吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1475-1486.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250604
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
针刺对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠股四头肌卫星细胞分化和凋亡的影响及其机制
郑曲1,2,3,董宝强1,3( ),林星星1,3,张宇1,关雪峰4,王超杰1,韩易言1(
),林星星1,3,张宇1,关雪峰4,王超杰1,韩易言1( )
)
- 1.辽宁中医药大学针灸推拿学院, 辽宁 沈阳 110847
2.辽宁省教育厅针灸生物学重点实验室, 辽宁 沈阳 110847
3.辽宁省针灸养生康复重点实验室, 辽宁 沈阳 110847
4.沈阳药科大学, 辽宁 沈阳 110016
Effect of acupuncture on differentiation and apoptosis of quadriceps muscle satellite cells in knee osteoarthritis model rats and its mechanism
Qu ZHENG1,2,3,Baoqiang DONG1,3( ),Xingxing LIN1,3,Xuefeng GUAN1,Yu ZHANG4,Chaojie WANG1,Yiyan Han1(
),Xingxing LIN1,3,Xuefeng GUAN1,Yu ZHANG4,Chaojie WANG1,Yiyan Han1( )
)
- 1.College of Acupuncture and massage,Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shenyang 110847,China
2.Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Biology,Education of Liaoning Province,Shenyang 110847,China
3.Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Health and Rehabilitation,Shenyang 110847,China
