吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 840-846.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240331
• 方法学 • 上一篇
慢性避水应激法建立大鼠肠易激综合征模型及其评价
刘婷婷1,张擎宇2,赵香顺3,石运来3,于燕南3,王正文4,陈少宗4( ),冯楚文1,5,6,杨添淞1,5,6(
),冯楚文1,5,6,杨添淞1,5,6( )
)
- 1.黑龙江中医药大学第一临床医学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040
2.山东省济南医院康复医学科,山东 济南 250013
3.山东中医药大学针灸推拿学院,山东 济南 250355
4.山东中医药大学针灸研究院,山东 济南 250355
5.黑龙江中医药大学附属第一医院康复二科,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040
6.黑龙江省中医药信息学重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150040
Establishment of irritable bowel syndrome model in rats by chronic water avoidance stress method and its evaluation
Tingting LIU1,Qingyu ZHANG2,Xiangshun ZHAO3,Yunlai SHI3,Yannan YU3,Zhengwen WANG4,Shaozong CHEN4( ),Chuwen FENG1,5,6,Tiansong YANG1,5,6(
),Chuwen FENG1,5,6,Tiansong YANG1,5,6( )
)
- 1.First Clinical Medical College,Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150040,China
2.Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,Ji’nan Hospital,Shandong Province,Jinan 250013,China
3.School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Massage,Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan 250355,China
4.Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion,Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan 250355 China
