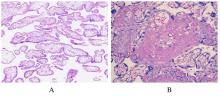
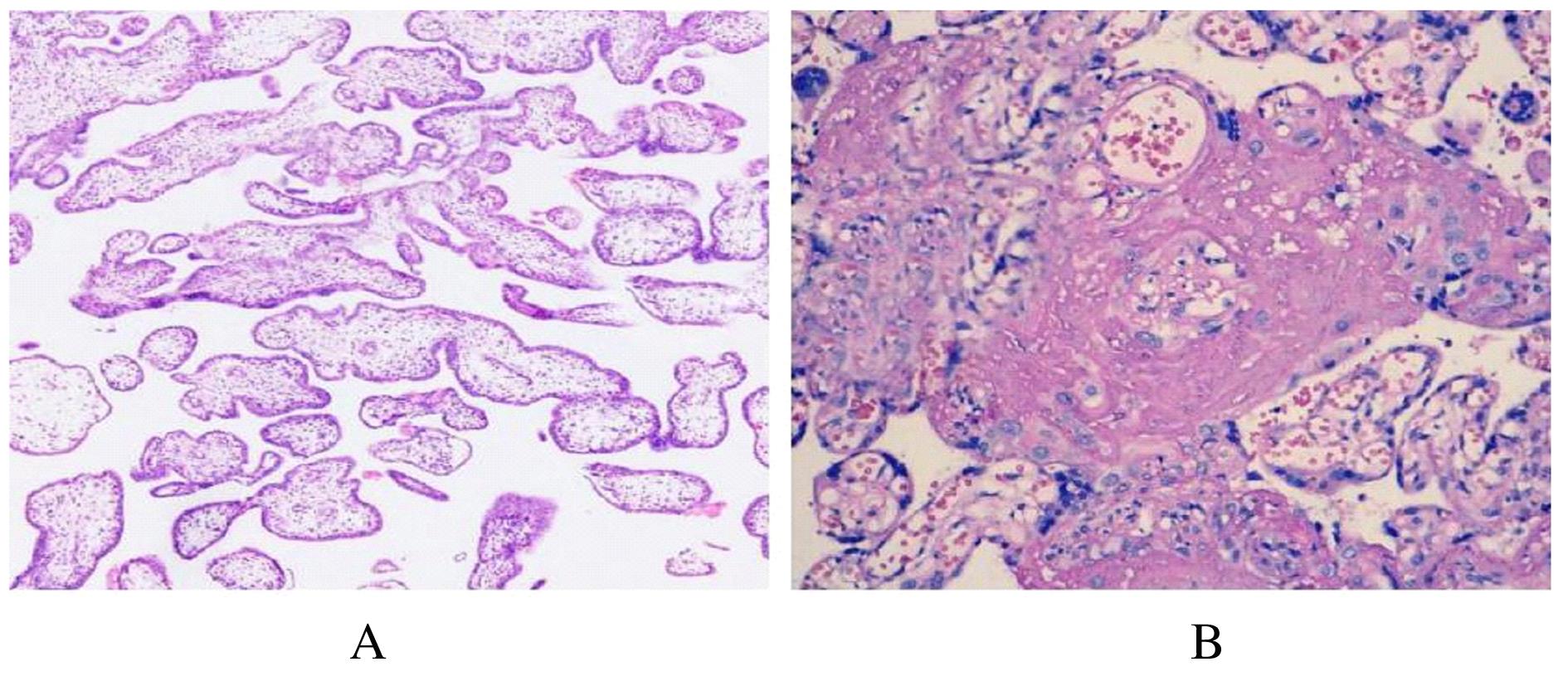
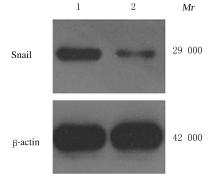
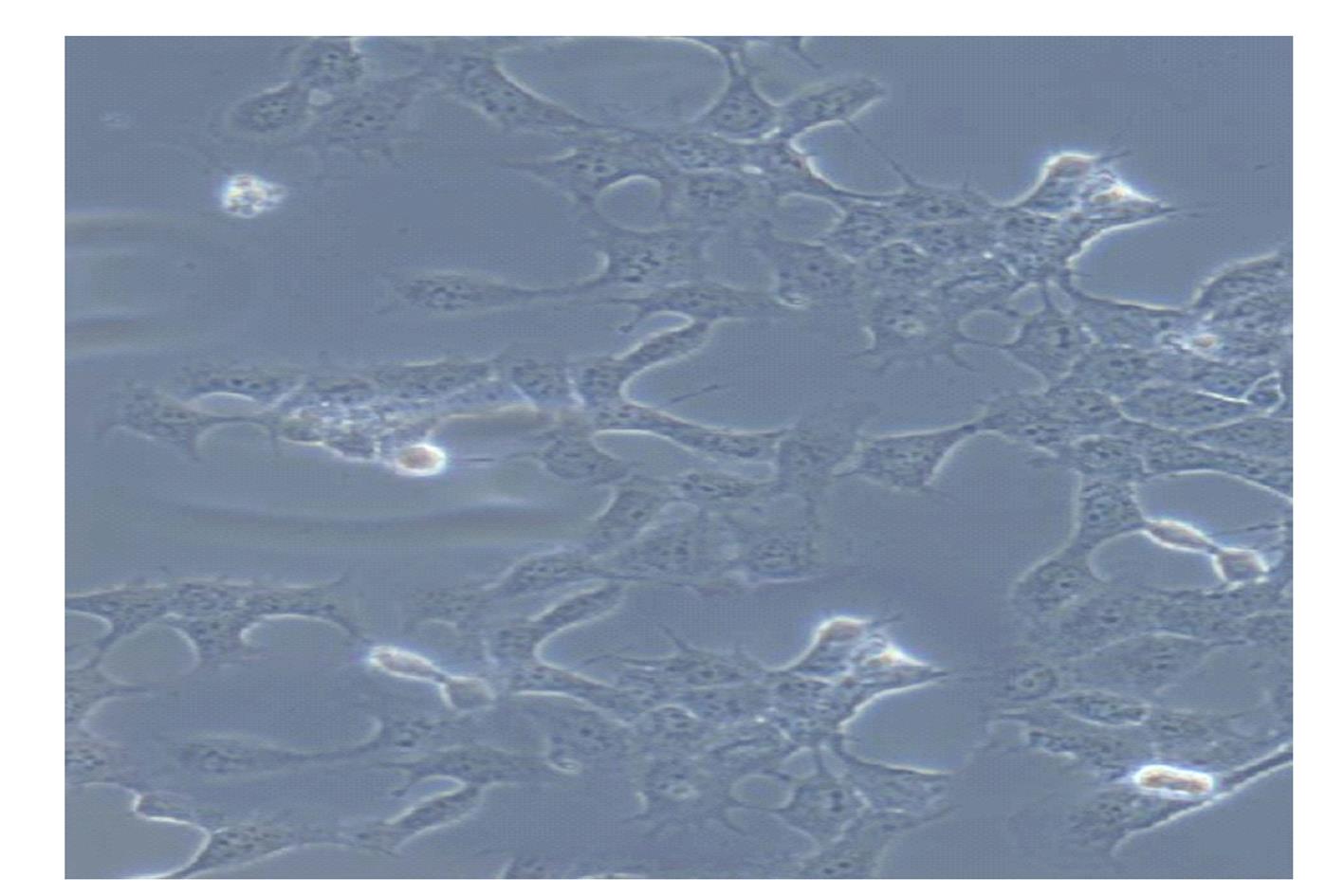
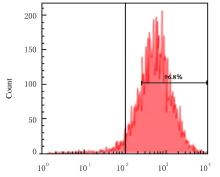
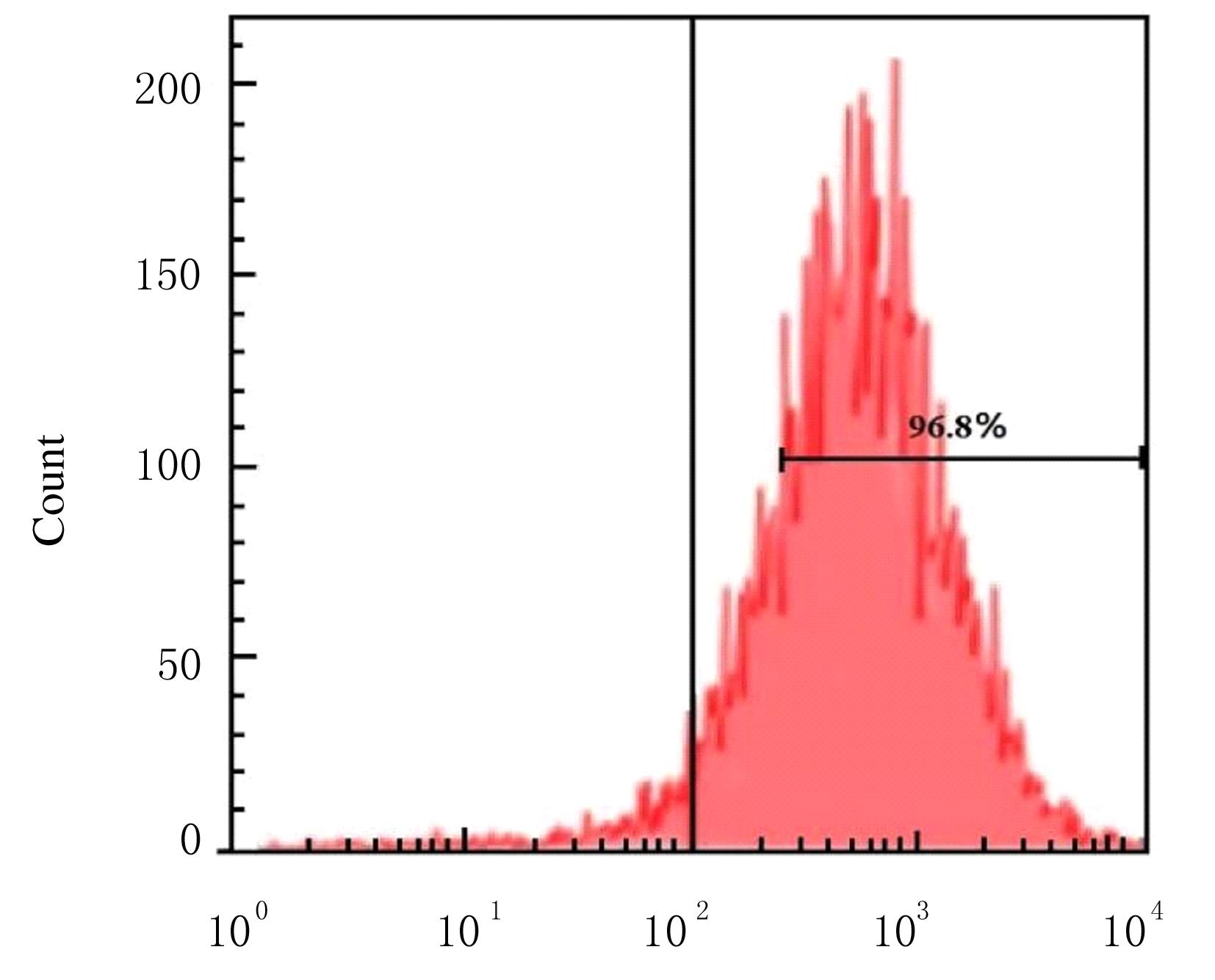
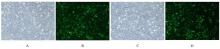
| 1 |
BECKERS K F, SONES J L. Maternal microbiome and the hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, preeclampsia[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2020,318(1):H1-H10.
|
| 2 |
LEVY M, KOVO M, SCHREIBER L, et al. Pregnancy outcomes in correlation with placental histopathology in subsequent pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia[J]. Pregnancy Hypertens, 2019, 18:163-168.
|
| 3 |
TENÓRIO M B, FERREIRA R C, MOURA F A, et al. Cross-talk between oxidative stress and inflammation in preeclampsia[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019:8238727.
