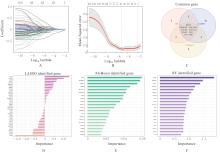
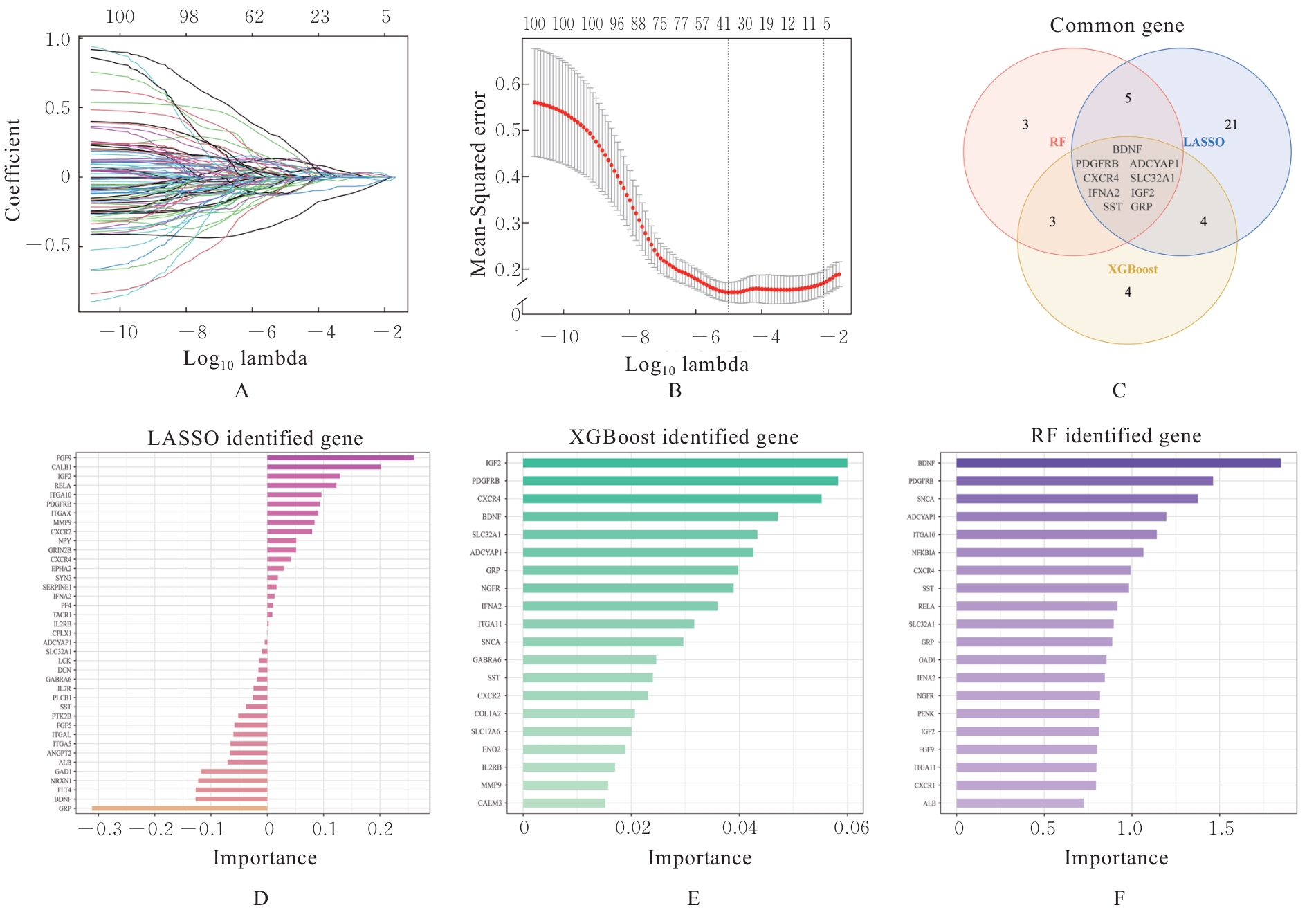
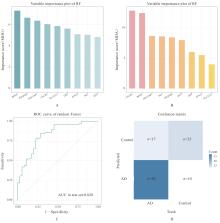
