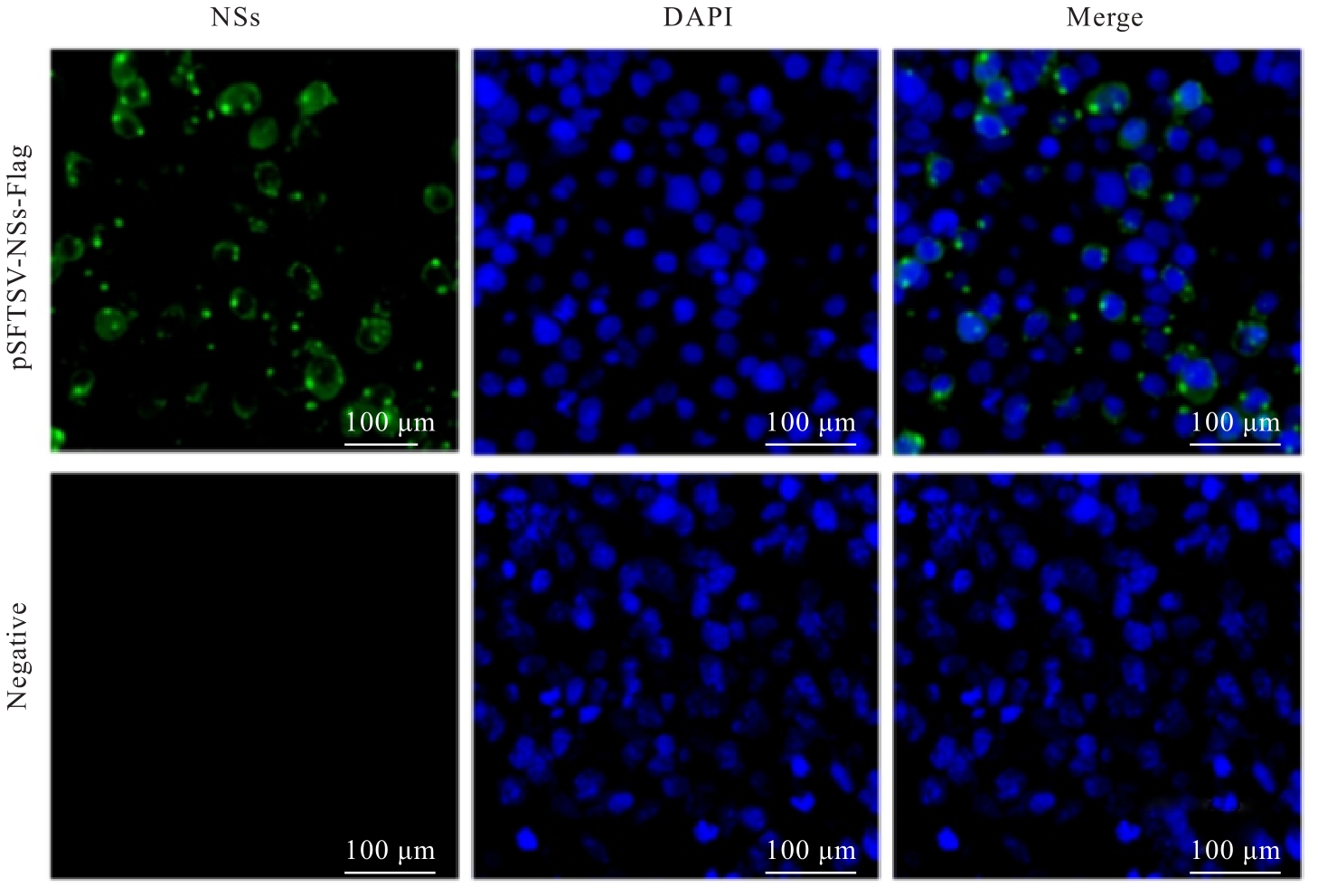
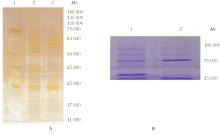
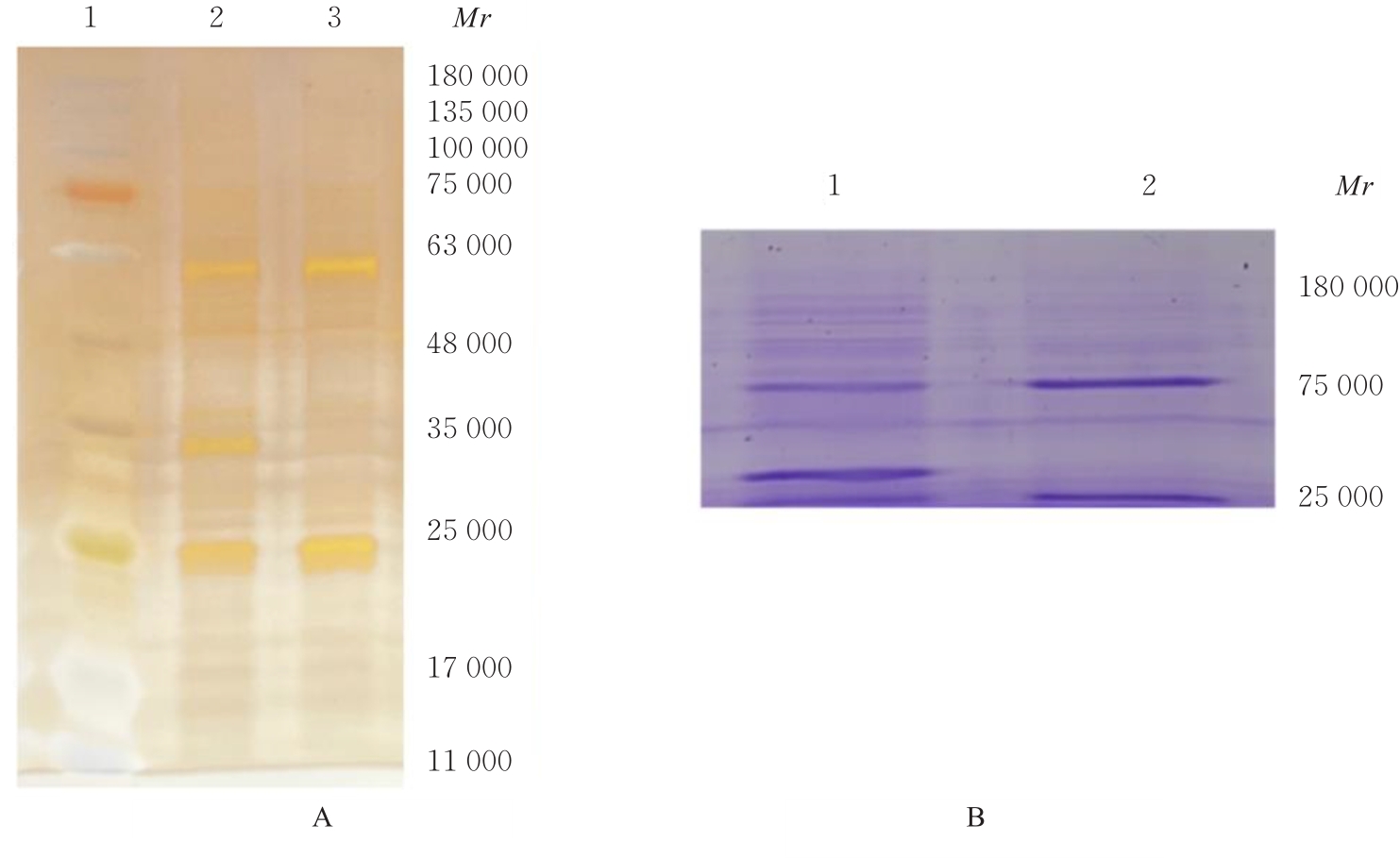
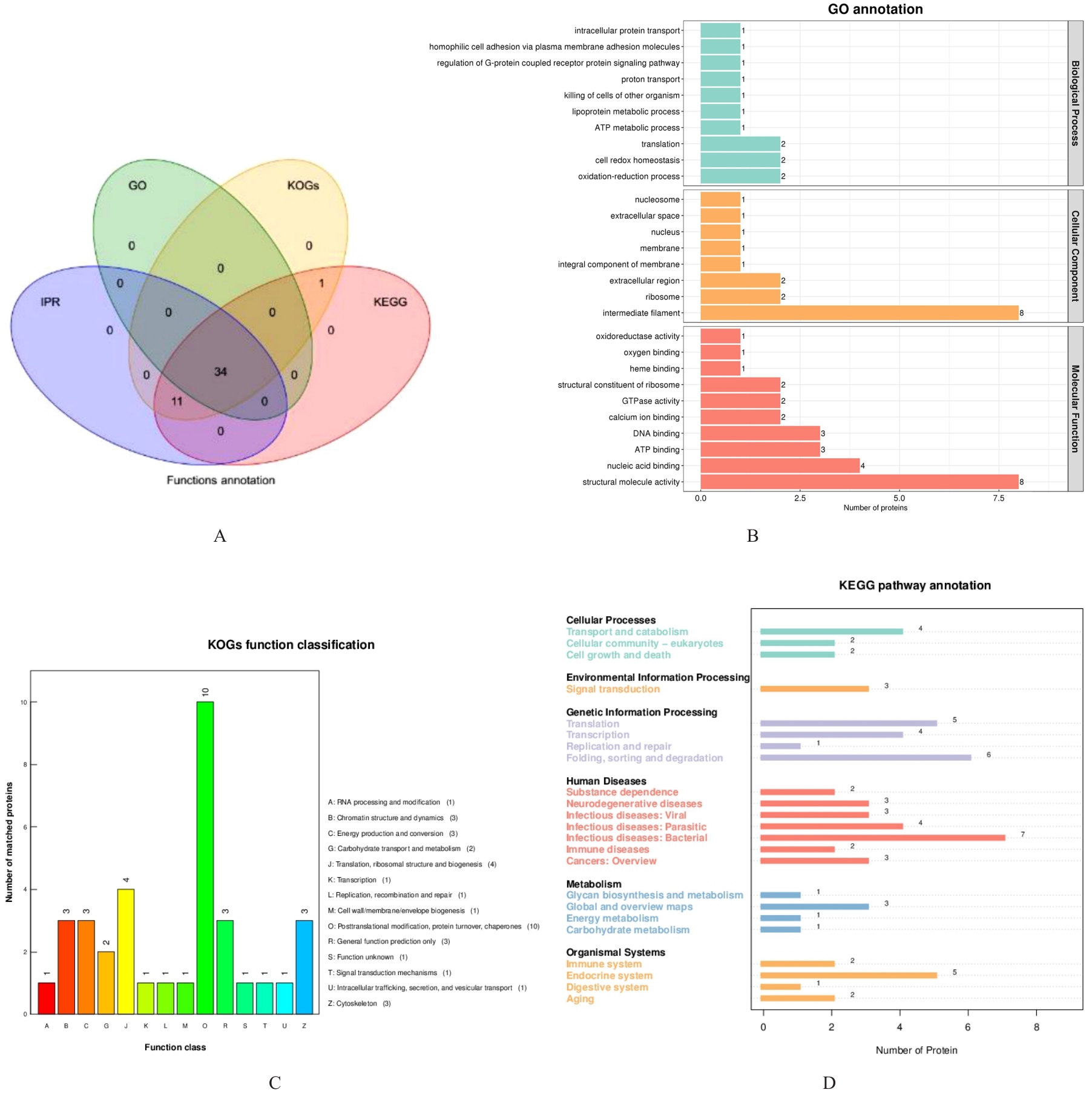
| 1 |
LUO L M, ZHAO L, WEN H L, et al. Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks as reservoir and vector of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in China[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2015, 21(10): 1770-1776.
|
| 2 |
BACHILLER S, JIMÉNEZ-FERRER I, PAULUS A, et al. Microglia in neurological diseases: a road map to brain-disease dependent-inflammatory response[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2018, 12: 488.
|
| 3 |
