吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 929-938.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250409
玉米须总黄酮对大鼠尿酸性肾病的改善作用及其机制
路静1,刘萌萌1,韩跃威2,黄晓巍1,3,王雨辰1,林贺1,张天柱1( ),林喆1,律广富1,4(
),林喆1,律广富1,4( )
)
- 1.长春中医药大学药学院中药资源重点研究室,吉林 长春 130117
2.长春赛斯医疗生物工程 有限公司技术部,吉林 长春 130021
3.长春中医药大学东北亚中医药研究院基础研究所,吉林 长春 130117
4.长春中医药大学吉林省人参科学研究院药理组,吉林 长春 130117
Ameliorative effect of total flavonoids from corn silk on urate nephropathy in rats and its mechanism
Jing LU1,Mengmeng LIU1,Yuewei HAN2,Xiaowei HUANG1,3,Yuchen WANG1,He LIN1,Tianzhu ZHANG1( ),Zhe LIN1,Guangfu LYU1,4(
),Zhe LIN1,Guangfu LYU1,4( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Resource Science,School of Pharmacy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Technical Department,Changchun Seth Medical & Biological Engineering Co. ,Changchun 130021,China
3.Basic Research Institute,Northeast Asia Institute of Chinese Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
4.Department of Pharmacology,Jilin Ginseng Academy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
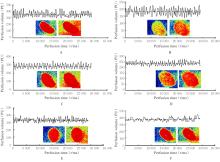
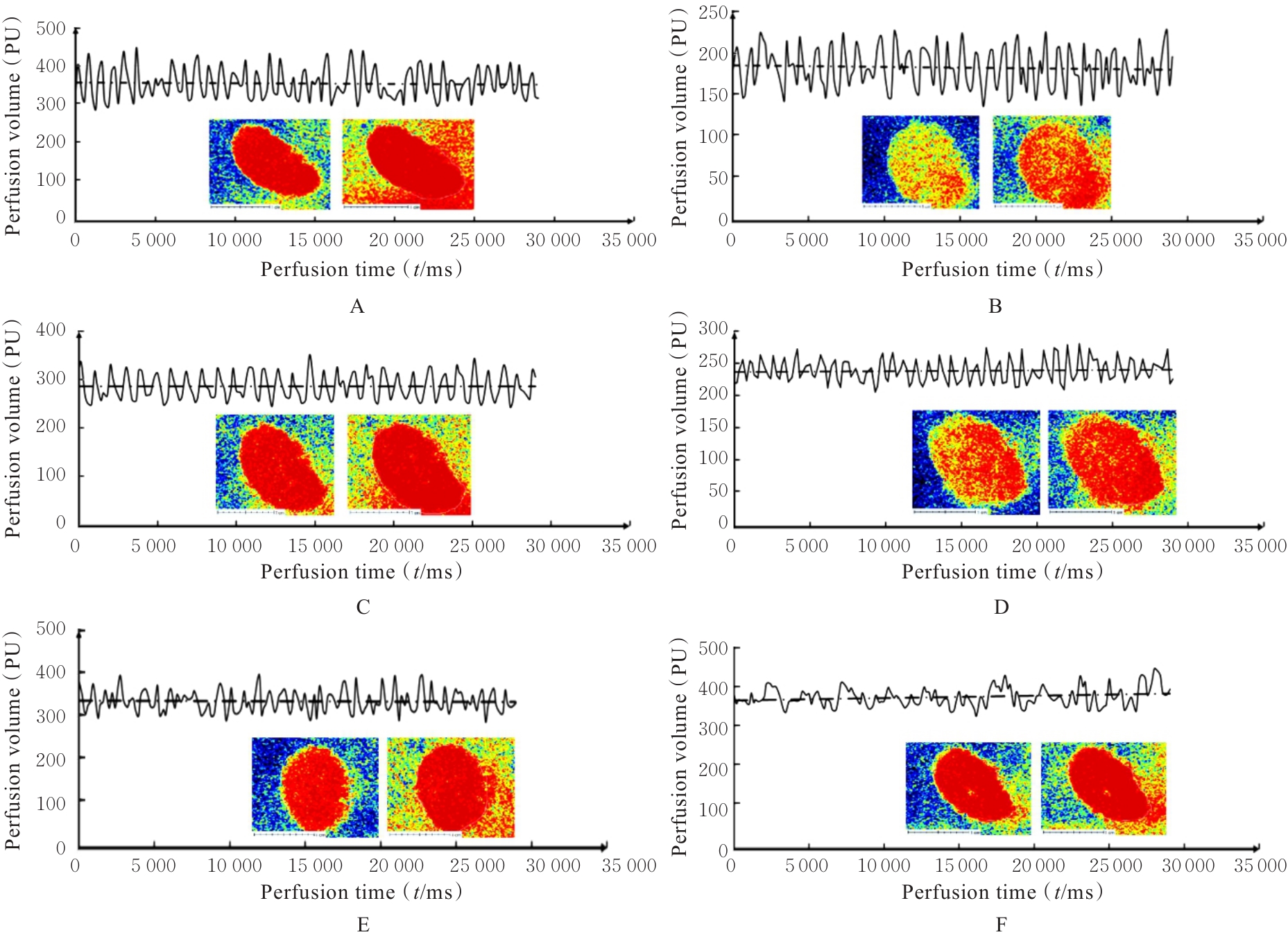
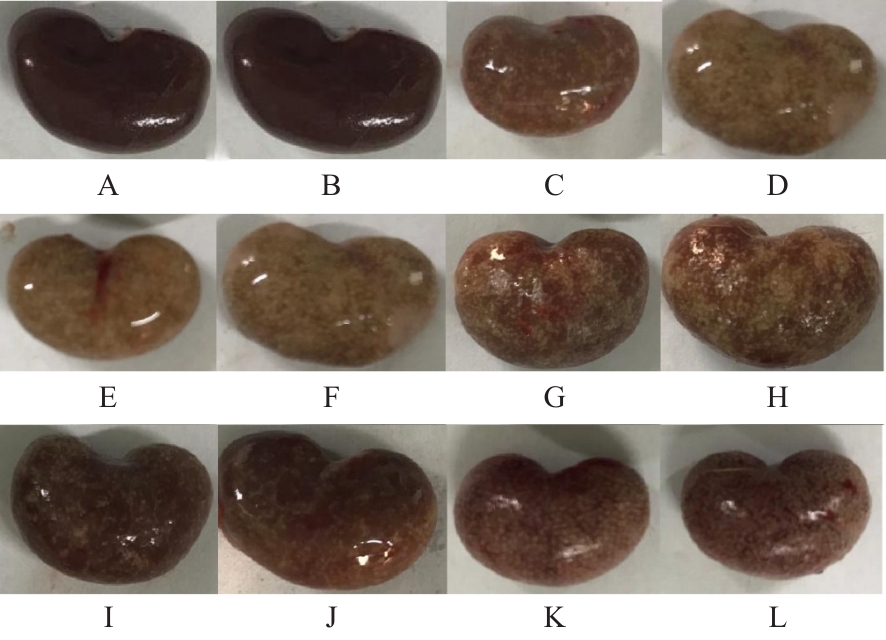
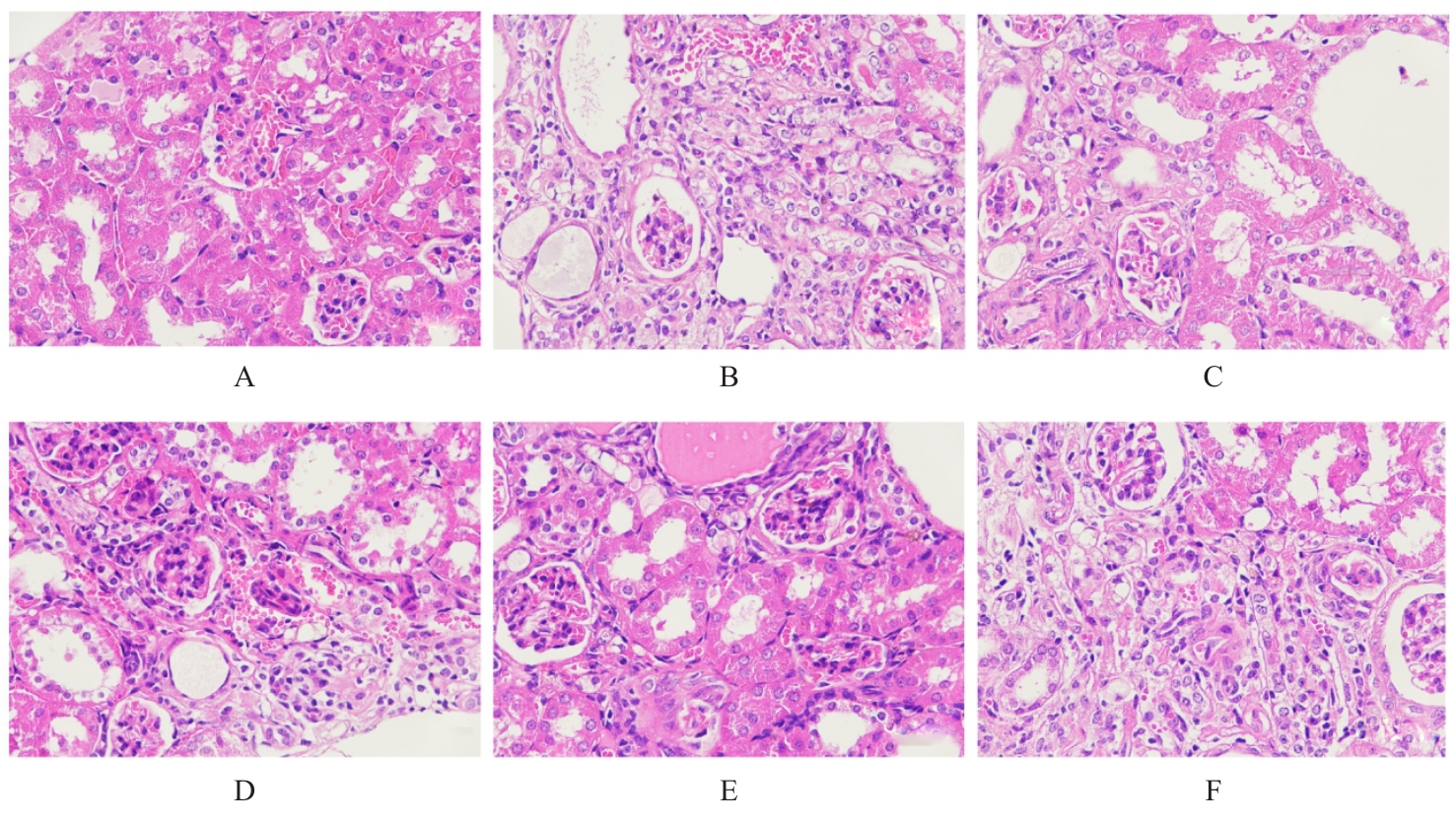
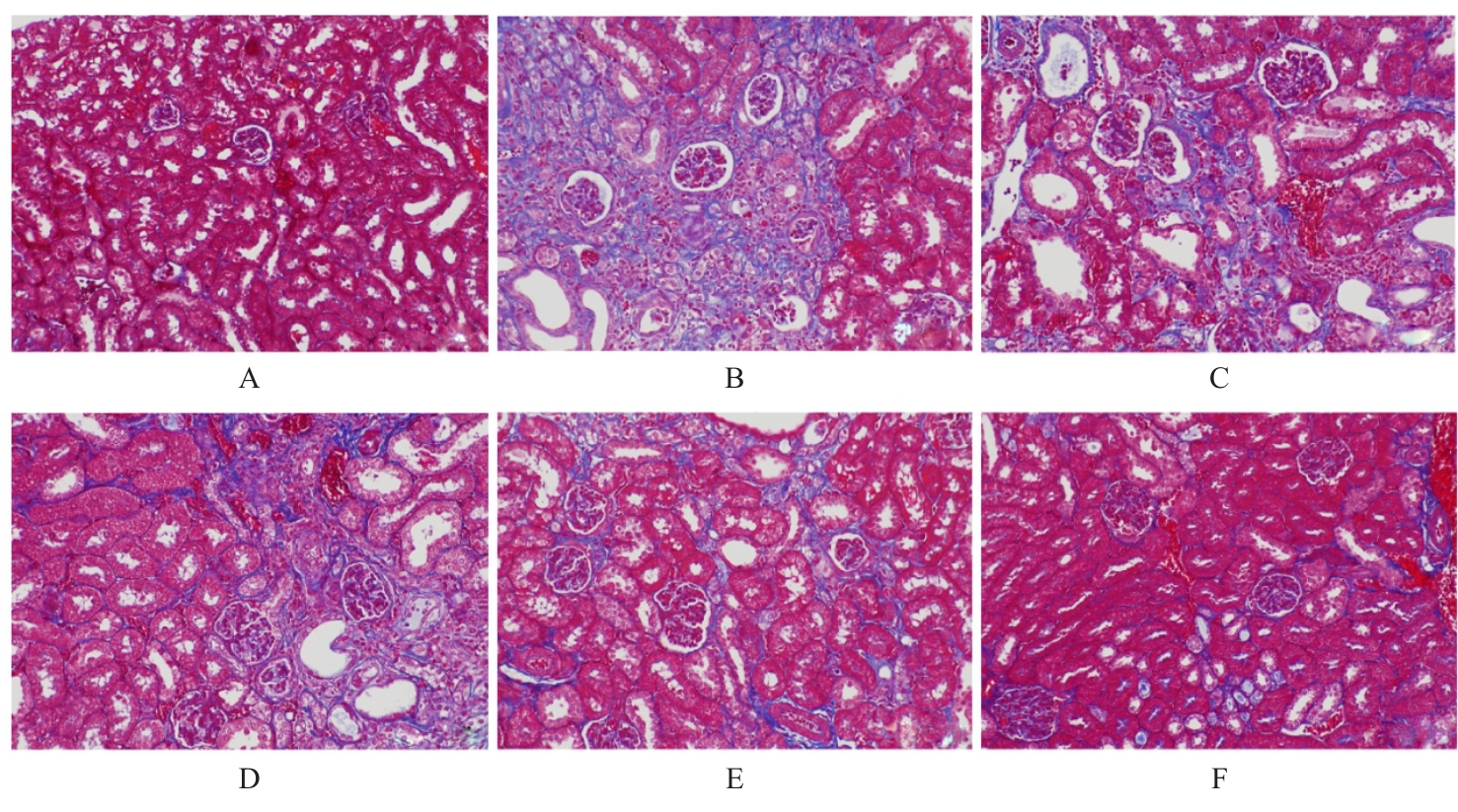
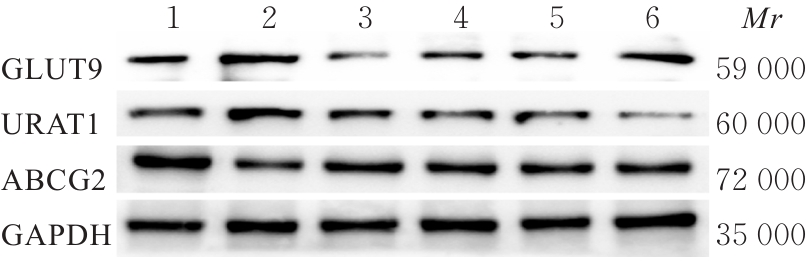
目的 探讨玉米须总黄酮(TFCS)对尿酸性肾病模型大鼠肾脏损伤的改善作用,并阐明其可能的机制。 方法 60只Wistar雄性大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、阳性对照组[苯溴马隆(BZM)组,5 mg·kg-1·d-1]、低剂量TFCS组(20 mg·kg-1·d-1)、中剂量TFCS组(40 mg·kg-1·d-1)和高剂量TFCS组(80 mg·kg-1·d-1),每组10只。除对照组外,其余各组大鼠灌服350 mg·kg-1氧嗪酸钾+ 70 mg·kg-1腺嘌呤4周,建立尿酸性肾病大鼠模型,不同剂量TFCS组大鼠连续灌服TFCS 2周。