| 1 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
|
| 2 |
KNUPPEL A, FENSOM G K, WATTS E L, et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations and risk of 30 cancers: prospective analyses in UK biobank[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(18): 4014-4021.
|
| 3 |
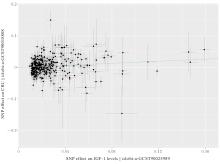
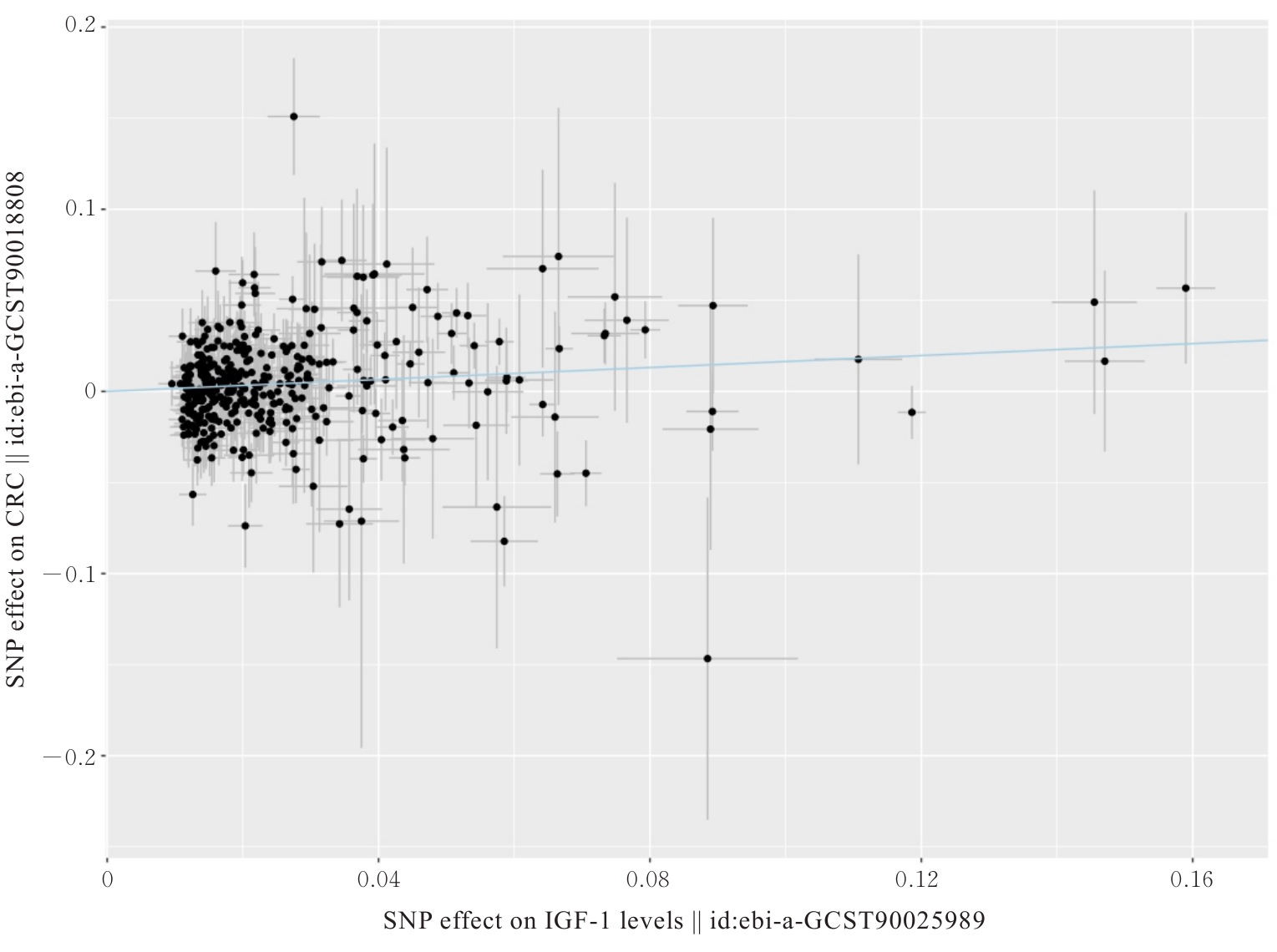
MURPHY N, CARRERAS-TORRES R, SONG M Y, et al. Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 associate with risk of colorectal cancer based on serologic and mendelian randomization analyses[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(5): 1300-1312.e20.
|
| 4 |
DEVESA J, ALMENGLÓ C, DEVESA P. Multiple effects of growth hormone in the body: is it really the hormone for growth?[J]. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes, 2016, 9: 47-71.
|
| 5 |
JENSEN-CODY S O, POTTHOFF M J. Hepatokines and metabolism: deciphering communication from the liver[J]. Mol Metab, 2021, 44: 101138.
|
| 6 |
MUKHERJEE A, ALZHANOV D, ROTWEIN P. Defining human insulin-like growth factor Ⅰ gene regulation[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 311(2): E519-E529.
|
| 7 |
ÁLVAREZ-NAVA F, LANES R. GH/IGF-1 signaling and current knowledge of epigenetics; a review and considerations on possible therapeutic options[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(10): 1624.
|
| 8 |
KASPRZAK A, SZAFLARSKI W. Role of alternatively spliced messenger RNA (mRNA) isoforms of the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) in selected human tumors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(19): 6995.