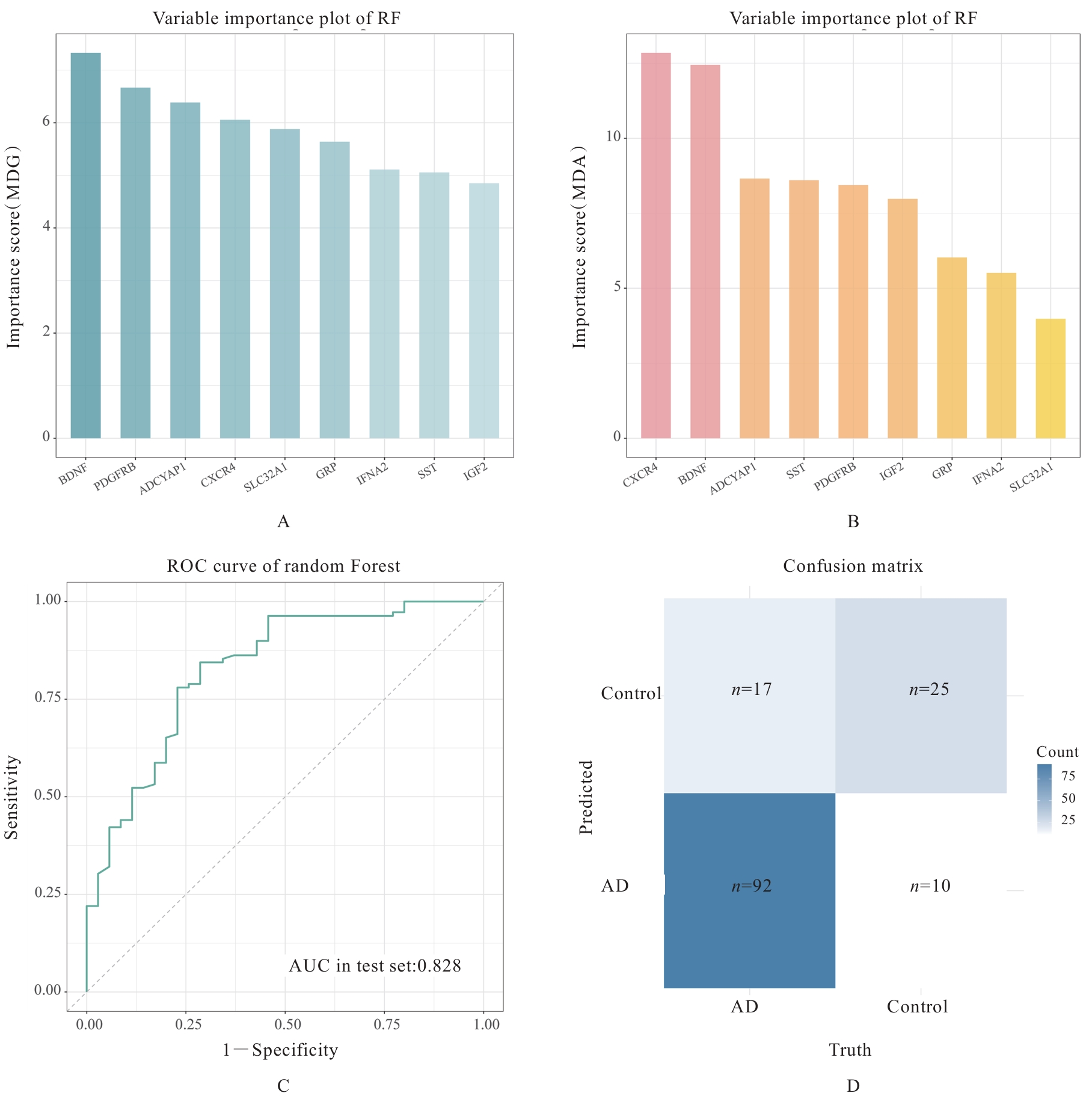
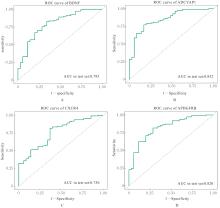
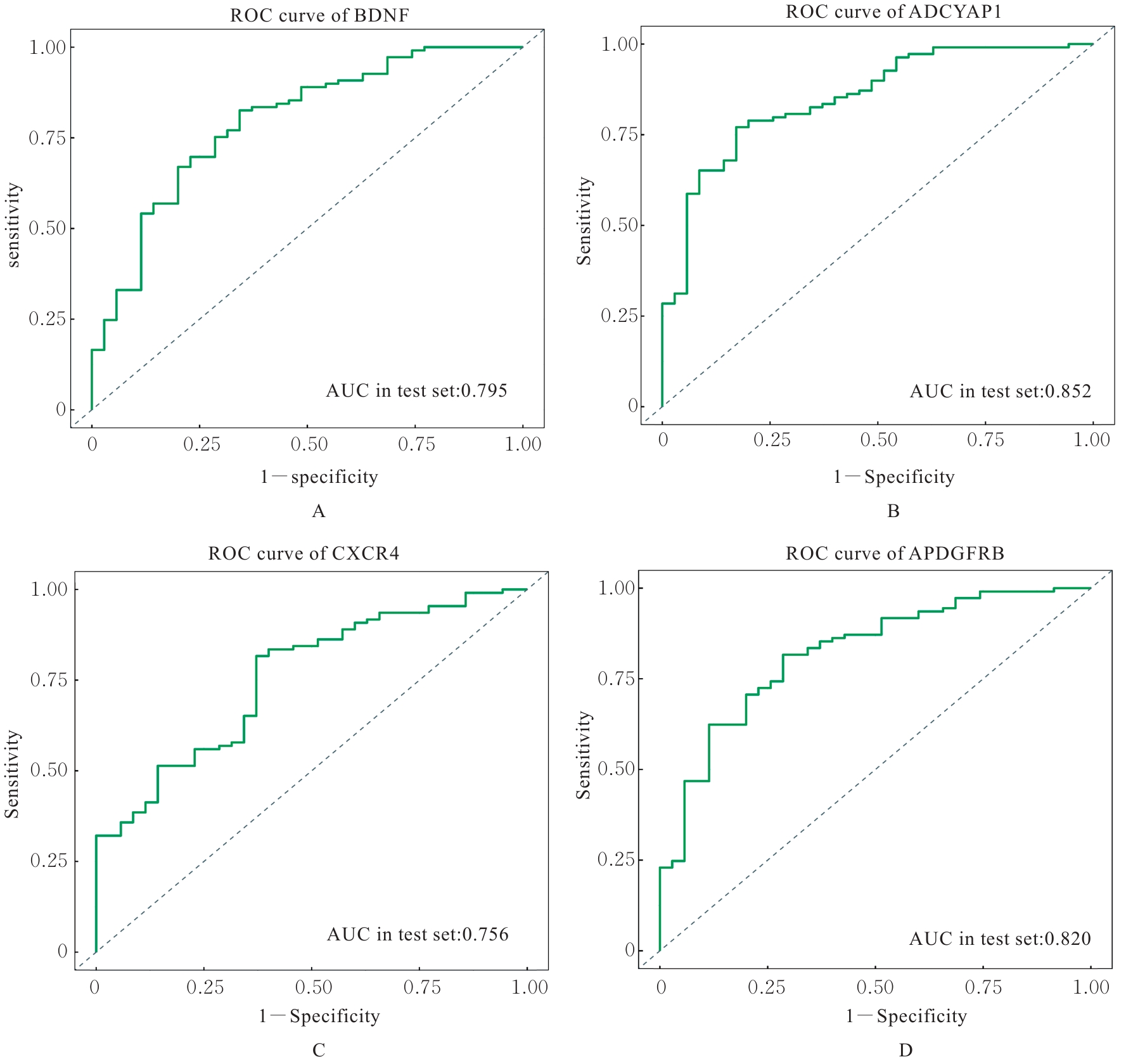
