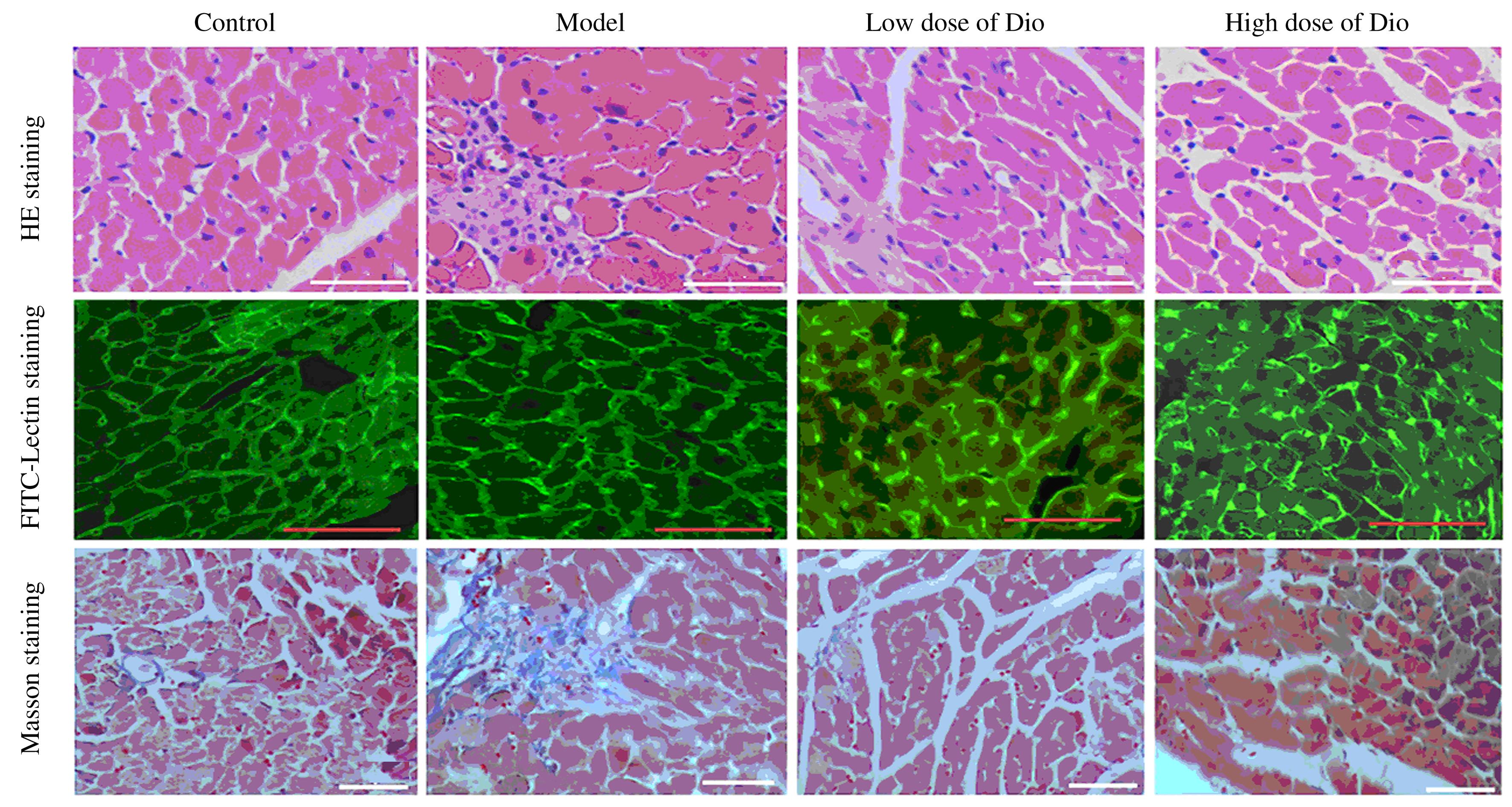
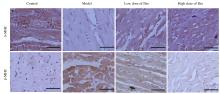
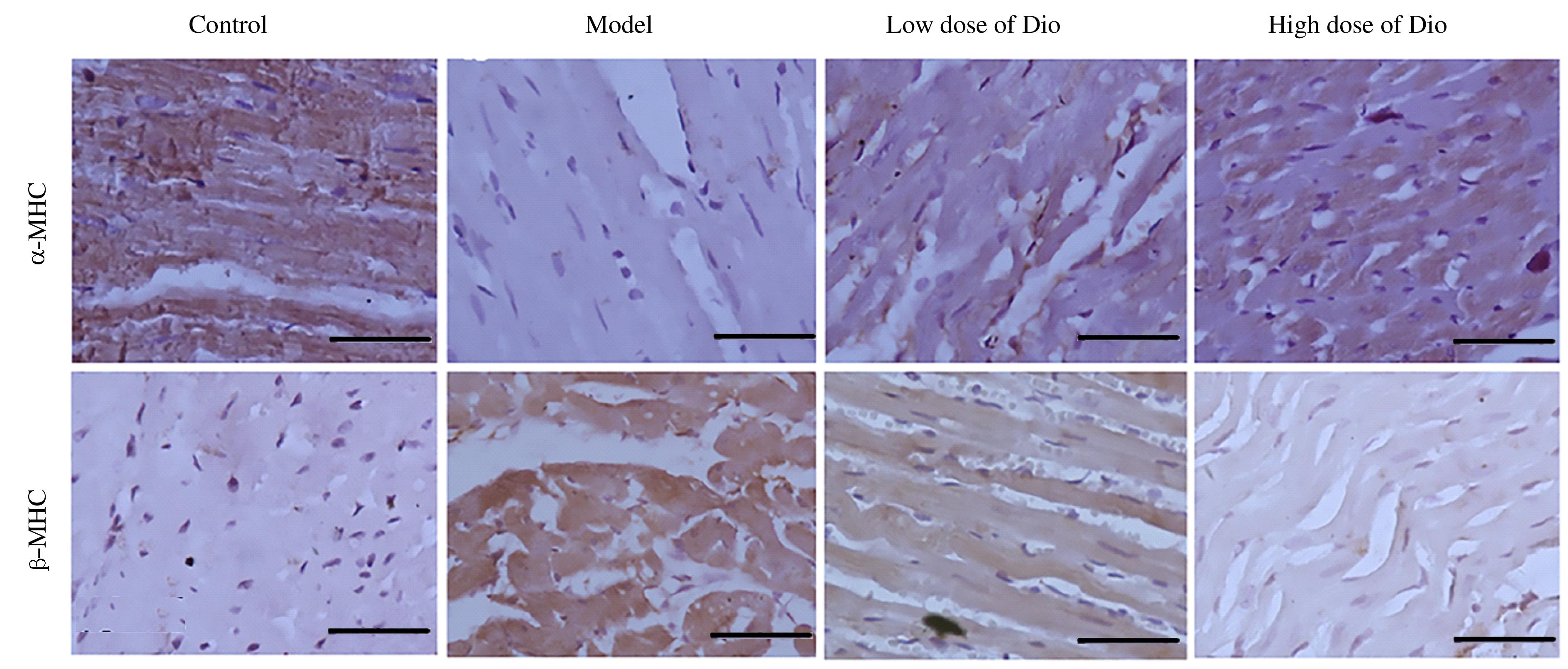
| 1 |
中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2019概要 [J]. 中国循环杂志, 2020, 35(9):833-854.
|
| 2 |
GIBB A A, HILL B G. Metabolic coordination of physiological and pathological cardiac remodeling[J]. Circ Res, 2018, 123(1):107-128.
|
| 3 |
SHIMIZU I, MINAMINO T. Physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy [J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2016, 97:245-262.
|
| 4 |
NAKAMURA M, SADOSHIMA J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2018, 15(7):387-407.
