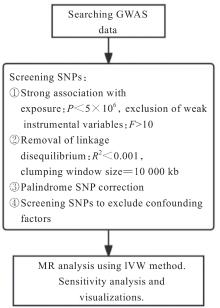
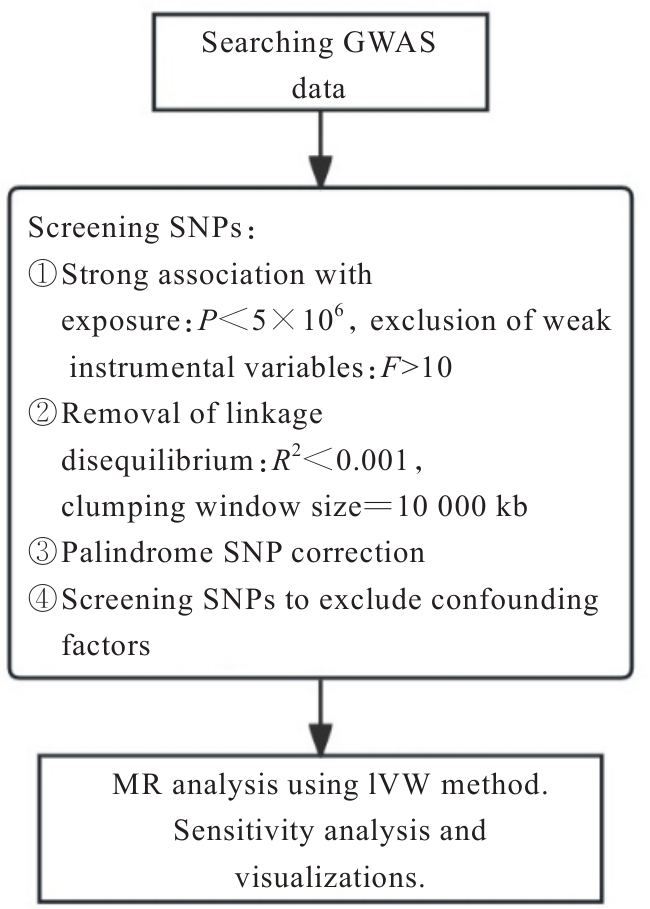
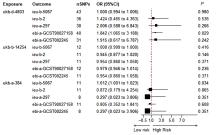
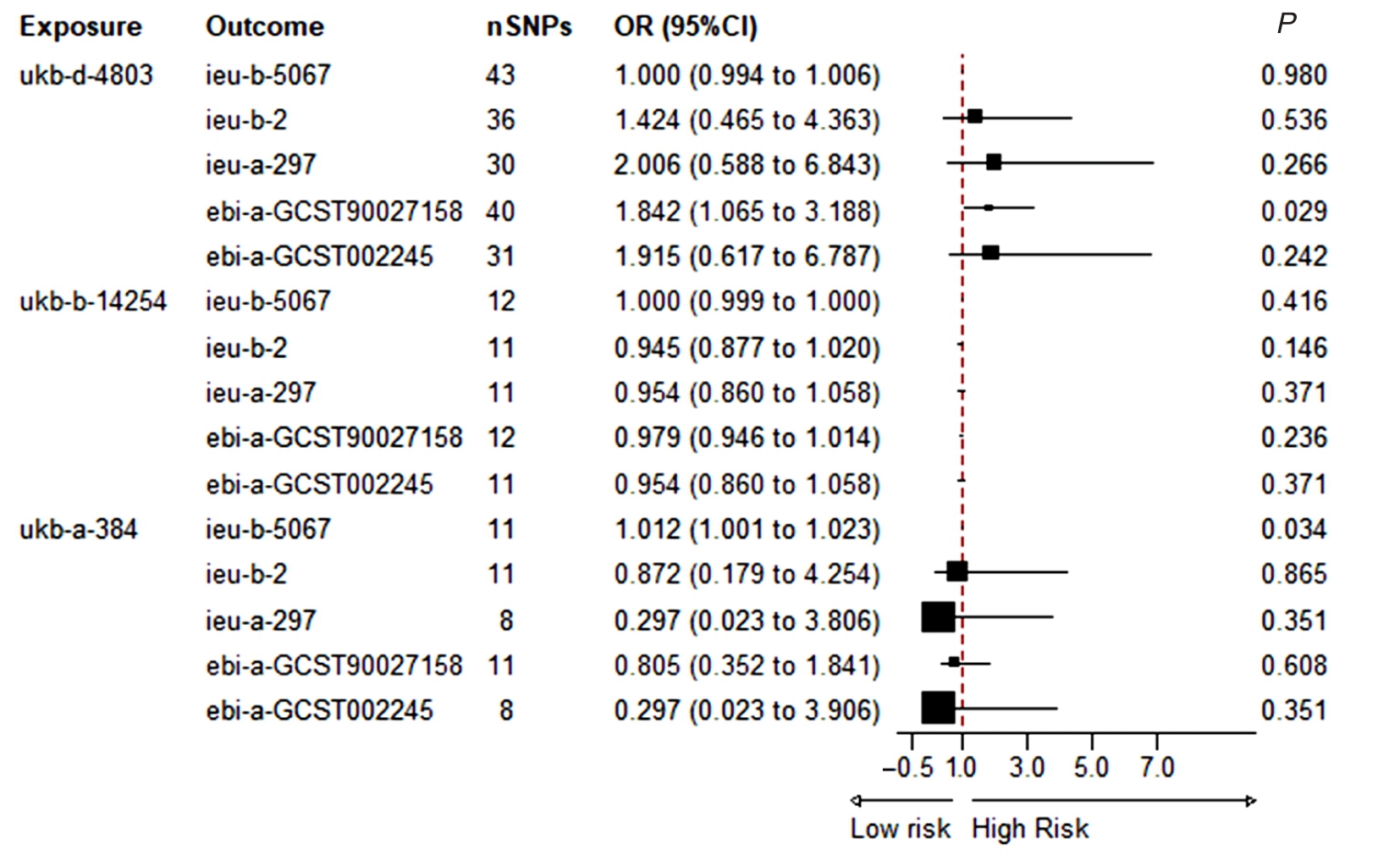
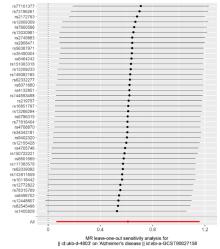
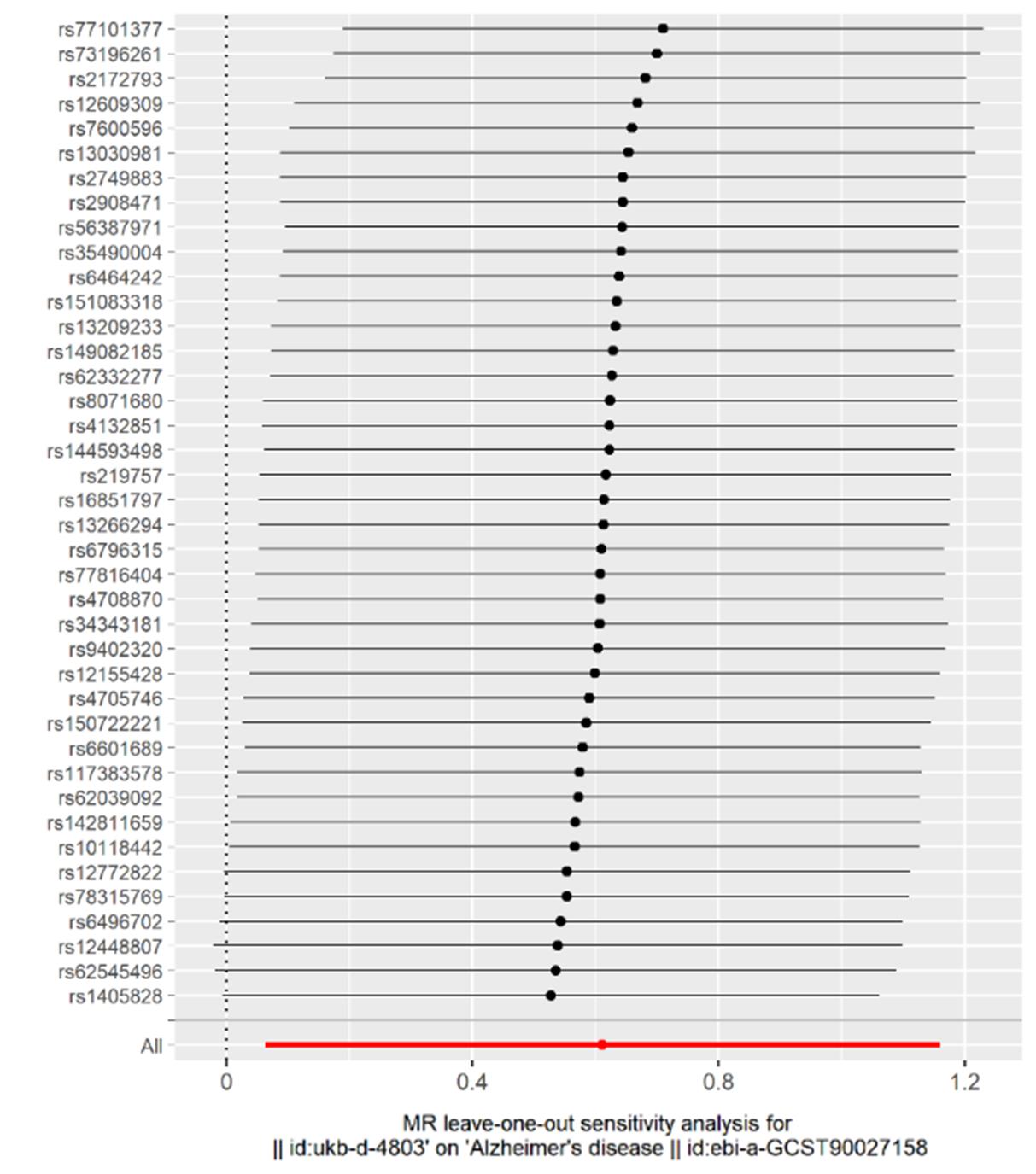
| [1] |
RAJAN K B, WEUVE J, BARNES L L, et al. Population estimate of people with clinical Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment in the United States (2020-2060)[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2021, 17(12): 1966-1975.
|
| [2] |
National Institute on Aging Alzheimer’s Association. 2024 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures [J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2024, 20(5): 3708-3821.
|
| [3] |
张志英, 尹 榕. 血清淀粉样蛋白P与阿尔兹海默病和血管性痴呆的相关性研究[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2023, 40(2): 182-183.
