吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 397-406.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210220
敲低ALKBH3对膀胱癌细胞生长、迁移与肿瘤血管生成的抑制作用及其机制
- 河南省南阳市第一人民医院泌尿外科,河南 南阳 473010
Inhibitory effect of ALKBH3 knockdown on growth, migration and tumor angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells and its mechanism
Qi ZHAO( ),Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU
),Changhai HE,Zhi WANG,Xuefeng WANG,Xiaofei LIU
- Department of Urinary Surgery,Nanyang First People’s Hospital,Nanyang 473010,Henan Province,China
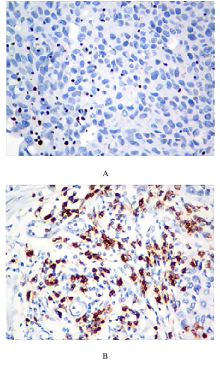
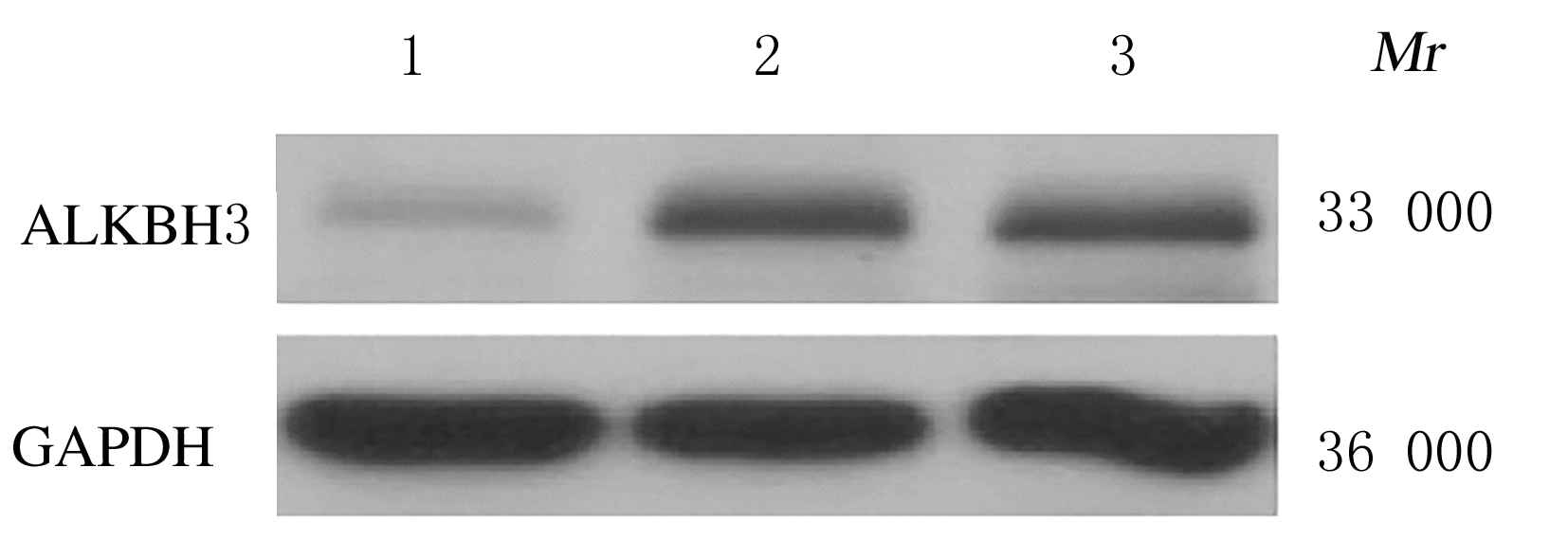