4.Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
摘要:
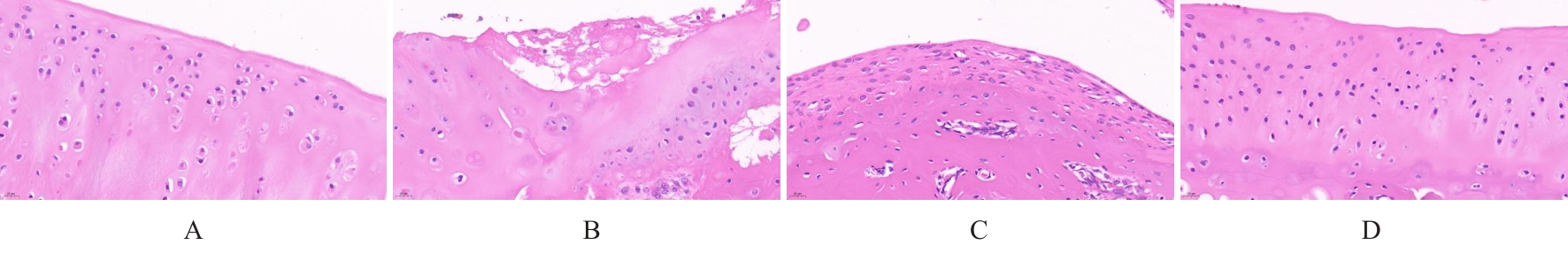
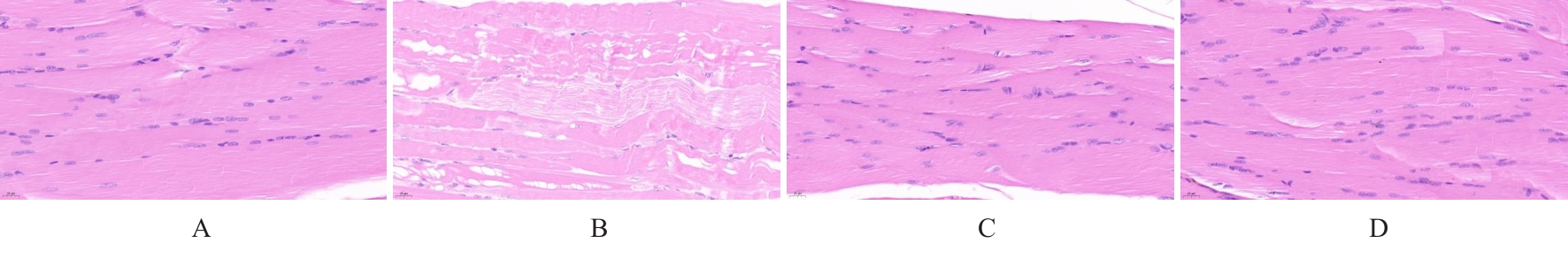
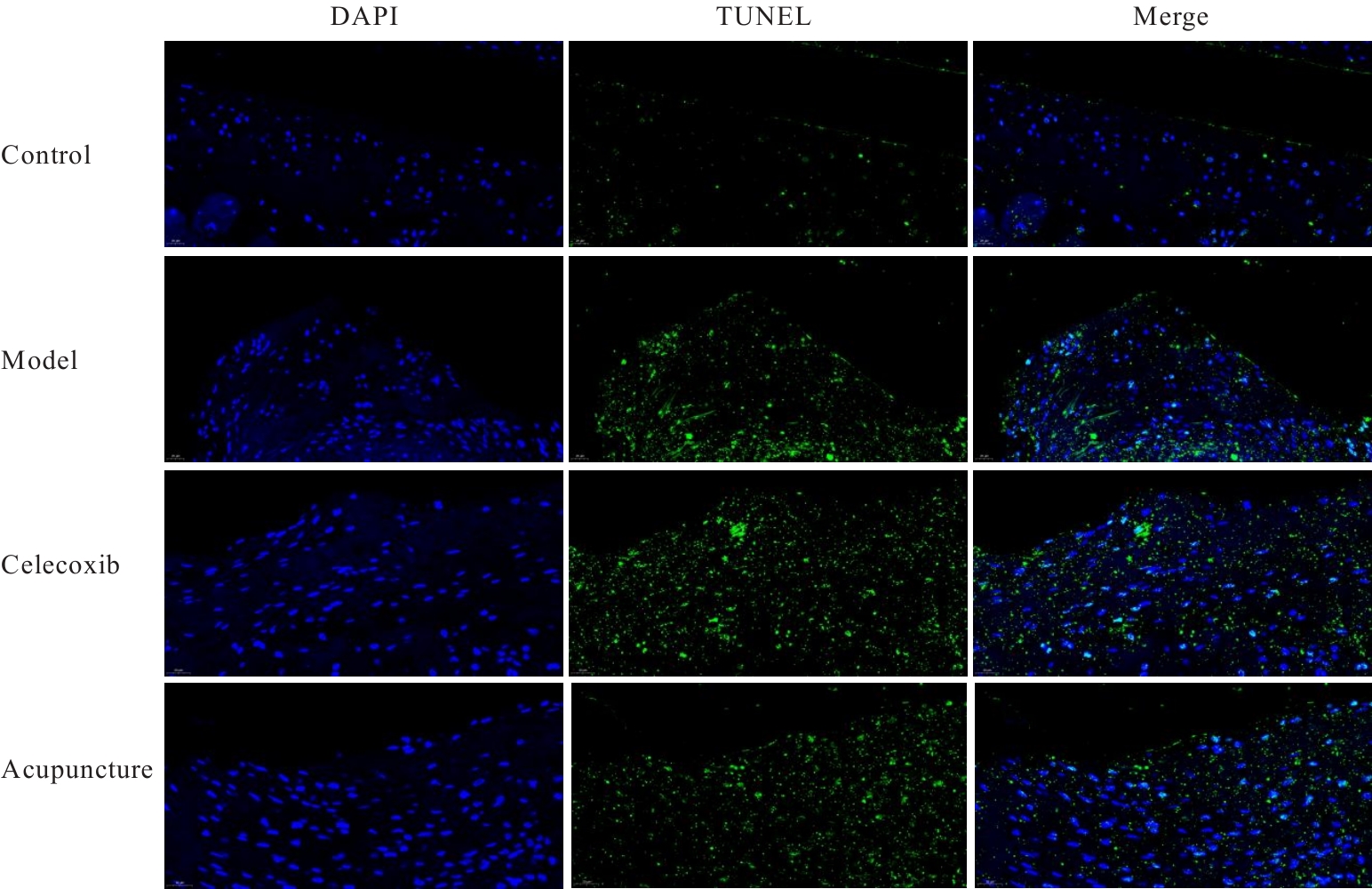
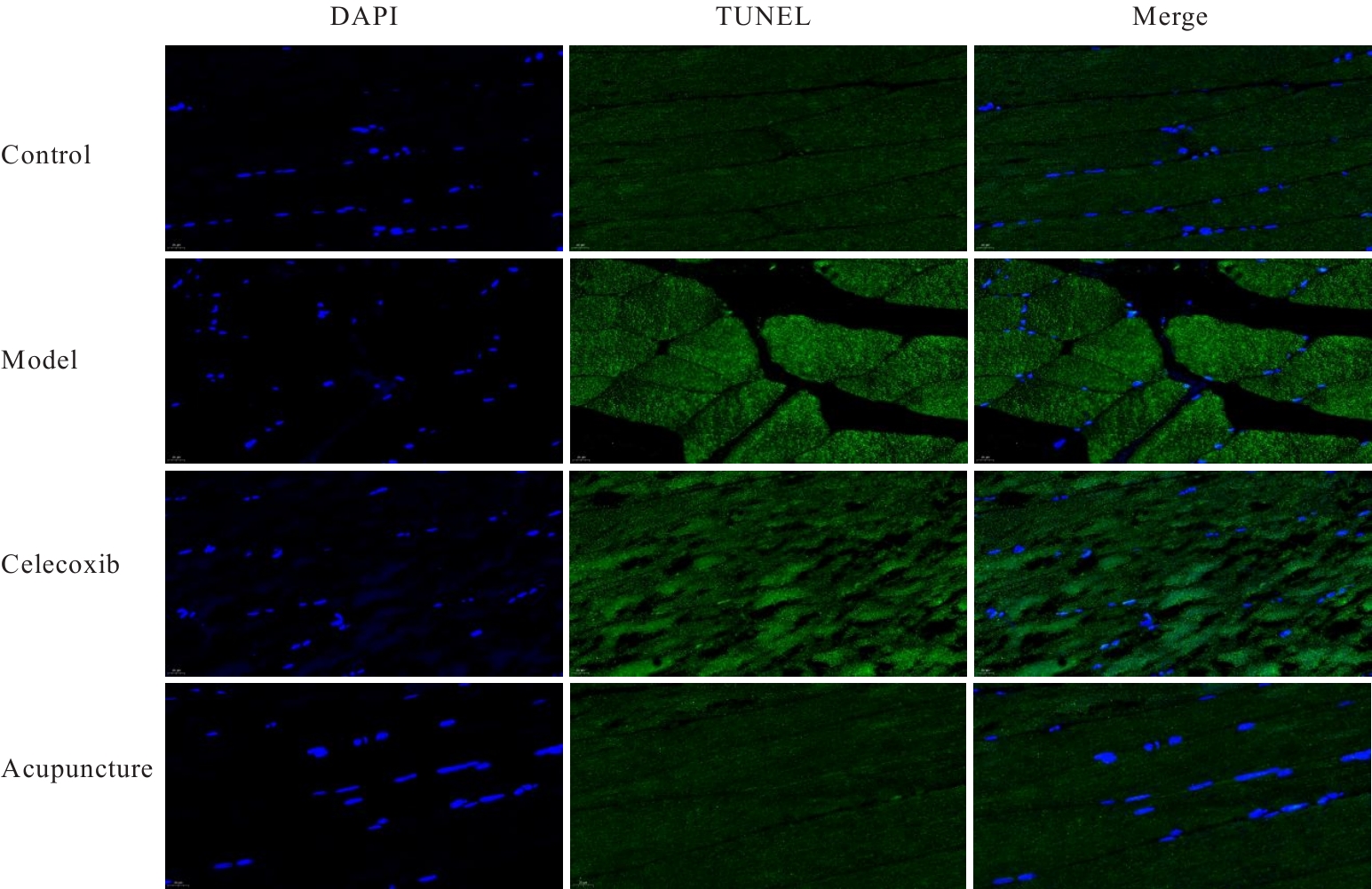
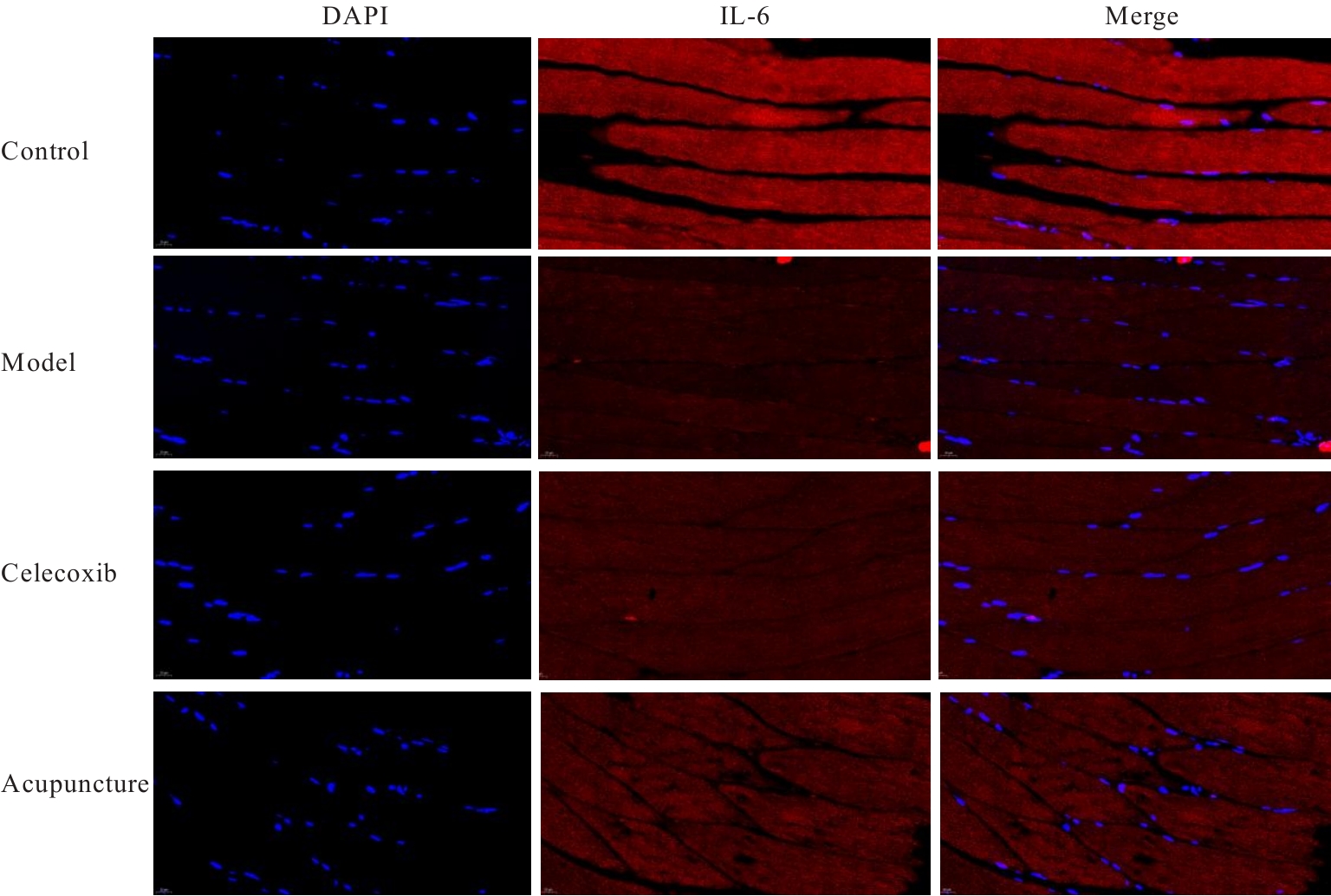
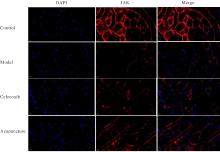
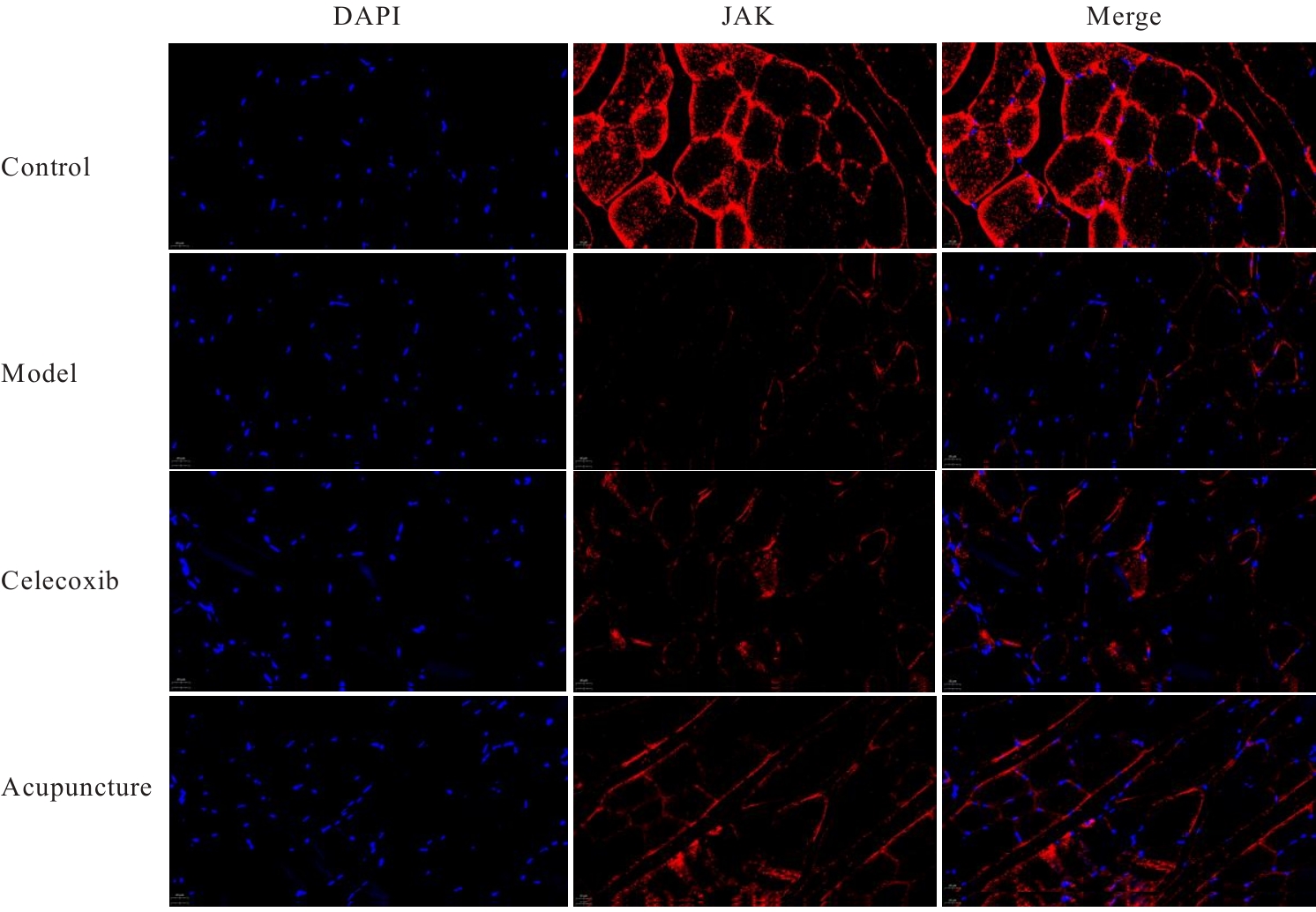
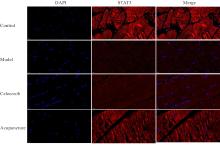
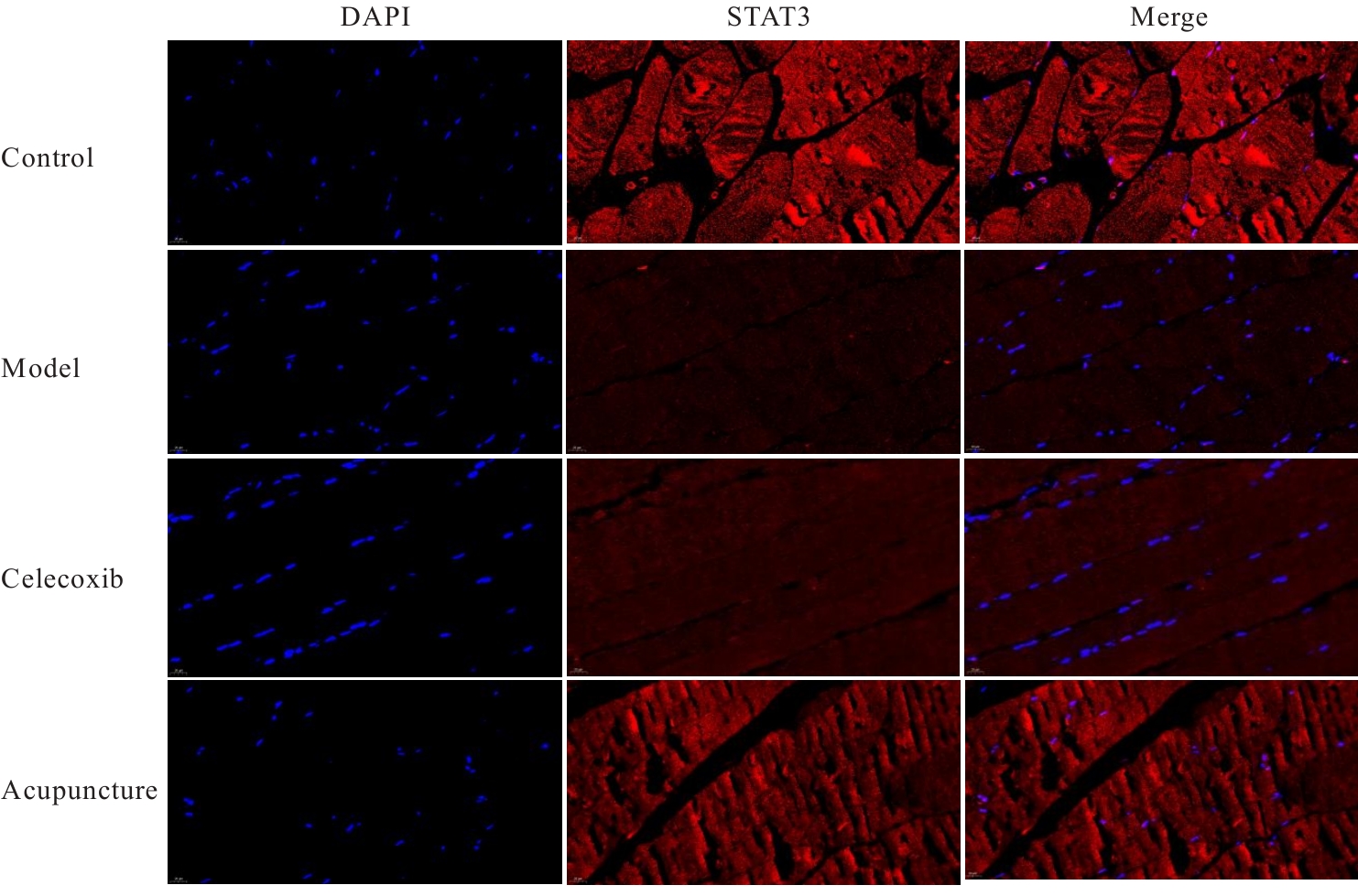
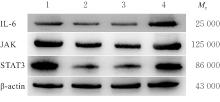
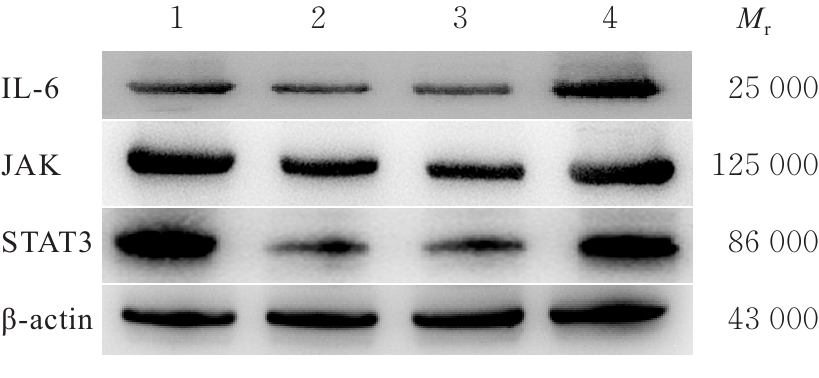
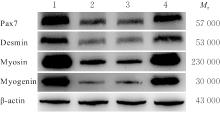