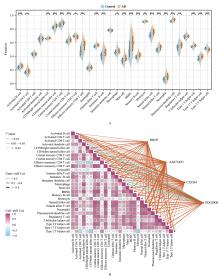
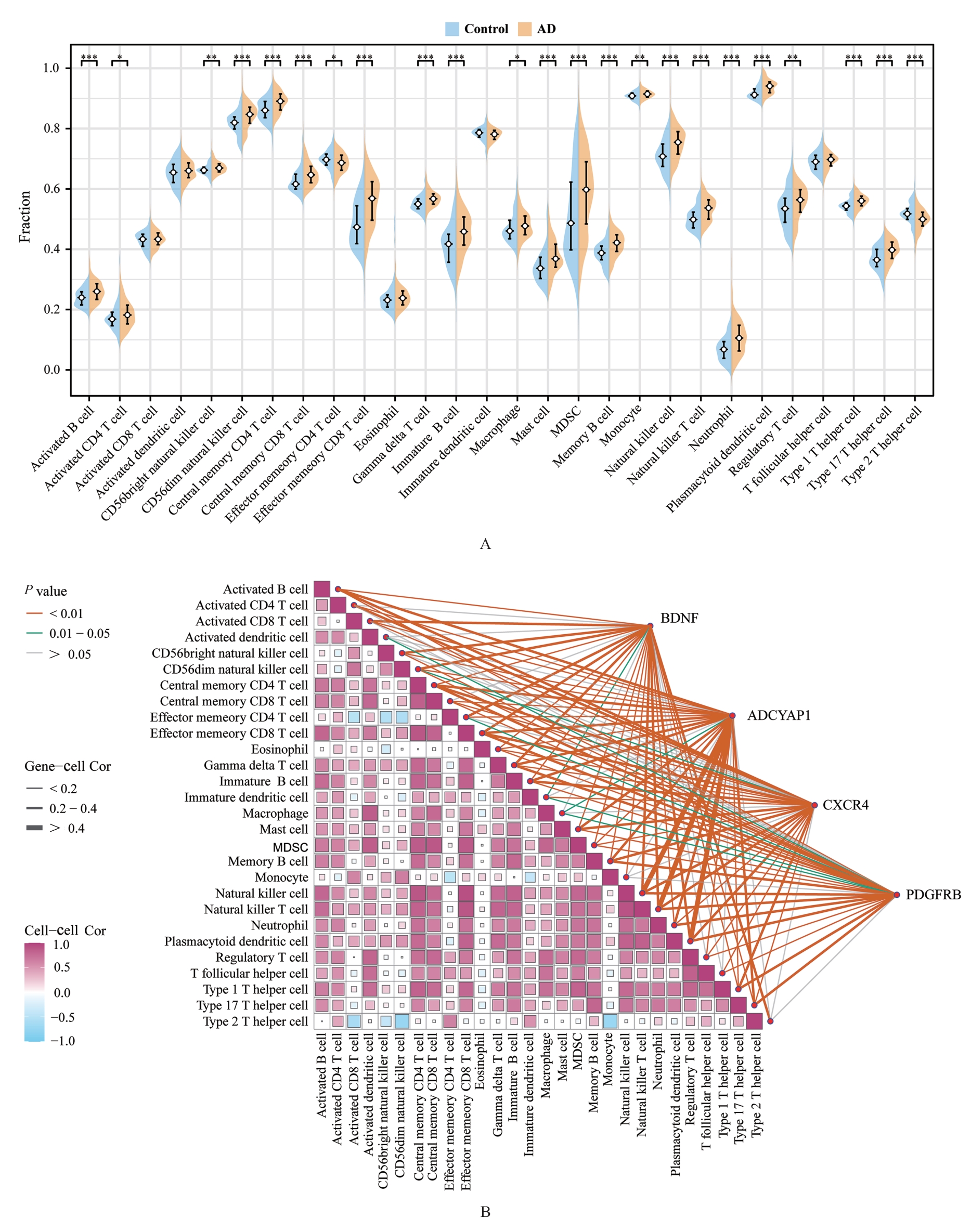
| [1] |
LANE C A, HARDY J, SCHOTT J M. Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Eur J Neurol, 2018, 25(1): 59-70.
