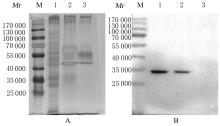
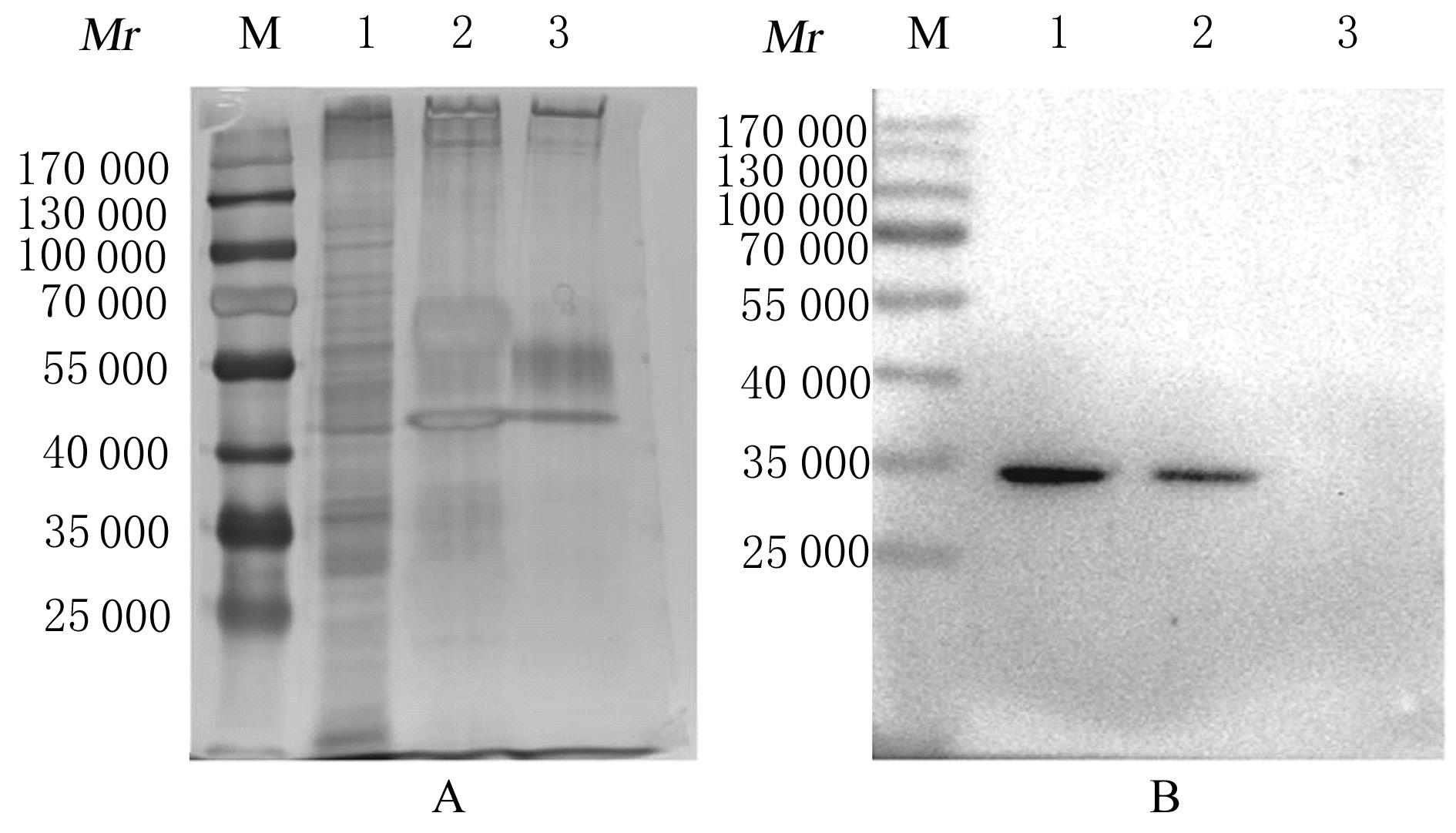
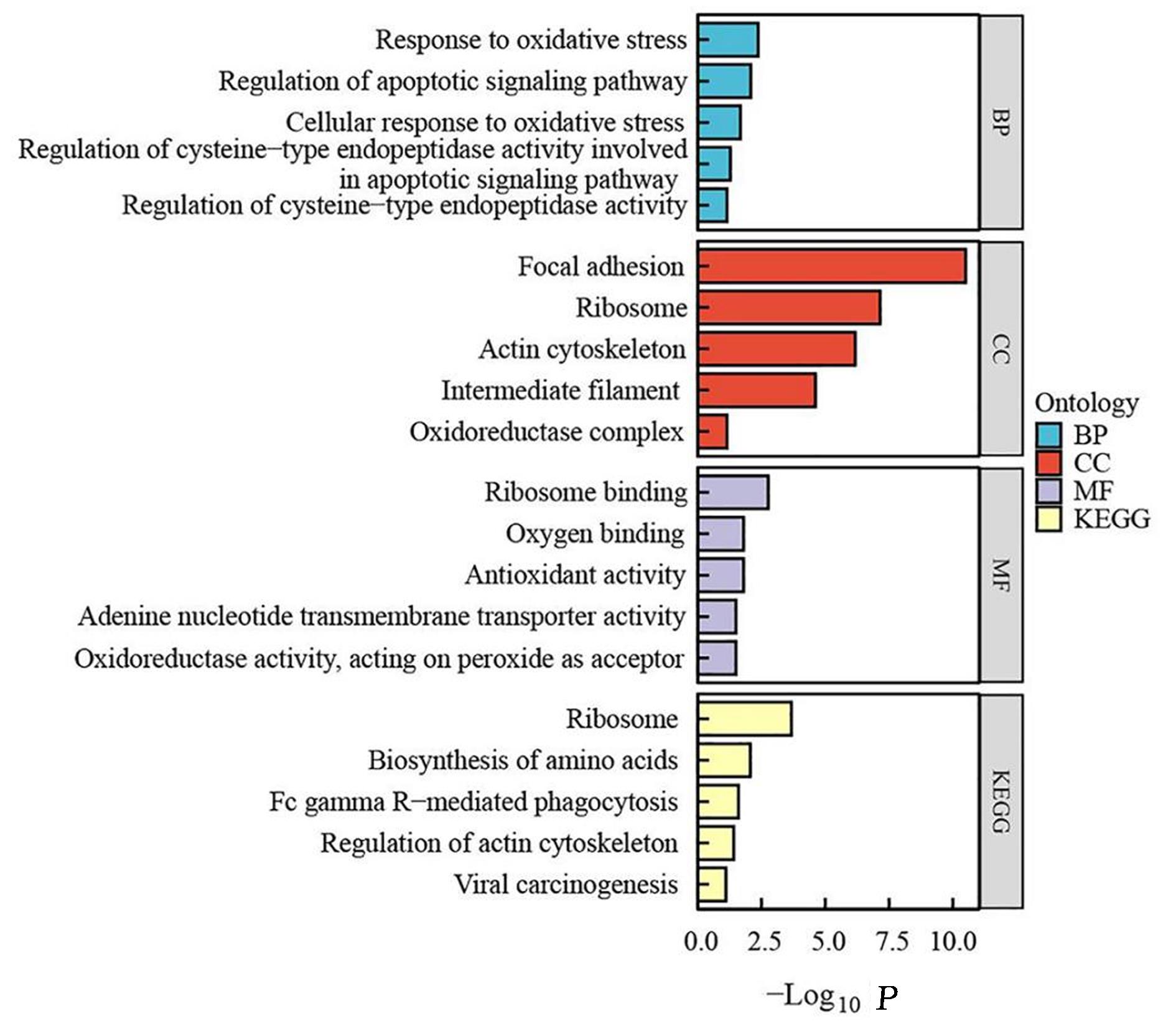
| 1 |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.
|
| 2 |
CAO W, CHEN H D, YU Y W, et al. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020[J]. Chin Med J, 2021, 134(7): 783-791.
|
| 3 |
KIRKIN V, DIKIC I. Ubiquitin networks in cancer[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2011, 21(1): 21-28.
|
| 4 |
LI Z Y, WANG Y, LI Y D, et al. Ube2s stabilizes β-Catenin through K11-linked polyubiquitination to promote mesendoderm specification and colorectal cancer development[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(5): 456.
|
| 5 |
TANG H, FANG T, JI M, et al. UBE2S exerts oncogenic activities in urinary bladder cancer by ubiquitinating TSC1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 578: 7-14.