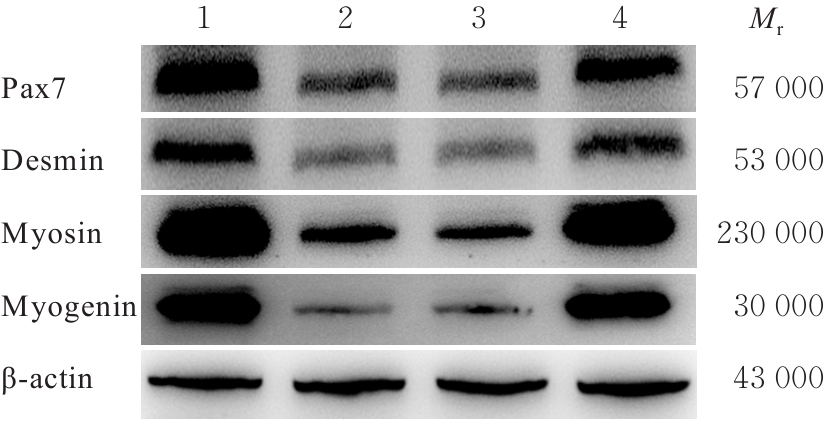
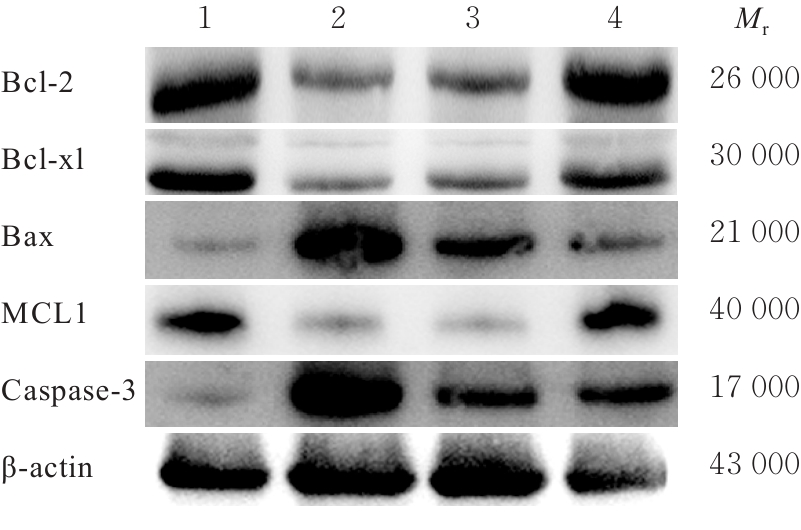
目的 探讨针刺对膝骨关节炎(KOA)模型大鼠股四头肌卫星细胞分化和凋亡的影响,并阐明其相关机制。 方法 选取40只SPF级大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、塞来昔布组和针刺组,每组10只。对照组大鼠仅切开关节腔后缝合,模型组、塞来昔布组和针刺组大鼠复制KOA模型。测量各组大鼠患肢股骨段最大周长、大鼠体质量和股四头肌湿重,计算各组大鼠股四头肌湿重维持率和股四头肌湿重/体质量比值。HE染色观察各组大鼠关节软骨和股四头肌组织病理形态表现,末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶(TdT)介导的缺口末端标记法(TUNEL)检测各组大鼠关节软骨和股四头肌组织中细胞凋亡指数,免疫荧光法检测各组大鼠股四头肌组织中白细胞介素6(IL-6)、Janus激酶(JAK)及信号转导与转录激活因子3(STAT3)蛋白表达水平,Western blotting 