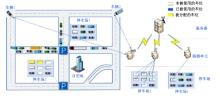
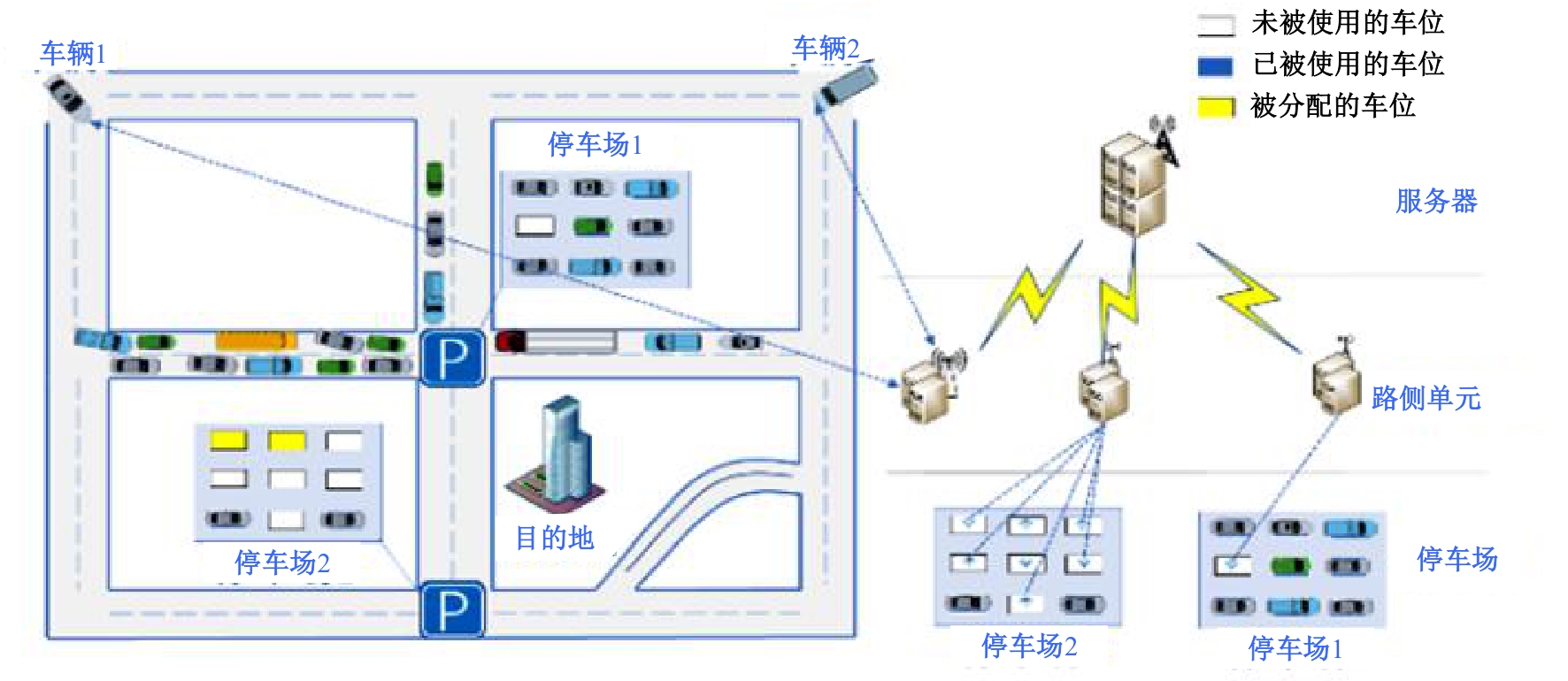
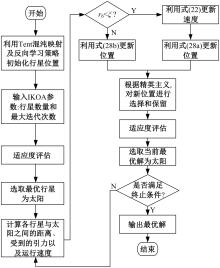
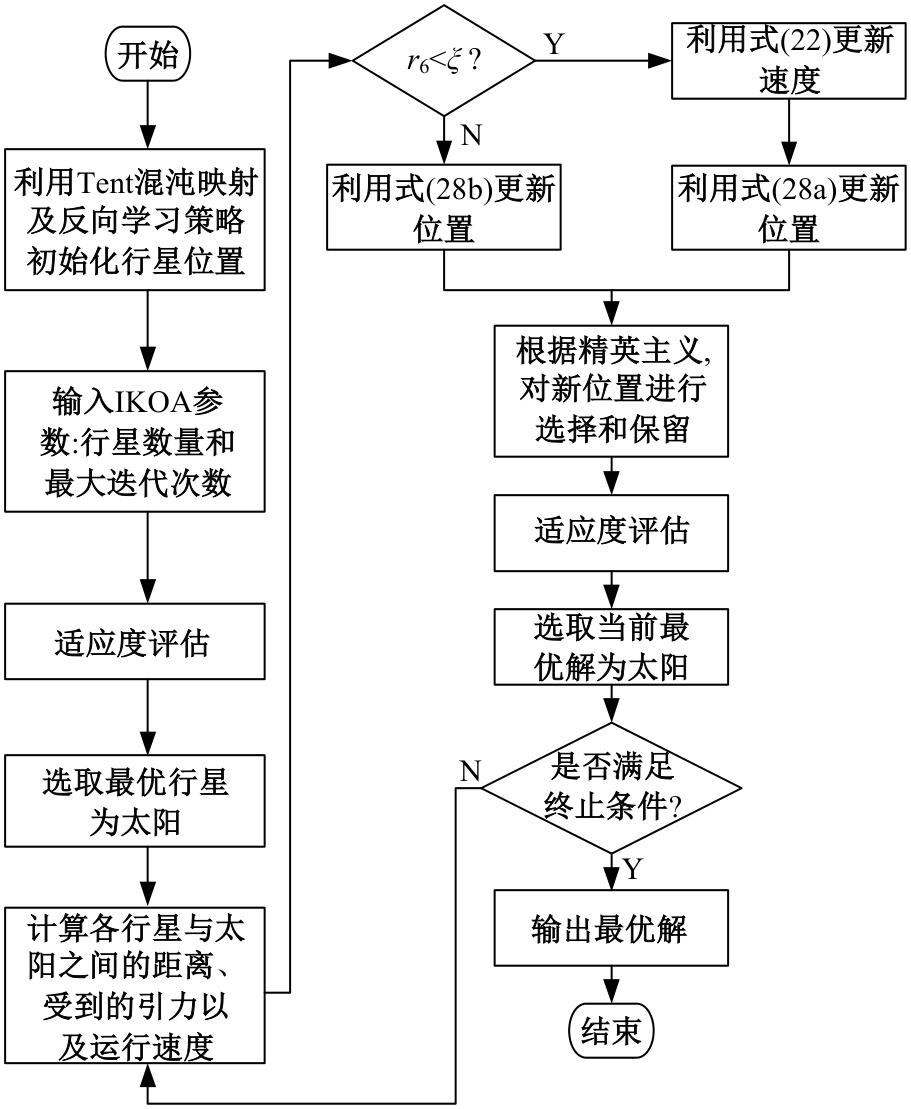
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 3907-3917.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240484
Regional parking allocation model based on improved Kepler optimization algorithm
Zhe WANG1( ),Wen-bo FAN1(
),Wen-bo FAN1( ),Xin LIU1,Huan YANG2,Xian-min SONG2,Bai-ting YANG3
),Xin LIU1,Huan YANG2,Xian-min SONG2,Bai-ting YANG3
- 1.Center for Big Data and Network Management,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Changchun Polytechnic,Changchun 130033,China
CLC Number:
- U491.2
| [1] | Shoup D C. Cruising for parking[J]. Transport Policy, 2006, 13(6): 479-486. |
| [2] | Chu C P, Wang C Y, Hu S R. Application of e-tag in pricing road tolls and parking fees for traffic congestion mitigation[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2017, 25: 2913-2922. |
| [3] | Bao H X H, Ng J. Tradable parking permits as a transportation demand management strategy: A behavioural investigation[J]. Cities, 2022, 120: 103463. |
| [4] | Lin T, Rivano H, Le M F. A survey of smart parking solutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(12): 3229-3253. |
| [5] | Shao C, Yang H, Zhang Y, et al. A simple reservation and allocation model of shared parking lots[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 71: 303-312. |
| [6] | Jiang B, Fan Z P. Optimal allocation of shared parking slots considering parking unpunctuality under a platform-based management approach[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2020, 142: 102062. |
| [7] | Kim O T T, Tran N H, Pham C, et al. Parking assignment: Minimizing parking expenses and balancing parking demand among multiple parking lots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2019, 17(3): 1320-1331. |
| [8] | Nakazato T, Fujimaki Y, Namerikawa T. Parking lot allocation using rematching and dynamic parking fee design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(4): 1692-1703. |
| [9] | 卢凯, 林茂伟, 邓兴栋, 等. 停车总成本最小的停车位动态分配与诱导模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 46(9): 82-91, 98. |
