吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1178-1186.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210514
Rho/ROCK信号通路在阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征大鼠急性缺血性卒中发生中的作用
嵇朋1,郭向东2,孙根1,寇启星1,屈雪萍1,孙雅静1,江利敏3( )
)
- 1.河南省郑州市第三人民医院 河南大学肿瘤医院神经内科,河南 郑州 450000
2.河南中医药大学第一附属医院耳鼻喉科,河南 郑州 450000
3.河南中医药大学第一附属医院体检中心,河南 郑州 450000
Role of Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in occurrence of acute ischemic stroke in rats with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome
Peng JI1,Xiangdong GUO2,Gen SUN1,Qixing KOU1,Xueping QU1,Yajing SUN1,Limin JIANG3( )
)
- 1.Department of Neurology,Third People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou City,Henan Provine,Cancer Hospital,Henan University,Zhengzhou 450000,Henan,China
2.Department of Otolaryngology,First Affiliated Hospital,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450000,China
3.Physical Examination Center,First Affiliated Hospital,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 450000,Zhengzhou 450000,China
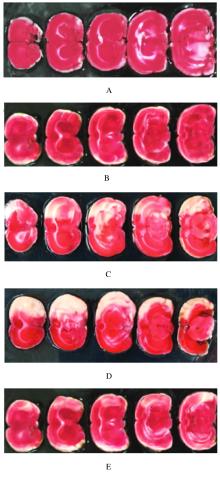
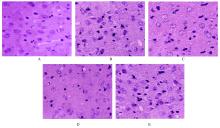
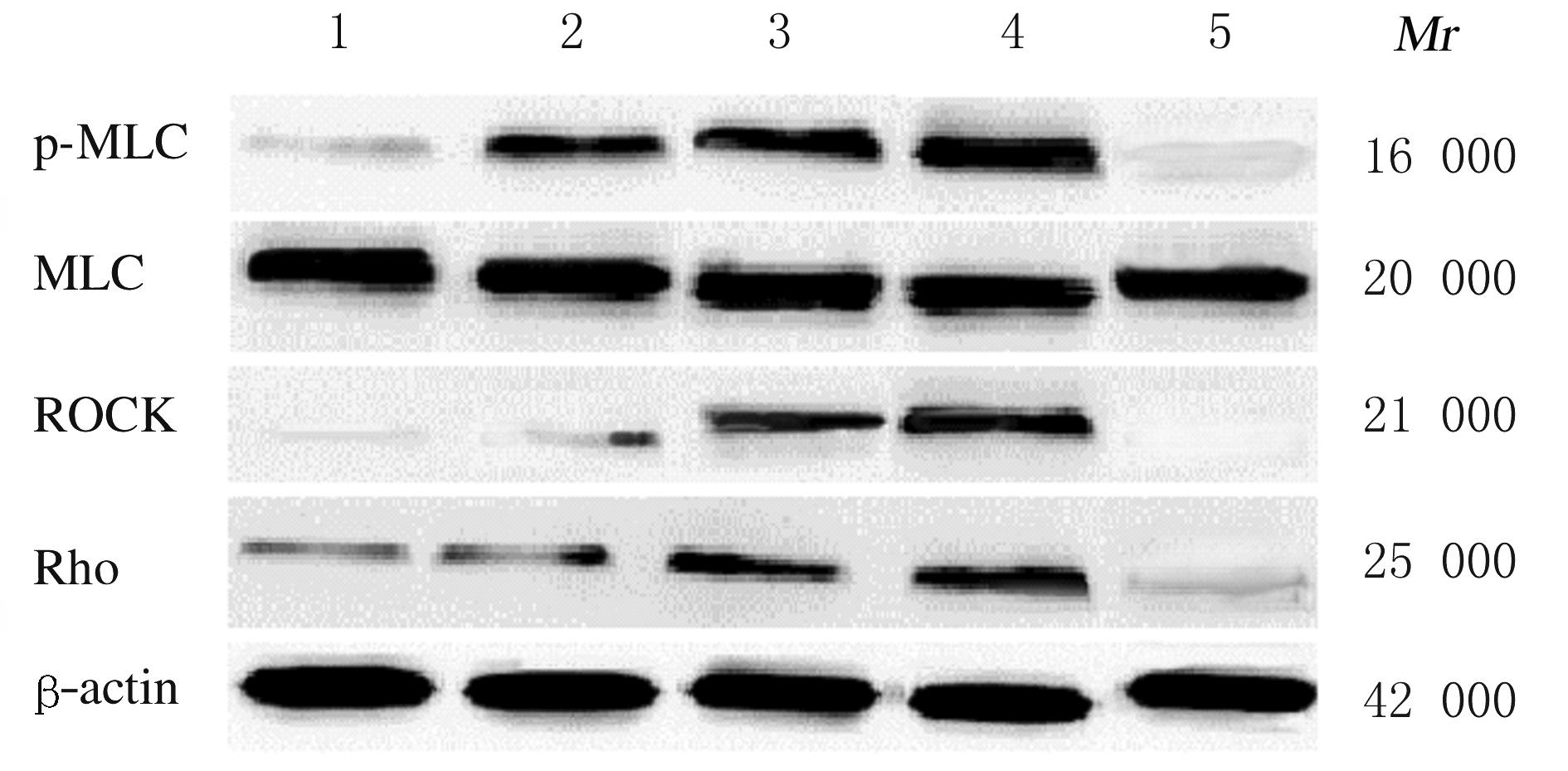