|
| [2] |
KHAN S, BARVE K H, KUMAR M S. Recent advancements in pathogenesis,diagnostics and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2020,18(11):1106-1125.
|
| [3] |
HU Y, ZHOU G, ZHANG C, et al. Identify compounds’target against Alzheimer’s disease based on in-silico approach[J]. Curr Alzheimer Res, 2019, 16(3): 193-208.
|
| [4] |
TWAROWSKI B, HERBET M. Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease-pathomechanism,diagnosis and treatment: A review[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(7): 6518.
|
| [5] |
BREIJYEH Z, KARAMAN R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s disease: causes and treatment[J]. Molecules,2020,25(24):5789.
|
| [6] |
BATEMAN R J, BARTHéLEMY N R, HORIE K. Another step forward in blood-based diagnostics for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Nat Med, 2020, 26(3):314-316.
|
| [7] |
MERKIN A, KRISHNAMURTHI R, MEDVEDEV O N. Machine learning, artificial intelligence and the prediction of dementia[J]. Curr Opin Psychiatry, 2022,35(2): 123-129.
|
| [8] |
SUN X, ZHANG H, YAO D, et al. Integrated bioinformatics analysis identifies Hub genes associated with viral infection and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2022, 85(3): 1053-1061.
|
| [9] |
HUANG R, WANG W, CHEN Z, et al. Identifying immune cell infiltration and effective diagnostic biomarkers in Crohn’s disease by bioinformatics analysis[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1162473.
|
| [10] |
WANG W, CHEN Z, HUA Y. Bioinformatics prediction and experimental validation identify a novel cuproptosis-related gene signature in human synovial inflammation during osteoarthritis progression[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13(1): 127.
|
| [11] |
WU T, HU E, XU S, et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data[J]. Innovation(Camb), 2021, 2(3): 100141.
|
| [12] |
MOUSAVIAN Z, KHODABANDEH M, SHARIFI-ZARCHI A, et al. StrongestPath: a Cytoscape application for protein-protein interaction analysis[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2021, 22(1): 352.
|
| [13] |
时 承, 姚旭峰. 机器学习用于帕金森病诊断的研究进展[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2024, 41(5): 640-645.
|
| [14] |
龚玉芳, 邓海霞, 卢燕, 等. 基于生物信息学建立与验证心肌梗死铁死亡基因诊断模型及免疫分析[J/OL]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志: 1-10[2025-08-10]. .
|
| [15] |
ROSTAGNO A A. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 24(1): 107.
|
| [16] |
SCHELTENS P, DE STROOPER B, KIVIPELTO M,et al. Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Lancet,2021,397(10284):1577-1590.
|
| [17] |
HU R, ZHANG W, HAN Z, et al. Identification of immune-related target and prognostic biomarkers in PBMC of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2023, 23(1): 234.