法检测各种大鼠股四头肌组织中IL-6/JAK/STAT3信号通路、肌卫星细胞及凋亡相关蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠患侧后腿围度、股四头肌湿重、湿重维持率和湿重/体质量比值均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,塞来昔布组和针刺组大鼠患侧后腿围度、股四头肌湿重、湿重维持率和湿重/体质量比值均明显升高(P<0.05);与塞来昔布组比较,针刺组大鼠患侧后腿围度、股四头肌湿重、湿重维持率和湿重/体质量比值均明显升高(P<0.05)。HE染色观察,对照组大鼠膝关节软骨保持完整,软骨细胞聚集且水平排列,边缘平整,股四头肌细胞呈长圆柱状,有序排列,形态规则;模型组大鼠膝关节软骨较薄,边缘粗糙,软骨层数减少,排列无序,股四头肌纤维排列紊乱,部分肌纤维溶解和肌细胞膜损伤,并伴有肌纤维碎片和大量炎症渗出液;塞来昔布组大鼠膝关节软骨形态大体正常,偶见软骨排列不规律和厚度减少,偶尔可见散在的坏死软骨细胞,股四头肌肌纤维和肌膜较为完整,有新生肌纤维的出现,部分肌纤维边缘模糊,伴有少量细胞碎片和轻微炎症浸润;针刺组大鼠膝关节软骨结构保持完整,边缘平滑,偶尔边缘粗糙,软骨细胞聚集且排列有序。