吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (4): 938-945.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220413
悬钩子根多糖对2型糖尿病小鼠胰腺线粒体功能的改善作用
代敏敏1,常影2,许娜2,王燕3,徐梦4,徐文悦4,马佳旺4,刘文森3( ),陈正爱1(
),陈正爱1( )
)
- 1.延边大学基础医学院药理学教研室,吉林 延吉 133002
2.吉林医药学院药学院药理学教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
3.军事医学科学院军事兽医研究所,吉林 长春 130118
4.吉林农业大学 生命科学学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,吉林 长春 130118
Improvement effect of Rubus root polysaccharide on pancreatic mitochondrial function in type 2 diabetic mice
Minmin DAI1,Ying CHANG2,Na XU2,Yan WANG3,Meng XU4,Wenyue XU4,Jiawang MA4,Wensen LIU3( ),Zhengai CHEN1(
),Zhengai CHEN1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pharmacology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
2.Department of Pharmacology,School of Pharmacy,Jilin Medical University,Jilin 132013,China
3.Institute of Military Veterinary Medicine,Academy of Military Medical Sciences,Changchun 130118,China
4.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,School of Life Sciences,Jilin Agricultural University,Changchun 130118,China
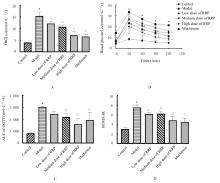
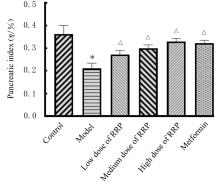
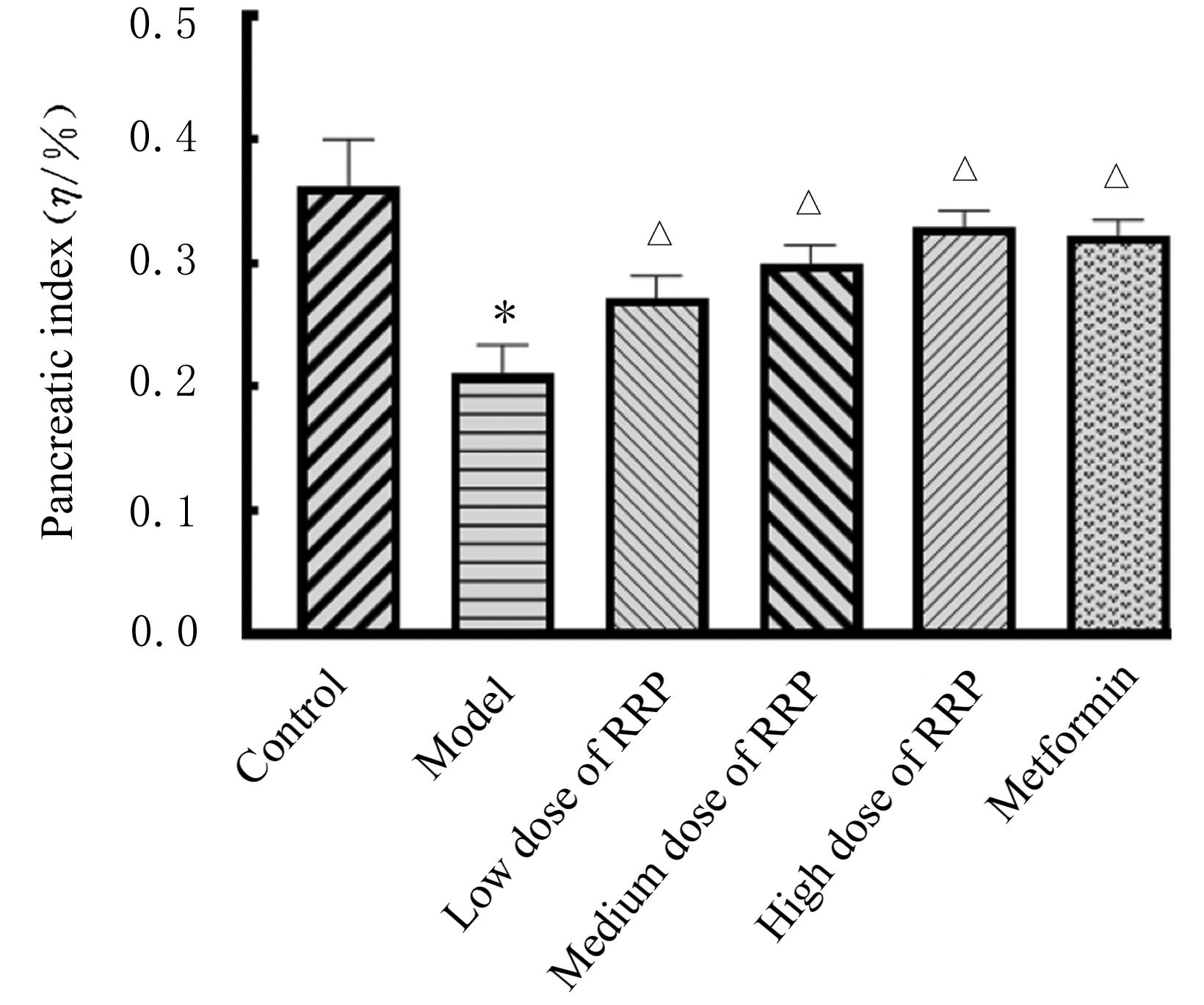
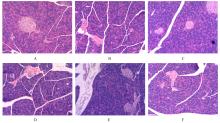
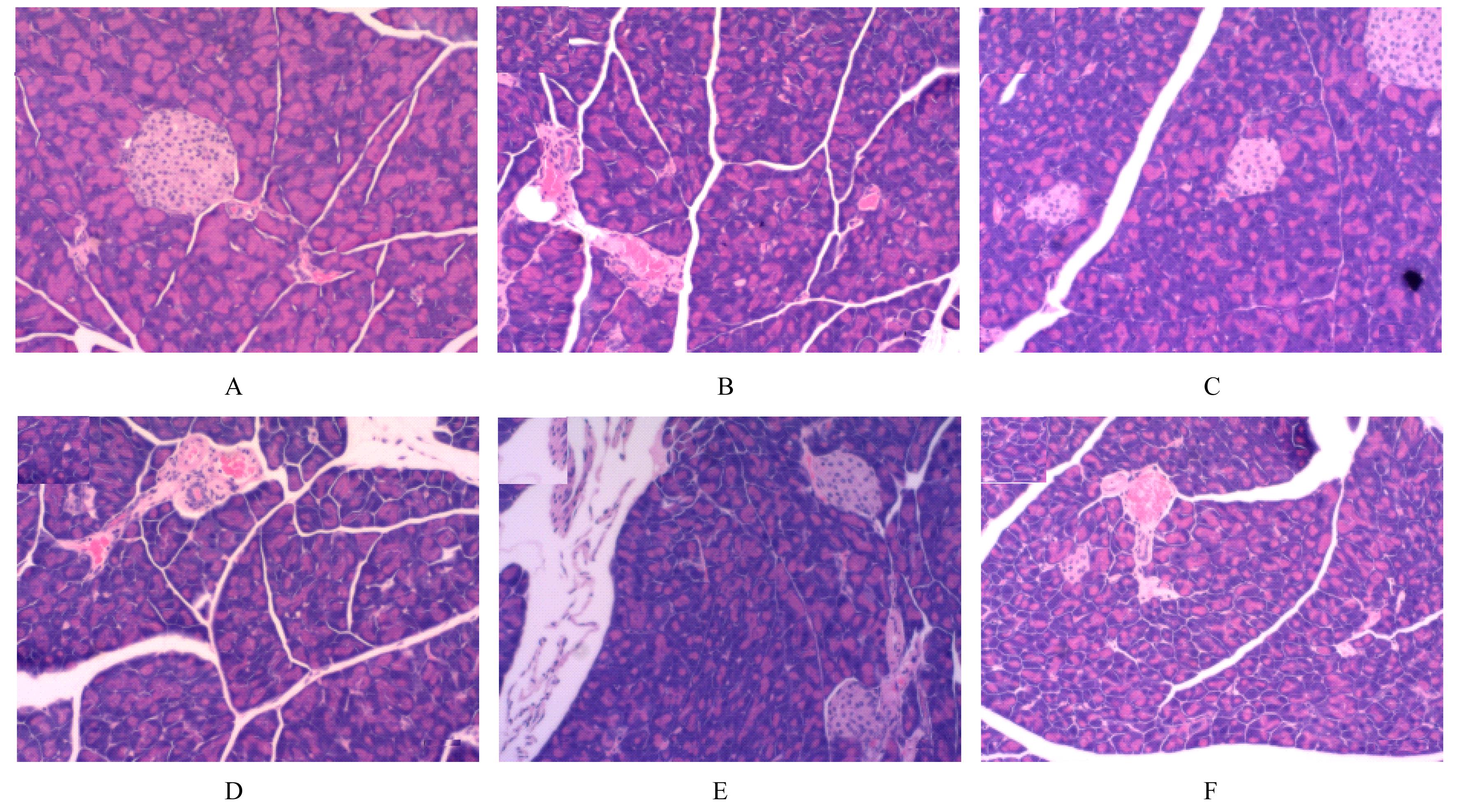
摘要: 探讨悬钩子根多糖(RRP)对2型糖尿病(T2DM)小鼠胰腺线粒体功能的改善作用,并阐明其作用机制。 70只健康雄性C57BL/6J小鼠适应性饲养1周,随机选取10只小鼠作为对照组,其余60只小鼠按照高脂肪饮食联合腹腔注射低剂量链脲佐菌素(STZ)的方法建立T2DM小鼠模型。从52只造模成功的小鼠中随机选取50只小鼠分为模型组,低、中和高剂量RRP组,二甲双胍组,每组10只。每日1次连续10周灌胃给药,对照组和模型组小鼠灌胃等体积生理盐水。实验过程中每日观察小鼠的一般状态,每周监测空腹血糖(FBG)水平,每4周进行口服葡萄糖耐量试验(OGTT)。连续灌胃10周后,计算各组小鼠 OGTT时间-血糖曲线下面积(AUC)和稳态模型胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR),检测各组小鼠血清中空腹胰岛素(FINS)、C肽、胰高血糖素(GC)水平和线粒体功能相关指标。