|
| [18] |
LIU X, ZHAO J, XUE L, et al. A comparison of transcriptome analysis methods with reference genome[J]. BMC Genomics, 2022, 23(1): 232.
|
| [19] |
SOFER T, KURNIANSYAH N, AGUET F,et al. Benchmarking association analyses of continuous exposures with RNA-seq in observational studies[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2021, 22(6): bbab194.
|
| [20] |
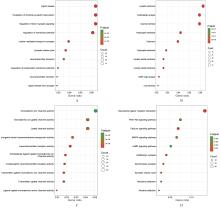
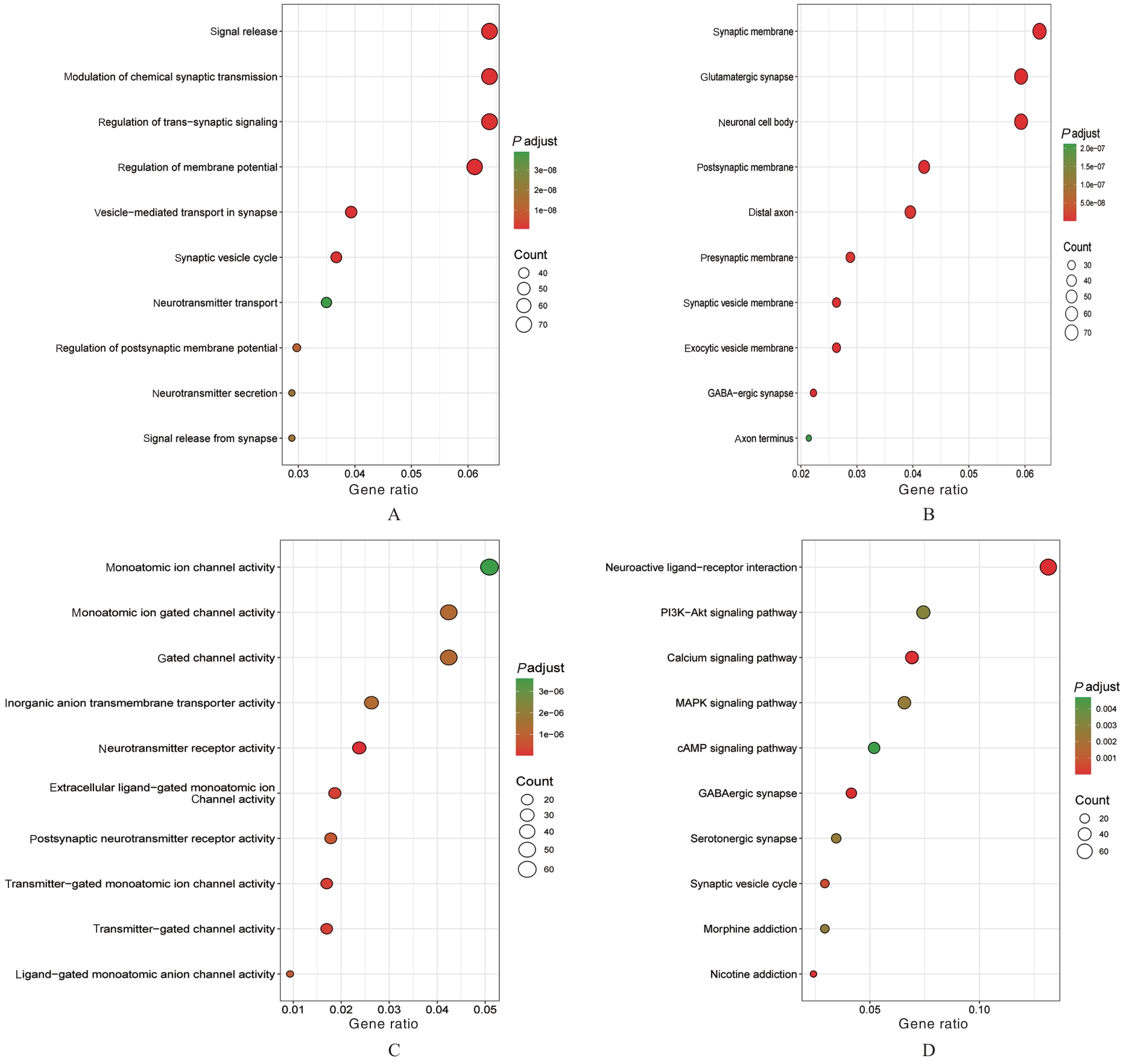
PINKY P D, PFITZER J C, SENFELD J, et al. Recent insights on glutamatergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and therapeutic implications[J]. Neuroscientist, 2023, 29(4): 461-471.