LI Z F, HU J L, CUI L B, et al. Increased prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Eastern China clustered with multiple genotypes and reasserted virus during 2010-2015[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 6503.
|
| 4 |
GAI Z T, ZHANG Y, LIANG M F, et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients[J]. J Infect Dis, 2012, 206(7): 1095-1102.
|
| 5 |
YU X J, LIANG M F, ZHANG S Y, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 364(16): 1523-1532.
|
| 6 |
LI J C, WANG Y N, ZHAO J, et al. A review on the epidemiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome[J]. Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi, 2021, 42(12): 2226-2233.
|
| 7 |
李春晶, 刘庆华, 全传松, 等. 发热伴血小板减少综合征免疫系统损伤的研究进展[J]. 国际免疫学杂志, 2023, 46(2): 189-195.
|
| 8 |
LI J, LI S, YANG L, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: a highly lethal bunyavirus[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 2021, 47(1): 112-125.
|
| 9 |
NING Y J, FENG K, MIN Y Q, et al. Disruption of type Ⅰ interferon signaling by the nonstructural protein of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus via the hijacking of STAT2 and STAT1 into inclusion bodies[J]. J Virol, 2015, 89(8): 4227-4236.
|
| 10 |
WU X D, QI X, LIANG M F, et al. Roles of viroplasm-like structures formed by nonstructural protein NSs in infection with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus[J]. FASEB J, 2014, 28(6): 2504-2516.
