吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1243-1249.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240507
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
新型抗癫痫药Q808对颞叶癫痫大鼠的改善作用及其机制
- 延边大学附属医院儿科,吉林 延吉 133000
Ameliorative effect of novel antiepileptic drug Q808 on rats with temporal lobe epilepsy and its mechanism
Weiwei ZHENG,Fan GAO,Zhenlin YANG,Jiarui LI,Jingjing GUO,Jinzi LI( )
)
- Department of Pediatrics,Affiliated Hospital,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China
摘要:
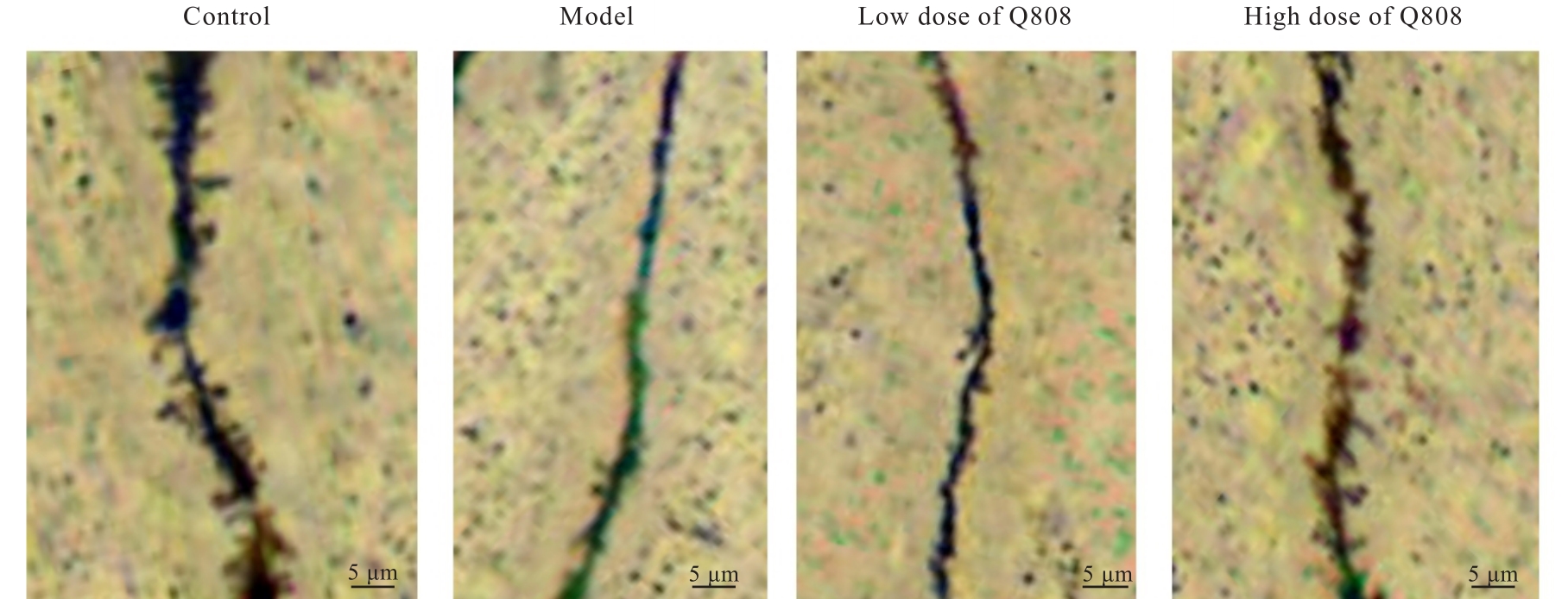
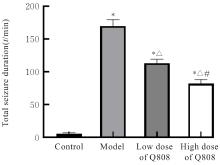
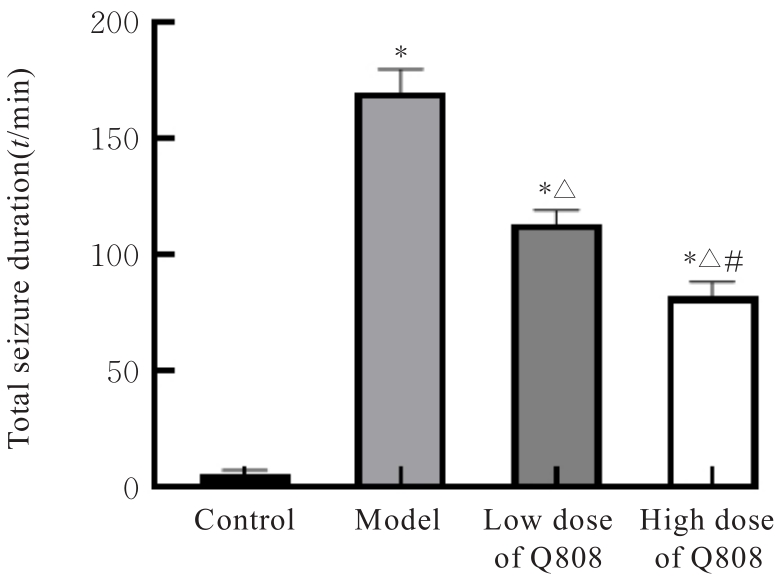
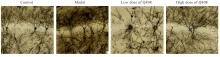
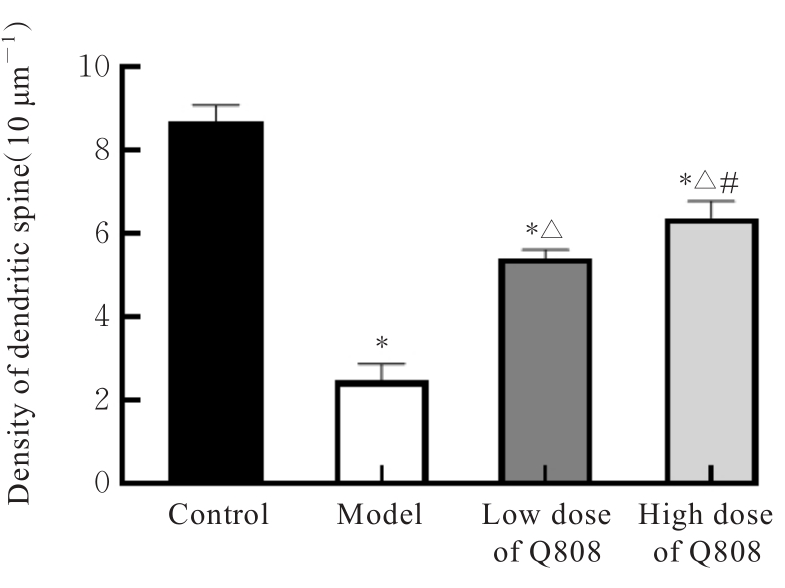
目的 探讨新型抗癫痫药6-(4-氯苯氧基)-四唑(5,1-a)酞嗪(Q808)对颞叶癫痫(TLE)大鼠神经元损伤的改善作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 采用腹腔注射Q808的方法制备TLE大鼠模型。将45只造模成功大鼠随机分为模型组、低剂量Q808组和高剂量Q808组,每组15只,低剂量Q808组和高剂量Q808组大鼠分别采用20和80 mg·kg-1 Q808灌胃,模型组大鼠采用等量0.3%羧甲纤维素钠灌胃,另选15只健康SD大鼠作为对照组。