|
| 9 |
HU J X, LIU X Y, CHI J W, et al. Expressions of IGF-1, ERK, GLUT4, IRS-1 in metabolic syndrome complicated with colorectal cancer and their associations with the clinical characteristics of CRC[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2018, 21(4): 883-891.
|
| 10 |
ZELJKOVIC A, MIHAJLOVIC M, STEFANOVIC A, et al. Potential use of serum insulin-like growth factor 1 and E-cadherin as biomarkers of colorectal cancer[J]. Colorectal Dis, 2020, 22(12): 2078-2086.
|
| 11 |
CHOI Y J, LEE D H, HAN K D, et al. Adult height in relation to risk of cancer in a cohort of 22 809 722 Korean adults[J]. Br J Cancer, 2019, 120(6): 668-674.
|
| 12 |
ZHOU E, WANG L, SANTIAGO C N, et al. Adult-attained height and colorectal cancer risk: a cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2022, 31(4): 783-792.
|
| 13 |
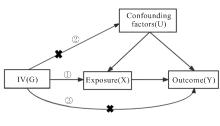
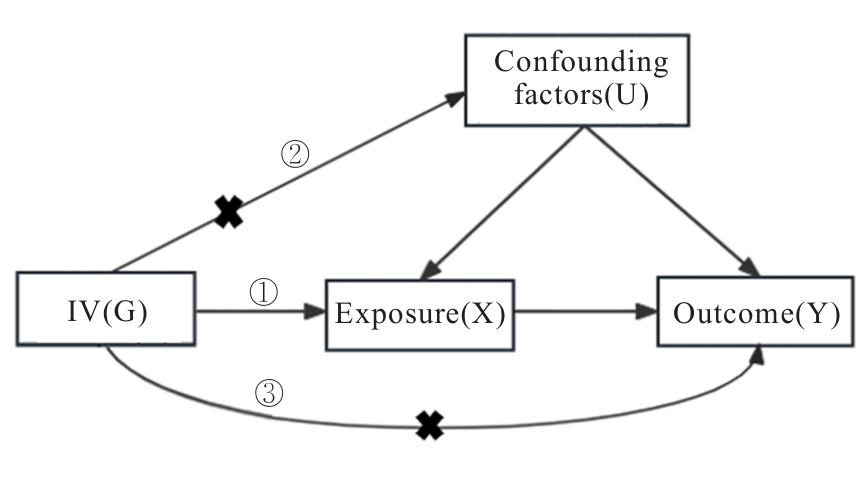
于天琦, 徐文涛, 苏雅娜, 等. 孟德尔随机化研究基本原理、方法和局限性[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2021, 21(10): 1227-1234.
|
| 14 |
HEMANI G, BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2018, 27(R2): R195-R208.
|
| 15 |
BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK P C, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted Median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2016, 40(4): 304-314.
|
| 16 |
BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2): 512-525.
|
| 17 |
董朋涛, 王 峥, 李晓羽, 等. 炎症因子与糖尿病肾病的因果关系: 双向孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2024, 24(5): 543-549.
|
| 18 |
VERBANCK M, CHEN C Y, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50(5): 693-698.
|
| 19 |
HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data[J]. PLoS Genet, 2017, 13(11): e1007081.
|
| 20 |
DURAIYARASAN S, ADEFUYE M, MANJUNATHA N, et al. Colon cancer and obesity: a narrative review[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(8): e27589.
|
| 21 |
JIANG B, ZHANG X, DU L L, et al. Possible roles of insulin, IGF-1 and IGFBPs in initiation and progression of colorectal cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(6): 1608-1613.
|
| 22 |
KAAKS R, TONIOLO P, AKHMEDKHANOV A, et al. Serum C-peptide, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-Ⅰ, IGF-binding proteins, and colorectal cancer risk in women[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2000, 92(19): 1592-1600.
|
| 23 |
FUCHS C S, GOLDBERG R M, SARGENT D J, et al. Plasma insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like binding protein-3, and outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from intergroup trial N9741[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(24): 8263-8269.
|
| 24 |
曹欢易, 关海霞, 傅晓莹. 内分泌疾病与非酒精性脂肪性肝病[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(1): 11-16.
|
| 25 |
WALKIEWICZ K, NOWAKOWSKA-ZAJDEL E, KOZIEŁ P, et al. The role of some ADAM-proteins and activation of the insulin growth factor-related pathway in colorectal cancer[J]. Cent Eur J Immunol, 2018, 43(1): 109-113.
|
| 26 |
CRAWLEY D J, HOLMBERG L, MELVIN J C, et al. Serum glucose and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 985.
|
| 27 |
DE PERGOLA G, SILVESTRIS F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer[J]. J Obes, 2013, 2013: 291546.
|
| 28 |
SUH S, KIM K W. Diabetes and cancer: cancer should be screened in routine diabetes assessment[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2019, 43(6): 733-743.
|
| 29 |
KASPRZAK A. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signaling in glucose metabolism in colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(12): 6434.
|
| 30 |
BONONI G, MASONI S, DI BUSSOLO V, et al. Historical perspective of tumor glycolysis: a century with otto Warburg[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86(Pt 2): 325-333.
|
| 31 |
FUKUDA R, HIROTA K, FAN F, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(41): 38205-38211.
|
| 32 |
WERNER H. The IGF1 signaling pathway: from basic concepts to therapeutic opportunities[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14882.
|
 ),王素珍1(
),王素珍1( )
)
 ),Suzhen WANG1(
),Suzhen WANG1( )
)