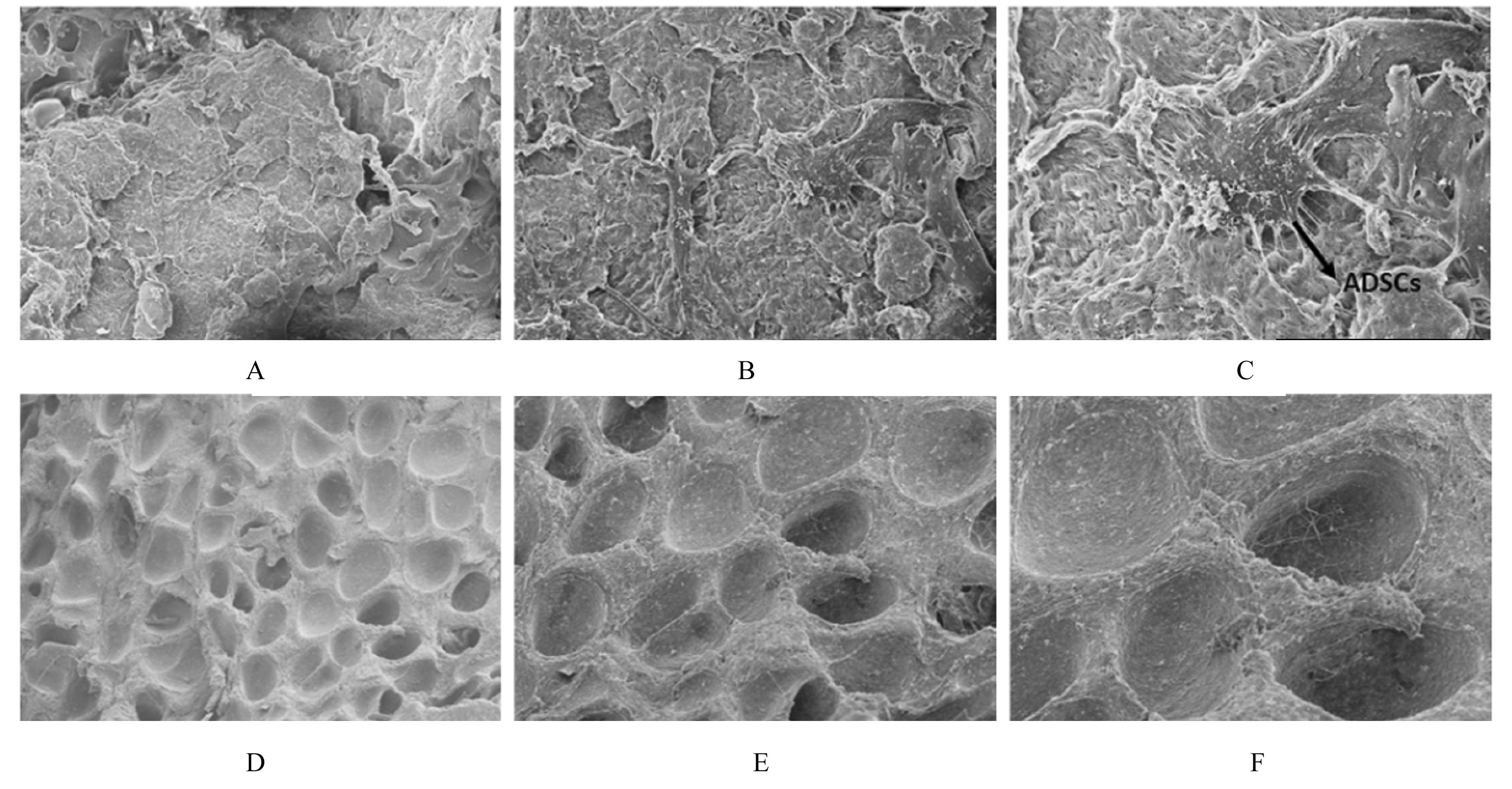
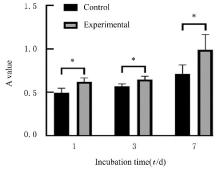
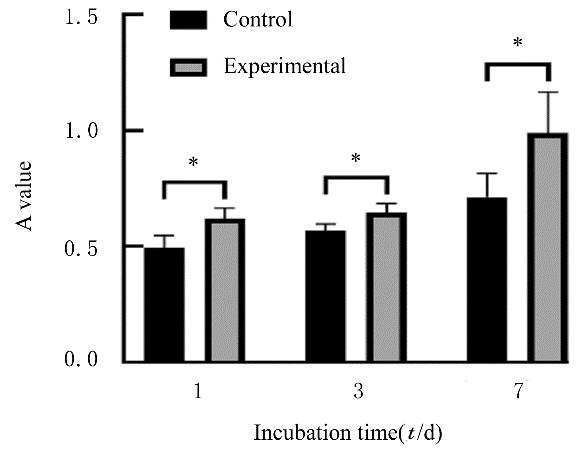
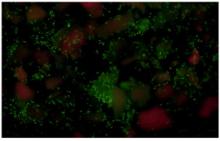
| 1 |
PARK C, KIM K H, LEE Y M, et al. Advanced engineering strategies for periodontal complex regeneration[J]. Materials, 2016, 9(1): 57.
