吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 323-329.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210210
孕鼠DEHP暴露对子代神经行为的影响及其机制
楼张琪1,余起帆2,申雪知2,陈泓卿2,罗煜烽2,陈千叶2,郑国芬2,丁悦敏2( ),张雄1(
),张雄1( )
)
- 1.浙江大学医学院基础医学系,浙江 杭州 310058
2.浙大城市学院医学院临床医学系,浙江 杭州 310015
Effect of DEHP exposure in pregnant mice on neurobehavior of offsprings and its mechanism
Zhangqi LOU1,Qifan YU2,Xuezhi SHEN2,Hongqing CHEN2,Yufeng LUO2,Qianye CHEN2,Guofen ZHENG2,Yuemin DING2( ),Xiong ZHANG1(
),Xiong ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Basic Medical Sciences,College of Medical Sciences,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,China
2.Department of Clinical Medical Sciences,School of Medical Sciences,Zhejiang University City College,Hangzhou 310015,China
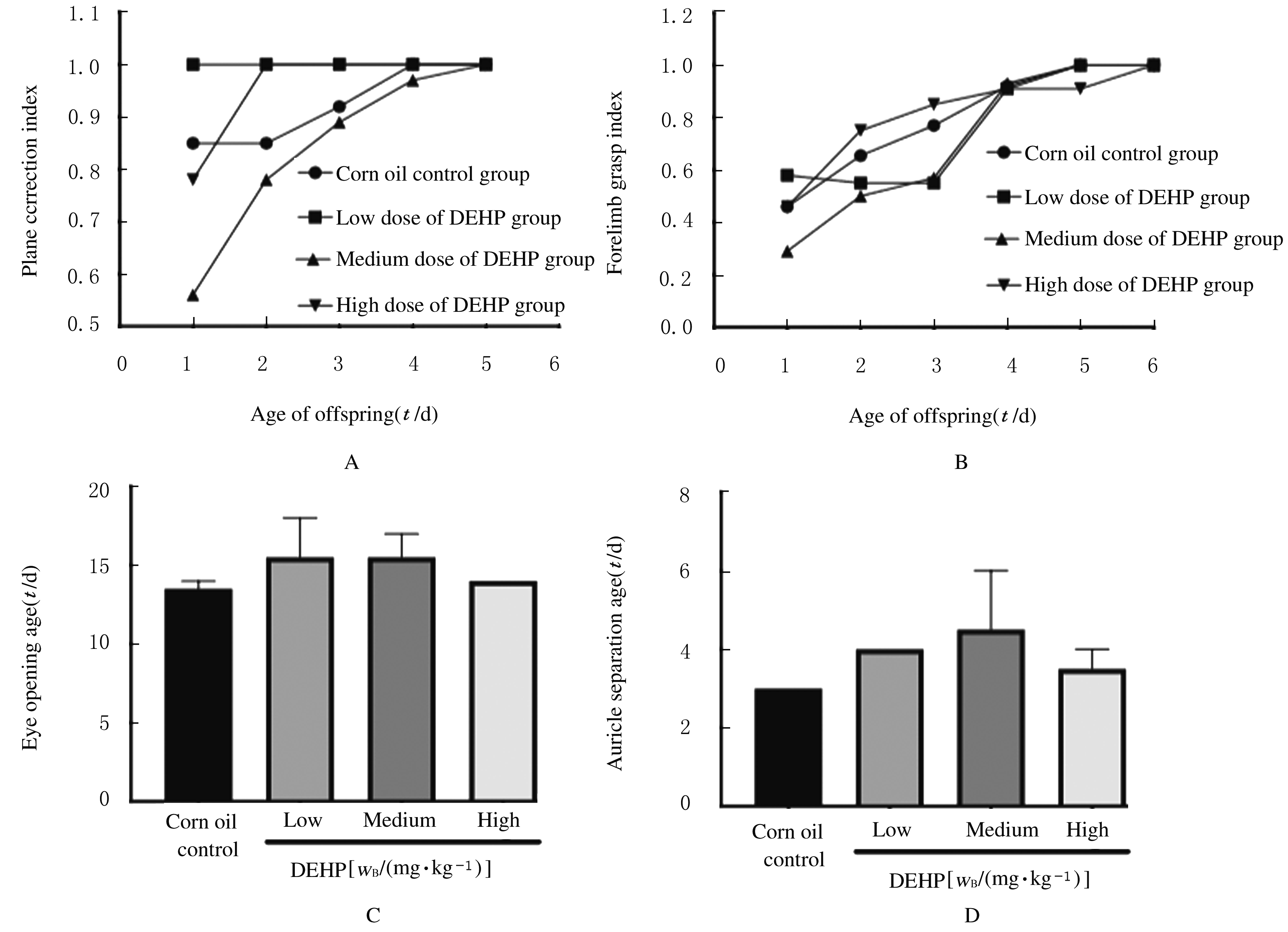
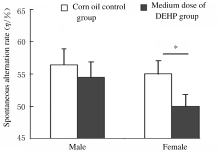
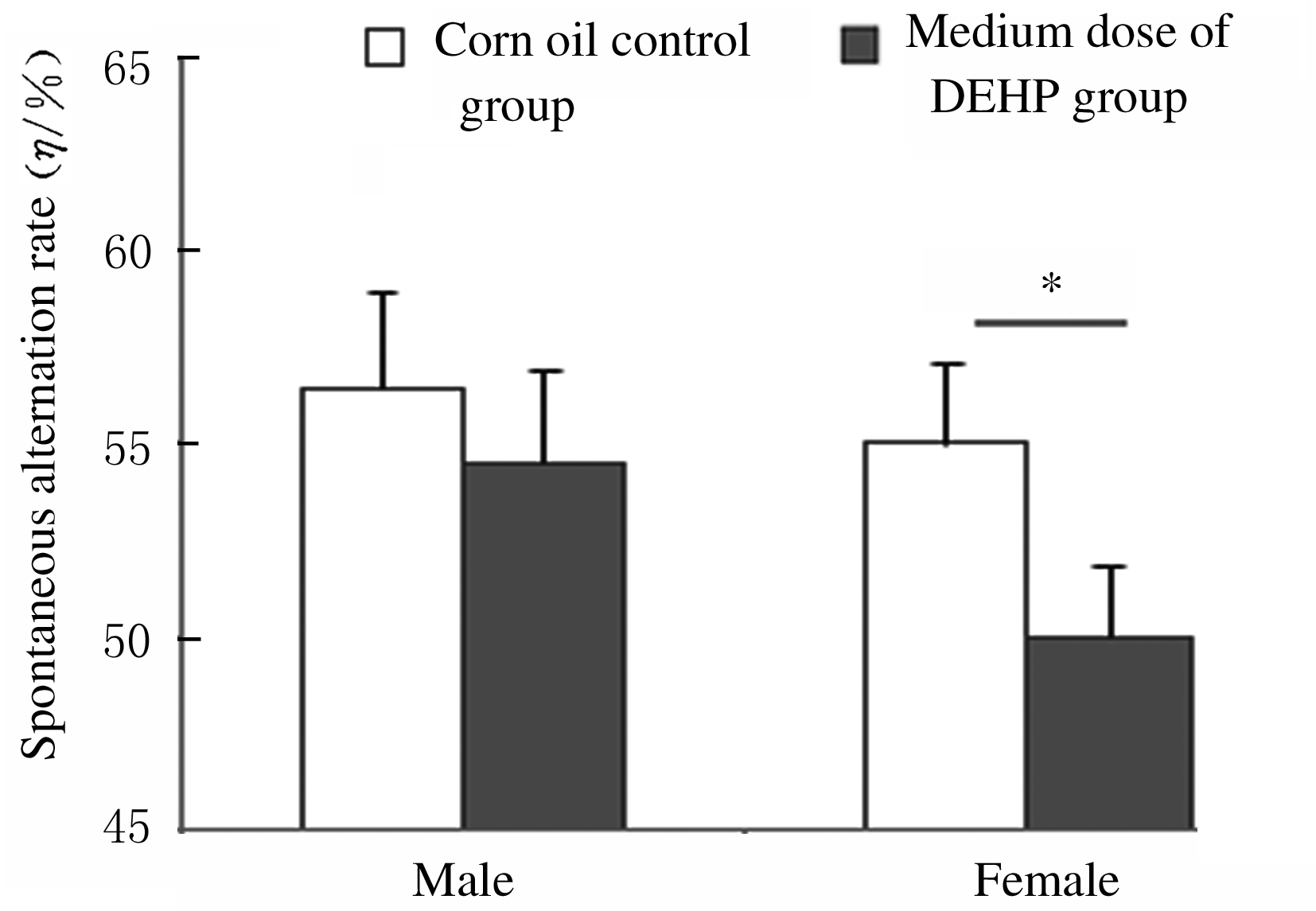
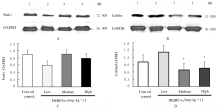
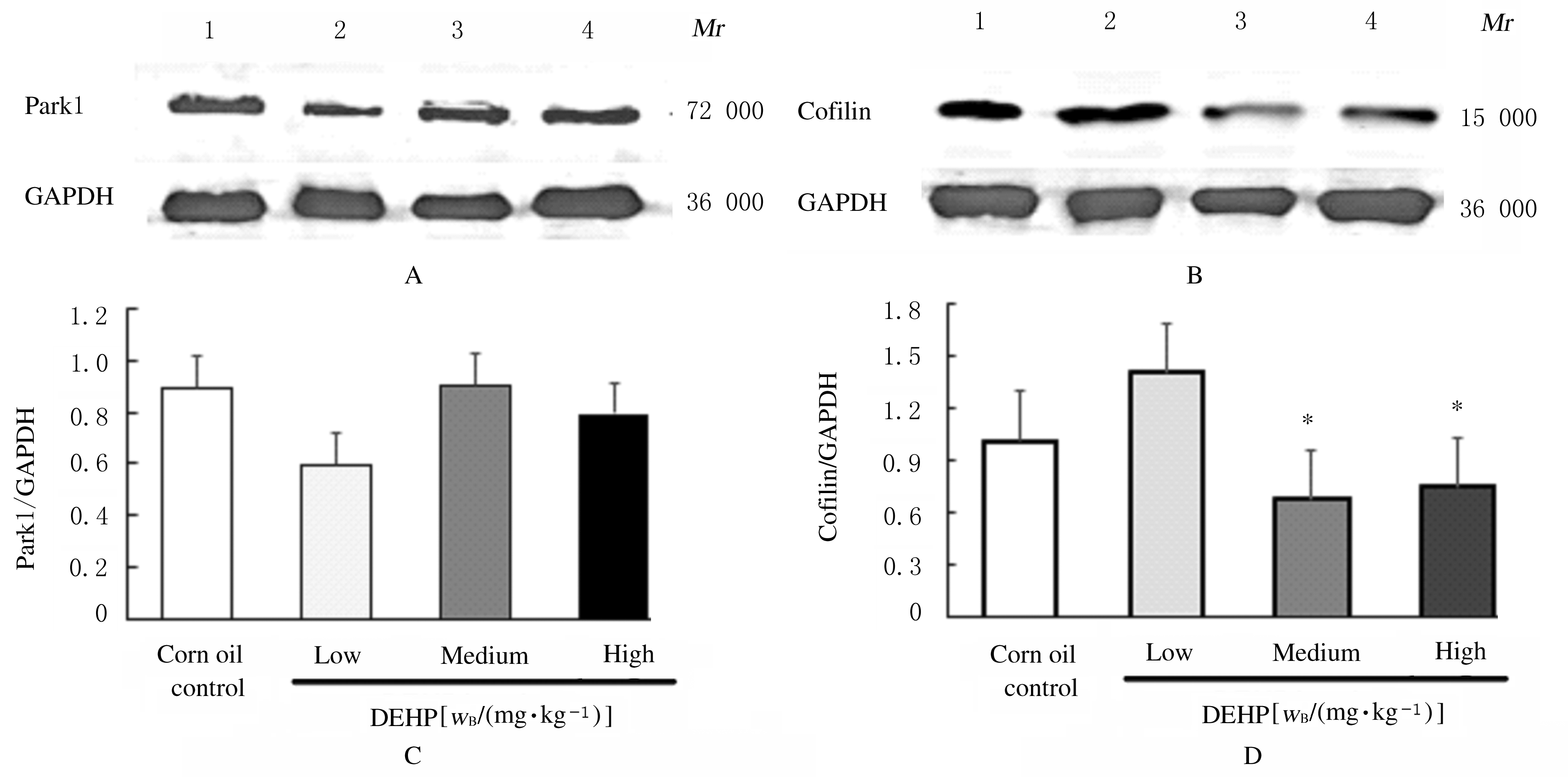
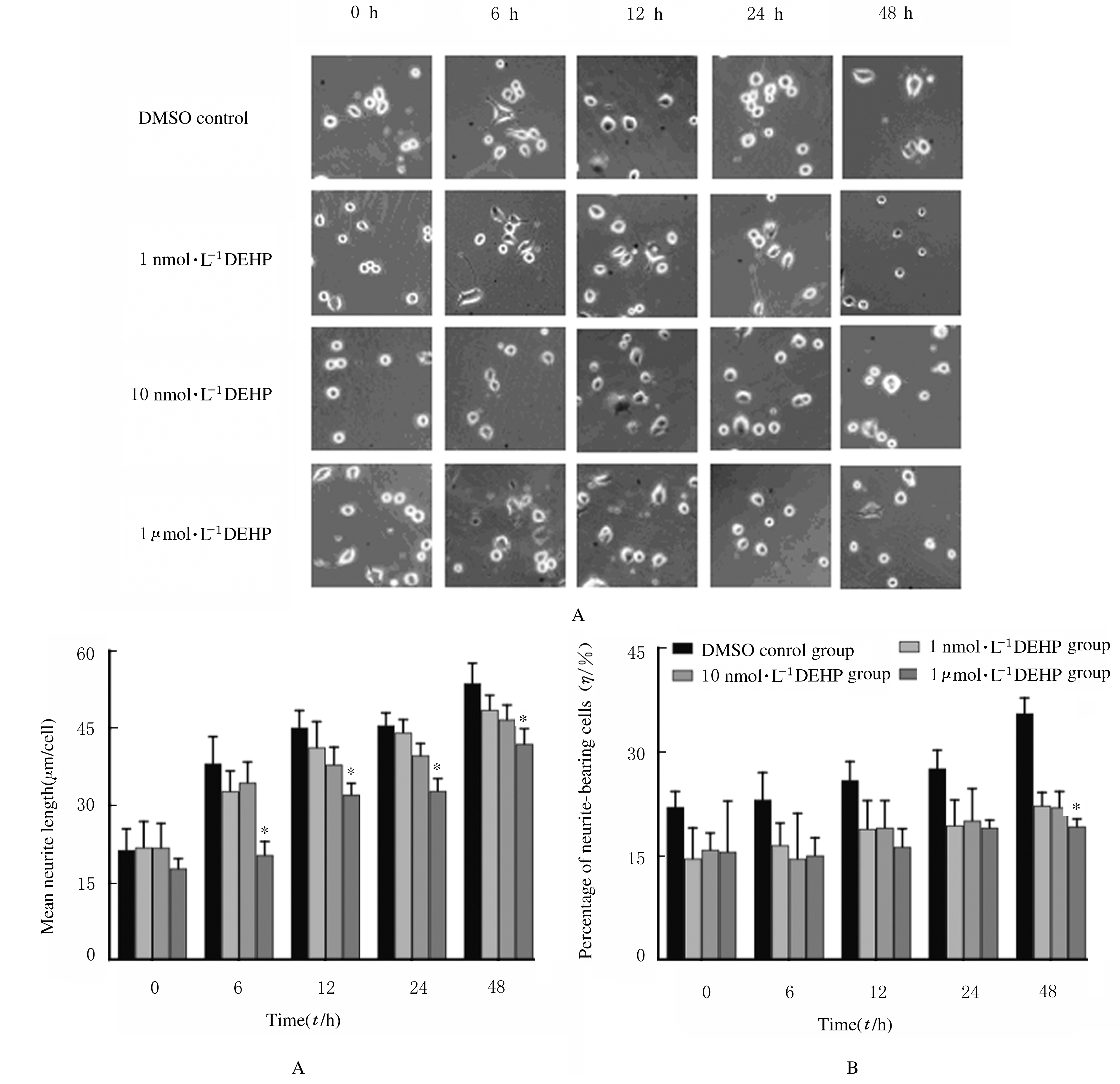
