吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 680-690.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250313
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
赤芍活性成分联合应用对粪肠球菌的抑制作用及其机制
- 吉林大学口腔医院牙体牙髓科,吉林 长春 130021
Inhibitory effect of combined application of active components of Paeoniae Rubra Radix on Enterococcus faecalis and its mechanism
Jiani ZHANG,Jie SAI,Yu ZHOU,Miao YANG,Shufen SUN( )
)
- Department of Endodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
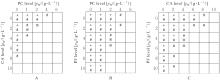
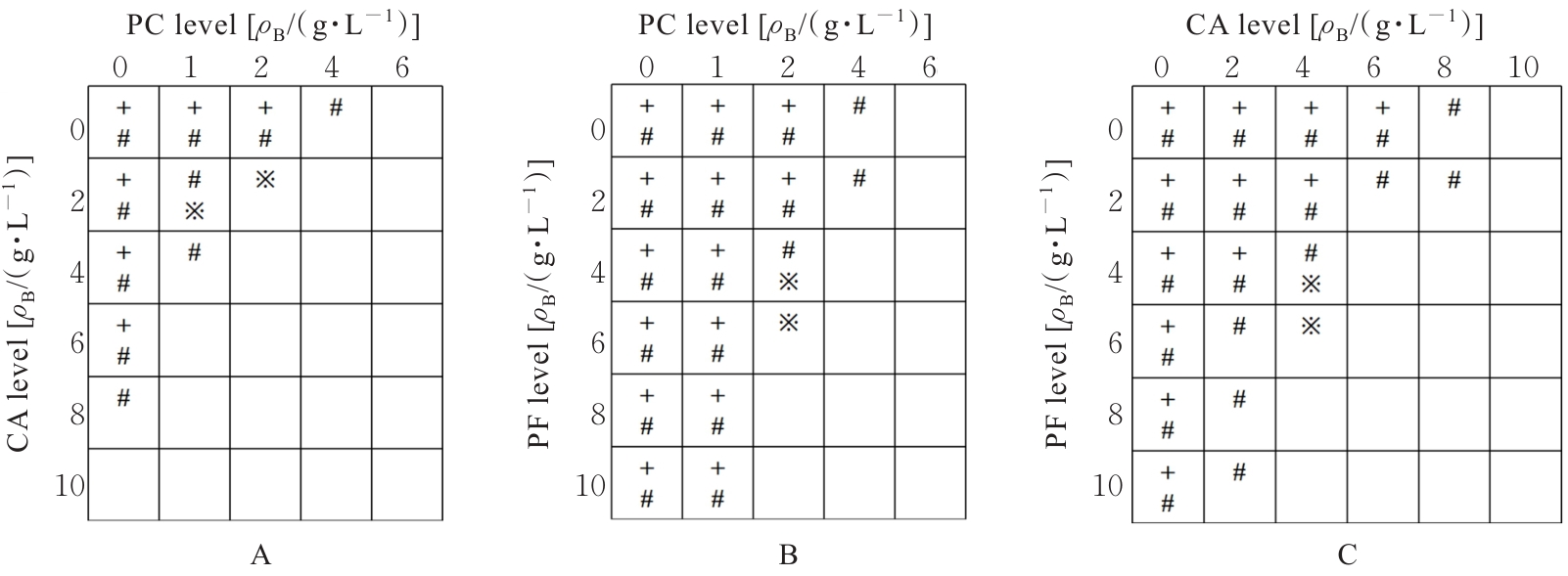
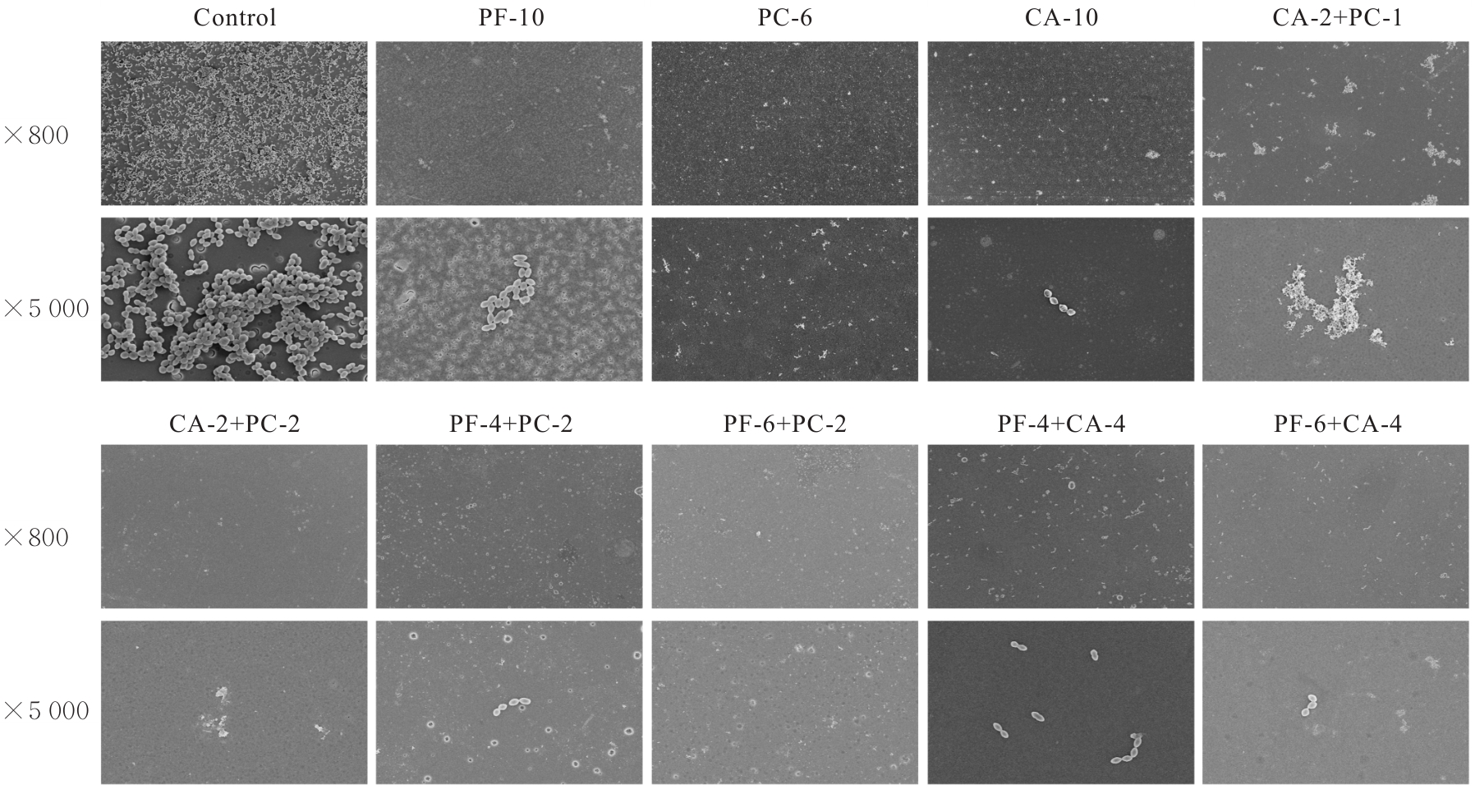