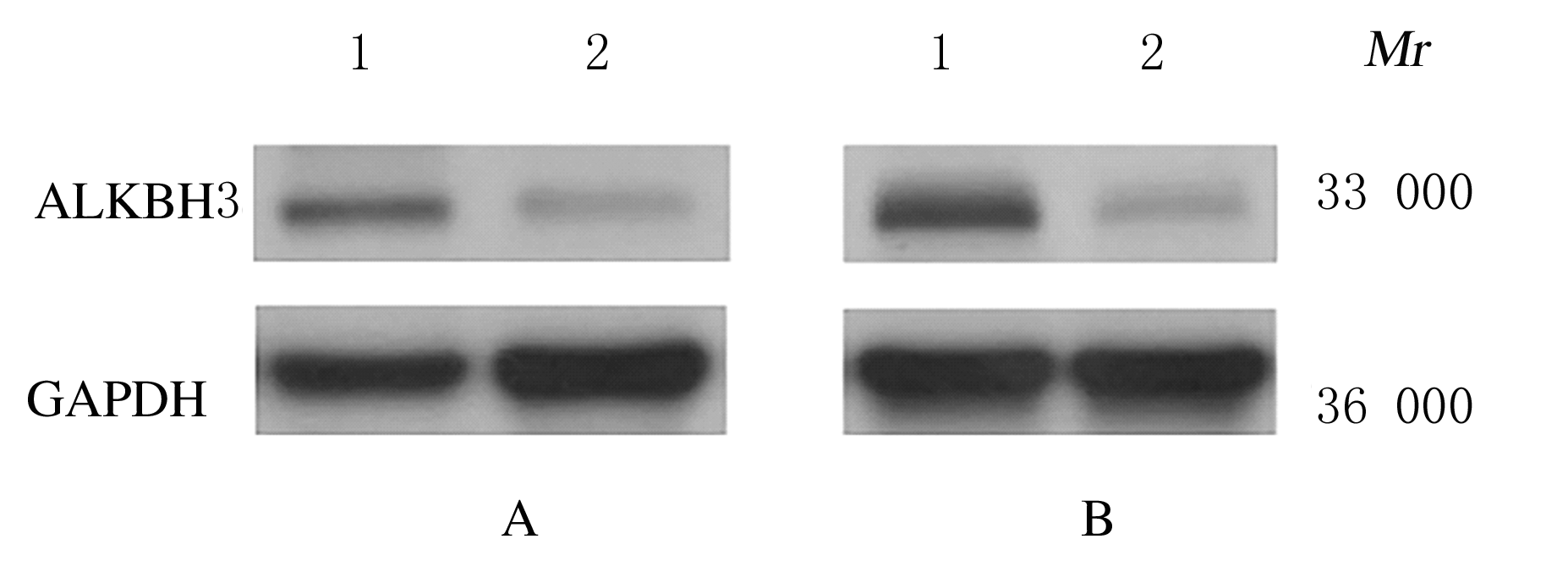
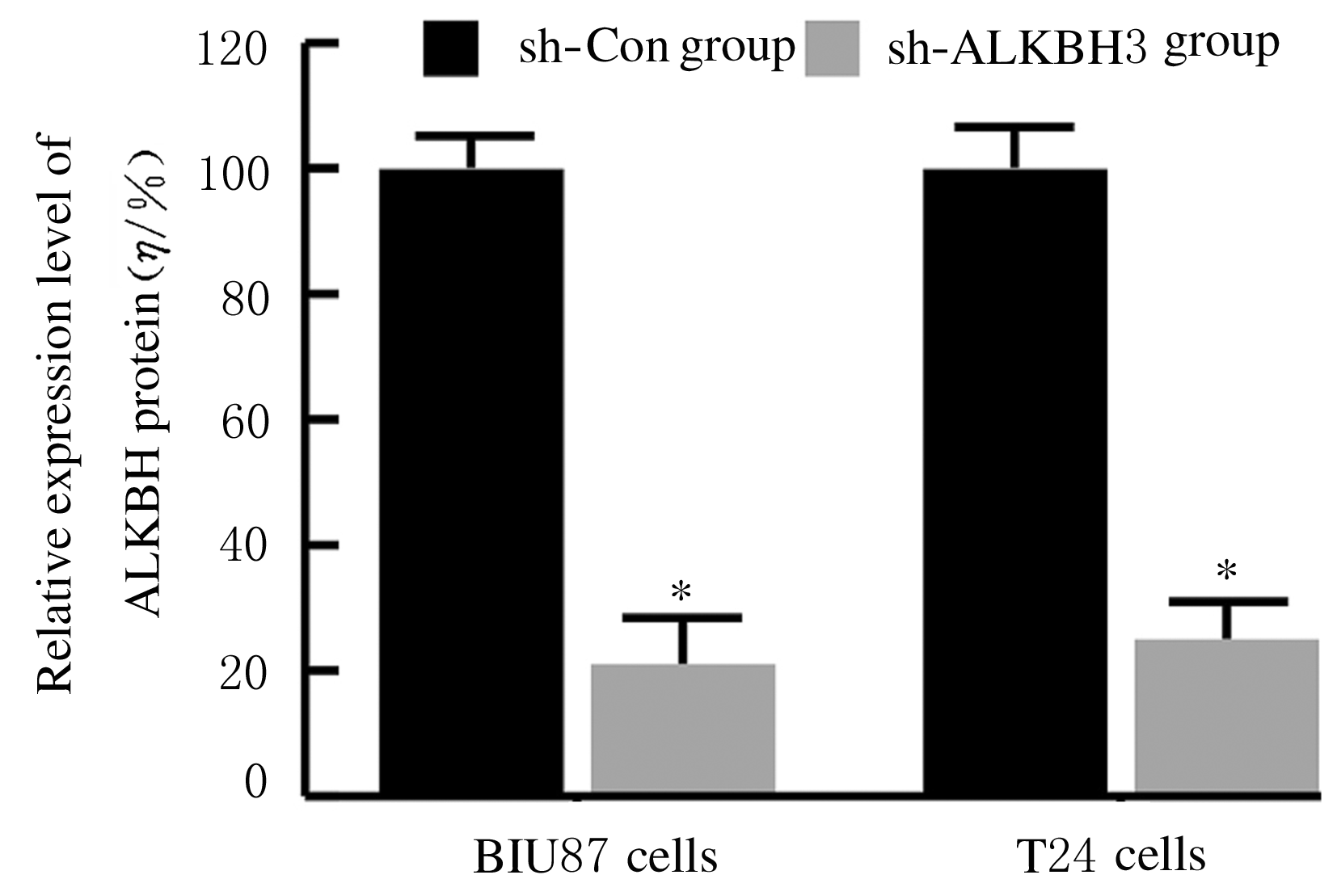
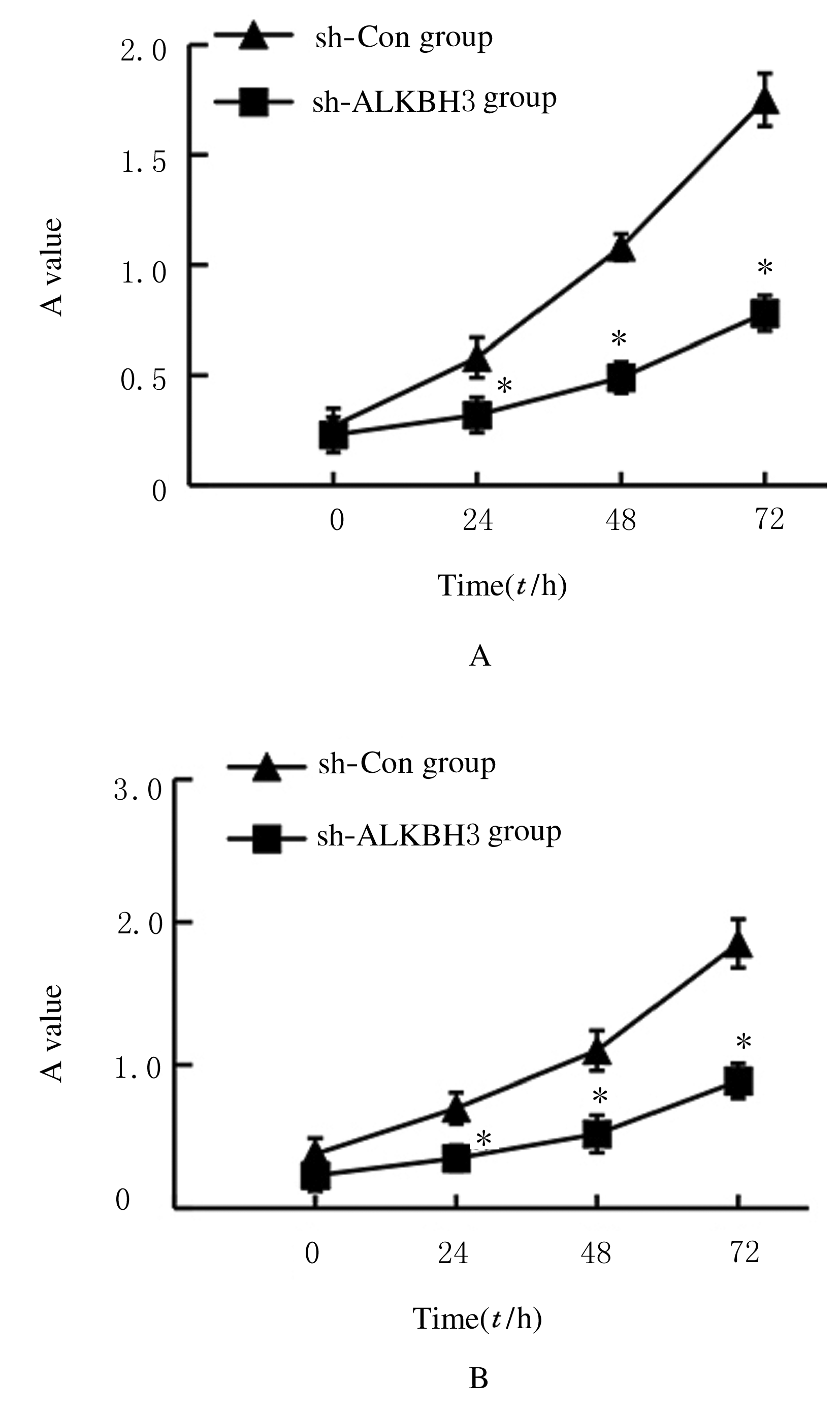
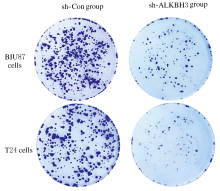
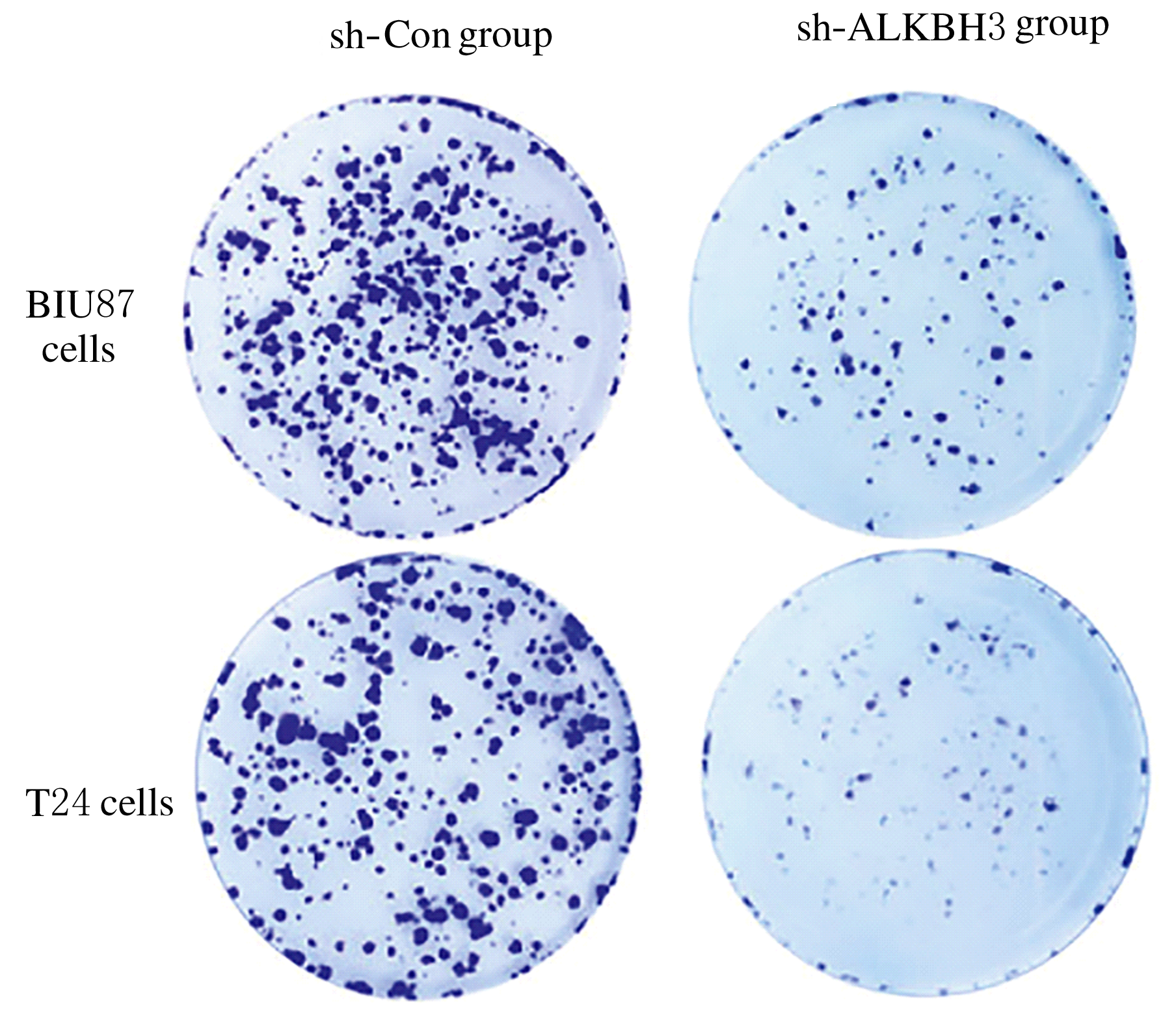
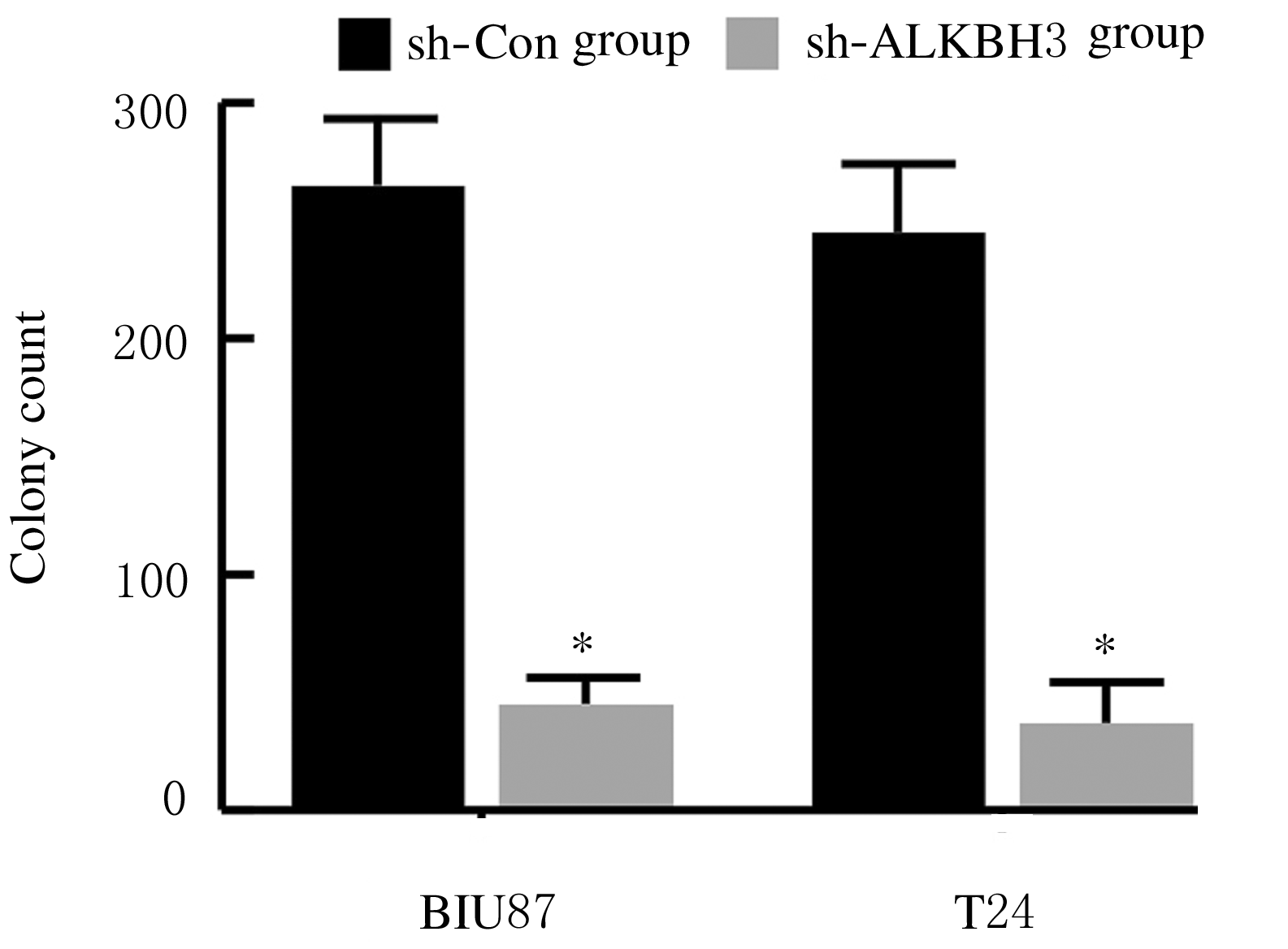
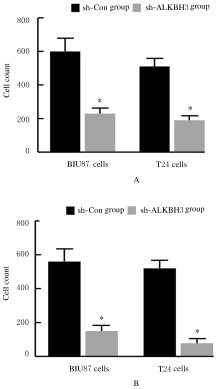
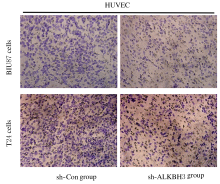
