吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 672-679.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250312
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
水蛭素对小鼠脑卒中后抑郁的改善作用及其机制
- 南阳医学高等专科学校第一附属医院神经外科,河南 南阳 473058
Improvement effect of hirudin on post-stroke depression in mice and its mechanism
Dan ZHAO( ),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI
),Bo SHI,Zhixuan WEI,Qunjian CUI
- Department of Neurosurgery,First Affiliated Hospital,Nanyang Medical College,Nanyang 473058,China
摘要:
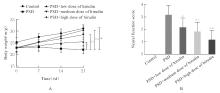
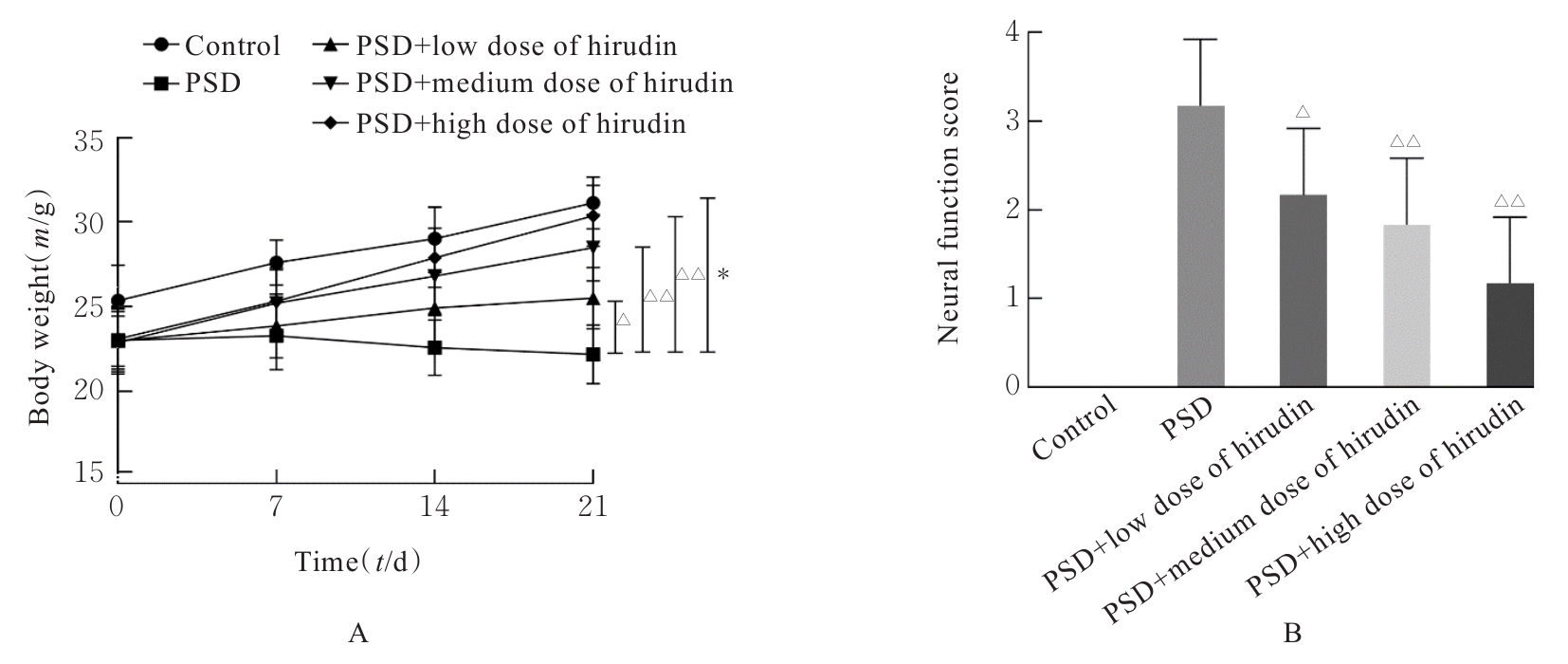
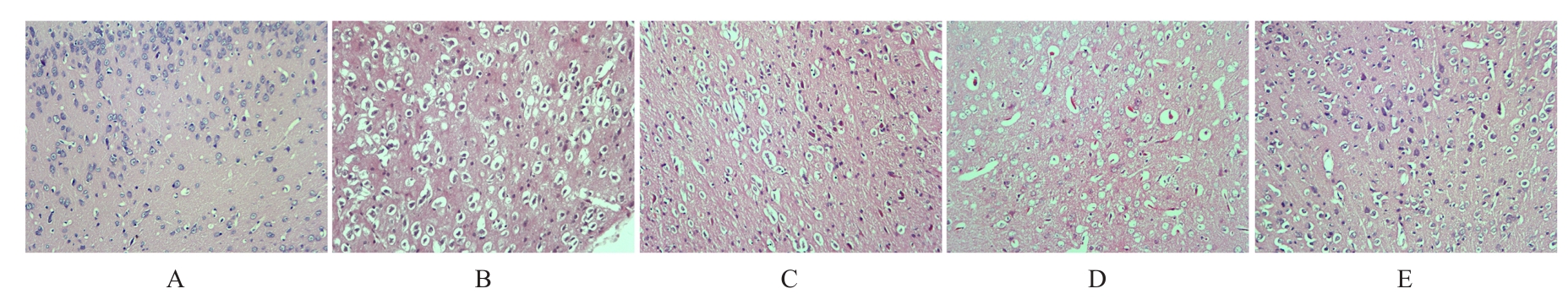
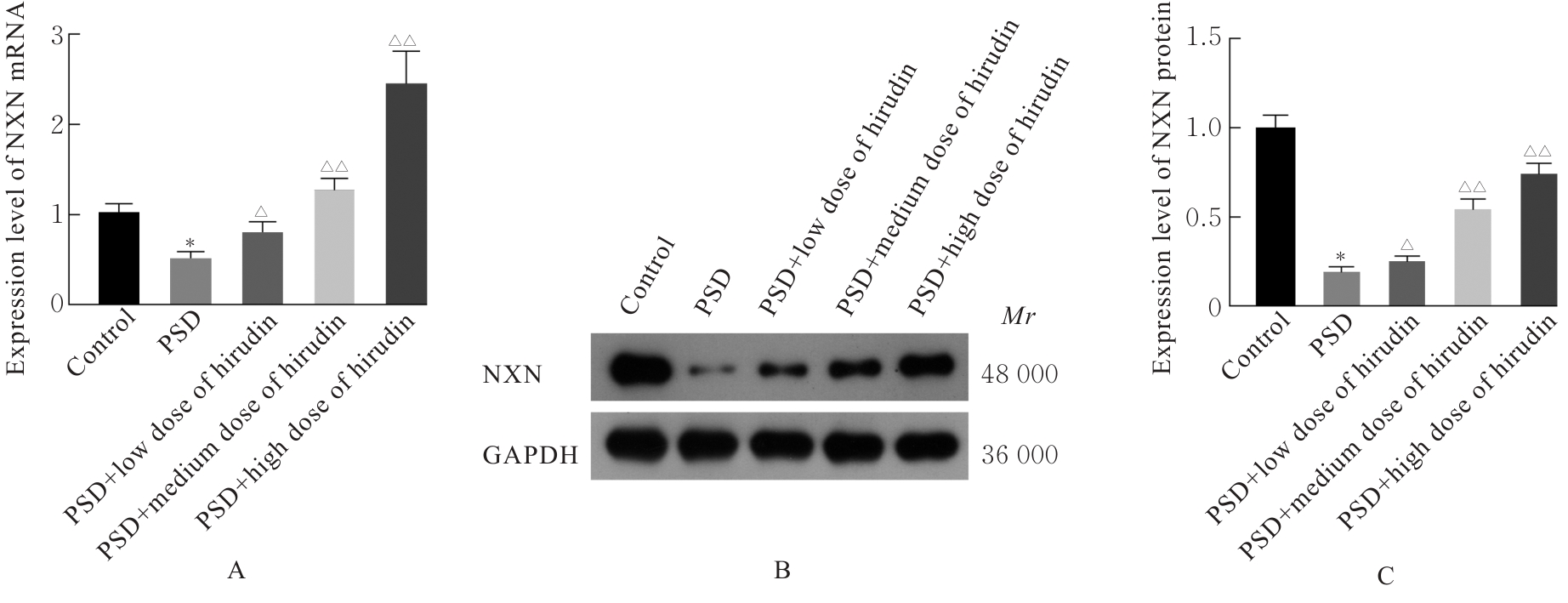
目的 探讨水蛭素对小鼠脑卒中后抑郁(PSD)的影响,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 60只雄性C57BL/6小鼠随机分为对照组、PSD组、PSD+低剂量水蛭素组、PSD+中剂量水蛭素组和PSD+高剂量水蛭素组,每组12只。