吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 1008-1013.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210426
氧降和复氧速率对阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停患者昼夜血压的影响
- 1.吉林大学第一医院呼吸内科睡眠中心, 吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学基础医学院 生理学教研室, 吉林 长春 130021
Effects of deoxygenation and reoxygenation speeds on diurnal and nocturnal blood pressure in obstructive sleep apnea patients
Yue CHEN1,Lei YU2,Xiaoxin LAN1,Siqi JIA1,Haibo Yuan1( )
)
- 1.Department of Respiratory Medicine and Sleep Center,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Physiology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
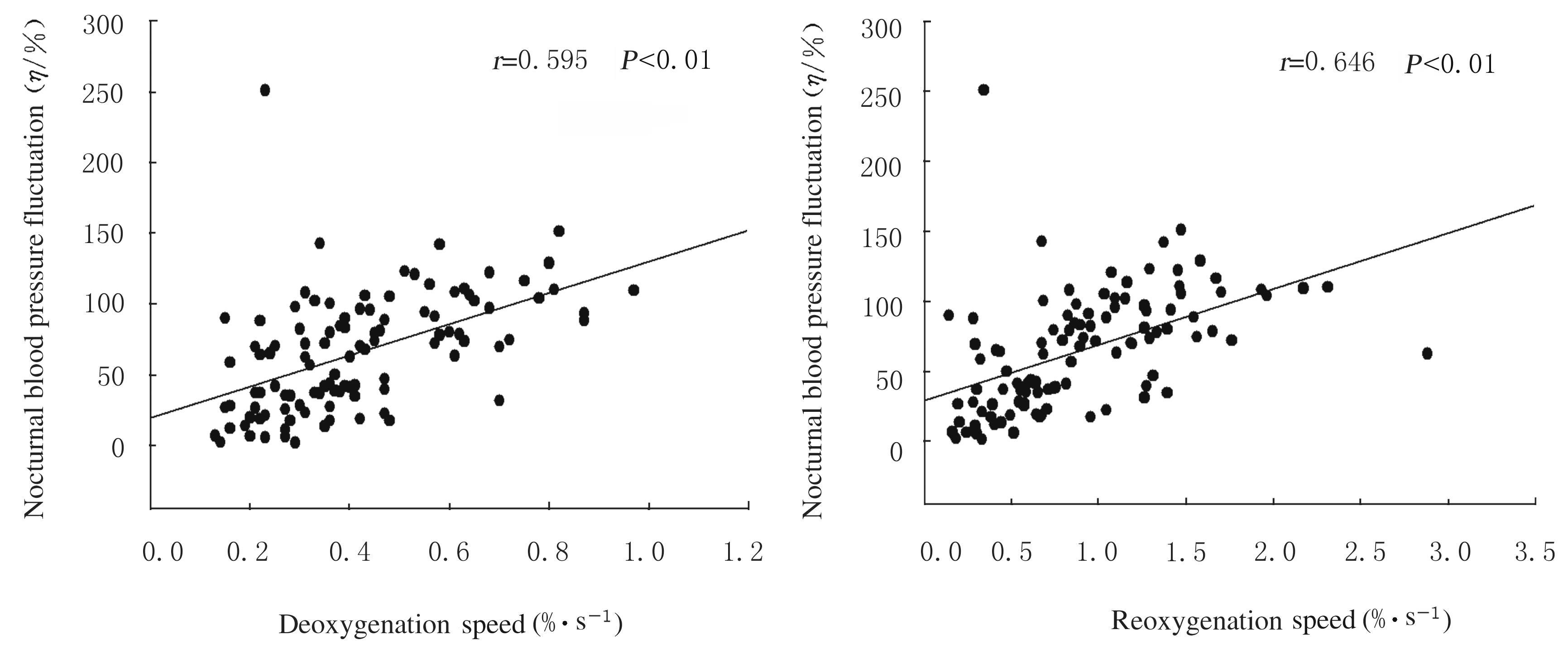
摘要: 探讨阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停(OSA)患者睡眠中氧降速率和复氧速率对患者昼夜间血压的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 收集106例OSA患者整夜多导睡眠呼吸监测资料,包括睡眠参数、呼吸事件参数和当天清醒期及睡眠期无创多点连续血压监测资料。根据OSA患者每个呼吸事件的氧降幅度与氧降时间的比值获得氧降速率,同样方法获得复氧速率。根据血压监测结果将患者分为OSA并发高血压组(OSA+HT组,59例)和OSA未并发高血压组(OSA-HT组,47例),分析2组患者氧降速率和复氧速率的差异,分别对所有入组患者进行氧降和复氧速率与白天血压值、夜间血压值以及夜间血压波动性(NBPF)的相关性分析。 OSA+HT组患者氧降速率和复氧速率明显高于OSA-HT组(P<0.01)。氧降速率与患者夜间收缩压、舒张压、平均动脉压及白天舒张压和平均动脉压均呈正相关关系(r=0.311,P=0.001;r =0.245,P=0.011;r=0.308,P=0.001;r=0.203,P=0.037;r =0.219,P=0.024),复氧速率与患者夜间收缩压、舒张压、平均动脉压及白天舒张压和平均动脉压均呈正相关关系(r=0.327,P=0.001;r=0.288,P=0.003;r=0.343,P=0.000;r=0.250,P=0.01;r=0.259,P=0.007);氧降速率和复氧速率均与OSA患者NBPF呈正相关关系(r=0.595,P<0.01;r=0.646,P<0.01)。 OSA患者间歇性氧降和复氧的损害与其昼夜血压升高有直接关联,氧降与复氧速率的变化是导致OSA患者NBPF的重要因素。
中图分类号:
- R332