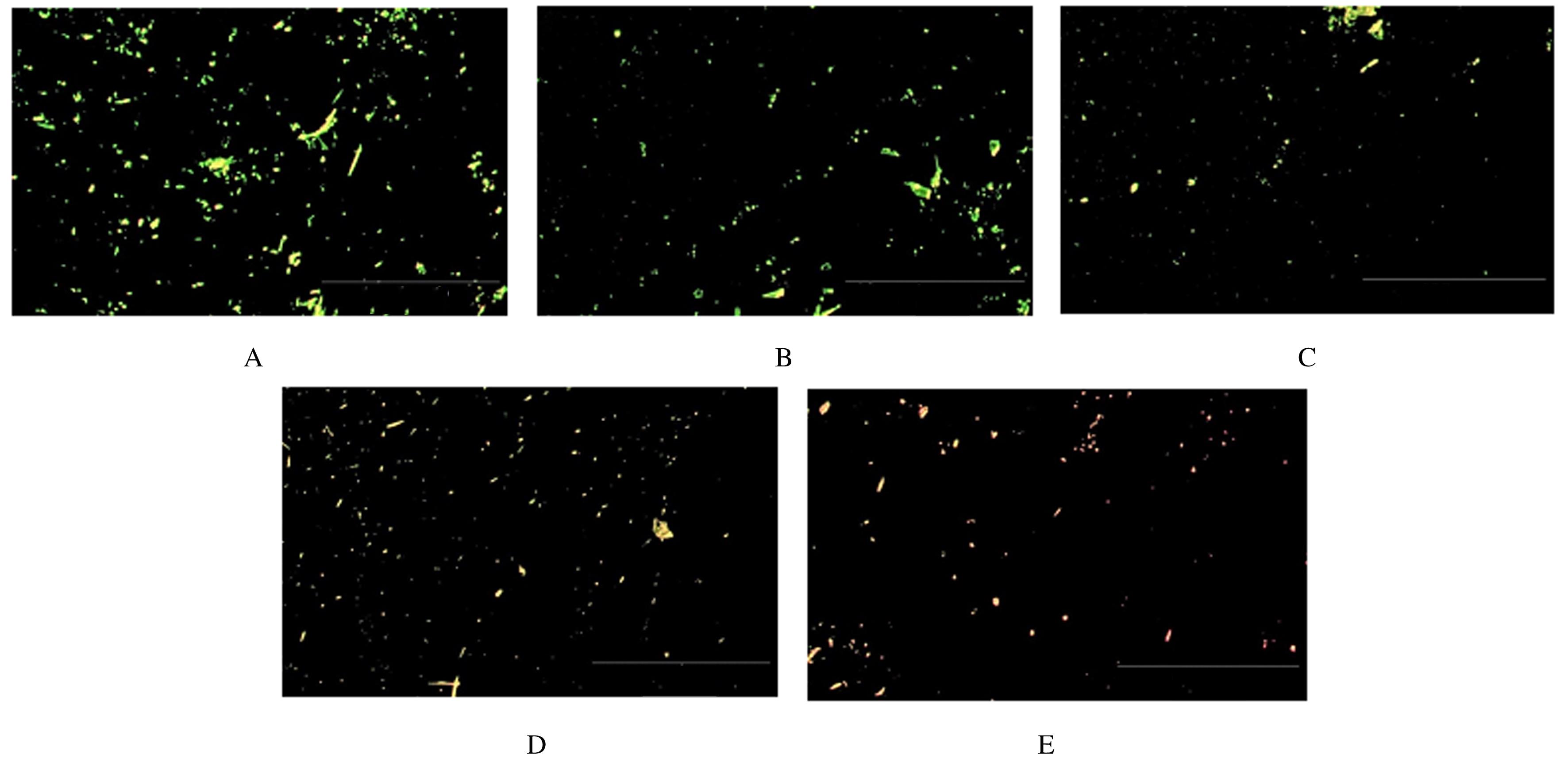
| 1 |
SU M X, YAO S Y, GU L S, et al. Antibacterial effect and bond strength of a modified dental adhesive containing the peptide nisin[J]. Peptides, 2018, 99: 189-194.
|
| 2 |
CHRYSANTHAKOPOULOS N A. Placement, replacement and longevity of composite resin-based restorations in permanent teeth in Greece[J]. Int Dent J, 2012, 62(3): 161-166.
|
| 3 |
ZHANG N, MELO M A, BAI Y, et al. Novel protein-repellent dental adhesive containing 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine[J]. J Dent, 2014, 42(10): 1284-1291.
|
| 4 |
ZHANG N, ZHANG K, WEIR M D, et al. Effects of water-aging for 6 months on the durability of a novel antimicrobial and protein-repellent dental bonding agent[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2018, 10(2): 18.
|
| 5 |
许晓虎,戴杏竹,赵望泓. 纳米防龋材料的研究进展[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2018, 26(7): 472-476.