|
| 6 |
HU L, CHENG X B, BINDER Z, et al. Molecular and clinical characterization of UBE2S in glioma as a biomarker for poor prognosis and resistance to chemo-radiotherapy[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 640910.
|
| 7 |
ZHANG M J, LIU Y, YIN Y, et al. UBE2S promotes the development of ovarian cancer by promoting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to regulate cell cycle and apoptosis[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 62.
|
| 8 |
HU W J, LI M, CHEN Y G, et al. UBE2S promotes the progression and Olaparib resistance of ovarian cancer through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2021, 14(1): 121.
|
| 9 |
LIN T H, HSU W H, TSAI P H, et al. Dietary flavonoids, luteolin and quercetin, inhibit invasion of cervical cancer by reduction of UBE2S through epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling[J]. Food Funct, 2017, 8(4): 1558-1568.
|
| 10 |
LIU Z, XU L J. UBE2S promotes the proliferation and survival of human lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. BMB Rep, 2018, 51(12): 642-647.
|
| 11 |
HO J Y, LU H Y, CHENG H H, et al. UBE2S activates NF-κB signaling by binding with IκBα and promotes metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2021, 44(6): 1325-1338.
|
| 12 |
QIN Y N, DU J, FAN C F. Ube2S regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer[J].Int J Med Sci,2020,17(2): 274-279.
|
| 13 |
GUO Y J, CHEN X Y, ZHANG XW, et al. UBE2S and UBE2C confer a poor prognosis to breast cancer via downregulation of Numb [J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 992233.
|
| 14 |
PENG S M, CHEN X, HUANG C Y, et al. UBE2S as a novel ubiquitinated regulator of p16 and β-catenin to promote bone metastasis of prostate cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(8): 3528-3543.
|
| 15 |
PAN Y H, YANG M, LIU L P, et al. UBE2S enhances the ubiquitination of p53 and exerts oncogenic activities in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 503(2): 895-902.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG R Y, LIU Z K, WEI D, et al. UBE2S interacting with TRIM28 in the nucleus accelerates cell cycle by ubiquitination of p27 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 64.
|
| 17 |
GUI L, ZHANG S C, XU Y Z, et al. UBE2S promotes cell chemoresistance through PTEN-AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 357.
|
| 18 |
MA Y L, LI K Z, LI S J, et al. Prognostic value of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 S overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 119: 225-231.
|
| 19 |
GOEMAN J J. L1 penalized estimation in the Cox proportional hazards model[J]. Biom J, 2010, 52(1): 70-84.
|
| 20 |
COMBS J A, DENICOLA G M. The non-essential amino acid cysteine becomes essential for tumor proliferation and survival[J]. Cancers,2019,11(5): 678.
|
| 21 |
ANGELI J P F, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B,et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice[J].Nat Cell Biol,2014, 16(12): 1180-1191.
|
| 22 |
YANG W S, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH M E,et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(1/2): 317-331.
|
| 23 |
JIANG X J, STOCKWELL B R, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2021,22(4):266-282.
|
| 24 |
MATSCHKE V, THEISS C, MATSCHKE J. Oxidative stress: the lowest common denominator of multiple diseases[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2019, 14(2): 238-241.
|
| 25 |
WANG J, CHEN W, WEI W W, et al. Oncogene TUBA1C promotes migration and proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts a poor prognosis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(56): 96215-96224.
|
| 26 |
JIANG K Q, DONG C Y, YIN Z L, et al. Exosome-derived ENO1 regulates integrin α6β4 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(11): 972.
|
| 27 |
XU H, DONG X Y, CHEN Y M, et al. Serum exosomal hnRNPH1 mRNA as a novel marker for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2018, 56(3): 479-484.
|
| 28 |
CHEN Y H, PENG C H, CHEN J R, et al. WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 127.
|
| 29 |
YANG C X, SHAO Y D, WANG X J, et al. The effect of the histone chaperones HSPA8 and DEK on tumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2653.
|
| 30 |
DUAN F F, WU H, JIA D W, et al. O-GlcNAcylation of RACK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(6): 1191-1202.
|
| 31 |
HUANG S L, DONG C R, LI D, et al. ARPC2: a pan-cancer prognostic and immunological biomarker that promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 896080.
|
 )
)
 )
)