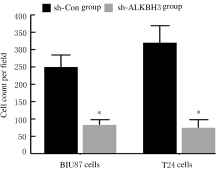
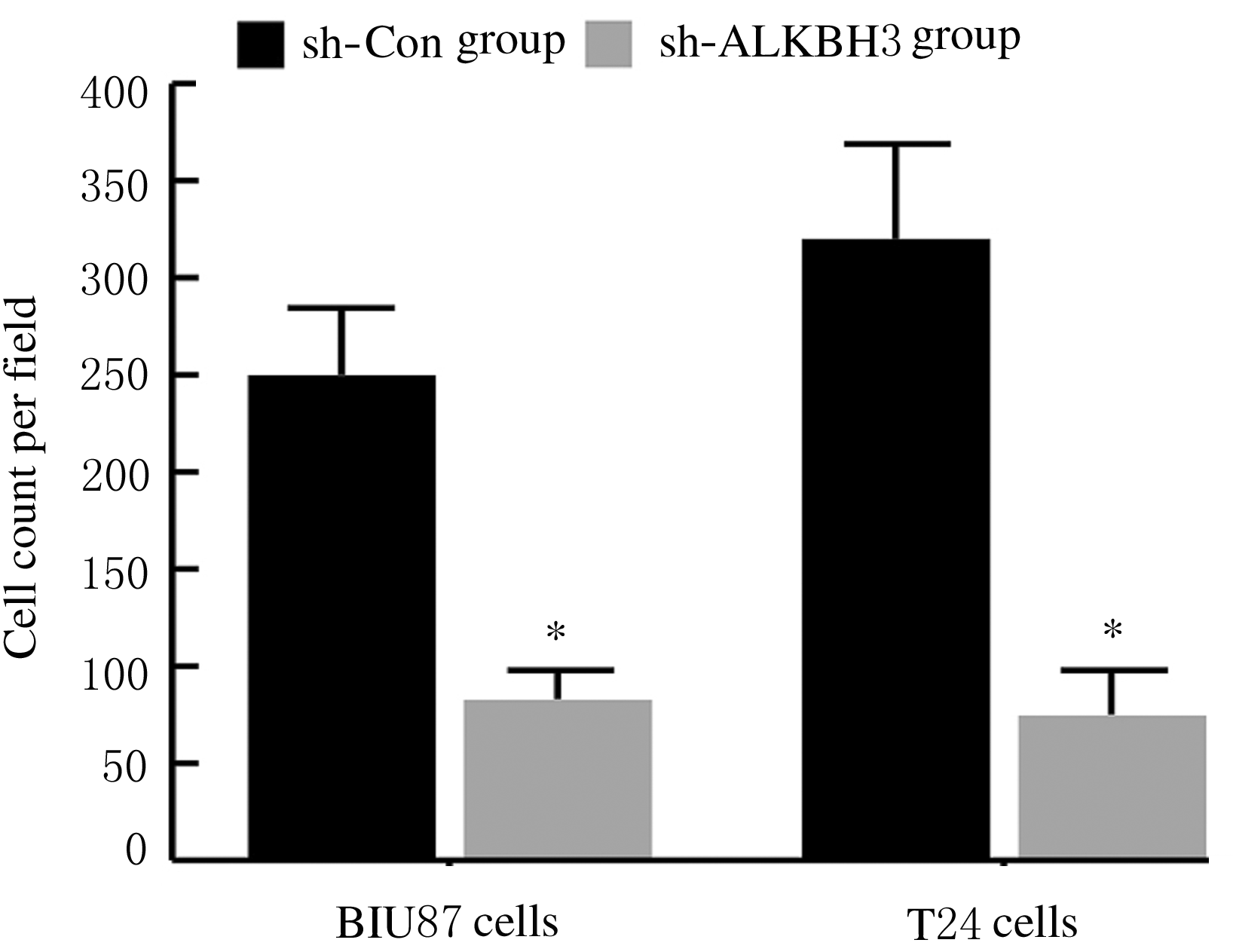
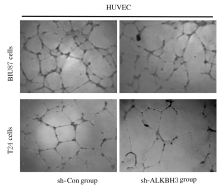
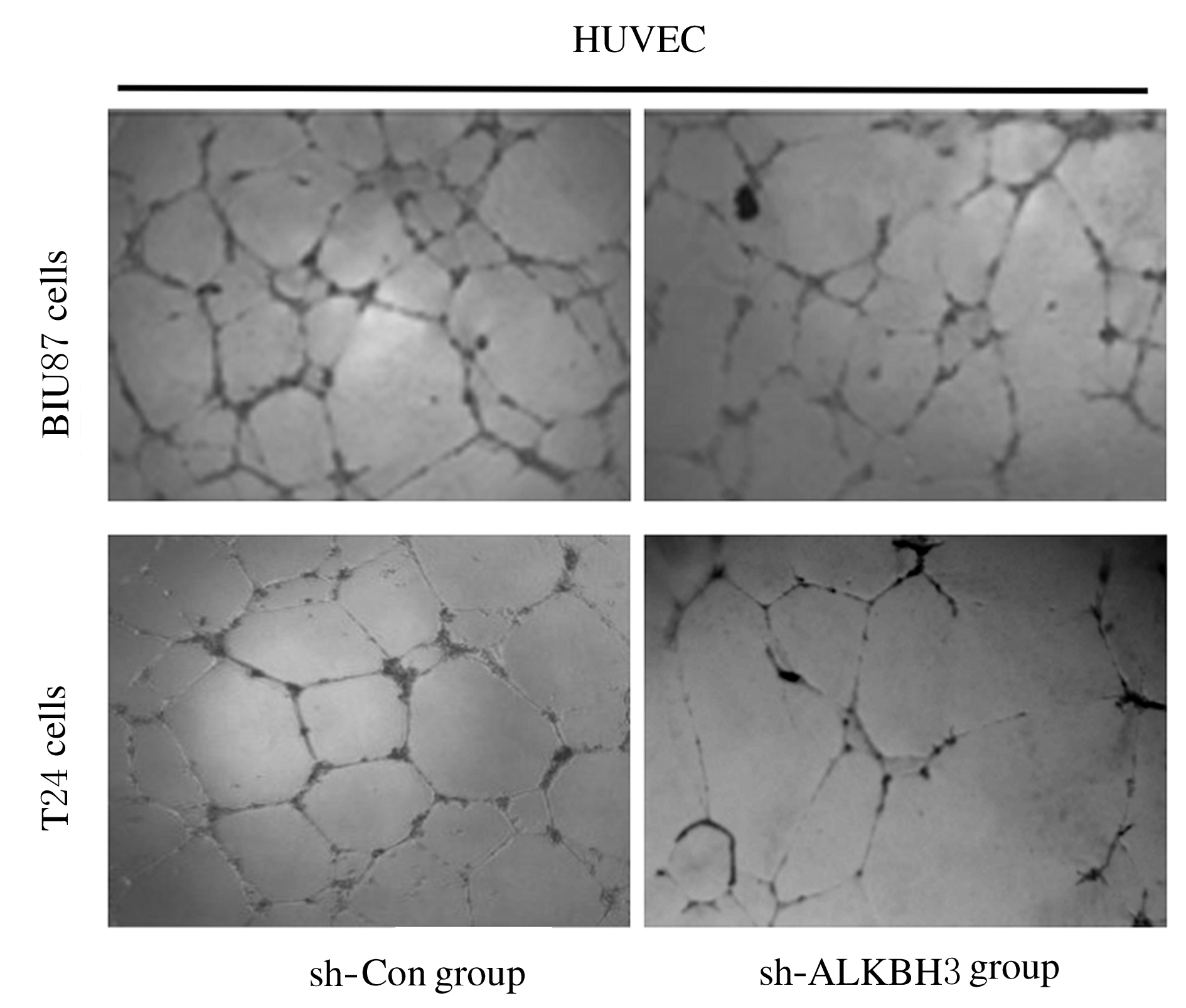
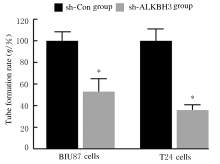
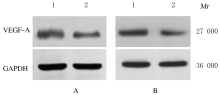
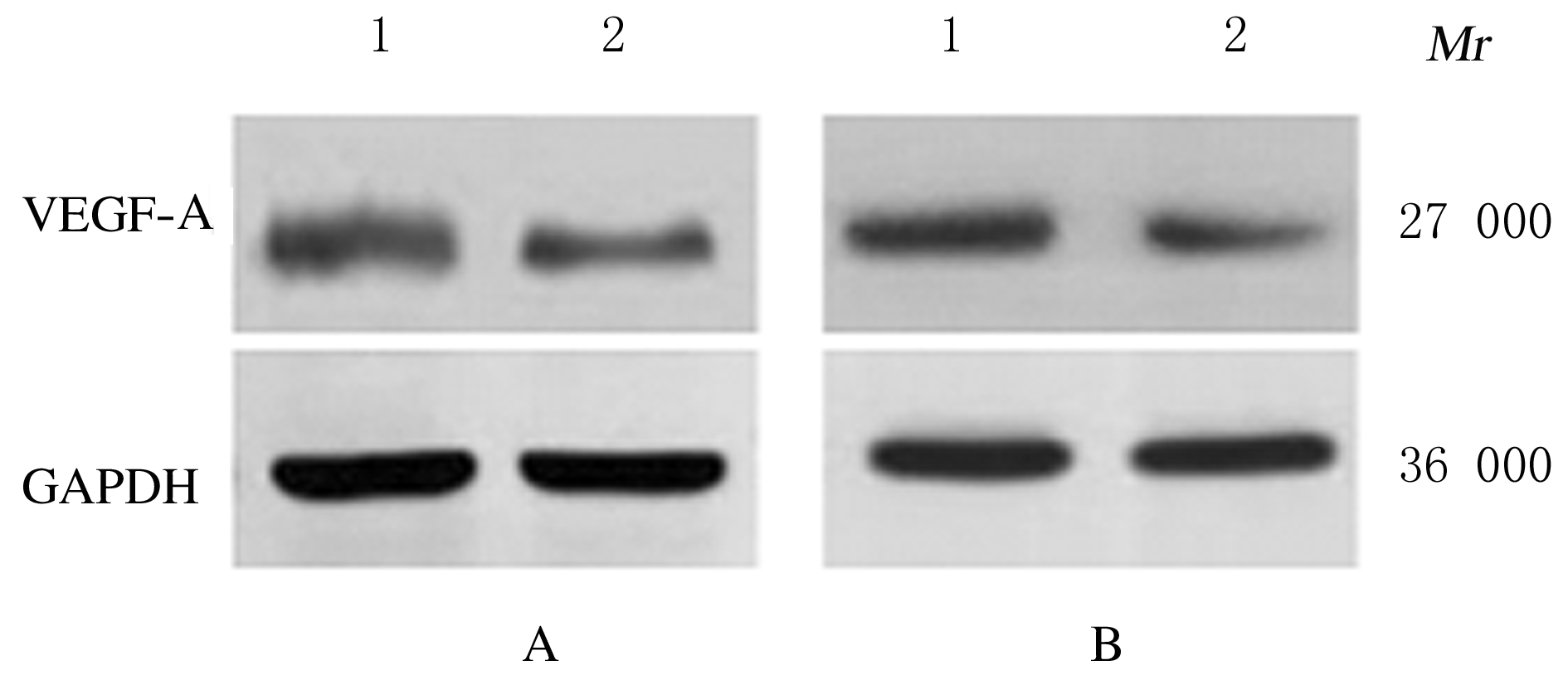
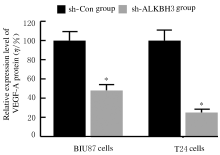
