吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 180-186.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210125
人源单核细胞增生李斯特菌的基因组进化及耐药性分析
姚广,陆玉颖,张庆华,朱海霞,陈益伟,孙东,庄振,张峰,刘鼎,宋治( )
)
- 中南大学湘雅三医院神经内科,湖南 长沙 410008
Genomic evolution and drug resistance analysis of human-derived Listeria monocytogenes
Guang YAO,Yuying LU,Qinghua ZHANG,Haixia ZHU,Yiwei CHEN,Dong SUN,Zhen ZHUANG,Feng ZHANG,Ding LIU,Zhi SONG( )
)
- Department of Neurology,Third Xiangya Hospital,Central South University,Changsha 410008,China
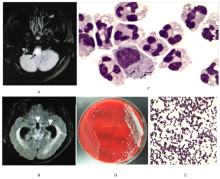
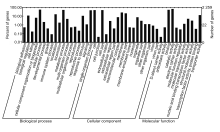
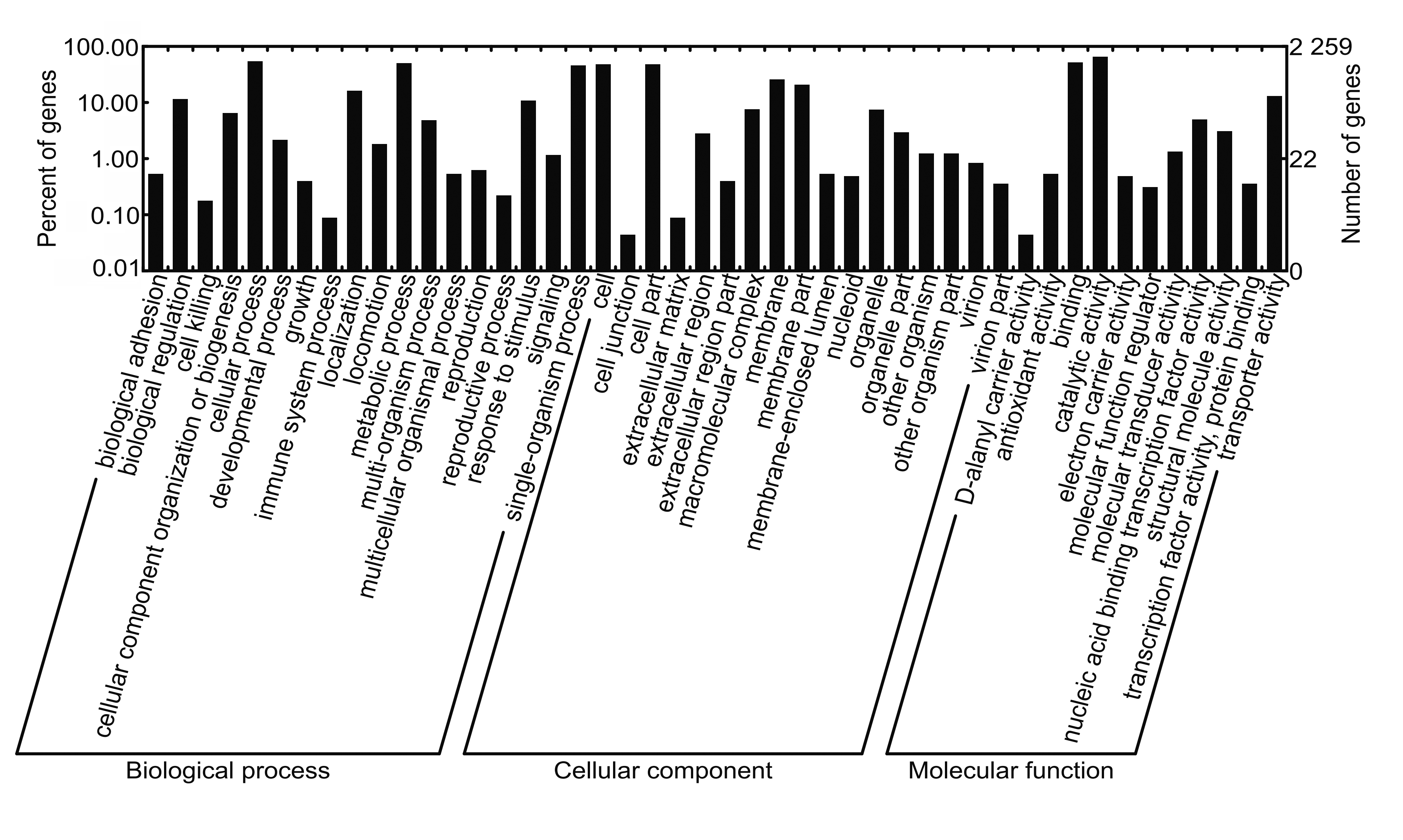
