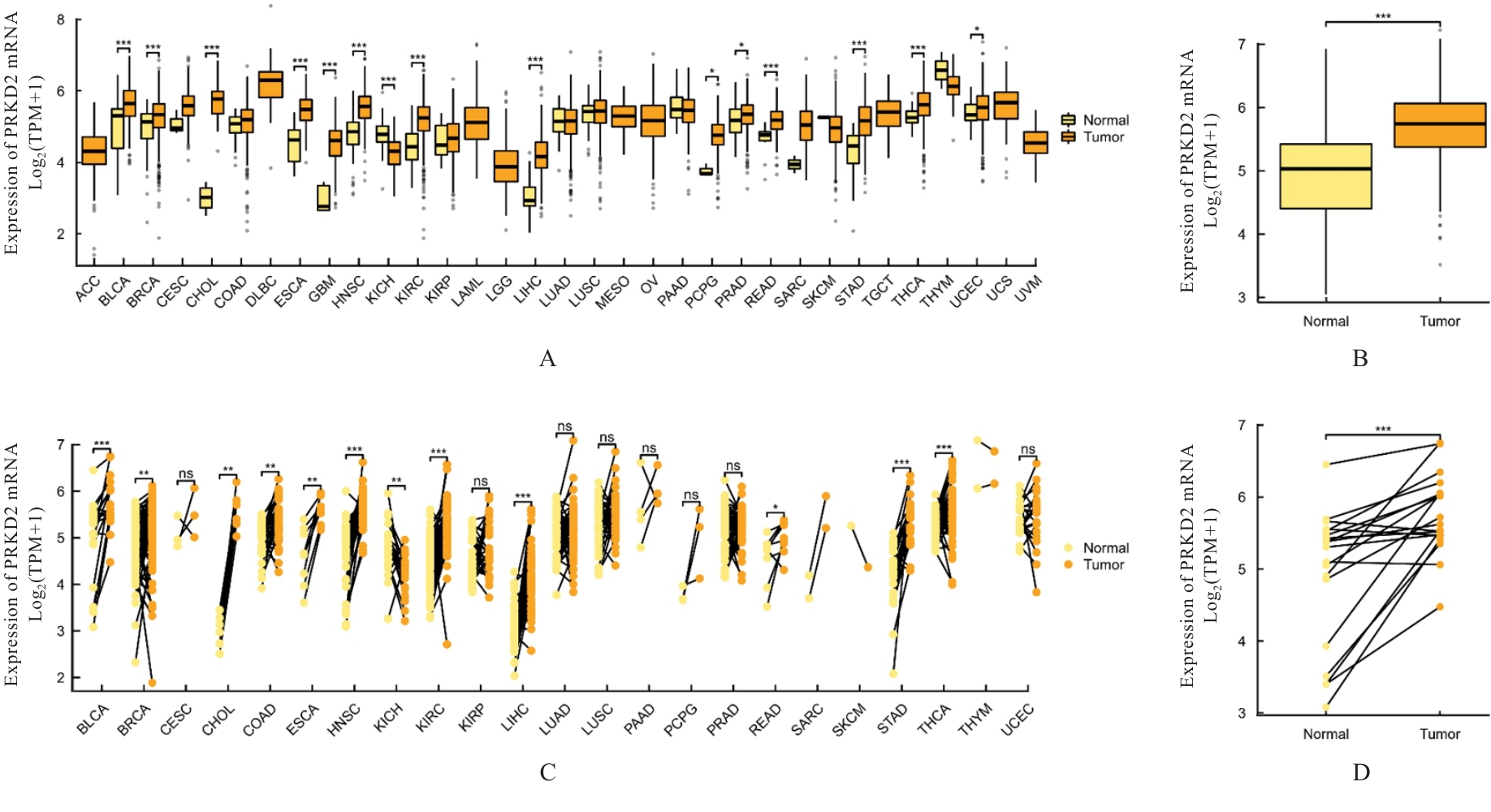
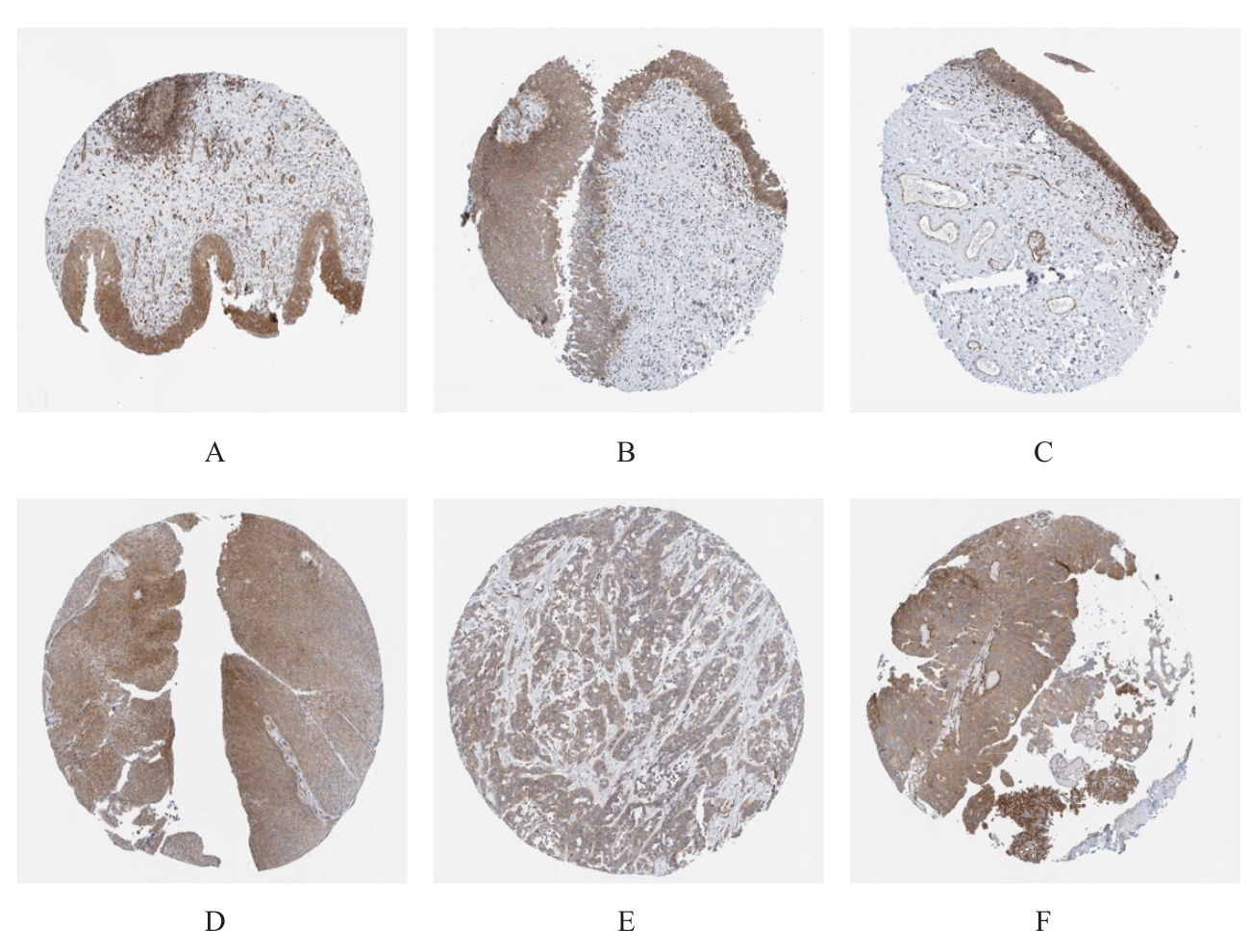
| 1 |
HUANG Q, ZI H, LUO L S, et al. Secular trends of morbidity and mortality of prostate, bladder, and kidney cancers in China, 1990 to 2019 and their predictions to 2030[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 1164.
|
| 2 |
BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-263.
|
| 3 |
FENG R J, WANG X, CHEN H W, et al. Knockdown of PRKD2 enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in cervical cancer via the TP53/CDKN1A pathway[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2023, 23(2): 159-170.
|
| 4 |
LIU Y Q, XU Y W, ZHENG Z T, et al. Serine/threonine-protein kinase D2-mediated phosphorylation of DSG2 threonine 730 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression[J]. J Pathol, 2024. 263(1): 99-112.
|
| 5 |
CHALFANT V, RIVEROS C, SINGH P, et al. Potential role for protein kinase D inhibitors in prostate cancer[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2023,101(4): 341-349.
|
| 6 |
AZOITEI N, DIEPOLD K, BRUNNER C, et al. HSP90 supports tumor growth and angiogenesis through PRKD2 protein stabilization[J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(23): 7125-7136.