|
| 4 |
RAMBALDI M P, WEINER E, MECACCI F, et al. Immunomodulation and preeclampsia[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2019, 60:87-96.
|
| 5 |
SU M T, WANG C Y, TSAI P Y, et al. Aspirin enhances trophoblast invasion and represses soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 production: a putative mechanism for preventing preeclampsia [J]. J Hypertens, 2019, 37(12):2461-2469.
|
| 6 |
HE T Q, QIAO Y, LV Y, et al. lncRNA FAM99A is downregulated in preeclampsia and exerts a regulatory effect on trophoblast cell invasion, migration and apoptosis[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 20(2): 1451-1458.
|
| 7 |
ZOU A X, CHEN B, LI Q X, et al. MiR-134 inhibits infiltration of trophoblast cells in placenta of patients with preeclampsia by decreasing ITGB1 expression[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(8): 2199-2206.
|
| 8 |
WANG H, LI J M, WEI W, et al. Regulation of ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 by Snail contributes to chemoresistance in colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2020, 111(1):84-97.
|
| 9 |
YAO Y H, PANG T Y, CHENG Y, et al. Positive correlative over-expression between eIF4E and snail in nasopharyngeal carcinoma promotes its metastasis and resistance to cisplatin[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2020, 26(3): 1639-1649.
|
| 10 |
宋 燕, 唐龙英. 转录因子Snail在子痫前期患者胎盘及子痫前期大鼠模型中的表达[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2019, 38(10): 4686-4692.
|
| 11 |
杨 唅, 李名花. 基于代谢组学的子痫前期发病机制研究[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2018, 33(24): 5979-5982.
|
| 12 |
范思斯, 潘 玫, 秦海燕, 等. 外周血β-HCG mRNA表达与妊娠滋养细胞肿瘤血行转移的相关研究[J]. 实用癌症杂志, 2015, 30(6): 806-811.
|
| 13 |
郭广丽, 张英奎, 李雅丽, 等. 河北省胎盘早剥流行病学特点和危险因素分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(12):1621-1625.
|
| 14 |
CHIARELLO D I, ABAD C, ROJAS D, et al. Oxidative stress: Normal pregnancy versus preeclampsia[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2020, 1866(2):165354.
|
| 15 |
FILIPEK A, JUREWICZ E. Preeklampsja-choroba kobiet w ciąży[J]. Postepy Biochem, 2018, 64(4): 232-229.
|
| 16 |
GUO X B, ZHU R, LUO A P, et al. EIF3H promotes aggressiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating Snail stability[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1): 175.
|
| 17 |
WIECZOREK-SZUKALA K, KOPCZYNSKI J, KOWALSKA A, et al. Snail-1 overexpression correlates with metastatic phenotype in BRAFV600E positive papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(9): 2701.
|
| 18 |
CAO F, YIN L X. PAK1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by facilitating EMT via directly up-regulating Snail[J]. Genomics, 2020, 112(1): 694-702.
|
| 19 |
LU W, MA Y Y, SHAO Q Q, et al. ROS/p53/miR‑335‑5p/Sp1 axis modulates the migration and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of JEG‑3 cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 21(3): 1208-1216.
|
| 20 |
WU D C, SHI L, CHEN X J, et al. β-TrCP suppresses the migration and invasion of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia by down-regulating Snail[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2020, 395(2):112230.
|
| 21 |
BISWAS K H. Molecular mobility-mediated regulation of E-cadherin adhesion[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2020, 45(2): 163-173.
|
| 22 |
AGRAVAL H, YADAV U C S. MMP-2 and MMP-9 mediate cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in airway epithelial cells via EGFR/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway: Amelioration by fisetin[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2019, 314: 108846.
|
| 23 |
LI Q, WANG T J, HUANG S Y, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 affects the migration and invasion of trophoblast cells by regulating FOS expression in early-onset preeclampsia[J]. Pregnancy Hypertens, 2020, 21: 50-57.
|
 ),Aiping ZHANG,Yuqin LI
),Aiping ZHANG,Yuqin LI