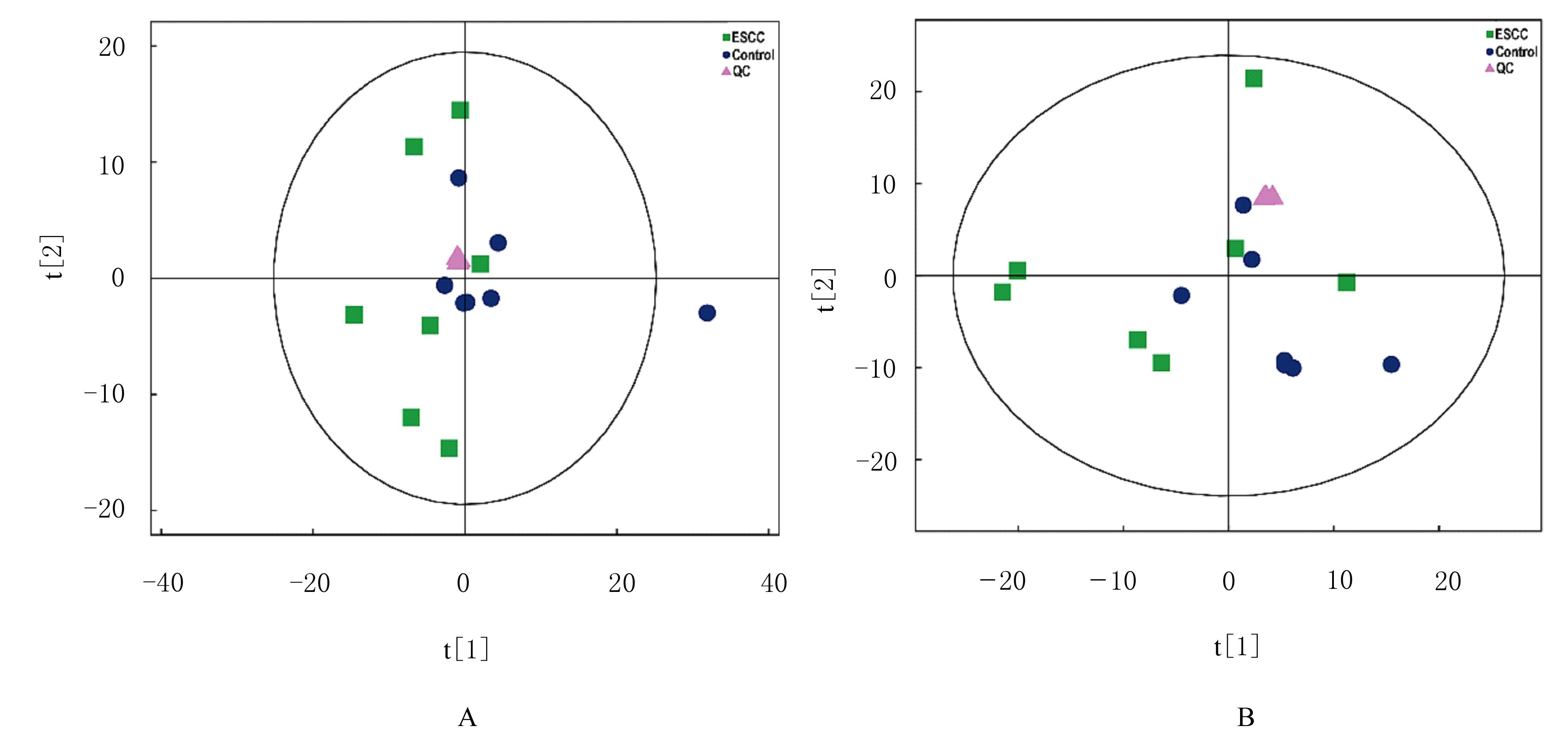
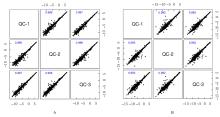
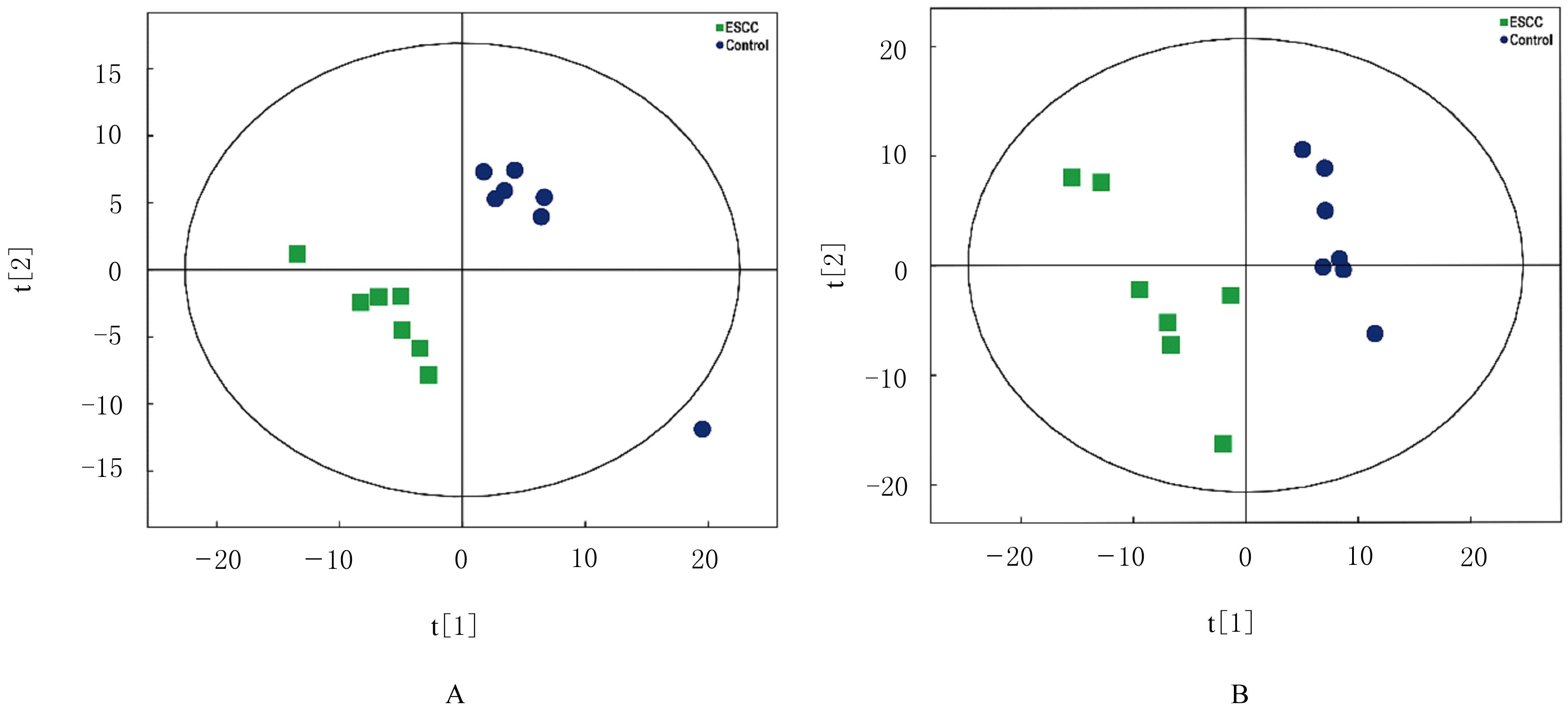
| 1 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249.
|
| 2 |
RUSTGI A K, EL-SERAG H B. Esophageal carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(26): 2499-2509.
|
| 3 |
PENNATHUR A, GIBSON M K, JOBE B A, et al. Oesophageal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2013, 381(9864): 400-412.
|
| 4 |
ZHANG X L, XU L, SHEN J M, et al. Metabolic signatures of esophageal cancer: NMR-based metabolomics and UHPLC-based focused metabolomics of blood serum[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2013,1832(8): 1207-1216.