|
| 5 |
LYON R C, ZANELLA F, OMENS J H, et al. Mechanotransduction in cardiac hypertrophy and failure[J]. Circ Res, 2015, 116(8):1462-1476.
|
| 6 |
CAMICI P G, TSCHÖPE C, DI CARLI M F, et al. Coronary microvascular dysfunction in hypertrophy and heart failure[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2020, 116(4):806-816.
|
| 7 |
马 纳, 李亚静, 范吉平. 香叶木素药理作用研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2018, 20(9):214-217.
|
| 8 |
MO G L, HE Y, ZHANG X Q, et al. Diosmetin exerts cardioprotective effect on myocardial ischaemia injury in neonatal rats by decreasing oxidative stress and myocardial apoptosis[J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2020, 47(10): 1713-1722.
|
| 9 |
MEEPHAT S, PRASATTHONG P, RATTANAKANOKCHAI S, et al. Diosmetin attenuates metabolic syndrome and left ventricular alterations via the suppression of angiotensin Ⅱ/AT1 receptor/gp91phox/p-NF-κB protein expression in high-fat diet fed rats[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(4):1469-1481.
|
| 10 |
MA X W, SONG Y, CHEN C, et al. Distinct actions of intermittent and sustained β-adrenoceptor stimulation on cardiac remodeling[J].Sci China Life Sci,2011,54(6):493-501.
|
| 11 |
HANIF W, ALEX L, SU Y, et al. Left atrial remodeling, hypertrophy, and fibrosis in mouse models of heart failure[J]. Cardiovasc Pathol, 2017,30:27-37.
|
| 12 |
CHEN H H, ZHAO P, ZHAO W X, et al. Stachydrine ameliorates pressure overload-induced diastolic heart failure by suppressing myocardial fibrosis[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2017, 9(9):4250-4260.
|
| 13 |
GOLLAPUDI S K, TARDIFF J C, CHANDRA M. The functional effect of dilated cardiomyopathy mutation (R144W) in mouse cardiac troponin T is differently affected by α- and β-myosin heavy chain isoforms[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2015, 308(8): H884-H893.
|
| 14 |
PENG C, LUO X M, LI S, et al. Phenylephrine-induced cardiac hypertrophy is attenuated by a histone acetylase inhibitor anacardic acid in mice[J]. Mol Biosyst, 2017, 13(4): 714-724.
|
| 15 |
MERINO D, VILLAR A V, GARCÍA R,et al.BMP-7 attenuates left ventricular remodelling under pressure overload and facilitates reverse remodelling and functional recovery[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2016, 110(3):331-345.
|
| 16 |
YOU J Y, WU J, ZHANG Q, et al. Differential cardiac hypertrophy and signaling pathways in pressure versus volume overload[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2018, 314(3): H552-H562.
|
| 17 |
SCHÜTTLER D, CLAUSS S, WECKBACH L T,et al. Molecular mechanisms of cardiac remodeling and regeneration in physical exercise[J].Cells, 2019,8(10): E1128.
|
| 18 |
GALLO S, VITACOLONNA A, BONZANO A,et al. ERK: a key player in the pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(9): E2164.
|
| 19 |
NOMURA S, SATOH M, FUJITA T, et al. Cardiomyocyte gene programs encoding morphological and functional signatures in cardiac hypertrophy and failure [J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1):4435.
|
| 20 |
ZHANG P, HU C X, LI Y Y, et al. Vangl2 is essential for myocardial remodeling activated by Wnt/JNK signaling[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2018, 365(1): 33-45.
|
| 21 |
LI R T, YAN G J, ZHANG Q, et al. miR-145 inhibits isoproterenol-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by targeting the expression and localization of GATA6[J]. FEBS Lett, 2013, 587(12): 1754-1761.
|
| 22 |
XU W, WANG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Cardiac specific overexpression of hHole attenuates isoproterenol-induced hypertrophic remodeling through inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) signalling[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2016, 16(5): 515-523.
|
 ),Jiang LI1
),Jiang LI1