采用大脑中动脉栓塞(MCAO)法建立小鼠脑卒中模型,采用慢性不可预见的中等应激刺激(CUMS)结合孤养法建立小鼠抑郁模型,PSD+低剂量水蛭素组、PSD+中剂量水蛭素组和PSD+高剂量水蛭素组小鼠在建立抑郁模型的同时分别经尾静脉注射10、20及40 U·kg-1水蛭素干预,对照组和PSD组小鼠经尾静脉注射等量生理盐水。记录CUMS刺激第0、7、14和21天时各组小鼠体质量,计算各组小鼠LONGA神经功能评分,糖水偏好实验、悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验检测各组小鼠糖水偏好率、悬尾及强迫游泳不动时间,HE染色观察各组小鼠内侧前额叶皮质(mPFC)脑区组织病理形态表现,生化试剂盒检测各组小鼠内侧前额叶皮层(mPFC)脑区组织中丙二醛(MDA)和还原性谷胱甘肽(GSH)水平及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,2',7'-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)荧光探针法检测各组小鼠mPFC脑区组织中活性氧(ROS)阳性率,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)和Western blotting法检测各组小鼠mPFC脑区组织中核氧化还原蛋白(NXN)mRNA及蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,CUMS刺激第0、7、14和21天PSD组小鼠体质量均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与PSD组比较,CUMS刺激第14和21天PSD+低剂量水蛭素组、PSD+中剂量水蛭素组及PSD+高剂量水蛭素组小鼠体质量均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),神经功能评分均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。