持续灌胃治疗4周后,观察各组大鼠行为表现,采用PONEMAH 6.X实验动物遥测平台记录各组大鼠脑电图,采用高尔基染色观察各组大鼠海马CA1神经元树突形态表现和神经元树突棘密度,采用Western blotting法检测各组大鼠海马组织中突触可塑性特异性蛋白钙/钙调素依赖性蛋白激酶Ⅱ(CaMKⅡ)蛋白表达水平。 结果 对照组大鼠活动正常,无抽搐等异常表现;模型组、低剂量Q808和高剂量Q808组大鼠出现不同程度活动减少、震颤点头、失去平衡、肌肉强直和前肢的抽搐,逐渐转变为全身肌肉强直和站立,随后向后跌倒,发作间期无抽搐发作。与对照组比较,模型组、低剂量Q808和高剂量Q808组大鼠癫痫发作总持续时间明显延长(P<0.01);与模型组比较,低剂量Q808和高剂量Q808组大鼠癫痫发作总持续时间明显缩短(P<0.01)。对照组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元树突分布较为规律,树突网密集有序;模型组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元树突排列紊乱,大量树突缠结,形成较粗大的神经纤维束;与模型组比较,低剂量Q808和高剂量Q808组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元树突网络有所恢复,排列相对规律。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元树突棘密度明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,低剂量Q808和高剂量Q808组大鼠海马组织CA1区神经元树突棘密度明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组、低剂量Q808组和高剂量Q808组大鼠海马组织中CaMKⅡ蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,低剂量Q808组和高剂量Q808组大鼠海马组织中CaMKⅡ蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。 结论 新型抗癫痫药Q808对TLE模型大鼠有改善作用,其机制可能与Q808能减轻海马组织CA1区神经元树突病变和增加突触可塑性相关蛋白CaMKⅡ蛋白表达水平有关。
中图分类号:
- R742.1