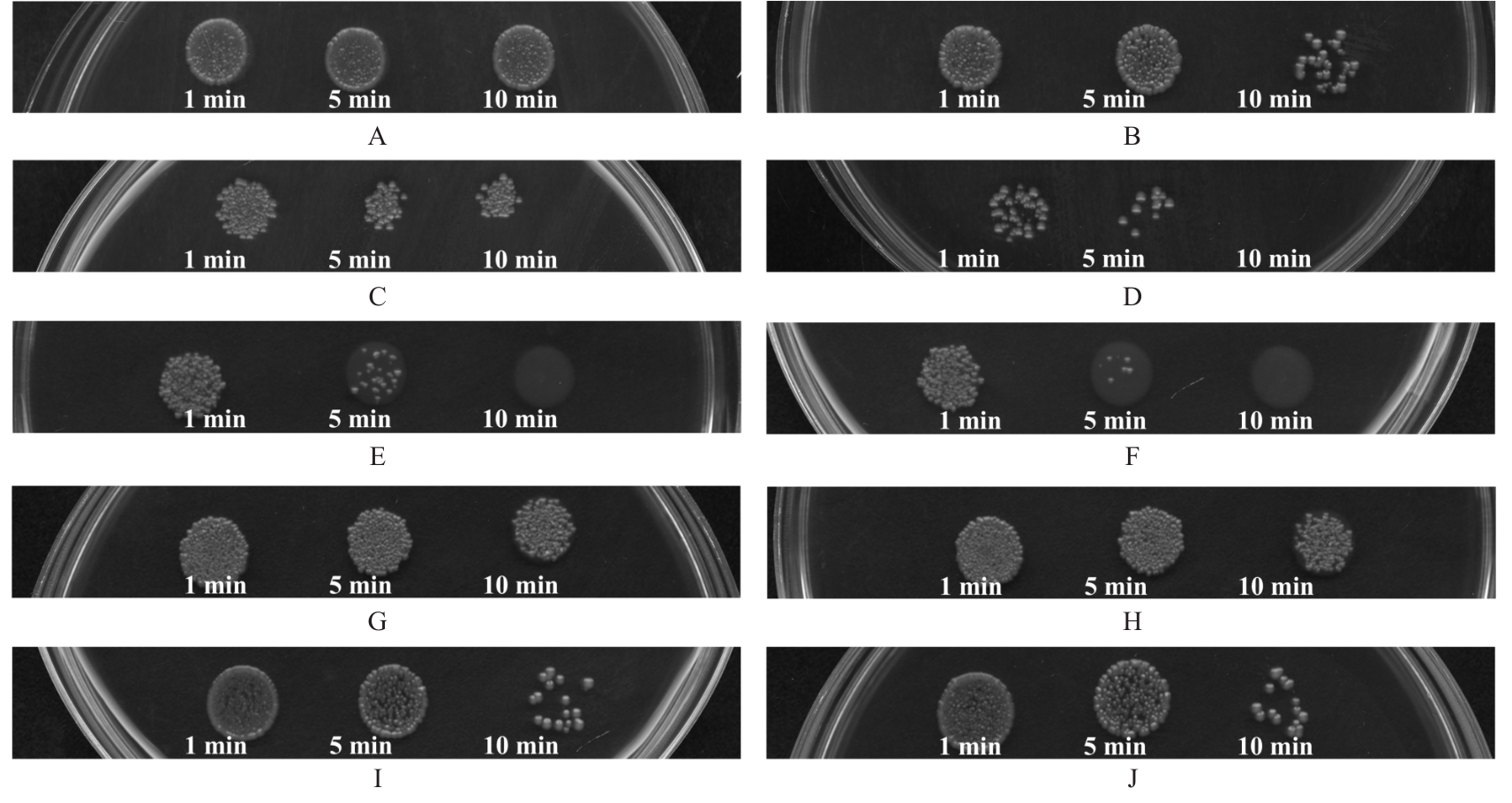
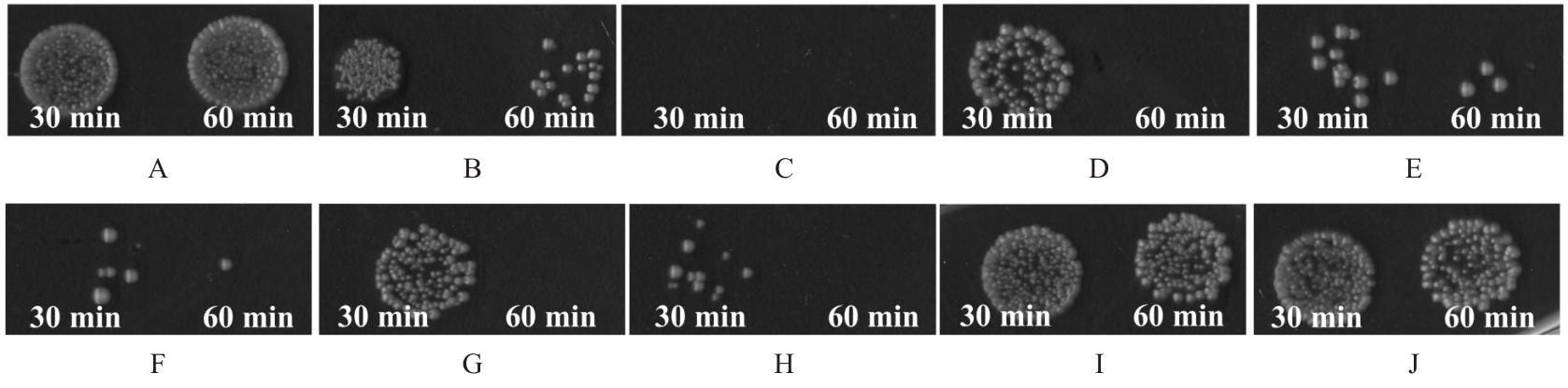
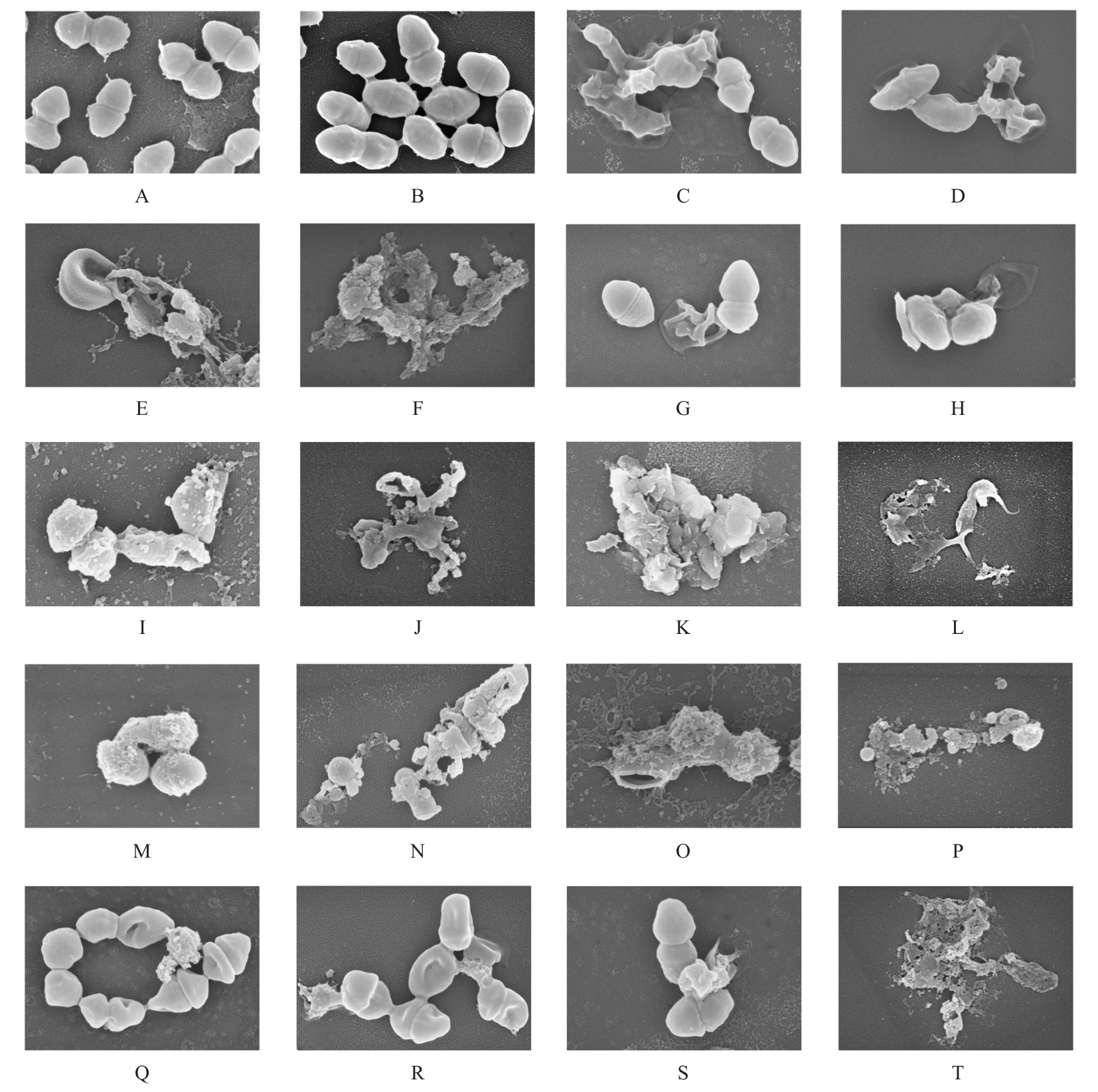
目的 探讨赤芍活性成分芍药苷(PF)、原花青素(PC)和绿原酸(CA),联合应用对粪肠球菌(E.faecalis)及生物膜的抑制作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 采用微量稀释法检测CA、PC和PF对E.faecalis的最小抑菌浓度(MIC)及最小杀菌浓度(MBC),棋盘稀释法检测赤芍3种活性成分联合应用部分抑菌浓度指数(FICI)和部分杀菌浓度指数(FBCI)。实验分为对照组、高浓度单药组(PF-10组、PC-6组和CA-10组)及药物联合应用组(CA-2+PC-1组、CA-2+PC-2组、PF-4+PC-2组、PF-6+PC-2组、PF-4+CA-4组和PF-6+CA-4组)。结晶紫染色检测3种活性成分联合应用各组E.faecalis生物膜形成情况,扫描电镜(SEM)观察赤芍3种活性成分联合应用各组E.faecalis生物膜形态表现,点板试验检测赤芍3种活性成分联合应用对各组E.faecalis浮游菌和生物膜的抑制作用,SEM观察赤芍3种活性成分联合应用各组E.faecalis胞膜损伤情况,试剂盒检测赤芍3种活性成分联合应用各组E.faecalis浮游菌和生物膜中腺嘌呤核苷三磷酸(ATP)水平。 