吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 222-227.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220128
鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎2例报告及文献复习
- 吉林大学中日联谊医院呼吸内科,吉林 长春 130033
Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia:A report of 2 cases and literature review
Luowei HE,Ye WANG,Dujuan YU,Zhiying CHEN( )
)
- Department of Respiratory Medicine,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
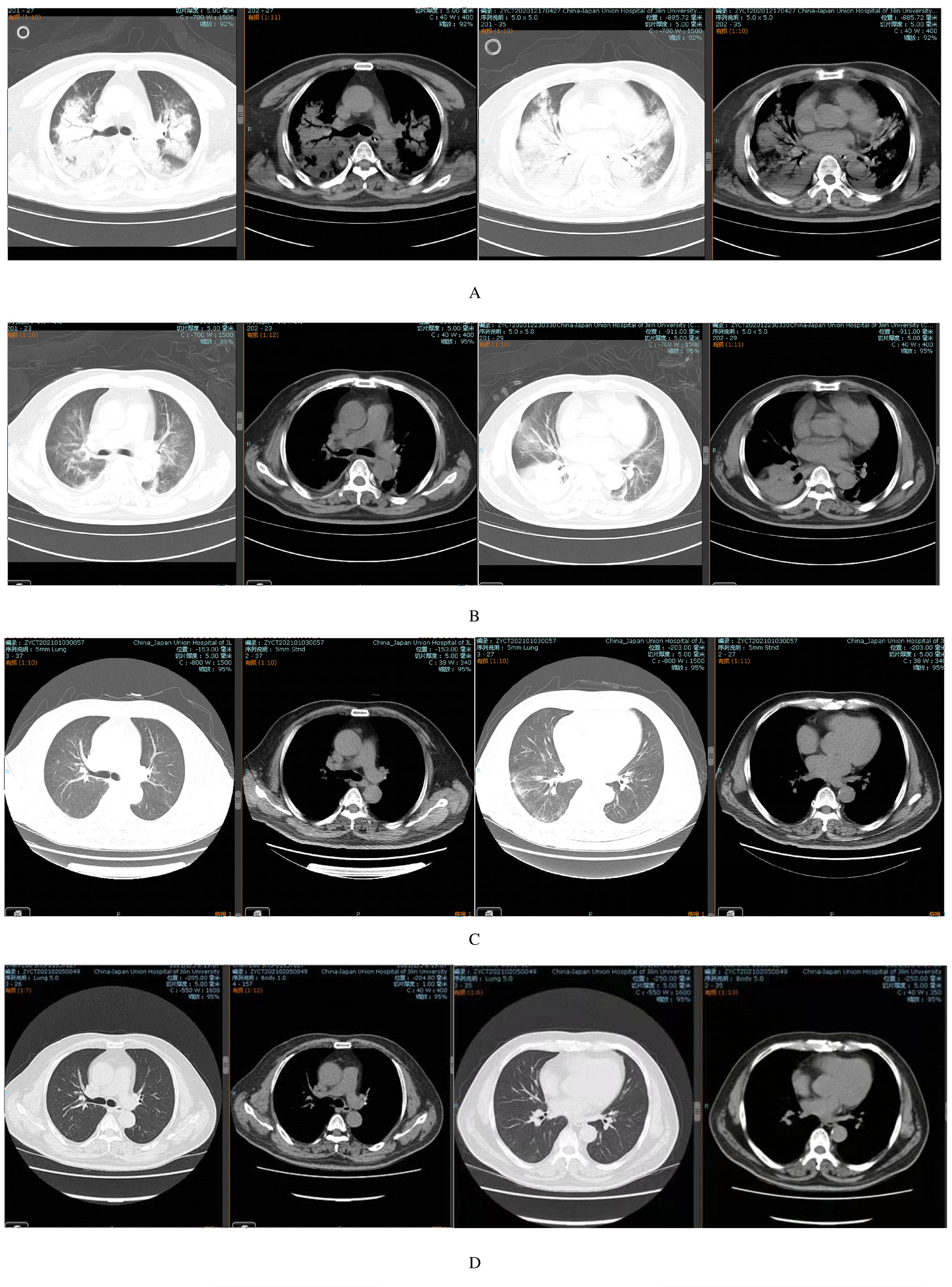
摘要: 分析鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎患者的临床表现、诊断方法和治疗过程,提高临床医生对该病的认识,以进一步提高其临床诊治效率并改善其预后。 收集2例鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎患者的临床资料,对诊治经过进行总结,分析患者的感染指标、氧合功能和肺部影像学的动态变化,对比培养法、血清学方法和宏基因组二代测序技术(mNGS)等病原学诊断方法,分析喹诺酮类和四环素类药物治疗鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎的效果。 2例患者均以发热、咳嗽和咳痰为首发症状,病情进展较快,分别于发病的第8天和第3天出现呼吸困难,1例患者于发病第10天进展为急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS),需机械通气辅助治疗。2例患者血常规中白细胞计数分别为12.69×109 L-1和4.4×109 L-1,降钙素原分别为0.27和0.06 μg·L-1,气道分泌物常规培养及血清学检查未能明确病原体。2例患者初步诊断均为社区获得性肺炎,经验性应用喹诺酮类药物治疗效果均不佳。采用mNGS方法并结合鸟类接触史,最终确诊为鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎,采用四环素类抗生素治疗后,患者症状、体征和影像学异常均明显好转,随访复查肺部CT,病灶基本吸收。 鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎的发生与鸟类接触史有关,病情进展比较迅速。mNGS技术可作为快速病原学诊断方法,有利于鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎的早期诊断和及时选用敏感药物治疗,从而改善该病预后。以多西环素和替加环素为代表的新一代四环素类药物对鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎的疗效肯定。
中图分类号:
- R563.1