吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4): 858-865.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220403
柠檬苦素对营养性肥胖大鼠脂质代谢和肠道菌群的影响
- 贵州省遵义市第一人民医院 遵义医科大学第三附属医院儿童重症医学科,贵州 遵义 563000
Effects of limonin on lipid metabolism and intestinal flora in nutritionally obese rats
Shuang HUANG,Chen CHEN,Bo HUANG( )
)
- Department of Pediatric Intensive Medicine,Zunyi First People’s Hospital,Guizhou Province,Third Affiliated Hospital,Zunyi Medical University,Zunyi 563000,China
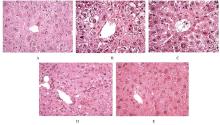
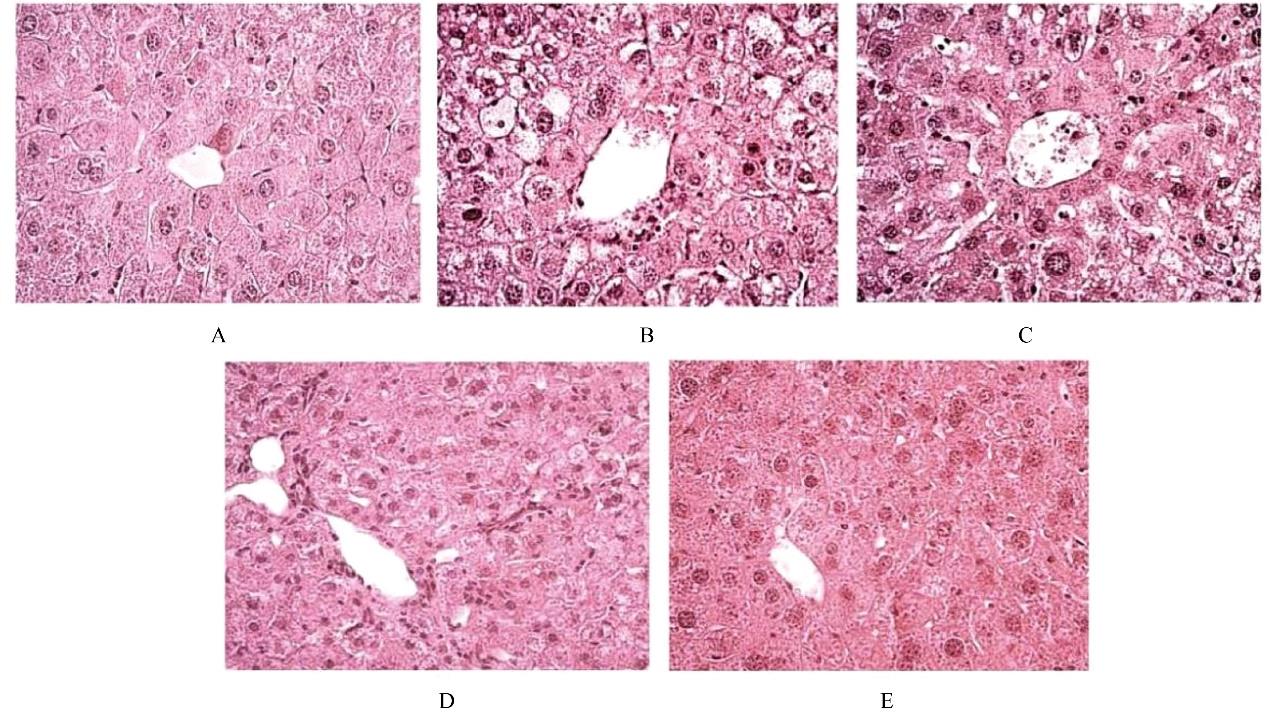