|
| 6 |
BOUTSIOUKI C, FRANKENBERGER R, LÜCKER S, et al. Inhibition of secondary caries in vitro by addition of chlorhexidine to adhesive components[J]. Dent Mater, 2019, 35(3): 422-433.
|
| 7 |
MACHADO A H S, GARCIA I M, MOTTA A S D, et al. Triclosan-loaded chitosan as antibacterial agent for adhesive resin[J]. J Dent, 2019, 83: 33-39.
|
| 8 |
FEITOSA S A, PALASUK J, KAMOCKI K, et al. Doxycycline-encapsulated nanotube-modified dentin adhesives[J]. J Dent Res, 2014, 93(12): 1270-1276.
|
| 9 |
DELAVIZ Y, LIU T W, DEONARAIN A R, et al. Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole[J]. Dent Mater, 2019, 35(2): 229-243.
|
| 10 |
陈 慧, 程 磊. 防龋粘接材料的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2017, 44(1): 92-97.
|
| 11 |
NABAVI S M, MARCHESE A, IZADI M, et al. Plants belonging to the genus Thymus as antibacterial agents: from farm to pharmacy[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 173: 339-347.
|
| 12 |
NABAVI S F, DI LORENZO A, IZADI M, et al. Antibacterial effects of cinnamon: from farm to food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries[J]. Nutrients, 2015, 7(9): 7729-7748.
|
| 13 |
COCCO A R, ROSA W L, SILVA A F, et al. A systematic review about antibacterial monomers used in dental adhesive systems: Current status and further prospects[J]. Dent Mater, 2015, 31(11): 1345-1362.
|
| 14 |
ESTEBAN FLOREZ F L, HIERS R D, LARSON P, et al. Antibacterial dental adhesive resins containing nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2018, 93: 931-943.
|
| 15 |
YAN H Y, WANG S L, HAN L, et al. Chlorhexidine-encapsulated mesoporous silica-modified dentin adhesive[J]. J Dent, 2018, 78:83-90.
|
| 16 |
GUO X, CHENG Q, YU G, et al. The functions of hydrophobic elastic polyurethane combined with an antibacterial triclosan derivative in the dentin restoration interface[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2020, 102: 103471.
|
| 17 |
SHREAZ S, WANI W A, BEHBEHANI J M,et al. Cinnamaldehyde and its derivatives, a novel class of antifungal agents[J]. Fitoterapia, 2016, 112: 116-131.
|
| 18 |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂使用标准: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
|
| 19 |
HE T F, WANG L H, NIU D B, et al. Cinnamaldehyde inhibit Escherichia coli associated with membrane disruption and oxidative damage[J]. Arch Microbiol, 2019, 201(4): 451-458.
|
| 20 |
ELGAMILY H, SAFY R, MAKHARITA R. Influence of medicinal plant extracts on the growth of oral pathogens Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus: an In-vitro study[J]. Open Access Maced J Med Sci, 2019, 7(14): 2328-2334.
|
| 21 |
HE T F, ZHANG Z H, ZENG X A, et al. Determination of membrane disruption and genomic DNA binding of cinnamaldehyde to Escherichia coli by use of microbiological and spectroscopic techniques[J]. J Photochem Photobiol B, 2018, 178: 623-630.
|
| 22 |
LIU S, HOU Y, LIU W, et al. Components of the calcium-calcineurin signaling pathway in fungal cells and their potential as antifungal targets[J]. Eukaryot Cell, 2015, 14(4): 324-334.
|
| 23 |
WANG S Y, CHEN P F, CHANG S T. Antifungal activities of essential oils and their constituents from indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum) leaves against wood decay fungi[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2005, 96(7): 813-818.
|
| 24 |
FILHO J G, VIZOTO N L, LUIZA DE AGUIAR LOESCH M, et al. Genetic and physiological effects of subinhibitory concentrations of oral antimicrobial agents on Streptococcus mutans biofilms[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 150: 104669.
|
| 25 |
SONG Y M, ZHOU H Y, WU Y, et al. In vitro evaluation of the antibacterial properties of tea tree oil on planktonic and biofilm-forming Streptococcus mutans [J]. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2020, 21(6): 227.
|
| 26 |
AKHLAGHI N, SADEGHI M, FAZELI F, et al. The antibacterial effects of coffee extract, chlorhexidine, and fluoride against Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus plantarum: an in vitro study[J]. Dent Res J (Isfahan), 2019, 16(5): 346-353.
|
| 27 |
MARTINS M L, LEITE K L F, PACHECO-FILHO E F, et al. Efficacy of red propolis hydro-alcoholic extract in controlling Streptococcus mutans biofilm build-up and dental enamel demineralization[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2018, 93: 56-65.
|
| 28 |
LI F, CHEN J, CHAI Z, et al. Effects of a dental adhesive incorporating antibacterial monomer on the growth, adherence and membrane integrity of Streptococcus mutans[J]. J Dent,2009,37(4): 289-296.
|
| 29 |
GONG H, GUO X, CAO D, et al. Photopolymerizable and moisture-curable polyurethanes for dental adhesive applications to increase restoration durability[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2019, 7(5): 744-754.
|
 )
)