吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1150-1155.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240431
间皮瘤患者18F-FDG PET/CT影像学表现及其在诊断中的应用
- 吉林大学第一医院核医学科,吉林 长春 130021
Imaging findings of 18F-FDG PET/CT in mesothelioma patients and its application in diagnosis
Shuangyan ZHAO,Hongguang ZHAO,Qiuyu LIN,Benzheng JIAO,Chenghe LIN( )
)
- Department of Nuclear Medicine,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
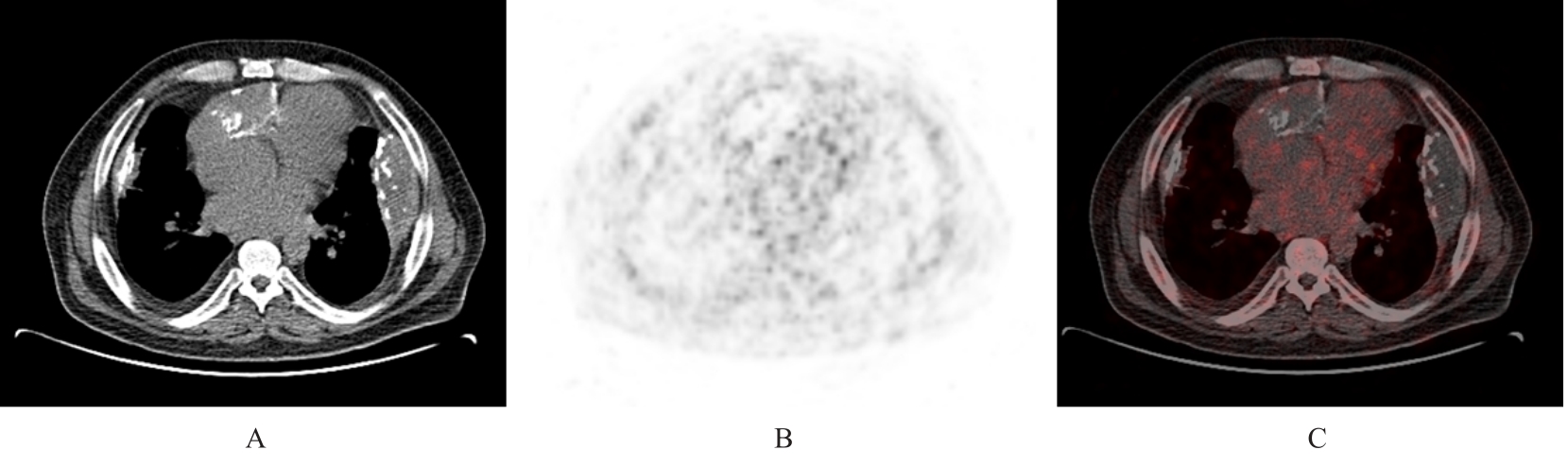
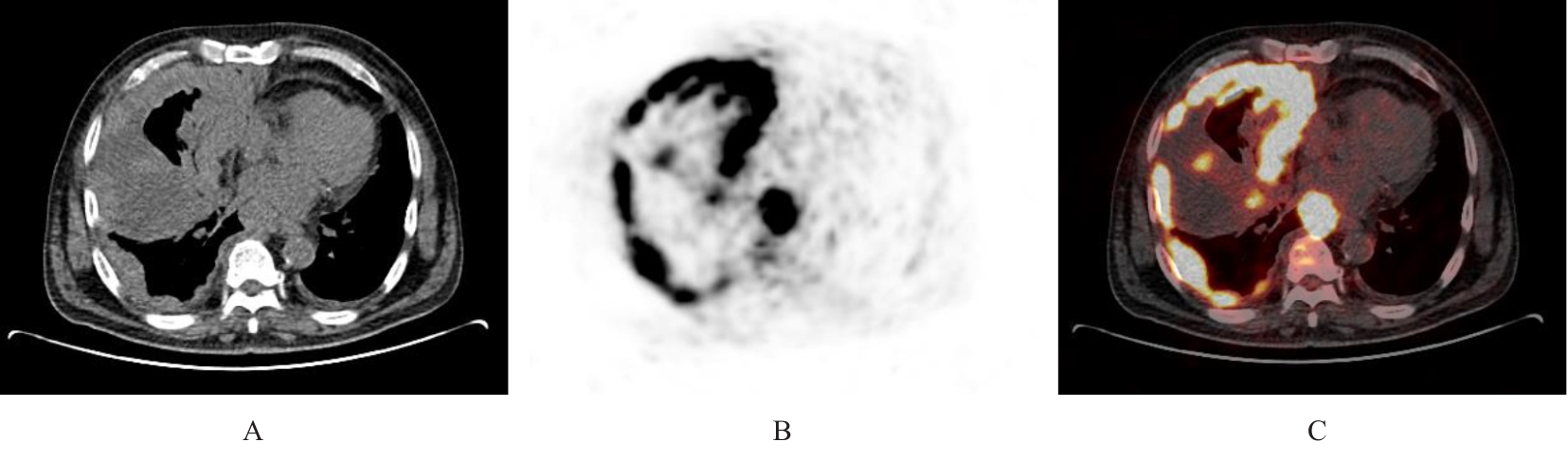
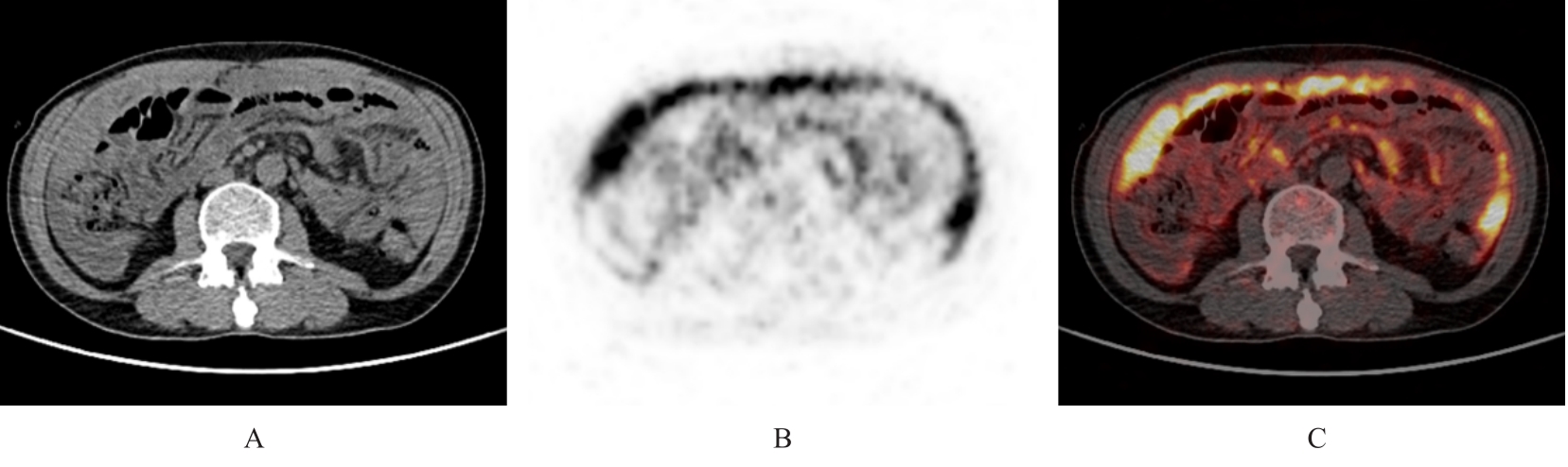
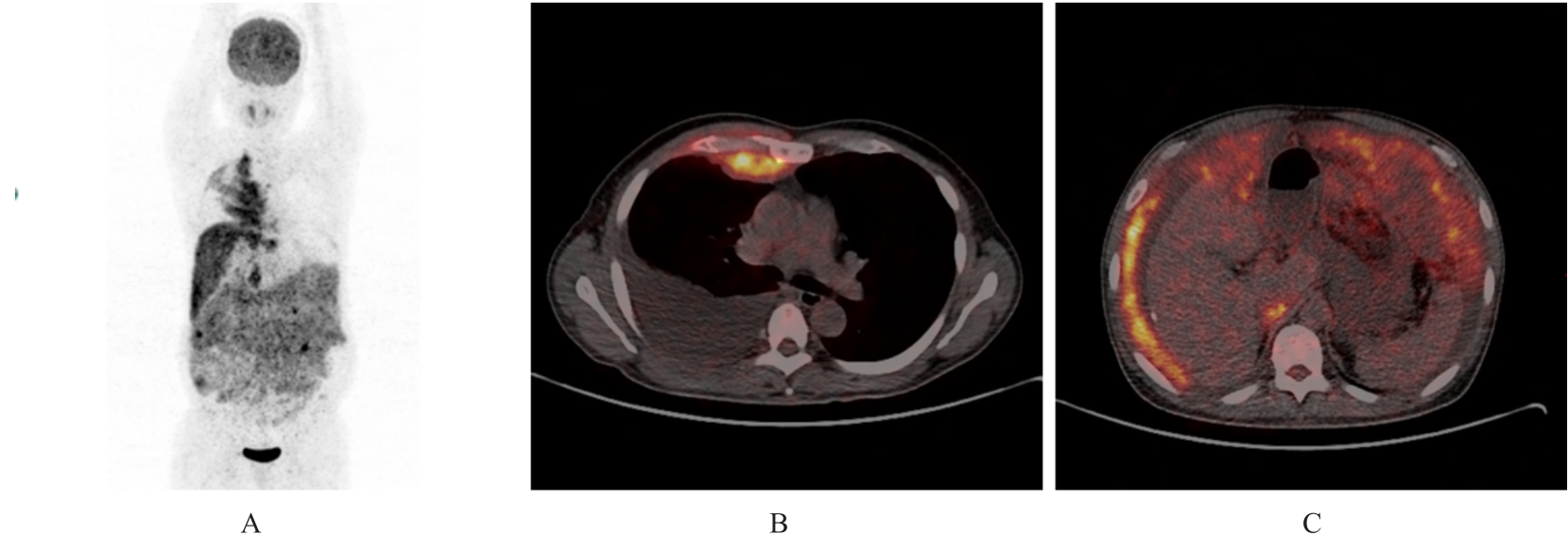
目的 分析胸膜和腹膜间皮瘤患者18F-氟代脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射扫描/计算机断层扫描(18F-FDG PET/CT)影像学表现,以期提高对该病的诊断水平。 方法 回顾性分析经病理证实的22例胸膜和腹膜间皮瘤患者(其中恶性间皮瘤21例,良性间皮瘤1例)18F-FDG PET/CT影像资料和免疫组织化学结果,对其影像表现和葡萄糖代谢特征进行归纳总结。 结果 恶性胸膜间皮瘤患者多表现为单侧胸膜弥漫性增厚伴放射性摄取增高,厚度为1.0~10.6 