| Lu Kai, Lin Maowei, Deng Xing-dong, et al. Dynamic allocation and inducement model of parking spaces with minimum total parking cost[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 82-91, 98. | |
| [10] | Wang Y, Chen Q. Dynamic parking allocation model in a multidestination multiple parking lot system[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2022, 14(5): 195-208. |
| [11] | 张水潮, 蔡逸飞, 黄锐, 等. 基于预约需求的共享停车平台泊位分配方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(3): 137-143, 162. |
| Zhang Shui-chao, Cai Yi-fei, Huang Rui, et al. Shared parking space allocation method considering reservation demand[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020,20(3): 137-143, 162. | |
| [12] | 刘永红, 罗霞, 胡剑鹏. 考虑临时和预约需求的共享泊位动态分配方法[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息,2022, 22(1): 171-181. |
| LIU Yonghong, LUO Xia, HU Jianpeng. Dynamic allocation method for shared berth considering immediate and reservation demands[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(1): 171-181. | |
| [13] |
Abdel-Basset M, Mohamed R, Azeem S A A, et al. Kepler optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic algorithm inspired by Kepler's laws of planetary motion. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023 (May 23): 268. DOI: 1016/j.knosys. 2023. 110454 .
doi: 1016/j.knosys. 2023. 110454 |
| [1] | De-hua WU,Rong-feng CHEN. Characteristics of passenger-cargo mixed traffic flow in intelligent network and agglomeration lane-change strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2588-2596. |
| [2] | Yue HOU,Jin-song GUO,Wei LIN,Di ZHANG,Yue WU,Xin ZHANG. Multi-view video speed extraction method that can be segmented across lane demarcation lines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1692-1704. |
| [3] | Sheng JIANG,Yi-di WANG,Rui-lin XIE,Miao-lei XIA. Traffic accident anticipation baed on spatial-temporal relational learning and convolutional gated recurrent network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 954-962. |
| [4] | Li LI,Yu-jian BAO,Wen-chen YANG,Qing-ling CHU,Gui-ping WANG. Standardized constructing method of a roadside multi-source sensing dataset [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 529-536. |