|
| 11 |
SUN Q Y, QI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Synaptogyrin-2 promotes replication of a novel tick-borne bunyavirus through interacting with viral nonstructural protein NSs[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(31): 16138-16149.
|
| 12 |
TAO X L, WANG X F, YUAN Y, et al. Preparation of a polyclonal antibody against the non-structural protein, NSs of SFTSV[J]. Protein Expr Purif, 2021, 184: 105892.
|
| 13 |
LEE J K, SHIN O S. Nonstructural protein of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome phlebovirus inhibits TBK1 to evade interferon-mediated response[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2021, 31(2): 226-232.
|
| 14 |
FINN R D, ATTWOOD T K, BABBITT P C, et al. InterPro in 2017-beyond protein family and domain annotations[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(D1): D190-D199.
|
| 15 |
GALPERIN M Y, KRISTENSEN D M, MAKAROVA K S, et al. Microbial genome analysis: the COG approach[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2019, 20(4): 1063-1070.
|
| 16 |
KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, TANABE M, et al. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(D1): D353-D361.
|
| 17 |
SHEN H B, CHOU K C. A top-down approach to enhance the power of predicting human protein subcellular localization: hum-mPLoc 2.0[J]. Anal Biochem, 2009, 394(2): 269-274.
|
| 18 |
JIN J P, ZHANG H, KONG L, et al. PlantTFDB 3.0: a portal for the functional and evolutionary study of plant transcription factors[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(Database issue): D1182-D1187.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG H M, CHEN H, LIU W, et al. AnimalTFDB: a comprehensive animal transcription factor database[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(Database issue): D144-D149.
|
| 20 |
KANG L J, WENG N D, JIAN W Y. LC-MS bioanalysis of intact proteins and peptides[J]. Biomed Chromatogr, 2020, 34(1): e4633.
|
| 21 |
LI J P, ZHU H J. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)-based proteomics of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(11): 2718.
|
| 22 |
NARDONE V, CHAVES-SANJUAN A, NARDINI M. Structural determinants for NF-Y/DNA interaction at the CCAAT box[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech, 2017, 1860(5): 571-580.
|
| 23 |
LUNDU T, TSUDA Y, ITO R, et al. Targeting of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus structural proteins to the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartment) and Golgi complex[J]. Biomed Res, 2018, 39(1): 27-38.
|
| 24 |
QU B Q, QI X, WU X D, et al. Suppression of the interferon and NF-κB responses by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus[J]. J Virol, 2012, 86(16): 8388-8401.
|
| 25 |
SANTIAGO F W, COVALEDA L M, SANCHEZ-APARICIO M T, et al. Hijacking of RIG-I signaling proteins into virus-induced cytoplasmic structures correlates with the inhibition of type Ⅰ interferon responses[J]. J Virol, 2014, 88(8): 4572-4585.
|
| 26 |
FANG H C, WU B Q, HAO Y L, et al. KRT1 gene silencing ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via the activation of the Notch signaling pathway in mouse models[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(4): 3634-3646.
|
| 27 |
WU Y, ZHU Y H, GAO F, et al. Structures of phlebovirus glycoprotein Gn and identification of a neutralizing antibody epitope[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017, 114(36): E7564-E7573.
|
| 28 |
IBRAHIM I M, ABDELMALEK D H, ELFIKY A A. GRP78: a cell’s response to stress[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 226: 156-163.
|
| 29 |
王 博. 未折叠蛋白应答及HSP90在SFTSV复制过程中的功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019.
|
| 30 |
HWANG J, QI L. Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum: Crosstalk between ERAD and UPR pathways[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2018, 43(8): 593-605.
|
| 31 |
XIA T, TIAN H, ZHANG K W, et al. Exosomal ERp44 derived from ER-stressed cells strengthens cisplatin resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 1003.
|
| 32 |
GROENENDYK J, PENG Z L, DUDEK E, et al. Interplay between the oxidoreductase PDIA6 and microRNA-322 controls the response to disrupted endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis[J]. Sci Signal, 2014, 7(329): ra54.
|
| 33 |
RUMPANSUWON K, PROMMAHOM A, DHARMASAROJA P. eEF1A2 knockdown impairs neuronal proliferation and inhibits neurite outgrowth of differentiating neurons[J]. Neuroreport, 2022, 33(8): 336-344.
|
| 34 |
魏 迅, 秦新萌, 马 力, 等. 阿伐曲泊帕治疗慢性肝病相关性血小板减少症临床疗效分析[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(7): 567-570.
|
 )
)
 )
)