. Bridge vibration signal optimization filtering method based on improved CEEMD⁃multi⁃scale permutation entropy analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 216-226. |
| [4] | WEI Xiao-hui, LIU Zhi-liang, ZHUANG Yuan, LI Hong-liang, LI Xiang. Adaptive checkpoint mechanism supporting large-scale stream data processing [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 199-207. |
| [5] | TIAN Ya-nan, LI Yue, LIN Hong-bo, XU Xue-chun. Frequency-domain regularized Wiener filtering for seismic random noise suppression [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2043-2048. |
| [6] | JIANG Wan-lu,LU Chuan-qi,ZHU Yong. HHT and fuzzy C-means clustering-based fault recognition for axial piston pump [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 429-436. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jie, LI Yue. Reduction of random noise in seismic data by parallel radial-trace time-frequency peak filtering [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 882-887. |
| [8] | LIN Hong-bo, LI Yue, ZHANG Chao, MA Hai-tao. Based on fuzzy multi-level time-frequency peak filtering attenuation of seismic random noise [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 410-413. |
| [9] | WU Yong-zhi, LIU Yi-sheng, WAN Qiu-hua, DING Lin-hui. Dynamic interpolation error measuring system for high precision optical encoder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 309-313. |
| [10] | QUAN Yong, LUYi-Na, HUANG Yong-Ping, LI Wen-Hui, ZHANG Zhen-Hua, ZHOU Bin. Resampling of pointbased models [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 315-0319. |
| [11] | Quan Yong,Li Wen-hui,Lu Yi-nan,Zhang Zhen-hua . New method for simplification of 3D scattered points [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(增刊): 156-0162. |
| [12] | GANG Long-hui, JIANG Gui-yan, ZHANG Xiao-dong, WANG Jiang-feng. Screening and checking for ITS traffic sensor data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (1): 122-126. |
| [13] | CAI Zhong-yi, SUN Xi-hong, LI Ming-zhe, FENG Zhao-hua. Smoothing-finite element method for representation and differentiation of discrete experimental data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2003, (2): 64-68. |
|
||