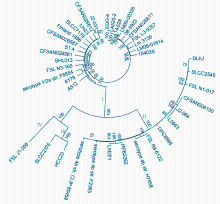
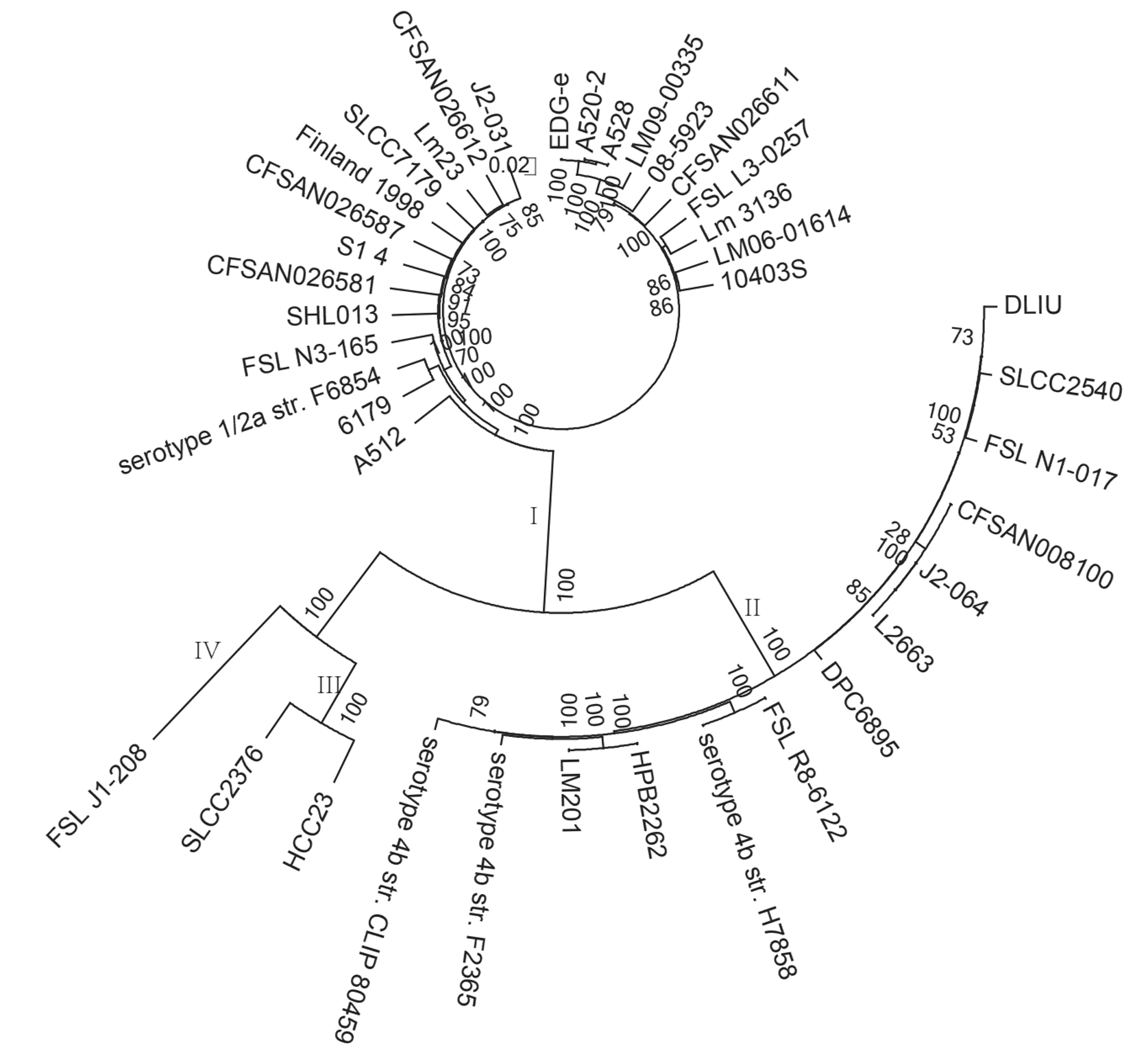
摘要: 利用新一代测序技术鉴定1例脑膜炎患者脑脊液中分离培养的单核细胞增生李斯特菌(LM),并进行基因组进化和耐药性分析,探讨患者病情迅速进展和治疗失败的原因。 从该例脑膜炎患者脑脊液中培养、分离并鉴定出LM,采用Illumina HiSeq 3000 系统进行细菌De novo测序,利用基因组装、基因预测、基因注释、单核苷酸多态性(SNP)分析和系统进化分析等生物信息学方法,构建LM属的进化树,并进行耐药基因分析。 患者脑脊液细菌分离培养,经质谱法鉴定为LM;经过测序,数据组装细菌基因组大小为3 008 507 bp。与数据库比较,获得的LM基因组-致率为88%,确定培养细菌为LM属;对比美国国家生物技术信息中心(NCBI)数据库中38个代表性LM基因组构建系统发生树,检测LM株与数据库中FSL N1-017和SLCC2540距离较近,并且共线性良好,与已报道的国内外人源感染的LM均无进化关系,为中国新发现的临床感染型致病LM。耐药性分析,检测到的LM基因组包含与主要协同转运蛋白超家族(MFS)转运体相关的耐药基因,其中4个基因与数据库EDG-e株转运体注释中的耐药基因相匹配,提示该菌株临床耐药性较强。 鉴定出来源于临床脑膜炎患者脑脊液培养菌为新型临床感染型致病LM菌株,且临床耐药性较强。
中图分类号:
- R446.5