结果 赤芍3种活性成分中PC的MIC为4 g·L-1,MBC为6 g·L-1;CA的MIC为8 g·L-1,MBC为10 g·L-1;PF的MIC和MBC均>10 g·L-1,选取PF浓度为10 g·L-1。PC与CA联合应用具有协同作用,PC与PF联合应用具有相加作用,CA与PF联合应用具有相加作用。结晶紫染色,与对照组比较,PF-10组、PC-6组、CA-10组和各药物联合应用组E.faecalis生物膜形成量均明显降低(P<0.01);与PF-10组比较,PC-6组、CA-10组、CA-2+PC-1组、CA-2+PC-2组、PF-4+PC-2组、PF-6+PC-2组和PF-6+CA-4组E.faecalis生物膜形成量均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。扫描电镜观察,对照组E.faecalis生物膜较厚,细菌之间紧密连接,形态规则,且细胞膜完整;PF-10组、PC-6组和CA-10组E.faecalis生物膜厚度明显降低,细菌间的排列变得相对疏松;各药物联合应用组可见E.faecalis生物膜均明显减少乃至完全消失,高倍镜下可见生物膜结构完全消失,细菌碎片相互黏附聚集,失去原有的细菌形态。点板试验,与对照组比较,作用5、10和30 min后PF-10组、PC-6组及CA-10组E.faecalis浮游菌菌落明显减少,提示其对E.faecalis的杀伤作用逐渐增强;各药物联合应用组中,PC与CA联合应用在5 min内可见E.faecalis浮游菌菌落明显减少,对E.faecalis浮游菌菌落的杀伤作用较强。与PC组和CA组比较,作用5、10和30 min后各药物联合应用组E.faecalis浮游菌菌落未见明显减少;与对照组比较,作用30和60 min后PF-10组、PC-6组及CA-10组E.faecalis生物膜菌落逐渐减少,提示高浓度单药组对E.faecalis生物膜中细菌表现出逐渐增强的杀伤作用。其中PC-6组生物膜杀伤效果最为明显,在处理30 min后未见菌落形成;在各药物联合应用组中,作用30 min后CA-2+PC-2组E.faecalis生物膜仅见少许菌落,提示其可有效杀伤生物膜中的细菌;与PC-6组和CA-10组比较,各药物联合应用组在低浓度即可达到高浓度单药组的杀伤效果。扫描电镜观察,对照组E.faecalis呈椭圆形,且细胞膜完整;PF组E.faecalis形态改变,细胞膜完整性受损;CA组大部分E.faecalis细胞膜相对完整,但E.faecalis表面出现皱缩和凹陷现象,少数E.faecalis细胞膜完整性遭到破坏;PC组E.faecalis细胞膜的完整性破坏最为严重,导致内容物外泄,细胞碎片相互聚集形成絮状结构;各药物联合应用组E.faecalis细胞膜破裂、内容物外泄和细菌残片聚集,尤其是PC与CA联合应用时,可观察到E.faecalis细胞膜的完整性破坏最为明显,内容物完全外泄;PF与CA联合应用时,可观察到细菌表面凹坑和皱缩,偶见细胞膜破裂。试剂盒检测,与对照组比较,各组E.faecalis浮游菌及生物膜中ATP水平均明显降低(P<0.01);与PF-10组比较,CA-10组、CA-2+PC-2组、PF-4+CA-4组和PF-6+CA-4组E.faecalis浮游菌中ATP水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),CA-10组和CA-2+PC-2组E.faecalis生物膜中ATP水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 结论 赤芍活性成分PF、PC和CA联合应用对E.faecalis及生物膜形成具有明显抑制作用,3种活性成分两两联合应用均有一定的协同或相加作用,其中PC与CA联合应用协同作用最为明显,作用机制可能与破坏E.faecalis胞膜完整性和抑制细菌中ATP水平有关。
中图分类号:
- R378.12