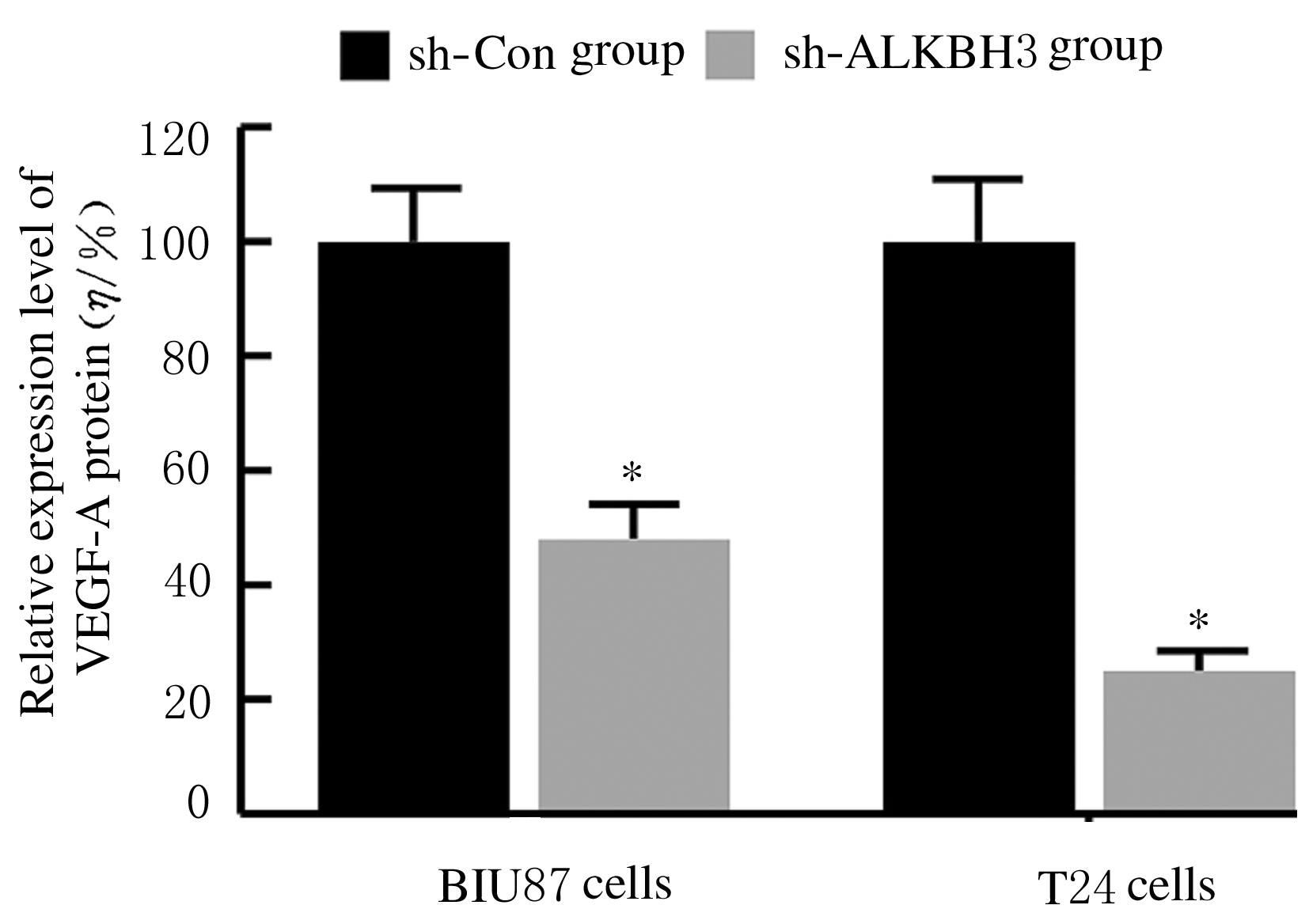
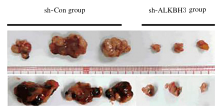
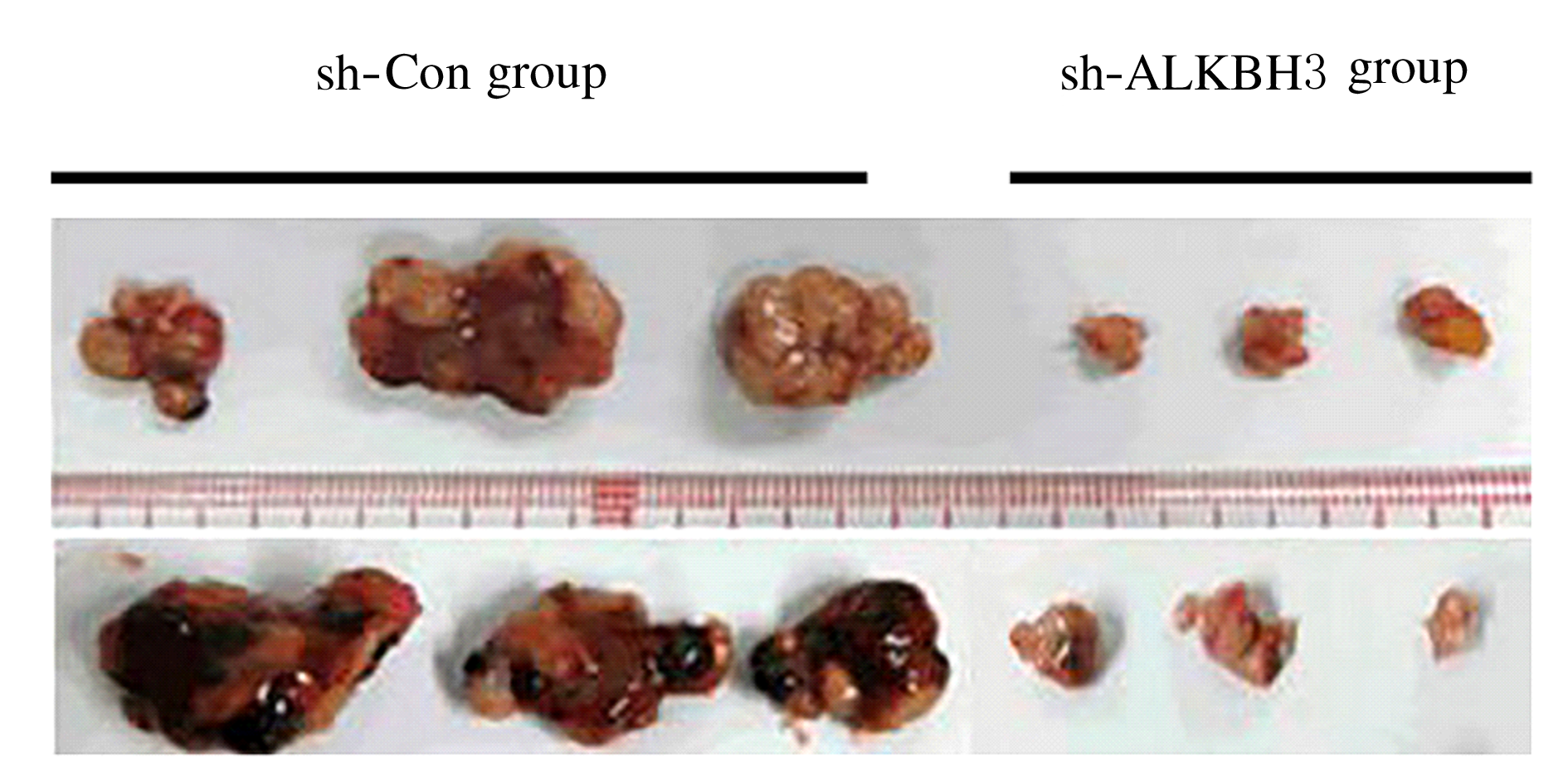
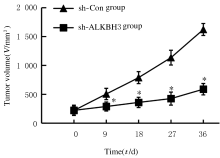
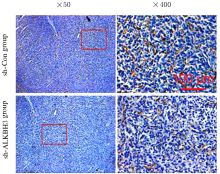
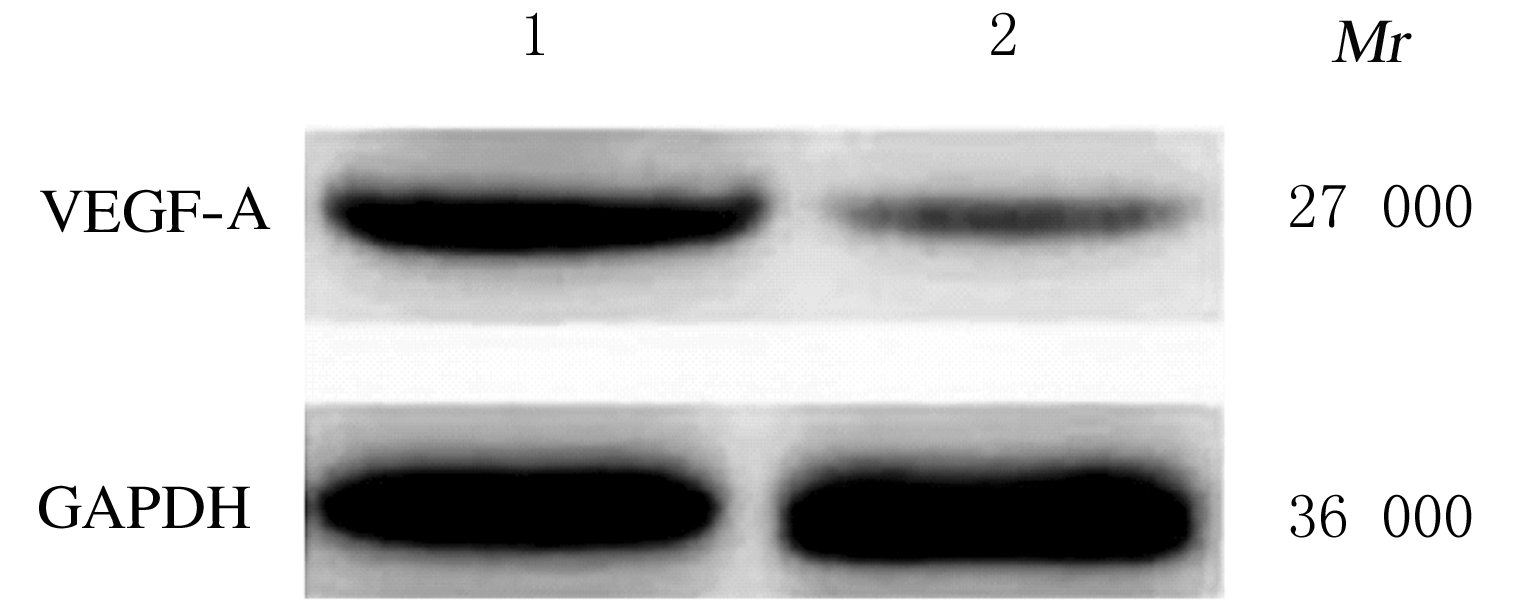
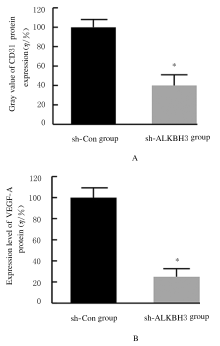
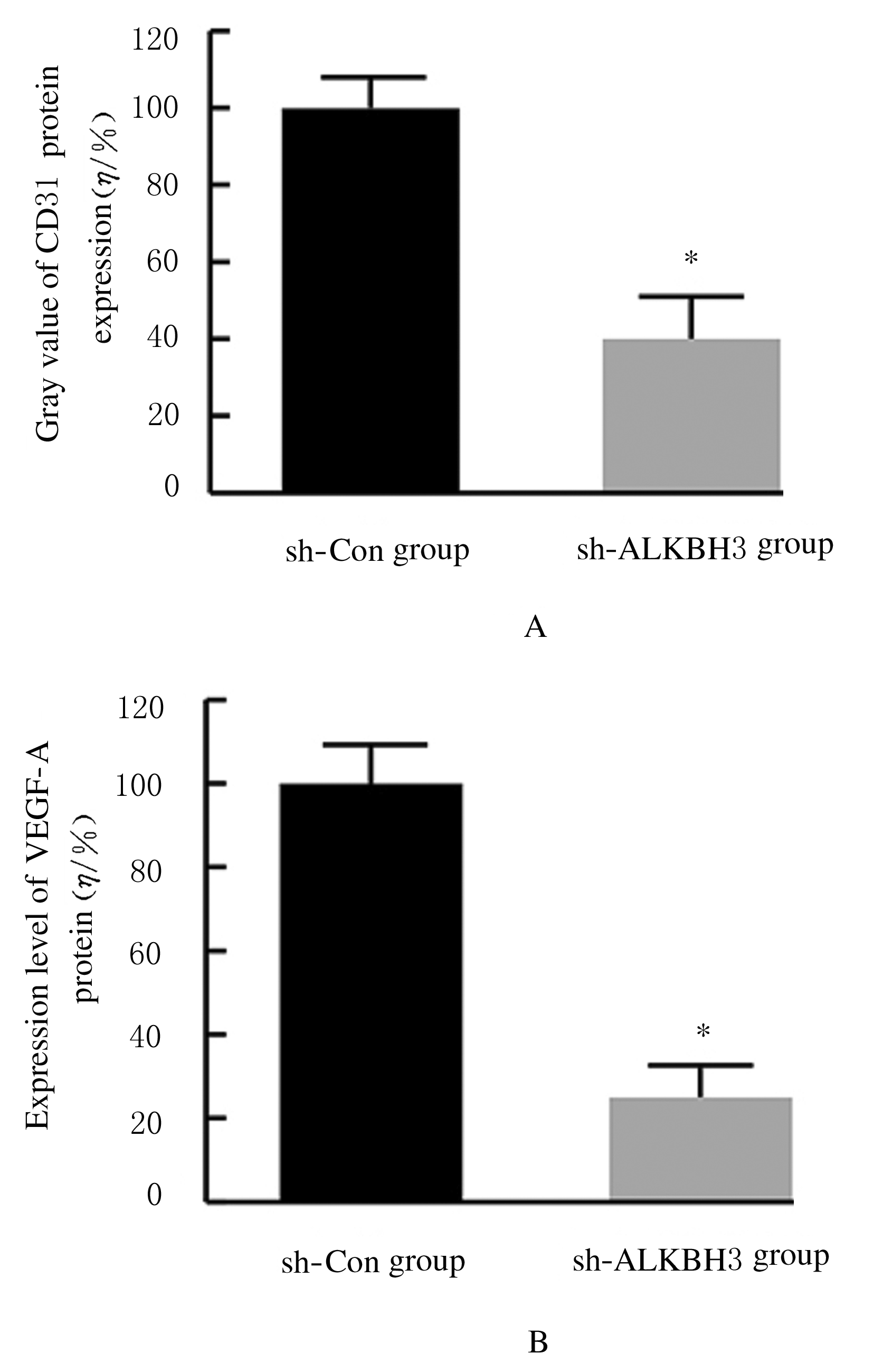