cm,平均半定量最大标准摄取值(SUVmax)为10.1,其中半数以上并发少量胸腔积液;恶性腹膜间皮瘤患者多数表现为腹膜、网膜和肠系膜弥漫增厚伴放射性摄取增高,厚度为1.2~6.6 cm,平均SUVmax为8.4,其中半数以上并发大量腹腔积液。恶性间皮瘤患者除原发部位外其他转移部位出现结节状、条片状和团块状不同程度异常放射性摄取17例,考虑为转移灶,平均SUVmax为7.4,大部分以病灶周围淋巴结转移为主,恶性胸膜间皮瘤患者可见骨骼和肌肉转移,恶性腹膜间皮瘤患者未见骨骼和肌肉转移。1例良性胸膜间皮瘤患者表现为双侧胸膜弥漫性增厚, 厚度约 3.5 cm, 未见明确异常放射性摄取, 并发少量胸腔积液。 结论 胸膜和腹膜间皮瘤患者18F-FDG PET/CT影像学表现具有一定的特征性,通过其胸膜和腹膜增厚方式及厚度、有无氟代脱氧葡萄糖(FDG)摄取及摄取程度可初步判断间皮瘤的良恶性,对间皮瘤临床早期诊断有一定的参考价值。PET/CT全身显像可确定间皮癌患者有无其他部位转移,对临床分期有一定的帮助。
中图分类号:
- R734.3