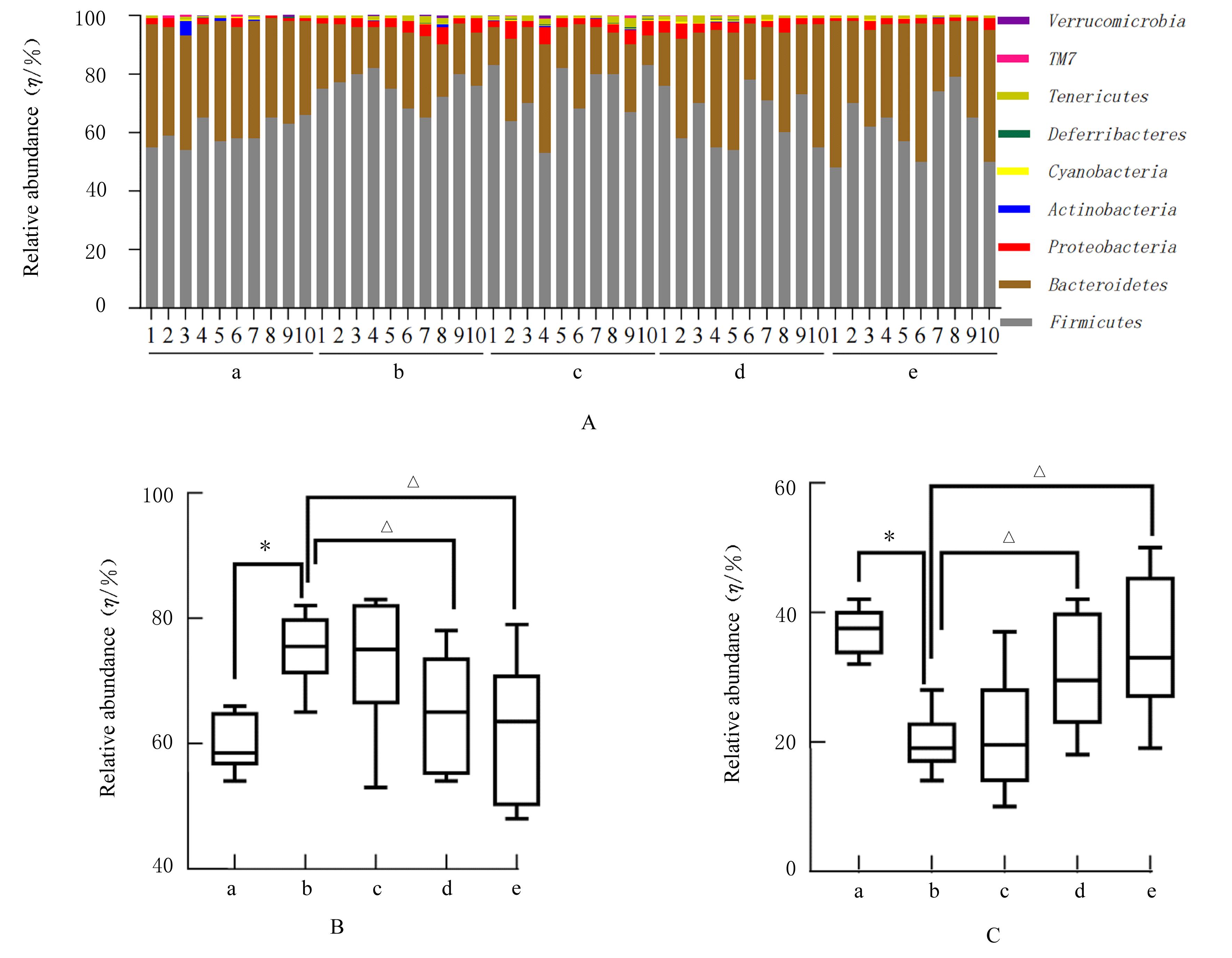
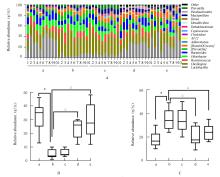
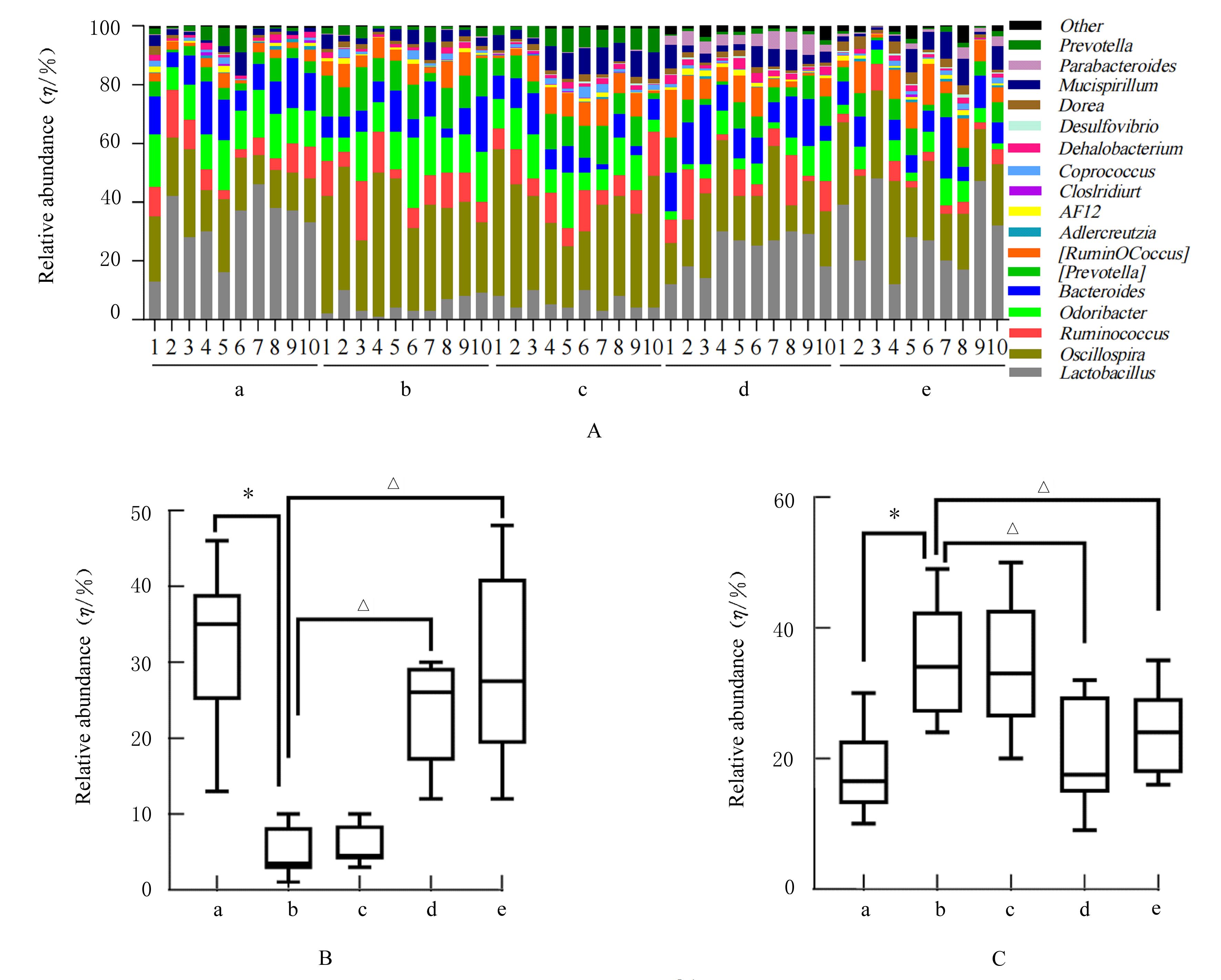
摘要: 探讨柠檬苦素对高脂饮食诱导的营养性肥胖大鼠脂质代谢和肠道菌群的影响,阐明其可能的作用机制。 3周龄SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、低剂量(12.5 mg·kg-1)柠檬苦素组、中剂量(25 mg·kg-1)柠檬苦素组和高剂量(50 mg·kg-1)柠檬苦素组,每组10只。除对照组外,其他各组大鼠均采用高脂饲料喂养制备营养性肥胖大鼠模型,造模成功后低、中和高剂量柠檬苦素组大鼠给予相应剂量柠檬苦素干预,每日1次,连续4周。记录给药前后各组大鼠体质量,计算李氏指数(Lee’s指数)和脂肪系数,检测各组大鼠血清总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)水平,HE染色观察各组大鼠肝组织病理形态表现和脂肪沉积情况,16S rRNA测序法分析各组大鼠粪便肠道菌群结构。 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠体质量、Lee’s指数和脂肪系数均明显升高(P<0.05),血清中TC、TG和LDL-C水平均明显升高(P<0.05),HDL-C水平明显降低(P<0.05),肝组织中可见脂肪变性和脂肪堆积,粪便中厚壁菌门和颤螺旋菌属相对丰度均明显升高(P<0.05),拟杆菌门和乳杆菌属相对丰度均明显降低(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,中、高剂量柠檬苦素组大鼠体质量、Lee’s指数和脂肪系数均明显降低(P<0.05),血清中TC、TG和LDL-C水平均明显降低(P<0.05),HDL-C水平明显升高(P<0.05),肝组织中脂肪变性和脂肪堆积明显改善,粪便中厚壁菌门和颤螺旋菌属相对丰度均明显降低(P<0.05),拟杆菌门和乳杆菌属相对丰度均明显升高(P<0.05),低剂量柠檬苦素组大鼠以上各项指标差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 柠檬苦素能够通过调节大鼠脂质代谢和肠道菌群结构,达到改善营养性肥胖大鼠肥胖的作用。
中图分类号:
- R285.5