吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 561-567.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220302
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
丹酚酸B对小鼠动脉粥样硬化病变和巨噬细胞胞葬作用的影响及其机制
- 上海中医药大学附属龙华医院心病科,上海 200032
Effects of salvianolic acid B on atherosclerosis and efferocytosis of macrophages of mice and their mechanisms
Yifan ZHANG,Jie DING,Min DU,Xiaoteng FENG,Ping LIU( )
)
- Department of Cardiology,Longhua Hospital,Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shanghai 200032,China
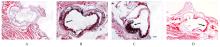
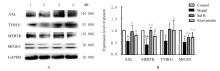
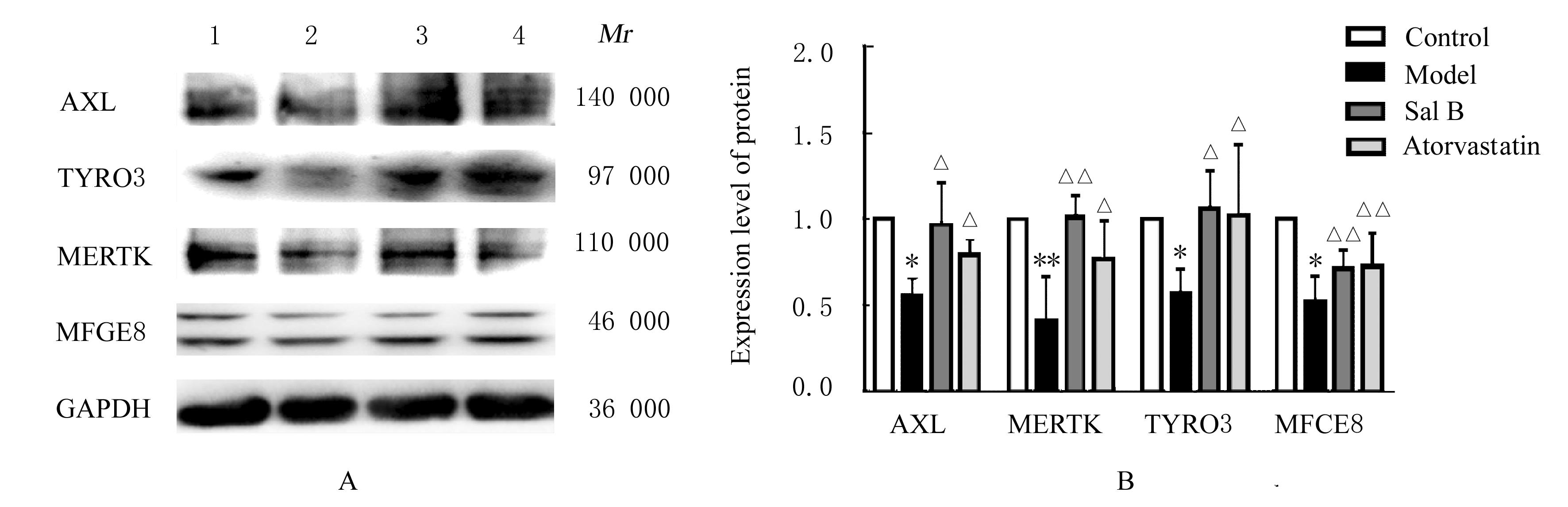
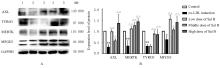
摘要: 探讨丹酚酸B(Sal B)对小鼠动脉粥样硬化病变和氧化型低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)诱导的小鼠巨噬细胞胞葬作用的影响,阐明Sal B抗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制。 将32只雄性低密度脂蛋白受体基因敲除(LDLR-/-)小鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、Sal B组和阿托伐他汀组,每组8只。对照组小鼠给予普通饲料喂养,其他各组小鼠给予高脂饲料喂养12周。对照组和模型组小鼠每日给予生理盐水腹腔注射,Sal B组小鼠给予Sal B溶液腹腔注射,阿托伐他汀组小鼠给予阿托伐他汀溶液灌胃。检测各组小鼠血清总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-c)水平,油红O染色法观察小鼠主动脉粥样硬化斑块面积百分率。RAW264.7细胞分为对照组、ox-LDL组(采用40 mg·L-1 ox-LDL诱导24 h),低、中和高剂量Sal B组(给予含1.25、2.50和5.00 mg·L-1 Sal B的培养基)。实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)和Western blotting法检测各组小鼠主动脉组织及RAW264.7细胞中AXL、MERTK、TYRO3和乳脂球表皮生长因子8 (MFGE8) mRNA及蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,模型组小鼠血清TC、TG和LDL-c水平升高(P<0.05),小鼠主动脉粥样硬化斑块面积百分率升高(P<0.05),小鼠主动脉组织中AXL、MERTK、TYRO3和MFGE8 mRNA及蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与模型组比较,Sal B和阿托伐他汀组小鼠血清TC、TG和LDL-c水平降低(P<0.01),小鼠主动脉粥样硬化斑块面积百分率降低(P<0.01),小鼠主动脉组织中AXL、MERTK、TYRO3和MFGE8 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与对照组比较,ox-LDL诱导组RAW264.7细胞中AXL、MERTK、TYRO3和MFGE8 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与ox-LDL诱导组比较,Sal B组RAW264.7细胞中AXL、MERTK、TYRO3、MFGE8 mRNA及蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 Sal B通过上调胞葬相关分子表达,促进LDLR-/-小鼠及RAW264.7细胞的胞葬作用,从而发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。
中图分类号:
- R543.5