摘要: 研究小GTP结合蛋白(Rho)/Rho相关卷曲螺旋形成蛋白激酶(ROCK)信号通路在阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征(OSAHS)大鼠急性缺血性卒中发生中的作用,为OSAHS后急性缺血性卒中病变的防治提供参考。 50只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、OSAHS组、卒中组、OSAHS后卒中组和Rho抑制剂组(C3转移酶5 μg·kg-1·d-1腹腔注射),每组10只。采用慢性间歇性低氧建立OSAHS模型,线栓法阻断大脑中动脉建立急性脑卒中模型。观察各组大鼠建模后的一般情况和脑皮质区组织病理形态表现,计算脑梗死体积。比较各组大鼠呼吸频率和神经功能损伤评分,采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法和Western blotting法检测各组大鼠脑组织中肌球蛋白轻链(MLC)、Rho和ROCK mRNA及蛋白表达水平。 与假手术组比较,其他各组大鼠均有精神状态不佳和脑皮层结构损伤等改变,其中OSAHS后卒中组大鼠变化最严重,Rho抑制剂组变化较轻。与假手术组比较,OSAHS组大鼠呼吸频率增加(P<0.05);与OSAHS组比较,卒中组大鼠呼吸频率降低(P<0.05);与卒中组比较,OSAHS后卒中组大鼠呼吸频率和Longa评分增加(P<0.05),Rho抑制剂组大鼠Longa评分降低(P<0.05);与OSAHS后卒中组比较,Rho抑制剂组大鼠呼吸频率与和Longa评分均降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,OSAHS组大鼠逃避潜伏期延长(P<0.05),穿越平台次数减少(P<0.05);与OSAHS组比较,卒中组大鼠逃避潜伏期延长(P<0.05),穿越平台次数减少(P<0.05);与卒中组比较,OSAHS后卒中组大鼠逃避潜伏期延长(P<0.05),穿越平台次数减少(P<0.05);与OSAHS后卒中组比较,Rho抑制剂组大鼠逃避潜伏期缩短(P<0.05),穿越平台次数增加(P<0.05)。与卒中组比较,OSAHS后卒中组大鼠脑梗死体积增大(P<0.05);与OSAHS后卒中组比较,Rho抑制剂组大鼠脑梗死体积缩小(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,OSAHS组大鼠脑组织中Rho和ROCK mRNA和蛋白表达水平及p-MLC/MLC比值升高(P<0.05);与OSAHS组比较,卒中组大鼠脑组织中Rho和ROCK mRNA及蛋白表达水平及其p-MLC/MLC比值升高(P<0.05);与卒中组比较,OSAHS后卒中组大鼠脑组织中Rho和ROCK mRNA及蛋白相表达水平及其p-MLC/MLC比值升高(P<0.05);与OSAHS后卒中组比较,Rho抑制剂组大鼠脑组织中Rho和ROCK mRNA及蛋白表达水平及其p-MLC/MLC比值降低(P<0.05)。 OSAHS的间歇性缺氧状态可损伤神经功能,Rho/ROCK信号通路可能在OSAHS大鼠急性缺血性卒中发生中起一定作用。
中图分类号:
- R543.5