| 1 |
BERNARDI M, ANGELI P, CLARIA J, et al. Albumin in decompensated cirrhosis: new concepts and perspectives[J]. Gut, 2020, 69(6):1127-1138.
|
| 2 |
MEKURIA A N, ROUTLEDGE M N, GONG Y Y, et al. Aflatoxins as a risk factor for liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol, 2020, 21(1):1-8.
|
| 3 |
NISHIKAWA H, ENOMOTO H, NISHIGUCHI S, et al. Liver cirrhosis and sarcopenia from the viewpoint of dysbiosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15):5254.
|
| 4 |
MEYER F, BANNERT K, WIESE M, et al. Molecular mechanism contributing to malnutrition and sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15):5357.
|
| 5 |
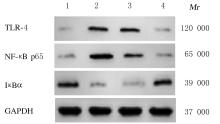
WANG J W, PAN Y B, CAO Y Q, et al. Loganin alleviates LPS-activated intestinal epithelial inflammation by regulating TLR4/NF-κB and JAK/STAT3 signaling pathways[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2020, 36(4):257-264.
|
| 6 |
顾叶云, 胡莹杰, 徐 蕾, 等. 黄芪、水蛭有效组分对经脂多糖诱导增生的大鼠肾小球系膜细胞IκB、NF-κB、PDGF-BB表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(2):866-868.
|
| 7 |
LI D Y, ZHAO L Q, LI Y X, et al. Gastro-protective effects of calycosin against precancerous lesions of gastric carcinoma in rats[J]. Drug Des Dev Ther, 2020, 14:2207-2219.
|
| 8 |
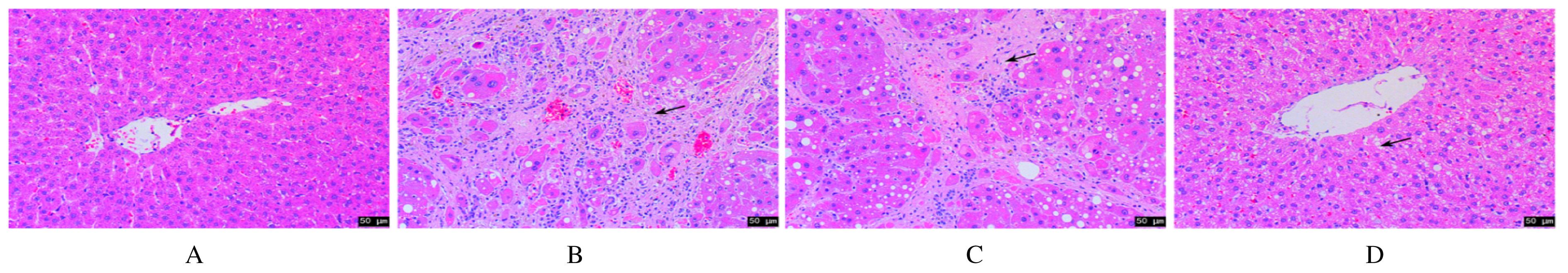
宾文婷, 常加松, 吴剑平. 四氯化碳加乙醇复合法诱导肝硬化大鼠模型的建立及验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(20):3224-3229.
|
| 9 |
高红杰. 参麦注射液对肝硬化大鼠模型肠道屏障功能的影响[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2020, 35(3):379-383.
