| 1 |
LI J H, WU T T, PENG W W, et al. Effects of resveratrol on cariogenic virulence properties of streptococcus mutans[J].BMCMicrobiol,2020,20(1): 99.
|
| 2 |
BEIGHTON D. The complex oral microflora of high-risk individuals and groups and its role in the caries process[J]. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol, 2005, 33(4): 248-255.
|
| 3 |
YANG Y, MAO M Y, LEI L, et al. Regulation of water-soluble glucan synthesis by the Streptococcus mutans dexA gene effects biofilm aggregation and cariogenic pathogenicity[J]. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2019, 34(2): 51-63.
|
| 4 |
BANAS J A. Virulence properties of streptococcus mutans[J]. Front Biosci, 2004, 9(1-3): 1267.
|
| 5 |
LI J J, CHA R T, LUO H Z, et al. Nanomaterials for the theranostics of obesity[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 223: 119474.
|
| 6 |
CRANE J K. Metal nanoparticles ininfection and immunity [J]. Immunol Invest, 2020, 49(7): 794-807.
|
| 7 |
LIAO C Z, LI Y C, TJONG S C. Visible-light active titanium dioxide nanomaterials with bactericidal properties[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(1): 124.
|
| 8 |
LIOU J W, CHANG H H. Bactericidal effects and mechanisms of visible light-responsive titanium dioxide photocatalysts on pathogenic bacteria[J]. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 2012, 60(4): 267-275.
|
| 9 |
IBRAHIM H M. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and inactivation of pathogenic bacteria using silver nanoparticles modified titanium dioxide thin films[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2015, 31(7): 1049-1060.
|
| 10 |
ZANE A, ZUO R F, VILLAMENA F A, et al. Biocompatibility and antibacterial activity of nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles for use in dental resin formulations[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2016, 11: 6459-6470.
|
| 11 |
SETHI D, SAKTHIVEL R. ZnO/TiO2 composites for photocatalytic inactivation of escherichia coli[J]. J Photochem Photobiol B, 2017, 168: 117-123.
|
| 12 |
ESPINOSA-CRISTÓBAL L F, MARTÍNEZ-CASTAÑÓN G A, TÉLLEZ-DÉCTOR E J, et al. Adherence inhibition of Streptococcus mutans on dental enamel surface using silver nanoparticles[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2013, 33(4): 2197-2202.
|
| 13 |
JOHNSON H A, WILLIAMSON R S, MARQUART M,et al. Photocatalytic activity and antibacterial efficacy of UVA-treated titanium oxides[J]. J Biomater Appl, 2020, 35(4/5): 500-514.
|
| 14 |
MYLONA Z, PANTERIS E, KEVREKIDIS T, et al. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on leaf cell structure and viability, and leaf elongation in the seagrass Halophila stipulacea[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2020, 719: 137378.
|
| 15 |
SUN J J, SUN J, WANG X K. Anatase TiO 2 with co-exposed (001) and (101) surface-based photocatalytic materials for energy conversion and environmental purification[J]. Chem Asian J, 2020, 15(24): 4168-4183.
|
| 16 |
SINGLA P, SHARMA M, PANDEY O P, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes using Zn-doped and undoped TiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Appl Phys A, 2014, 116(1): 371-378.
|
| 17 |
SHI Y Y, SUN B, ZHOU Z, et al. Size-controlled and large-scale synthesis of organic-soluble Ag nanocrystals in water and their formation mechanism[J]. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int, 2011, 21(6): 447-454.
|
| 18 |
CHOI J, PARK H, HOFFMANN M R. Effects of single metal-ion doping on the visible-light photoreactivity of TiO2 [J]. J Phys Chem C, 2010, 114(2): 783-792.
|
| 19 |
HOSSEINI-ZORI M. Co-doped TiO2 nanostructures as a strong antibacterial agent and self-cleaning cover: Synthesis, characterization and investigation of photocatalytic activity under UV irradiation[J]. J Photochem Photobiol B, 2018, 178: 512-520.
|
| 20 |
HU Z H, XU T, LIU P F, et al. Microstructures and optical performances of nitrogen-vanadium co-doped TiO2 with enhanced purification efficiency to vehicle exhaust[J]. Environ Res, 2021, 193: 110560.
|
| 21 |
THACKER M, CHEN Y N, LIN C P, et al. Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide mixed with calcium peroxide and methylcellulose for dental bleaching under visible light activation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(7): 3759.
|
| 22 |
AWARE D V, JADHAV S S. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic applications of Zn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by Sol-gel method[J]. Appl Nanosci, 2016, 6(7): 965-972.
|
| 23 |
ZIENTAL D, CZARCZYNSKA-GOSLINSKA B, MLYNARCZYK D T, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: prospects and applications in medicine[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2020, 10(2): 387.
|
| 24 |
HENRIKSEN-LACEY M, CARREGAL-ROMERO S, LIZ-MARZÁN L M. Current challenges toward in vitro cellular validation of inorganic nanoparticles[J]. Bioconjug Chem, 2017, 28(1): 212-221.