|
| [21] |
TIMMER N M, METAXAS A, VAN DER STELT I,et al. Cerebral level of vGlut1 is increased and level of glycine is decreased in TgSwDI mice[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2014, 39(1): 89-101.
|
| [22] |
D’ANGIOLINI S, BASILE M S, MAZZON E, et al. In silico analysis reveals the modulation of ion transmembrane transporters in the cerebellum of Alzheimer’s disease patients[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023, 24(18): 13924.
|
| [23] |
LONG H Z, CHENG Y, ZHOU Z W, et al. PI3K/AKT signal pathway: a target of natural products in the prevention and treatment of Alzheime’s disease and Parkinson’s disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021,12: 648636.
|
| [24] |
SCHALER A W, RUNYAN A M, CLELLAND C L,et al. PAC1 receptor-mediated clearance of tau in postsynaptic compartments attenuates tau pathology in mouse brain[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2021, 13(595):eaba7394.
|
| [25] |
SZEGECZKI V, HORVáTH G, PERéNYI H, et al. Alzheimer’s disease mouse as a model of testis degeneration[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(16): 5726.
|
| [26] |
CHOI S H, BYLYKBASHI E, CHATILA Z K, et al. Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6406): eaan8821.
|
| [27] |
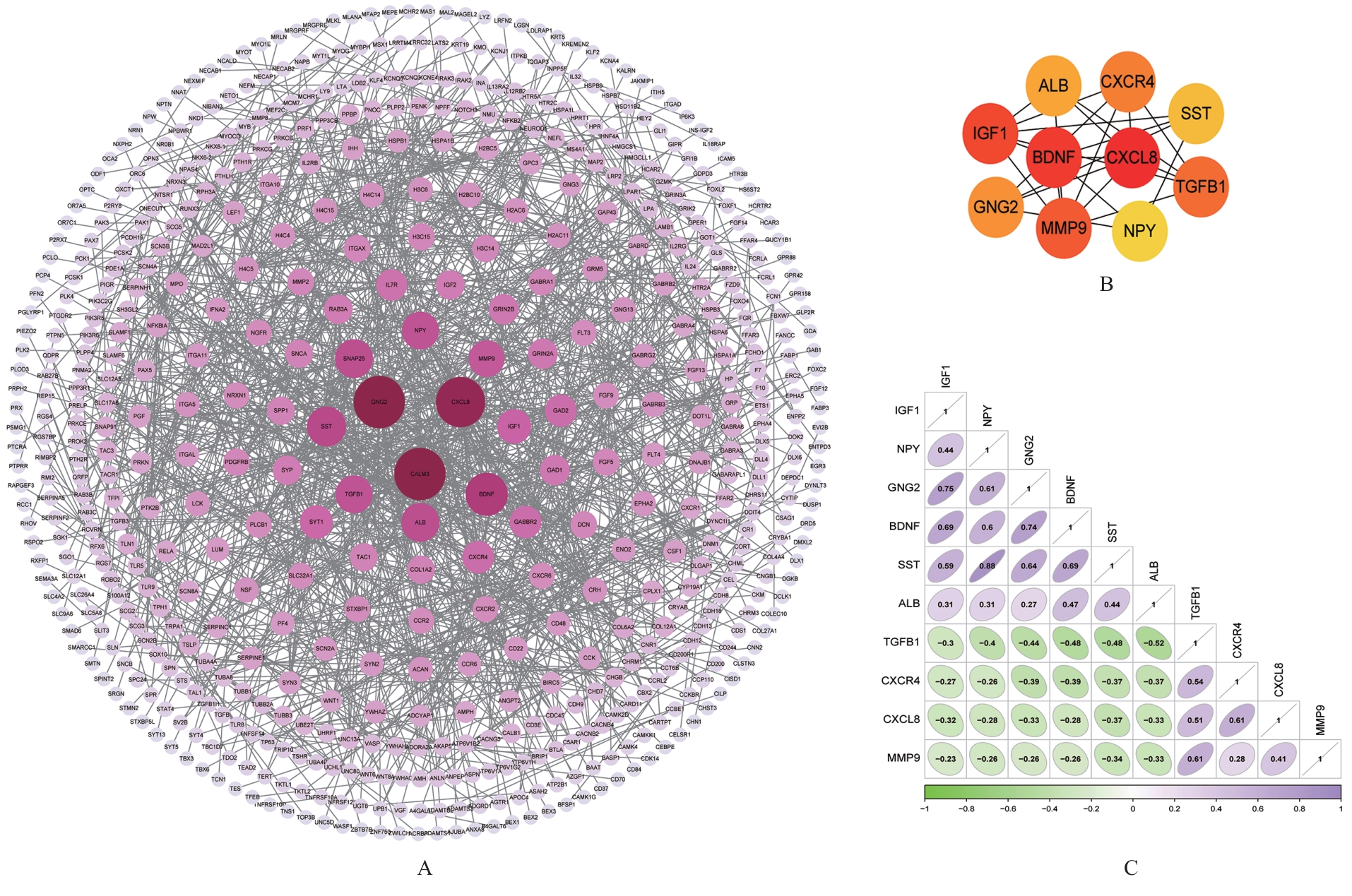
COLUCCI-D’AMATO L, SPERANZA L, VOLPICELLI F. Neurotrophic factor BDNF, physiological functions and therapeutic potential in depression,neurodegeneration and brain cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020, 21(20): 7777.