糖水偏好实验、悬尾实验和强迫游泳实验,与对照组比较,PSD组小鼠糖水偏好率明显降低(P<0.01),悬尾和强迫游泳不动时间均明显增加(P<0.01);与PSD组比较,PSD+低剂量水蛭素组、PSD+中剂量水蛭素组和PSD+高剂量水蛭素组小鼠糖水偏好率均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),悬尾和强迫游泳不动时间均明显减少(P<0.05或P<0.01)。HE染色,对照组小鼠mPFC脑区组织细胞形态正常,结构清晰,大小分布均匀;PSD组和PSD+低剂量水蛭素组小鼠mPFC脑区组织细胞明显减少,并出现严重空泡样变性,核仁固缩;PSD+中剂量水蛭素组和PSD+高剂量水蛭素组小鼠mPFC脑区组织细胞较PSD组明显增多,空泡样变性和核仁固缩明显改善。生化试剂盒和DCFH-DA荧光探针法,与对照组比较,PSD组小鼠mPFC脑区组织中GSH水平和SOD活性均明显降低(P<0.01),MDA水平和ROS阳性率均明显升高(P<0.01);与PSD组比较,PSD+低剂量水蛭素组、PSD+中剂量水蛭素组和PSD+高剂量水蛭素组小鼠mPFC脑区组织中GSH水平及SOD活性均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),MDA水平和ROS阳性率均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。RT-qPCR和Western blotting法,与对照组比较,PSD组小鼠mPFC脑区组织中NXN mRNA和蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01);与PSD组比较,PSD+低剂量水蛭素组、PSD+中剂量水蛭素组和PSD+高剂量水蛭素组小鼠mPFC脑区组织中NXN mRNA及蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 结论 水蛭素可促进PSD小鼠mPFC脑区组织氧化还原平衡,修复其神经功能损伤,改善PSD。
中图分类号:
- R749.13