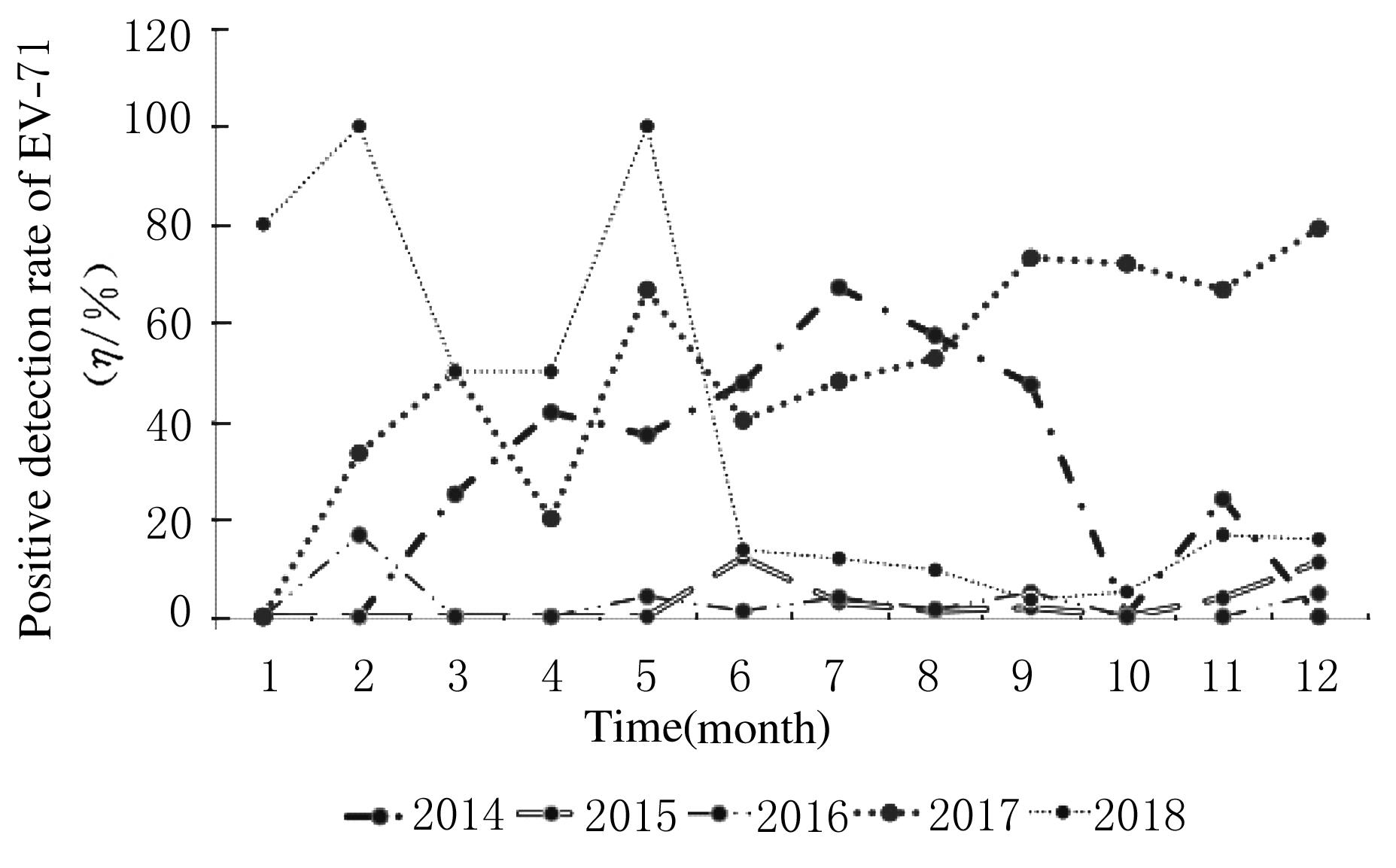
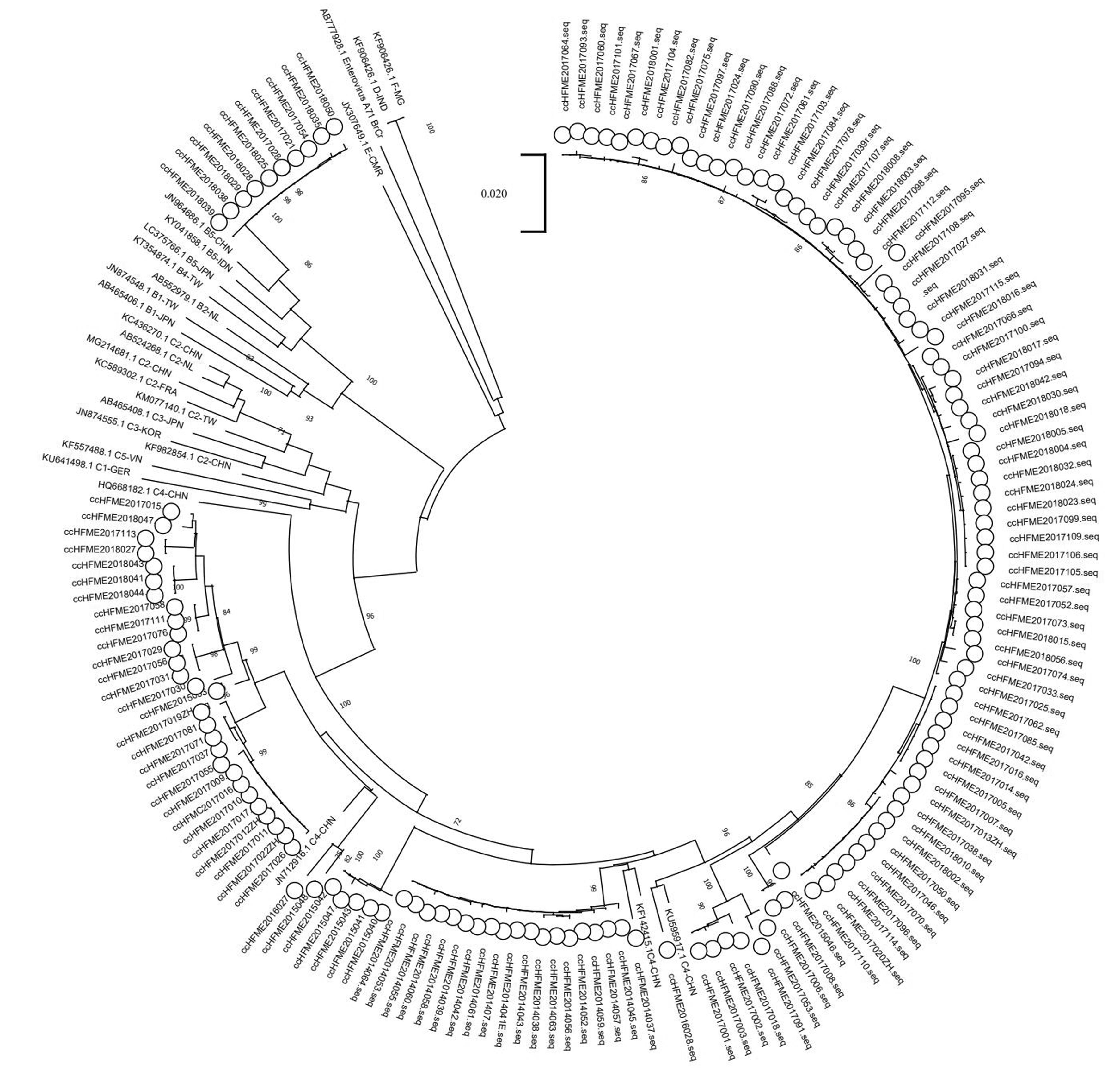
| 1 |
KOH W M, BOGICH T, SIEGEL K, et al. The epidemiology of hand, foot and mouth disease in Asia: a systematic review and analysis[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2016, 35(10): e285-e300.
|
| 2 |
CHANG L Y, HUANG L M, GAU S S, et al. Neurodevelopment and cognition in children after enterovirus 71 infection[J]. N Engl J Med, 2007,356(12): 1226-1234.
|
| 3 |
ZHANG J, SUN J L, CHANG Z R, et al. Characterization of hand, foot, and mouth disease in China between 2008 and 2009[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2011, 24(3): 214-221.
|
| 4 |
林渭淮, 郭英宁, 郭存三, 等. 吉林省流行手足口病的调查[J]. 吉林医学, 1985, 6(3): 34-37.