|
| [28] |
GAO L, ZHANG Y, STERLING K, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer’s disease and its pharmaceutical potential[J]. Transl Neurodegener,2022, 11(1): 4.
|
| [29] |
SHI H, KORONYO Y, RENTSENDORJ A, et al. Identification of early pericyte loss and vascular amyloidosis in Alzheimer’s disease retina[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2020, 139(5): 813-836.
|
| [30] |
WANG Q L, FANG C L, HUANG X Y, et al. Research progress of the CXCR4 mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Ibrain, 2022, 8(1): 3-14.
|
| [31] |
BRYSON K J, LYNCH M A. Linking T cells to Alzheimer’s disease: from neurodegeneration to neurorepair[J]. Curr Opin Pharmacol, 2016, 26: 67-73.
|
| [32] |
CAO W, ZHENG H. Peripheral immune system in aging and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2018,13(1): 51.
|
| [33] |
MOLLAZADEH H, CICERO A F G, BLESSO C N,et al. Immune modulation by curcumin:The role of interleukin-10[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2019, 59(1): 89-101.
|
| [34] |
TAYLOR X, CLARK I M, FITZGERALD G J, et al. Amyloid-β(Aβ) immunotherapy induced microhemorrhages are associated with activated perivascular macrophages and peripheral monocyte recruitment in Alzheimer’s disease mice[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2023, 18(1): 59.
|
 ),石福艳1,王金荣2(
),石福艳1,王金荣2( )
)
 ),Fuyan SHI1,Jinrong WANG2(
),Fuyan SHI1,Jinrong WANG2( )
)