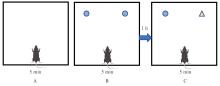
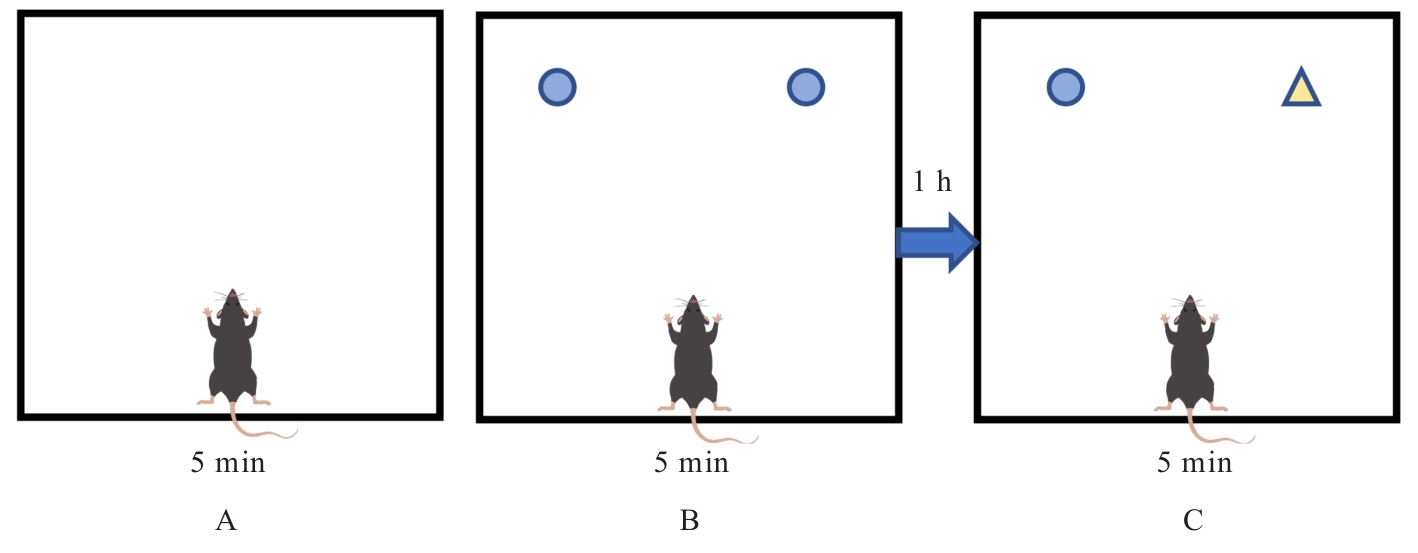
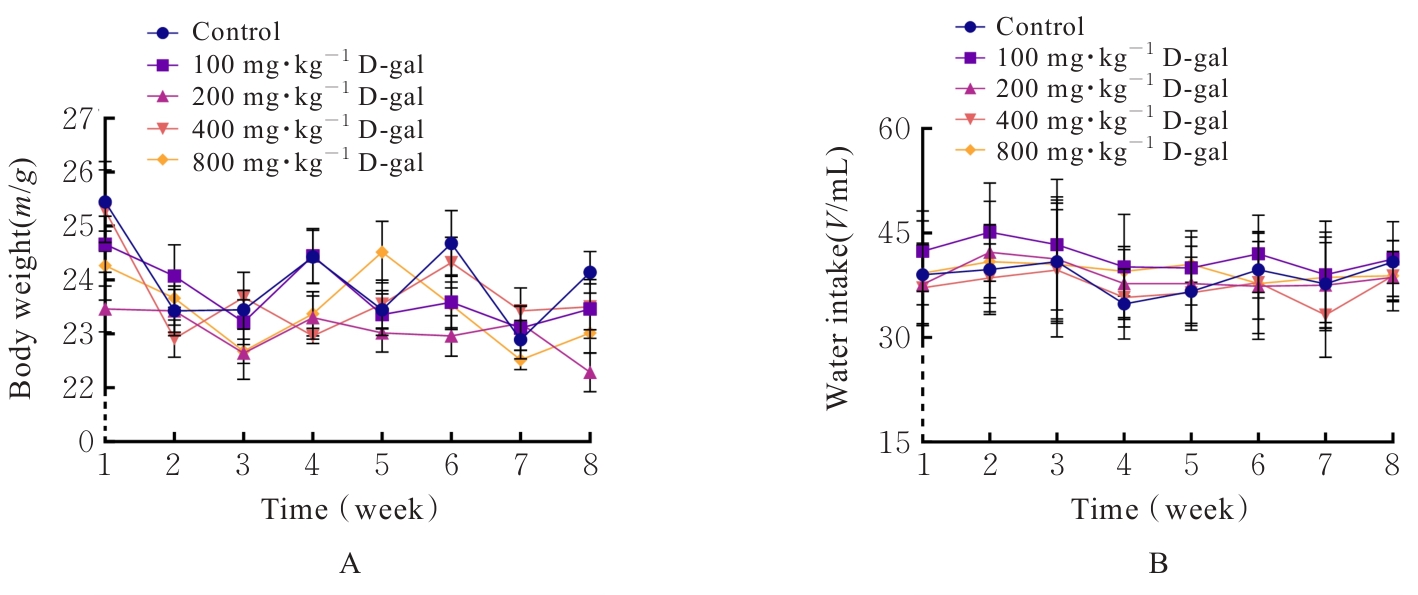
| [1] |
BO-HTAY C, SHWE T, HIGGINS L, et al. Aging induced by D-galactose aggravates cardiac dysfunction via exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction in obese insulin-resistant rats[J]. Geroscience, 2020, 42(1): 233-249.
|
| [2] |
魏孟伶, 贺绘宇, 王 娟, 等. 中老年人生物学衰老与认知功能的关系研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2025, 52(2): 342-348.
|
| [3] |
LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO M A, PARTRIDGE L, et al. Hallmarks of aging: an expanding universe[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(2): 243-278.
|
| [4] |
SUN W W, ZHU J H, QIN G Y, et al. Lonicera Japonica polysaccharides alleviate D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and restore gut microbiota in ICR mice[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 245: 125517.
|
| [5] |
JALBERT J J, DAIELLO L A, LAPANE K L. Dementia of the Alzheimer type[J]. Epidemiol Rev, 2008, 30: 15-34.
|
| [6] |
吴 薇. D-半乳糖致小鼠脑衰老早期阶段星形胶质细胞的活化及其作用机制[D]. 南京: 南京医科大学, 2010.
|
| [7] |
赵凡凡, 周玉枝, 高 丽, 等. D-半乳糖致衰老大鼠模型的研究进展[J]. 药学学报, 2017, 52(3): 347-354.
|
| [8] |
马佳丽, 宋莉艳, 李观纬, 等. D-gal诱导小鼠衰老模型建立的适宜浓度探索与模型评价[J]. 健康之路, 2016, 15(11): 5.
|