|
| 5 |
冯思霞.吉林省手足口病流行状况及临床特征分析[D].长春:吉林大学, 2010.
|
| 6 |
王凌燕. 长春市2011-2015年手足口病疫情特征分析及趋势预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
|
| 7 |
于 伟, 杜晓兰, 张 倩, 等. 2013-2018年辽宁省手足口病病原学监测及其分子特征分析[J]. 病毒学报, 2020, 36(1): 26-34.
|
| 8 |
国家卫生健康委员会手足口病诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中国病毒病杂志,2018,8(5):347-352.
|
| 9 |
ANG P Y, CHONG C W H, ALONSO S. Viral determinants that drive Enterovirus-A71 fitness and virulence[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2021, 10(1): 713-724.
|
| 10 |
APOSTOL L N, SHIMIZU H, SUZUKI A, et al. Molecular characterization of enterovirus-A71 in children with acute flaccid paralysis in the Philippines[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19(1): 370.
|
| 11 |
GRIFFITHS M J, OOI M H, WONG S C, et al. In enterovirus 71 encephalitis with cardio-respiratory compromise, elevated interleukin 1β, interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels are markers of poor prognosis[J]. J Infect Dis, 2012, 206(6): 881-892.
|
| 12 |
ZHAO J J, JIANG F C, ZHONG L F, et al. Age patterns and transmission characteristics of hand, foot and mouth disease in China[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16(1): 691.
|
| 13 |
曹 军, 蔡 群, 马广源, 等. 2016年-2018年无锡惠山区手足口病流行特征及CVA6型肠道病毒VP1基因特征[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2021,31(2):242-244, 248.
|
| 14 |
曹文萱, 宋志靖, 蒋小娟, 等. 天水市2014-2018年手足口病流行病学特征及病原学分析[J]. 中国初级卫生保健, 2021, 35(2): 59-62.
|
| 15 |
KIM H J, HYEON J Y, HWANG S,et al.Epidemiology and virologic investigation of human enterovirus 71 infection in the Republic of Korea from 2007 to 2012: a nationwide cross-sectional study[J].BMC Infect Dis,2016,16(1):425.
|
| 16 |
FU X M, WAN Z Z, LI Y P, et al. National epidemiology and evolutionary history of four hand, foot and mouth disease-related enteroviruses in China from 2008 to 2016[J]. Virol Sin, 2020, 35(1): 21-33.
|
| 17 |
CHUA K B, KASRI A R. Hand foot and mouth disease due to enterovirus 71 in Malaysia[J]. Virol Sin, 2011, 26(4): 221-228.
|
| 18 |
MAULEEKOONPHAIROJ J, VONGPUNSAWAD S, PUENPA J, et al. Complete genome sequence analysis of enterovirus 71 isolated from children with hand, foot, and mouth disease in Thailand, 2012-2014[J]. Virus Genes, 2015, 51(2): 290-293.
|
| 19 |
MA H C, LIU Y, WANG C L, et al. An interaction between glutathione and the capsid is required for the morphogenesis of C-cluster enteroviruses[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2014, 10(4):e1004052.
|
| 20 |
BROWN B A, OBERSTE M S, ALEXANDER J P Jr, et al. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of enterovirus 71 strains isolated from 1970 to 1998[J]. J Virol, 1999, 73(12): 9969-9975.
|
| 21 |
HAN Z Z, ZHANG Y, HUANG K Q, et al. Genetic characterization and molecular epidemiological analysis of novel enterovirus EV-B80 in China[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2018, 7(1): 193.
|
| 22 |
HUANG S W, TAI C H, FONVILLE J M, et al. Mapping enterovirus A71 antigenic determinants from viral evolution[J]. J Virol, 2015, 89(22): 11500-11506.
|
| 23 |
SANDEN S VAN DER, SACHS N, KOEKKOEK S M,et al. Enterovirus 71 infection of human airway organoids reveals VP1-145 as a viral infectivity determinant[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2018, 7(1): 84.
|
| 24 |
WANG L C, TANG S Q, LI Y M, et al. A comparison of the biological characteristics of EV71 C4 subtypes from different epidemic strains[J]. Virol Sin, 2010, 25(2): 98-106.
|
 )
)
 )
)