吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4): 905-914.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220409
丹参酮ⅡA对缺氧缺血性脑病新生大鼠海马组织中miR-132表达的调节作用及其机制
- 吉林大学第一医院二部儿科,吉林 长春 130031
Effects of tanshinone ⅡA on miR-132 expression in hippocampus tissue of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and its mechanism
Yang ZHANG( ),Meiyue CHEN,Ying CUI,Na LIU
),Meiyue CHEN,Ying CUI,Na LIU
- Department of Pediatrics,Second Department of First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130031,China
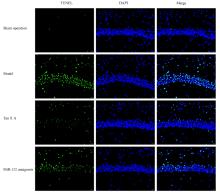
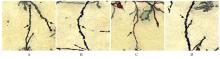
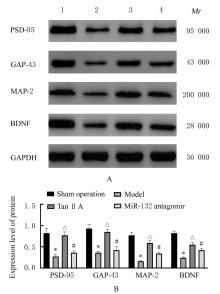
摘要: 探讨丹参酮 ⅡA(Tan ⅡA)对新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑病的干预作用,并阐明其作用机制。 40只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、Tan ⅡA组和miR-132抑制剂(miR-132 antagomir)组,每组10只。大鼠双重结扎颈总动脉并放入缺氧舱建立缺血缺氧性脑病模型。Tan ⅡA组大鼠造模后腹腔注射Tan ⅡA注射液(24 mg·kg-1),双侧脑室注射2 μg miR-132阴性对照质粒(NC);假手术组和模型组大鼠腹腔注射等量生理盐水;miR-132 antagomir组大鼠造模后腹腔注射Tan ⅡA注射液(24 mg·kg-1),双侧脑室注射2 μg miR-132 antagomir;各组大鼠连续注射7 d。实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法和荧光原位杂交检测各组大鼠海马组织中miR-132表达水平和表达强度,采用改良神经功能缺失评分评价各组大鼠神经功能,HE染色观察各组大鼠海马组织病理形态表现, TUNEL法检测各组大鼠海马组织中神经元细胞凋亡率,酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠海马组织中单胺类神经递质水平,高尔基染色检测各组大鼠海马组织中树突棘密度,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠海马组织中突触后致密物95(PSD-95)、生长相关蛋白43(GAP-43)、微管相关蛋白2(MAP-2)和脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)蛋白表达水平。 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织中miR-132表达水平和表达强度明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠海马组织中miR-132表达水平和表达强度明显升高(P<0.05);与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠海马组织中miR-132表达水平和表达强度明显降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠神经功能缺失评分明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠神经功能缺失评分明显降低(P<0.05);与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠神经功能缺失评分明显升高(P<0.05)。HE染色,假手术组大鼠海马组织无损伤;与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织损伤严重;与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠海马组织损伤明显改善;与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠海马组织损伤严重。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织神经元凋亡率明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠海马组织神经元凋亡率明显降低(P<0.05);与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠海马组织神经元凋亡率明显升高(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织中去甲肾上腺素、多巴胺和5-羟色胺水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠海马组织中去甲肾上腺素、多巴胺和5-羟色胺水平明显升高(P<0.05);与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠海马组织中去甲肾上腺素、多巴胺和5-羟色胺水平明显降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织中树突棘密度明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠海马组织中树突棘密度明显升高(P<0.05);与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠海马组织中树突棘密度明显降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织中PSD-95、GAP-43、MAP-2和BDNF蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,Tan ⅡA组大鼠海马组织中PSD-95、GAP-43、MAP-2和BDNF蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);与Tan ⅡA组比较,miR-132 antagomir组大鼠海马组织中PSD-95、GAP-43、MAP-2和BDNF蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。 Tan ⅡA可上调缺氧缺血性脑病新生大鼠海马组织中miR-132表达,改善新生大鼠神经功能和海马组织病理损伤,其机制可能与抑制海马神经元凋亡以及增加海马神经递质水平、树突棘密度、突触前蛋白、MAP-2和BDNF蛋白表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R-332