|
| [4] |
RABIPOUR S, RAJAGOPAL S, YU E, et al. APOE4 status is related to differences in memory-related brain function in asymptomatic older adults with family history of Alzheimer’s disease: baseline analysis of the PREVENT-AD task functional MRI dataset[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2020, 76(1): 97-119.
|
| [5] |
XU W, TAN L, WANG H F, et al. Education and risk of dementia: dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2016, 53(5): 3113-3123.
|
| [6] |
WANG Z D, MARSEGLIA A, SHANG Y, et al. Leisure activity and social integration mitigate the risk of dementia related to cardiometabolic diseases: a population-based longitudinal study[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2020, 16(2): 316-325.
|
| [7] |
WADHWA R, PAUDEL K R, MEHTA M, et al. Beyond the obvious: smoking and respiratory infection implications on Alzheimer’s disease[J]. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 2020, 19(9): 698-708.
|
| [8] |
ROMÁN G C, JACKSON R E, REIS J, et al. Extra-virgin olive oil for potential prevention of Alzheimer disease[J]. Rev Neurol (Paris), 2019, 175(10): 705-723.
|
| [9] |
TUNKEL D E, BAUER C A, SUN G H, et al. Clinical practice guideline: tinnitus[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 151(2 ): S1-S40.
|
| [10] |
OOSTERLOO B C, CROLL P H, BAATENBURG DE JONG R J, et al. Prevalence of tinnitus in an aging population and its relation to age and hearing loss[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 164(4): 859-868.