|
| 2 |
FARRELL E, BOTH S K, ODÖRFER K I, et al. In-vivo generation of bone via endochondral ossification by in-vitro chondrogenic priming of adult human and rat mesenchymal stem cells[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2011, 12: 31.
|
| 3 |
PAPADIMITROPOULOS A, SCOTTI C, BOURGINE P,et al. Engineered decellularized matrices to instruct bone regeneration processes[J]. Bone, 2015, 70: 66-72.
|
| 4 |
MAES C. Role and regulation of vascularization processes in endochondral bones[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2013, 92(4): 307-323.
|
| 5 |
STAMNITZ S, KLIMCZAK A. Mesenchymal stem cells, bioactive factors, and scaffolds in bone repair: from research perspectives to clinical practice[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(8): 1925.
|
| 6 |
GAWLITTA D, BENDERS K E, VISSER J, et al. Decellularized cartilage-derived matrix as substrate for endochondral bone regeneration[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2015, 21(3/4): 694-703.
|
| 7 |
KANG H J, LU S B, PENG J, et al. In vivo construction of tissue-engineered cartilage using adipose-derived stem cells and bioreactor technology[J]. Cell Tissue Bank, 2015, 16(1): 123-133.
|
| 8 |
HUANG Y X, YU X F, HE L J, et al. 3D porous acellular cartilage matrix scaffold with surface mediated sustainable release of TGF-β3 for cartilage engineering[J].Chin Chem Lett,2020,31(7):1797-1800.
|
| 9 |
BAHNEY C S, HU D P, TAYLOR A J, et al. Stem cell-derived endochondral cartilage stimulates bone healing by tissue transformation[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2014, 29(5): 1269-1282.
|
| 10 |
SUGAWARA A, SATO S. Application of dedifferentiated fat cells for periodontal tissue regeneration[J]. Hum Cell, 2014, 27(1): 12-21.
|
| 11 |
YANG Q, PENG J, GUO Q Y, et al. A cartilage ECM-derived 3-D porous acellular matrix scaffold for in vivo cartilage tissue engineering with PKH26-labeled chondrogenic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(15): 2378-2387.
|
| 12 |
FENG X K, LI Z Y, WEI J H, et al. Injectable cartilaginous template transformed BMSCs into vascularized bone[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 8244.
|
| 13 |
BENDERS K E M, RVAN WEEREN P, BADYLAK S F,et al. Extracellular matrix scaffolds for cartilage and bone regeneration[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 2013, 31(3): 169-176.
|
| 14 |
BENDERS K E, BOOT W, COKELAERE S M,et al. Multipotent stromal cells outperform chondrocytes on cartilage-derived matrix scaffolds[J].Cartilage, 2014,5(4): 221-230.
|
| 15 |
HORIKOSHI S, KAJIYA M, MOTOIKE S, et al. Clumps of mesenchymal stem cells/extracellular matrix complexes generated with xeno-free chondro-inductive medium induce bone regeneration via endochondral ossification[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(10): 1408.
|
| 16 |
FARRELL E, O PVAN DER JAGT, KOEVOET W, et al. Chondrogenic priming of human bone marrow stromal cells: a better route to bone repair? [J]. Tissue Eng Part C Methods, 2009, 15(2): 285-295.
|
| 17 |
杨艳兰 徐 普.干细胞修复牙槽骨缺损:微环境认知新进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2021,46(4): 404-409.
|
| 18 |
ZHAI C J, ZHANG X, CHEN J, et al. The effect of cartilage extracellular matrix particle size on the chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Regen Med, 2019, 14(7): 663-680.
|
| 19 |
HERRMANN M, VERRIER S, ALINI M. Strategies to stimulate mobilization and homing of endogenous stem and progenitor cells for bone tissue repair[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2015, 3: 79.
|
| 20 |
JEYAKUMAR V, AMRAISH N, NICULESCU-MORSZA E, et al. Decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix incorporated silk fibroin hybrid scaffolds for endochondral ossification mediated bone regeneration[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(8): 4055.
|
| 21 |
AANEI C M, FLANDRIN P, ELOAE F Z, et al. Intrinsic growth deficiencies of mesenchymal stromal cells in myelodysplastic syndromes[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2012, 21(10): 1604-1615.
|
| 22 |
DONG J, ZHU G, WANG T C, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes neural differentiation of mouse adipose-derived stem cells via the miRNA-124 signaling pathway[J].J Zhejiang Univ Sci B,2017,18(5):445-448.
|
| 23 |
WANG Z J, AN R Z, ZHAO J Y, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defects by tissue-engineered cartilage constructed with adipose-derived stem cells and acellular cartilaginous matrix in rabbits[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2014, 13(2): 4599-4606.
|
| 24 |
BORDBAR S, LOTFI BAKHSHAIESH N, KHANMOHAMMADI M, et al. Production and evaluation of decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogel for cartilage regeneration derived from knee cartilage[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2020, 108(4): 938-946.
|
 )
)