|
| 10 |
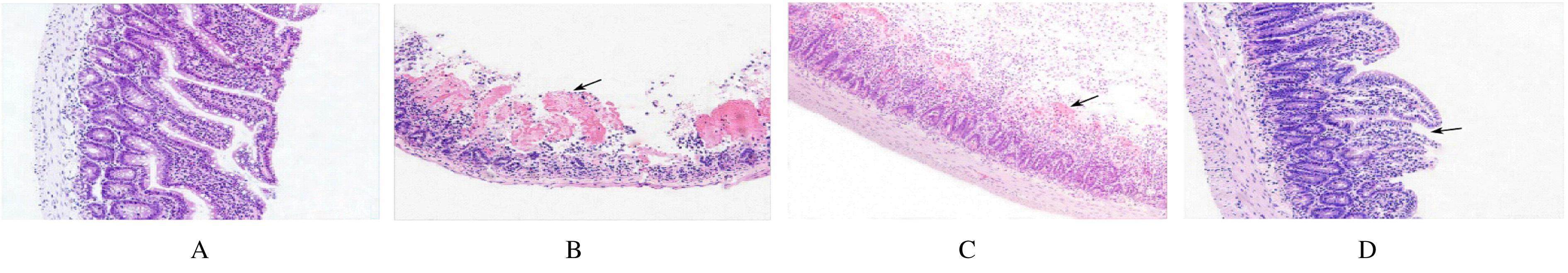
邓姗姗, 朱海涛, 陈 宇, 等. C57BL/6新生小鼠坏死性小肠结肠炎模型改建与评估[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志, 2018, 39(5):376-382.
|
| 11 |
HJORTH M, SVANBERG A, SJÖBERG D, et al. Liver cirrhosis turns life into an unpredictable roller coaster: A qualitative interview study[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2020, 29(23/24):4532-4543.
|
| 12 |
陈 韬,宁 琴.终末期肝病合并感染诊治专家共识(2021年版)[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2022,38(2):304-310.
|
| 13 |
周晓玲, 韦宛华, 陈 峭, 等. 麻黄升麻汤对肝硬化腹水并感染大鼠血清炎性因子的干预作用[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(4):1409-1414.
|
| 14 |
周 乐, 赵晓莉, 狄留庆, 等. 大鼠在体单向肠灌流模型研究毛蕊异黄酮的吸收特征[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2014, 30(2):160-163.
|
| 15 |
姚瀚勋, 李晓斌, 邱 晟, 等. 毛蕊异黄酮介导IκB/NF-κB信号通路对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(1):11-14.
|
| 16 |
PLAZA-DÍAZ J, SOLÍS-URRA P, RODRÍGUEZ-RODRÍGUEZ F, et al. The gut barrier, intestinal microbiota, and liver disease: molecular mechanisms and strategies to manage[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(21):8351.
|
| 17 |
THEN E, LUND C, UHLENHOPP D J, et al. Cirrhosis is associated with worse outcomes in ischemic colitis: A nationwide retrospective study[J]. Gastroenterol Res, 2020, 13(6):253-259.
|
| 18 |
CHO Y E, KIM D K, SEO W, et al. Fructose promotes leaky gut, endotoxemia, and liver fibrosis through ethanol-inducible cytochrome P450-2E1-mediated oxidative and nitrative stress[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(6):2180-2195.
|
| 19 |
WOODHOUSE C, SINGANAYAGAM A, PATEL V C. Modulating the gut-liver axis and the pivotal role of the faecal microbiome in cirrhosis[J]. Clin Med (Lond), 2020, 20(5):493-500.
|
| 20 |
辜雪莲,李俊峰,毛小荣.非酒精性脂肪性肝病相关肝细胞癌的研究进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2022,38(1):196-200.
|
| 21 |
WANG J, LYU W T, ZHANG W, et al. Discovery of natural products capable of inducing porcine host defense peptide gene expression using cell-based high throughput screening[J]. J Animal Sci Biotechnol, 2021, 12(1):14.
|
| 22 |
SUN Z G, HU Y Z, WANG Y G, et al. BuPiHeWei decoction ameliorates 5-Fu-Induced intestinal mucosal injury in the rats by regulating the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2019, 2019:5673272.
|
| 23 |
GRAHAM D B, XAVIER R J. Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7796):527-539.
|
| 24 |
张永虎, 张丹霞, 曾 良. 姜黄素通过TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路减轻脓毒症相关的急性肠损伤[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2020, 36(6):735-740.
|
| 25 |
ZHANG W H, SUN J K, SHEN X, et al. Effect of PA-MSAH preprocessing on the expression of TLR-4-NF-κB pathway and inflammatory factors in the intestinal tract of rats with septic shock[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 17(4):2567-2574.
|
| 26 |
CHAO L, ZHENG P, XIA L, et al. Calycosin attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis[J]. Iran J Basic Med Sci, 2017, 20(9):1056- 1062.
|