TUNEL法检测,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠关节软骨和股四头肌组织中细胞凋亡指数明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,塞来昔布组和针刺组大鼠关节软骨及股四头肌组织中细胞凋亡指数均明显降低(P<0.05);与塞来昔布组比较,针刺组大鼠关节软骨及股四头肌组织中细胞凋亡指数明显降低(P<0.05)。免疫荧光法检测,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠股四头肌组织中IL-6、JAK和STAT3蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,塞来昔布组和针刺组大鼠股四头肌组织中IL-6、JAK及STAT3蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与塞来昔布组比较,针刺组大鼠股四头肌组织中IL-6、JAK和STAT3蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。Western blotting法检测,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠股四头肌组织IL-6、JAK、STAT3、特异性蛋白配对盒转录因子7(Pax7)、肌间线蛋白(Desmin)、肌球蛋白(Myosin)和肌细胞生成素(Myogenin)蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,塞来昔布组和针刺组大鼠股四头肌组织中IL-6、JAK、STAT3、Pax7、Desmin、Myosin和Myogenin蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与塞来昔布组比较,针刺组大鼠股四头肌组织中IL-6、JAK、STAT3、Pax7、Desmin、Myosin和Myogenin蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠股四头肌组织中B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2),B细胞淋巴瘤xl(Bcl-xl)和髓系细胞白血病1(MCL1)蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)和半胱氨酸依赖性天冬氨酸特异性蛋白酶3(Caspase-3)蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,塞来昔布组和针刺组大鼠股四头肌组织中Bcl-2、Bcl-xl和MCL1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),Bax和Caspase-3蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05);与塞来昔布组比较,针刺组大鼠股四头肌组织中Bcl-2、Bcl-xl和MCL1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),Bax和Caspase-3蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 针刺可促进膝骨关节炎模型大鼠股四头肌卫星细胞分化,并抑制肌细胞凋亡,其机制可能与上调股四头肌组织中IL-6、JAK和STAT3蛋白表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R684.3