|
| [11] |
ESMAILI A A, RENTON J. A review of tinnitus[J]. Aust J Gen Pract, 2018, 47(4): 205-208.
|
| [12] |
HESSE G, MAZUREK B. Chronic tinnitus- Therapeutic aspects, based on the new German guideline[J]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr, 2022, 147(11): 682-687.
|
| [13] |
MAZUREK B, HESSE G, SATTEL H, et al. S3 guideline: chronic tinnitus: German society for otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery e. V. (DGHNO-KHC)[J]. HNO, 2022, 70(11): 795-827.
|
| [14] |
CHU H T, LIANG C S, YEH T C, et al. Tinnitus and risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: a retrospective nationwide population-based cohort study[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12134.
|
| [15] |
RICHMOND R C, DAVEY SMITH G. Mendelian randomization: concepts and scope[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2022, 12(1): a040501.
|
| [16] |
EMDIN C A, KHERA A V, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian randomization [J]. JAMA, 2017, 318(19): 1925-1926.
|
| [17] |
BOWDEN J, HOLMES M V. Meta-analysis and mendelian randomization: a review[J]. Res Synth Methods, 2019, 10(4): 486-496.
|
| [18] |
WOOTTON R E, LAWN R B, MILLARD L A C, et al. Evaluation of the causal effects between subjective wellbeing and cardiometabolic health: mendelian randomisation study[J]. BMJ, 2018, 362: k3788.
|
| [19] |
BIRNEY E, SORANZO N. Human genomics: The end of the start for population sequencing[J]. Nature, 2015, 526(7571): 52-53.
|
| [20] |
ZHOU B, FUKUSHIMA M. Clinical utility of the pathogenesis-related proteins in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(22): 8661.
|
| [21] |
XIE K P, WANG H, YAO X, et al. Hederagenin reduces Aβ-induced oxidative damage, decreases Aβ deposition, and promotes cell survival by the P13K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2025, 117(2): qiae124.
|
| [22] |
GONZALEZ-ORTIZ F, KIRSEBOM B E, CONTADOR J, et al. Plasma brain-derived tau is an amyloid-associated neurodegeneration biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 2908.
|
| [23] |
RUSEK M, SMITH J, EL-KHATIB K, et al. The role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: new potential treatment target[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(1): 864.
|
| [24] |
MENNINK L M, AALBERS M W, VAN DIJK P, et al. The role of inflammation in tinnitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(4): 1000.
|
| [25] |
CHEN J J, CHEN Y W, ZENG B Y, et al. Efficacy of pharmacologic treatment in tinnitus patients without specific or treatable origin: a network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials[J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2021, 39: 101080.
|
| [26] |
CRESSWELL M, CASANOVA F, BEAUMONT R N, et al. Understanding factors that cause tinnitus: a mendelian randomization study in the UK biobank[J]. Ear Hear, 2022, 43(1): 70-80.
|
| [27] |
HARERIMANA N V, LIU Y, GERASIMOV E S, et al. Genetic evidence supporting a causal role of depression in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 2022, 92(1): 25-33.
|
| [28] |
LIU Y L, XIAO X W, YANG Y, et al. The risk of Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive impairment characteristics in eight mental disorders: a UK Biobank observational study and Mendelian randomization analysis[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2024, 20(7): 4841-4853.
|
| [29] |
WANG R, KOGLER L, DERNTL B. Sex differences in Cortisol levels in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Neuroendocrinol, 2024, 72: 101118.
|
| [30] |
SZCZEPEK A J, MAZUREK B. Neurobiology of stress-induced tinnitus[J]. Curr Top Behav Neurosci, 2021, 51: 327-347.
|
| [31] |
SPENCER R L, DEAK T. A users guide to HPA axis research[J]. Physiol Behav, 2017, 178: 43-65.
|
| [32] |
SHARAN P, VELLAPANDIAN C. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis: unveiling the potential mechanisms involved in stress-induced Alzheimer’s disease and depression[J]. Cureus, 2024, 16(8): e67595.
|
 )
)