| [9] |
AZMAN K F, SAFDAR A, ZAKARIA R. D-galactose-induced liver aging model: Its underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2021, 150: 111372.
|
| [10] |
SUN K Y, YANG P Y, ZHAO R, et al. Matrine attenuates D-galactose-induced aging-related behavior in mice via inhibition of cellular senescence and oxidative stress[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 7108604.
|
| [11] |
KUMAR H, BHARDWAJ K, VALKO M, et al. Antioxidative potential of Lactobacillus sp. in ameliorating D-galactose-induced aging[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2022, 106(13): 4831-4843.
|
| [12] |
GONZALES M M, GARBARINO V R, POLLET E, et al. Biological aging processes underlying cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2022, 132(10): e158453.
|
| [13] |
WYSS-CORAY T. Ageing, neurodegeneration and brain rejuvenation[J]. Nature, 2016, 539(7628): 180-186.
|
| [14] |
LI M Q, ZHU M Z, QUAN W, et al. Acteoside palliates d-galactose induced cognitive impairment by regulating intestinal homeostasis[J]. Food Chem, 2023, 421: 135978.
|
| [15] |
ZHANG J J, HU R Y, CHEN K C, et al. 20(S)- protopanaxatriol inhibited D-galactose-induced brain aging in mice via promoting mitochondrial autophagy flow[J]. Phytother Res, 2023, 37(7): 2827-2840.