摘要: 探讨敲低烷基化修复同源体3(ALKBH3)对膀胱癌细胞生长、迁移与肿瘤血管生成的影响,并阐明其相关机制。 分别采用免疫组织化学和蛋白质印迹法检测膀胱上皮细胞癌和癌旁组织以及正常膀胱上皮细胞(SV-HRUC-1)和膀胱癌细胞(BIU87和T24)中ALKBH3蛋白表达水平。将BIU87和T24细胞分为sh-Con组(转染sh-Con)和sh-ALKBH3组(转染sh-ALKBH3)。采用CCK-8法、集落形成实验和Transwell小室实验分别检测2组细胞活性、集落数、迁移数和侵袭数。采用Transwell小室实验和小管形成实验分别检测2组细胞培养基诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)迁移数和小管形成率。构建异体移植瘤模型,采用游标卡尺定时检测2组瘤体体积,采用免疫组织化学检测瘤体组织中CD31蛋白表达水平。采用蛋白质印迹法检测体内和体外实验中2组细胞中血管内皮生长因子A(VEGF-A)蛋白表达水平。 与癌旁组织或SV-HRUC-1细胞比较,膀胱上皮细胞癌组织或膀胱癌细胞(BIU87和T24)中ALKBH3蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。体外实验,与sh-Con组比较,sh-ALKBH3组BIU87和T24细胞活性、迁移数和侵袭数以及其诱导的HUVEC迁移数和小管形成率均明显降低(P<0.01)。体内实验,与sh-Con组比较,sh-ALKBH3组瘤体体积减小(P<0.01),且瘤体组织中CD31蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。与sh-Con组比较,在体内外实验中sh-ALKBH3组VEGF-A蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01)。 敲低ALKBH3能抑制膀胱癌细胞的生长、迁移、侵袭和肿瘤血管生成,其机制可能与下调VEGF-A表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R737.14