取各组小鼠胰腺组织,计算胰腺指数,HE染色观察各组小鼠胰腺组织病理形态表现。 与对照组比较,模型组小鼠精神萎靡,毛发粗糙,自主活动减少;与模型组比较,各剂量RRP组和二甲双胍组小鼠精神状态较好,毛发有光泽,自主活动增加。与对照组比较,模型组小鼠体质量明显降低(P<0.05),饮水量和摄食量明显增加(P<0.05),血清FBG水平、OGTT的AUC和HOMA-IR明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,中和高剂量RRP组及二甲双胍组小鼠体质量明显增加(P<0.05),饮水量和摄食量明显减少(P<0.05),OGTT的AUC明显降低(P<0.05),各剂量RRP组小鼠血清FBG水平和HOMA-IR均明显降低(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,模型组小鼠血清FINS和C肽水平明显降低(P<0.05),GC水平明显升高(P<0.05),磷氧比(ADP/O)、呼吸控制率(RCR)、基础呼吸耗氧量和胰腺指数均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,中和高剂量RRP组及二甲双胍组小鼠血清FINS和C肽水平明显升高(P<0.05),GC水平明显降低(P<0.05),ADP/O和RCR明显升高(P<0.05),各剂量RRP组和二甲双胍组小鼠胰腺指数和基础呼吸耗氧量明显升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,模型组小鼠胰腺组织中胰岛形状不规则,胰岛细胞大小和数量明显减少,且伴有炎性浸润和坏死;与模型组比较,各剂量RRP组和二甲双胍组小鼠胰腺组织中胰岛形态完整,胰岛大小和数量增多,坏死面积减少。 RRP可以通过改善胰腺线粒体功能,促使胰岛素分泌增多,进而调节T2DM小鼠的血糖。
中图分类号:
- R285.5