| [5] | Nan YANG,Jun XIAO. Energy saving optimization control of urban intelligent transportation under sequential quadratic programming algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2223-2228. |
| [6] | Li LI,Xiao-qiang WU,Wen-chen YANG,Rui-jie ZHOU,Gui-ping WANG. Target recognition and tracking of group vehicles based on roadside millimeter-wave radar [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2104-2114. |
| [7] | Xiu-jian YANG,Xiao-han JIA,Sheng-bin ZHANG. Characteristics of mixed traffic flow taking account effect of dynamics of vehicular platoon [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [8] | Hai-long GAO,Yi-bo XU,De-zao HOU,Xue-song WANG. Short⁃term traffic flow prediction algorithm for road network based on deep asynchronous residual network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3458-3464. |
| [9] | Ming-hua GAO,Can YANG. Traffic target detection method based on improved convolution neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [10] | Xian-yan KUANG,Hui-chao LUO,Rui ZHONG,Peng OUYANG. Bus arrival time prediction based on wavelet neural network optimized by Beetle Antennae Search [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 110-117. |
| [11] | Jian ZHANG,Kun-run WU,Min YANG,Bin RAN. Double⁃ring adaptive control model of intersection during intelligent and connected environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 541-548. |
| [12] | ZHAO Hong-wei, LIU Yu-qi, DONG Li-yan, WANG Yu, LIU Pei. Dynamic route optimization algorithm based on hybrid in ITS [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1214-1223. |
| [13] | PAN Yi-yong, MA Jian-xiao, SUN Lu. Optimal path in dynamic network with random link travel times based on reliability [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 412-417. |
| [14] | PAN Yi-yong, SUN Lu. Adaptive reliable shortest path problem in stochastic traffic network [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1622-1627. |
| [15] | ZHAO Ying-ying, QU Zhao-wei, JIANG Sheng, HU Hong-yu, HU Jin-hui. Pedestrian crossing speed characteristic based on video detection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 298-303. |
|
||