|
| 7 |
VIVIAN J, RAO A A, NOTHAFT F A, et al. Toil enables reproducible, open source, big biomedical data analyses[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2017, 35(4): 314-316.
|
| 8 |
LOVE M I, HUBER W, ANDERS S, et al. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550.
|
| 9 |
YU G C, WANG L G, HAN Y Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters [J]. Omics, 2012, 16(5): 284-287.
|
| 10 |
HÄNZELMANN S, CASTELO R, GUINNEY J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data [J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013,14: 7.
|
| 11 |
BINDEA G, MLECNIK B, TOSOLINI M, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer [J]. Immunity, 2013, 39(4): 782-795.
|
| 12 |
LIU J F, LICHTENBERG T, HOADLEY K A A, et al. An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics[J]. Cell, 2018,173(2): 400-416.e11.
|
| 13 |
季新灿, 郭浩阳, 汪伟,等. 1990—2019年中国膀胱癌发病率趋势[J]. 济宁医学院学报, 2023, 46(2): 90-95.
|
| 14 |
LENIS A T, LEC P M, CHAMIE K, et al. Bladder cancer: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(19): 1980-1991.
|
| 15 |
LYU Z, JIN H W, YAN Z J, et al. Effects of NRP1 on angiogenesis and vascular maturity in endothelial cells are dependent on the expression of SEMA4D[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2020, 46(4): 1321-1334.
|
| 16 |
RUSSELL S K, HARRISON J K, OLSON B S, et al. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli infection-induced epithelial trained immunity impacts urinary tract disease outcome[J]. Nat Microbiol, 2023, 8(5):875-888.
|
| 17 |
JAMES C, GOMEZ K, DESAI S L, et al. Impact of intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin and chemotherapy on the bladder microbiome in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13:1125809.
|
| 18 |
DROBNER J C, LICHTBROUN B J, SINGER E A, et al. Examining the role of microbiota-centered interventions in cancer therapeutics: applications for urothelial carcinoma[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2023, 22: 15330338231164196.
|
| 19 |
ANTONELLI L, SEBRO K, LAHMAR A, et al.Association between antibiotic prophylaxis before cystectomy or stent removal and infection complications: A systematic review[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2023, 9(4): 631-636.
|
| 20 |
WU P, ZHANG G, ZHAO J, et al. Profiling the urinary microbiota in male patients with bladder cancer in china[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2018, 8:167.
|
| 21 |
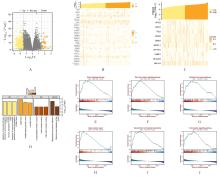
MARAVER A, FERNANDEZ-MARCOS P J, CASH T P, et al. NOTCH pathway inactivation promotes bladder cancer progression[J]. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125(2): 824-830.
|
| 22 |
ZHANG L, LI Y Q, ZHOU L L, et al. The m6A reader YTHDF2 promotes bladder cancer progression by suppressing RIG-I-mediated immune response[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(11): 1834-1850.
|
| 23 |
XIE H, GONG Y L, DAI J Y, et al. Genetic variations in base excision repair pathway and risk of bladder cancer: a case-control study in the United States[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2015, 54(1): 50-57.
|
| 24 |
LIU Y B, YANG W G, ZHAO L J, et al. Immune analysis of expression of IL-17 relative ligands and their receptors in bladder cancer: comparison with polyp and cystitis[J]. BMC Immunol, 2016, 17(1): 36.
|
| 25 |
叶德宇, 杨帅, 赵龙龙, 等. 炎性标志物对恶性肿瘤发生发展和预后的影响及其机制的研究进展 [J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(4): 1079-1087.
|
| 26 |
李瑞杰, 宁艺萍, 袁亚成, 等. 铁死亡的分子机制及其对膀胱癌的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2024, 49(2): 286-295.
|
| 27 |
CHEN Z H, ZHOU L J, LIU L L, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing highlights the role of inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts in bladder urothelial carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5077.