|
| [16] |
HE W, SONG H, YANG Z B, et al. Beneficial effect of GABA-rich fermented milk whey on nervous system and intestinal microenvironment of aging mice induced by D-galactose[J]. Microbiol Res, 2024, 278: 127547.
|
| [17] |
仝佳祥, 陈 杨, 李 璇, 等. 枸杞叶改善D-半乳糖致亚急性衰老小鼠学习与记忆能力的效应部位与作用机制研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2024, 26(1): 48-60.
|
| [18] |
AN J R, LIU J T, GAO X M, et al. Effects of liraglutide on astrocyte polarization and neuroinflammation in db/db mice: focus on iron overload and oxidative stress[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2023, 17: 1136070.
|
| [19] |
CHEN Y X, YANG H, WANG D S, et al. Gastrodin relieves cognitive impairment by regulating autophagy via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in vascular dementia[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2023, 671: 246-254.
|
| [20] |
吴志悦, 薛晓帆, 曾景蓉, 等. 端粒-端粒酶在神经退行性疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2024, 41(2): 169-174.
|
| [21] |
SIMONE M J, TAN Z S. The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of delirium and dementia in older adults: a review[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2011, 17(5): 506-513.
|
| [22] |
CHU Z X, HAN S, LUO Y, et al. Targeting gut-brain axis by dietary flavonoids ameliorate aging-related cognition decline: Evidences and mechanisms[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2024, 64(28): 10281-10302.
|
| [23] |
JESSEN F, AMARIGLIO R E, BUCKLEY R F, et al. The characterisation of subjective cognitive decline[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2020, 19(3): 271-278.
|
| [24] |
LIU H, SHEN L K, SUN Z Z, et al. Downregulated phosphoglycerate kinase 1 attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by reversing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress through the nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2/ARE pathway[J]. Neuroscience, 2023, 524: 94-107.
|
| [25] |
叶 蕾, 舒 姝, 徐 运, 等. 衰老中小胶质细胞对认知功能减退调控的研究进展[J]. 临床神经病学杂志, 2024, 37(1): 65-68.
|
| [26] |
YAO Y Q, LUO Y S, LIANG X M, et al. The role of oxidative stress-mediated fibro-adipogenic progenitor senescence in skeletal muscle regeneration and repair[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2025, 16(1): 104.
|
| [27] |
IMAI S I, GUARENTE L. NAD+ and sirtuins in aging and disease[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2014, 24(8): 464-471.
|
| [28] |
邢秋娟, 施 杞, 王拥军. D-半乳糖诱导衰老动物模型的机制及其在中医药方面的应用[J]. 上海中医药大学学报, 2010, 24(3): 93-98.
|
| [29] |
OPRESKO P L, SANFORD S L, DE ROSA M. Oxidative stress and DNA damage at telomeres[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2025, 17(6): a041707.
|
| [30] |
BARUCH K, DECZKOWSKA A, DAVID E, et al. Aging. Aging-induced type I interferon response at the choroid plexus negatively affects brain function[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6205): 89-93.
|
| [31] |
STERN Y. Cognitive reserve in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2012, 11(11): 1006-1012.
|
| [32] |
UYAR B, PALMER D, KOWALD A, et al. Single-cell analyses of aging, inflammation and senescence[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2020, 64: 101156.
|
| [33] |
KROEMER G, MAIER A B, CUERVO A M, et al. From geroscience to precision geromedicine: Understanding and managing aging[J]. Cell, 2025, 188(8): 2043-2062.
|
| [34] |
MAUS M, LÓPEZ-POLO V, MATEO L, et al. Iron accumulation drives fibrosis, senescence and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype[J]. Nat Metab, 2023, 5(12): 2111-2130.
|
| [35] |
VADDAVALLI P L, SCHUMACHER B. The p53 network: cellular and systemic DNA damage responses in cancer and aging[J]. Trends Genet, 2022, 38(6): 598-612.
|
| [36] |
GROSSE L, WAGNER N, EMELYANOV A, et al. Defined p16(high) senescent cell types are indispensable for mouse healthspan[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(1): 87-99.
|
 )
)
 )
)