5.Department of Rehabilitation,First Affiliated Hospital,Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150040,China
6.Heilongjiang Provincal Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Informotics,Harbin 150040,China
摘要:
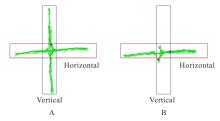
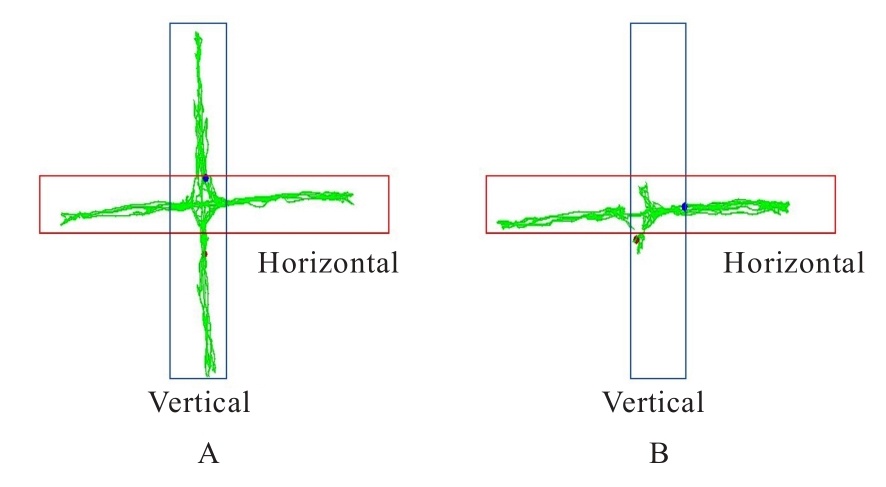
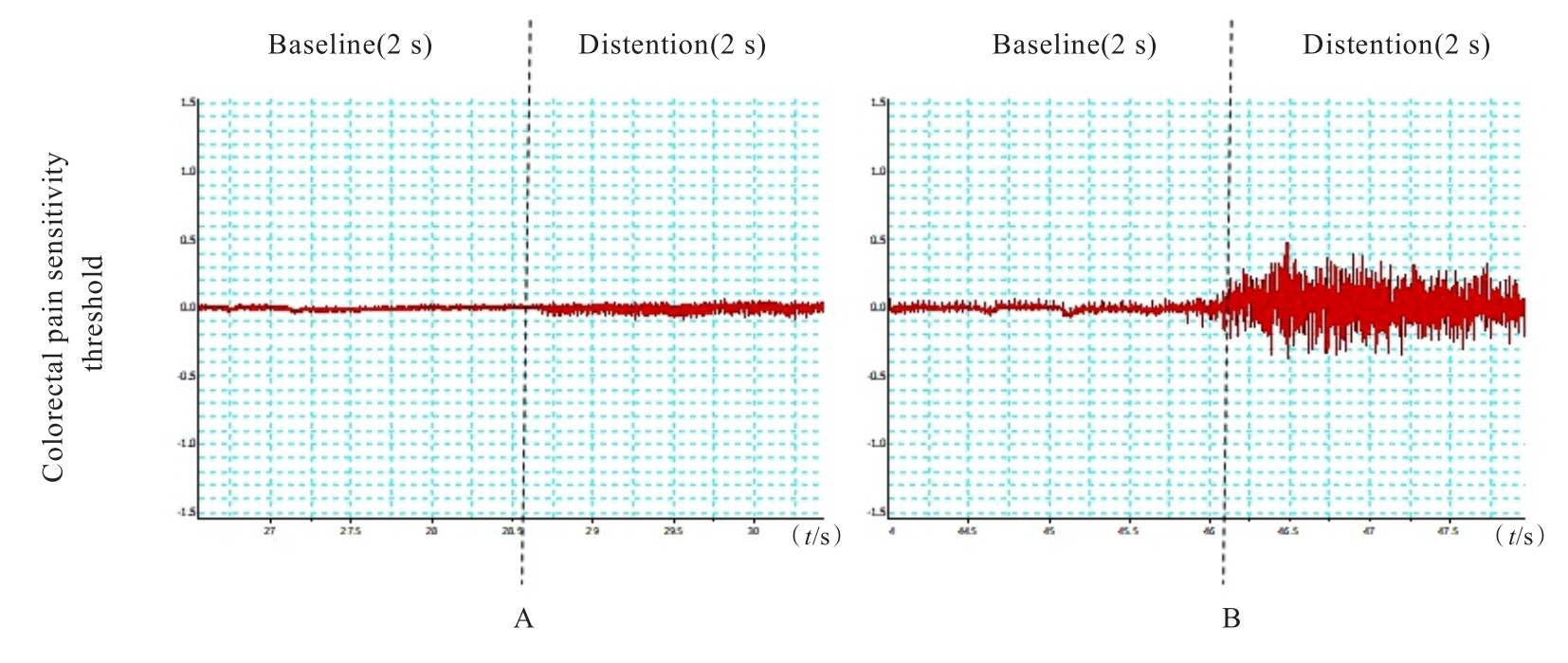
目的 探讨慢性避水应激(WAS)法建立肠易激综合征(IBS)大鼠模型的方法,并评价其可行性。 方法 30只雄性清洁型Wistar大鼠,随机分为对照组(n=10)和模型组(n=20),模型组大鼠每日采用WAS法诱导1 h,连续干预造模10 d;对照组大鼠不进行任何干预。造模结束后,观察并记录2组大鼠一般情况和体质量,采用高架十字迷宫(EPM)实验检测2组大鼠进入开放臂次数(OE)百分率和进入开放臂时间(OT)百分率,腹壁撤回反射(AWR)实验检测2组大鼠内脏敏感性,心电图检查2组大鼠心率变异性(HRV),腹外斜肌肌电图(EMG)检测2组大鼠结直肠痛敏阈值,多通道生理信号记录仪检测2组大鼠结肠慢波频率。 结果 2组大鼠在整个造模期间均无死亡情况,造模结束后,模型组大鼠均伴有精神状态欠佳、自主活动减少、少动、皮毛散乱且无光泽、易激惹和肛门口不净等情况;对照组大鼠精神状态、自主活动、皮毛和肛周无明显变化。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠体质量明显降低(P<0.05)。EPM实验,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠OE百分率和OT百分率均明显降低(P<0.01)。AWR实验,模型组中AWR半定量评分≥3分大鼠共12只,内脏痛大鼠模型造模成功率为60%。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠低频信号(LF)和LF/高频信号(HF)比值均明显升高(P<0.01),HF明显降低(P<0.05)。EMG法,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠结肠痛敏阈值明显降低(P<0.01),结肠慢波频率明显升高(P<0.01)。 结论 采用WAS法建立IBS大鼠模型,大鼠行为及精神情绪改变、内脏敏感性升高、结肠慢波频率加快和自主神经系统平衡性紊乱,WAS法可作为一种有效的造模方式,用于观察和评价IBS治疗的相关药物及干预方法。
中图分类号:
- R574.4