散斑血流成像仪检测各组大鼠肾脏血液灌注情况并计算各组大鼠肾脏系数,HE染色法和Masson染色法检测各组大鼠肾组织病理形态表现及纤维化程度,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠血清中尿酸(UA)、肌酐(Cr)、血尿素氮(BUN)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平以及尿液中β2-微球蛋白(β2-MG)和微量白蛋白(ALB)水平,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠肾组织中尿酸盐转运蛋白1(URAT1)、葡萄糖转运蛋白9(GLUT9)和ATP结合转运蛋白G2(ABCG2)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肾脏血流灌注量明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BZM组和低、中及高剂量TFCS组大鼠肾脏血流灌注量均升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肾脏质量增加,肉眼可观察到肾脏表面有白色颗粒状斑点,无血色,体积增加;与模型组比较,BZM组和中及高剂量TFCS组大鼠肾脏体积减小,颜色趋于对照组,表面白色颗粒状斑点明显减少。与模型组比较, BZM组和中及高剂量TFCS组大鼠肾脏系数降低(P<0.01)。HE染色法,对照组大鼠肾组织结构无异常;模型组大鼠肾组织可见少量棕黄色尿酸结晶沉积,间质结缔组织增生;与模型组比较,BZM组和不同剂量TFCS组大鼠肾组织损伤均有不同程度减轻,炎症浸润减轻。Masson染色法,对照组大鼠肾组织未见明显胶原纤维沉积;模型组大鼠肾组织可见大量蓝色胶原纤维沉积,胶原容积分数(CVF)较对照组升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BZM组和不同剂量TFCS组大鼠CVF降低(P<0.01)。ELISA法,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠血清中UA、Cr、BUN、IL-6和TNF-α水平升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BZM组和中及高剂量TFCS组大鼠血清中UA、Cr、BUN、IL-6和TNF-α水平降低(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠尿液中β2-MG和ALB水平升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BZM组和不同剂量TFCS组大鼠尿液中β2-MG和ALB水平降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。Western blotting法,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肾组织中URAT1和GLUT9蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01),ABCG2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,BZM组和不同剂量TFCS组大鼠肾组织中URAT1和GLUT9蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),ABCG2蛋白表达水平均升高(P<0.01)。 结论 TFCS能明显减轻尿酸性肾病模型大鼠的肾脏损伤,其机制可能与TFCS降低肾组织中URAT1和GLUT9蛋白表达水平及升高ABCG2蛋白表达水平有关联。
中图分类号:
- R96