摘要: 探讨围生期邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(DEHP)暴露对小鼠神经行为的影响,阐明DEHP影响神经行为的可能机制。 选用受孕的ICR小鼠32只,随机分为3个不同剂量DEHP和玉米油对照组,于怀孕第3天起至孕17 d止,每天分别给予低剂量(10 mg?kg-1)、中剂量(50 mg?kg-1)、高剂量(250 mg?kg-1)DEHP和玉米油灌胃,在仔鼠出生后观察其神经发育学指标,并在7周龄后进行神经行为学检测;利用Western blotting法检测仔鼠大脑前额叶皮层组织中丝切蛋白(cofilin)和P21蛋白激活激酶1(Pak1)蛋白表达水平。将体外培养的Neuro-2A细胞分为不同剂量DEHP组和二甲基亚砜(DMSO)对照组,分别用1 nmol?L-1、10 nmol?L-1、1 μmol?L-1 DEHP和DMSO孵育,在0、6、12、24和48 h利用细胞划痕实验观察细胞迁移能力,在相差显微镜下拍照观察细胞突起生长的情况。 与玉米油对照组比较,不同剂量DEHP组新生仔鼠神经发育学指标差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与玉米油对照组比较,中剂量DEHP组雌性仔鼠自由探索新环境的能力降低(P<0.01);与玉米油对照组比较,中剂量DEHP组仔鼠前额叶皮层组织中cofilin蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),但Pak1蛋白表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。细胞划痕实验,与DMSO对照组比较,不同剂量DEHP组细胞孵育12 h后,细胞迁移速率均降低(P<0.05);1 μmol?L-1 DEHP组孵育6 h后细胞平均突起长度均缩短(P<0.05),孵育48 h后有突起细胞百分比降低(P<0.05)。 ICR小鼠在孕期暴露于50 mg?kg-1及以上剂量的DEHP可导致仔鼠神经行为异常,1 μmol?L-1 DEHP孵育Neuro-2A细胞12 h后明显抑制细胞迁移和突起生长能力,其机制可能与DEHP抑制细胞骨架调控蛋白cofilin的表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R114