|
| 25 |
HORIE M, SUGINO S, KATO H, et al. Does photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles correspond to photo-cytotoxicity? Cellular uptake of TiO2 nanoparticles is important in their photo-cytotoxicity[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2016, 26(4): 284-294.
|
| 26 |
PIGEOT-RÉMY S, SIMONET F, ERRAZURIZ-CERDA E, et al. Photocatalysis and disinfection of water: identification of potential bacterial targets[J]. Appl Catal B Environ, 2011, 104(3/4): 390-398.
|
| 27 |
SONDI I, SALOPEK-SONDI B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2004, 275(1): 177-182.
|
| 28 |
MEURER L, PAYNE W, GUFFEY J S. Visible light as an inhibitor of campylobacter jejuni[J]. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2020, 55(1): 105818.
|
| 29 |
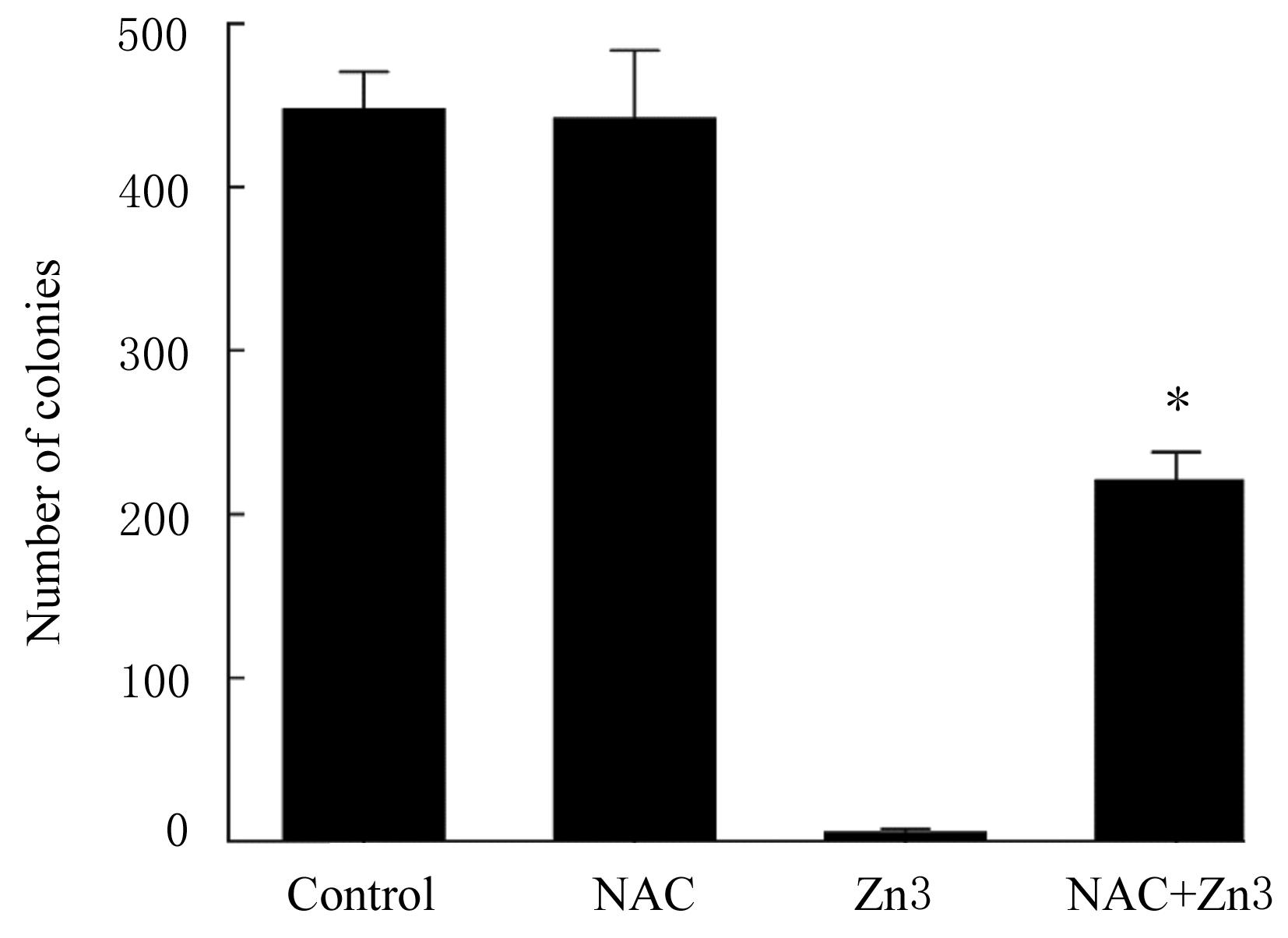
DODD S, DEAN O, COPOLOV D L, et al. N-acetylcysteine for antioxidant therapy: pharmacology and clinical utility[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2008, 8(12): 1955-1962.
|
 ),张红1(
),张红1( )
)
 ),Hong ZHANG1(
),Hong ZHANG1( )
)