|
| 5 |
王华光, 刘心娟, 雷圆圆, 等. 食管癌相关生物标志物的代谢组学研究进展[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2022, 29(14): 1080-1086.
|
| 6 |
BLAŽENOVIĆ I, KIND T, JI J,et al. Software tools and approaches for compound identification of LC-MS/MS data in metabolomics[J].Metabolites,2018,8(2): 31.
|
| 7 |
LUO D, DENG T T, YUAN W, et al. Plasma metabolomic study in Chinese patients with wet age-related macular degeneration[J]. BMC Ophthalmol, 2017, 17(1): 165.
|
| 8 |
GU Z B, LI L, TANG S K, et al. Metabolomics reveals that crossbred dairy buffaloes are more thermotolerant than Holstein cows under chronic heat stress[J].J Agric Food Chem,2018,66(49):12889-12897.
|
| 9 |
XUAN Q H, OUYANG Y, WANG Y F, et al. Multiplatform metabolomics reveals novel serum metabolite biomarkers in diabetic retinopathy subjects[J]. Adv Sci, 2020, 7(22): 2001714.
|
| 10 |
YANG T, HUI R T, NOUWS J, et al. Untargeted metabolomics analysis of esophageal squamous cell cancer progression[J]. J Transl Med, 2022, 20(1): 127.
|
| 11 |
VETTORE L, WESTBROOK R L, TENNANT D A. New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(2): 150-156.
|
| 12 |
吴清平, 周小燕. L-苹果酸研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 1990, 17(1): 30-33.
|
| 13 |
吴军林, 吴清平, 张菊梅. L-苹果酸的生理功能研究进展[J]. 食品科学, 2008, 29(11): 692-695.
|
| 14 |
LEONARDI R, SUBRAMANIAN C, JACKOWSKI S,et al. Cancer-associated isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations inactivate NADPH-dependent reductive carboxylation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(18): 14615-14620.
|
| 15 |
CHANG S, YIM S, PARK H. The cancer driver genes IDH1/2, JARID1C/KDM5C, and UTX/KDM6A: crosstalk between histone demethylation and hypoxic reprogramming in cancer metabolism[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2019, 51(6): 1-17.
|
| 16 |
CHEN X, XU W Z, WANG C, et al. The clinical significance of isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2017, 7(3): 700-714.
|
| 17 |
YAN H, PARSONS D W, JIN G L, et al. IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 360(8): 765-773.
|
| 18 |
魏 晨, 徐瑞华, 鞠怀强. 三羧酸循环的代谢物与肿瘤发生相关性的研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2021, 48(21): 1088-1092.
|
| 19 |
KISHTON R J, BARNES C E, NICHOLS A G, et al. AMPK is essential to balance glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolism to control T-ALL cell stress and survival[J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 23(4): 649-662.
|
| 20 |
ANDERSON N M, MUCKA P, KERN J G, et al. The emerging role and targetability of the TCA cycle in cancer metabolism[J].Protein Cell,2018,9(2): 216-237.
|
| 21 |
FLAVENY C A, GRIFFETT K, EL-GENDY B E D M,et al. Broad anti-tumor activity of a small molecule that selectively targets the Warburg effect and lipogenesis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2015, 28(1): 42-56.
|
| 22 |
LI Y M, BECK M, PÄßLER T, et al. A FDG-PET radiomics signature detects esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients who do not benefit from chemoradiation[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 17671.
|
| 23 |
ICARD P, SHULMAN S, FARHAT D, et al. How the Warburg effect supports aggressiveness and drug resistance of cancer cells?[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2018, 38: 1-11.
|
| 24 |
RAZ S, SHEBAN D, GONEN N, et al. Severe hypoxia induces complete antifolate resistance in carcinoma cells due to cell cycle arrest[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2014, 5(2): e1067.
|
| 25 |
CUI Y Y, YANG D W, WANG W J, et al. Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase decreases 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through metabolic reprogramming and promoting the Warburg effect[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2020, 59(8): 940-954.
|
 )
)