吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 842-848.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210404
腹部推拿疗法对慢性应激所致慢性疲劳综合征模型大鼠海马神经重塑及其海马-HPA轴的负反馈机制
- 天津中医药大学第一附属医院推拿科,天津 300193
Effect of abdominal manipulation on remodeling of hippocampal neurons in chronic stress-induced chronic fatigue syndrome and its mechanism of negative feedback regulation of hippocampus-HPA axis
Mingzhu PAN,Jian LI,Bing RONG,Jun JIA,Huanan LI( )
)
- Department of Tuina,First Affiliated Hospital,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin 300193,China
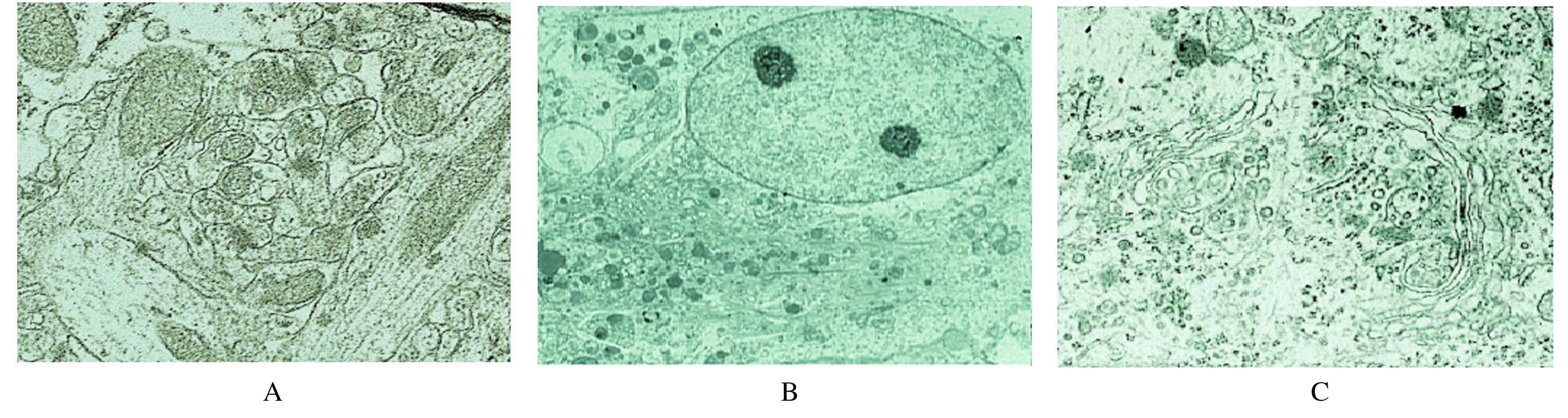
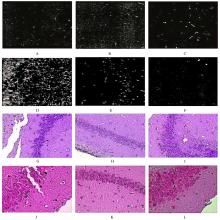
摘要: 观察腹部推拿对慢性应激所致慢性疲劳综合征(CFS)模型大鼠海马-下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺(海马-HPA)轴的影响,探讨其对海马神经的重塑作用机制。 选取成年健康Wistar雌性大鼠60只,分为正常组、模型组和实验组,每组20只,模型组和实验组大鼠采用复合应激方法复制CFS模型,实验组大鼠模型制作成功后进行腹部推拿干预,正常组大鼠不予以任何处理。采用行为学效应指标验证模型,电镜观察大鼠海马神经元超微形态表现,免疫组织化学法检测大鼠海马组织中FK506结合蛋白(FKBPs)、糖皮质激素受体(GR)和N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体(NMDAR)阳性表达率,酶联免疫吸附测定法(ELISA)检测大鼠血清中促肾上腺皮质激素(ACTH)、皮质醇(CORT)、促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素(CRH)和糖皮质激素(GC)水平。 大鼠行为学效应指标检测,与正常组比较,模型组和干预前实验组大鼠悬挂不动时间明显延长(P<0.05),力竭游泳时间明显缩短(P<0.05),水平运动速度明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,干预后实验组大鼠悬挂不动时间明显缩短(P<0.05),力竭游泳时间明显延长(P<0.05),水平运动速度明显增加(P<0.05)。电镜下观察,与正常组比较,模型组大鼠海马神经元胞体缩小,部分神经元胞膜内陷,有凋亡小体形成;与模型组比较,实验组大鼠海马神经元病变明显减轻。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织中FKBPs、GR和NMDAR阳性表达率明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,实验组大鼠海马组织中FKBPs、GR和NMDAR阳性表达率明显升高(P<0.05)。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠血清中ACTH、CORT、CRH和GC水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,实验组大鼠血清中ACTH、CORT、CRH和GC水平明显降低(P<0.05)。 腹部推拿疗法可以促进慢性应激反应所致的损伤性海马神经重塑,降低ACTH、CORT和CRH激素水平,通过FKBPs-GR-NMDAR通路维持海马-HPA轴负反馈平衡。
中图分类号:
- R244.1