|
| 28 |
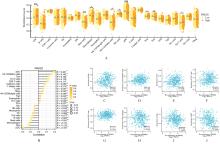
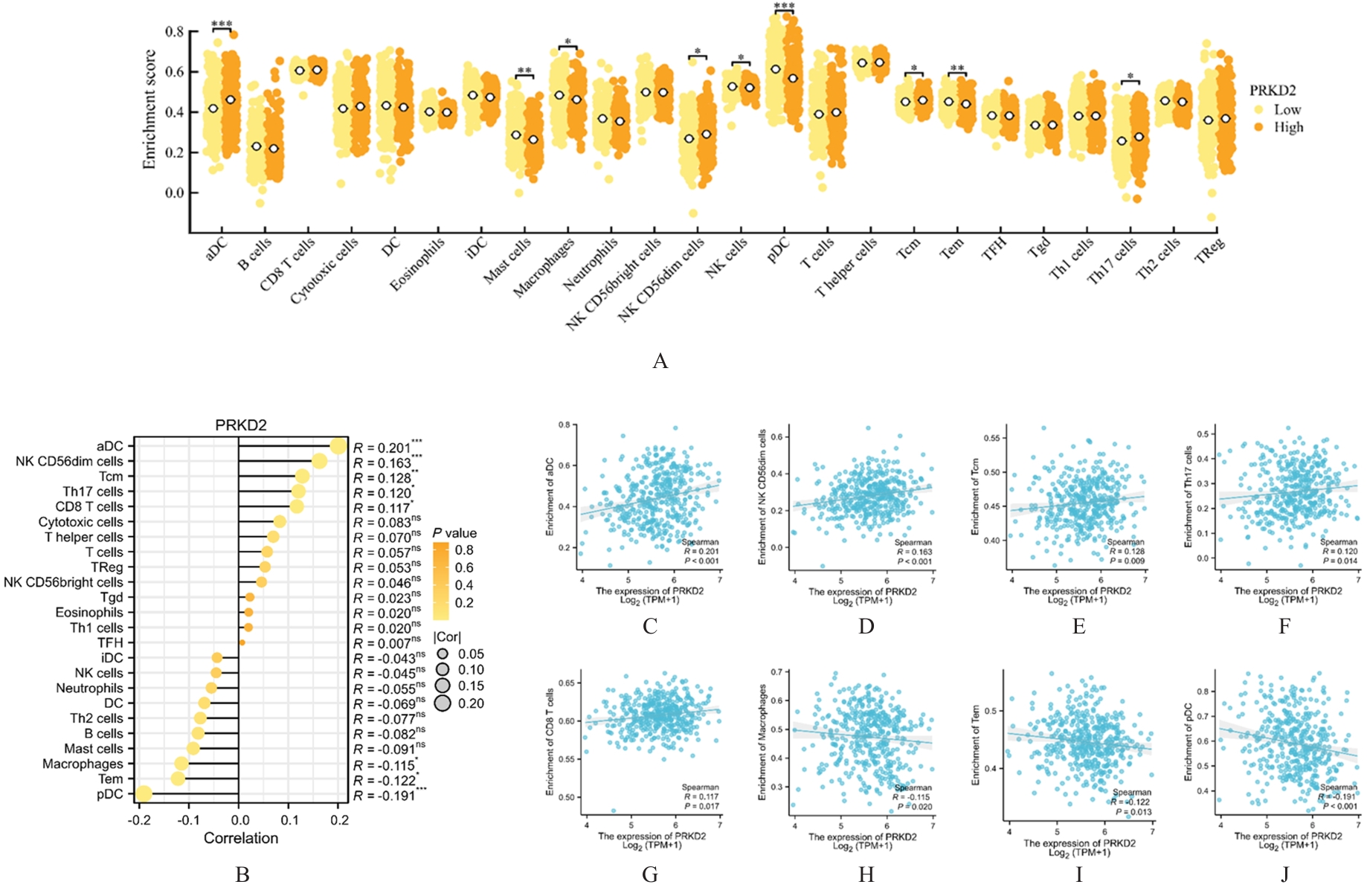
MUKHERJEE N, JI N N, TAN X, et al. KLRF1, a novel marker of CD56(bright) NK cells, predicts improved survival for patients with locally advanced bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2023, 12(7): 8970-8980.
|
| 29 |
RUBIO C, MUNERA-MARAVILLA E, LODEWIJK I, et al. Macrophage polarization as a novel weapon in conditioning tumor microenvironment for bladder cancer: can we turn demons into gods?[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2019, 21(4): 391-403.
|
| 30 |
CHEN J Q, SALAS L A, WIENCKE J K, et al. Genome-scale methylation analysis identifies immune profiles and age acceleration associations with bladder cancer outcomes[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2023, 32(10):1328-1337.
|
| 31 |
LIU Y, SONG H, ZHOU Y H, et al.The oncogenic role of protein kinase D3 in cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(3): 735-739.
|
| 32 |
GRIVENNIKOV S I, GRETEN F R, KARIN M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer[J]. Cell, 2010, 140(6):883-899.
|
 )
)
 )
)