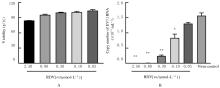
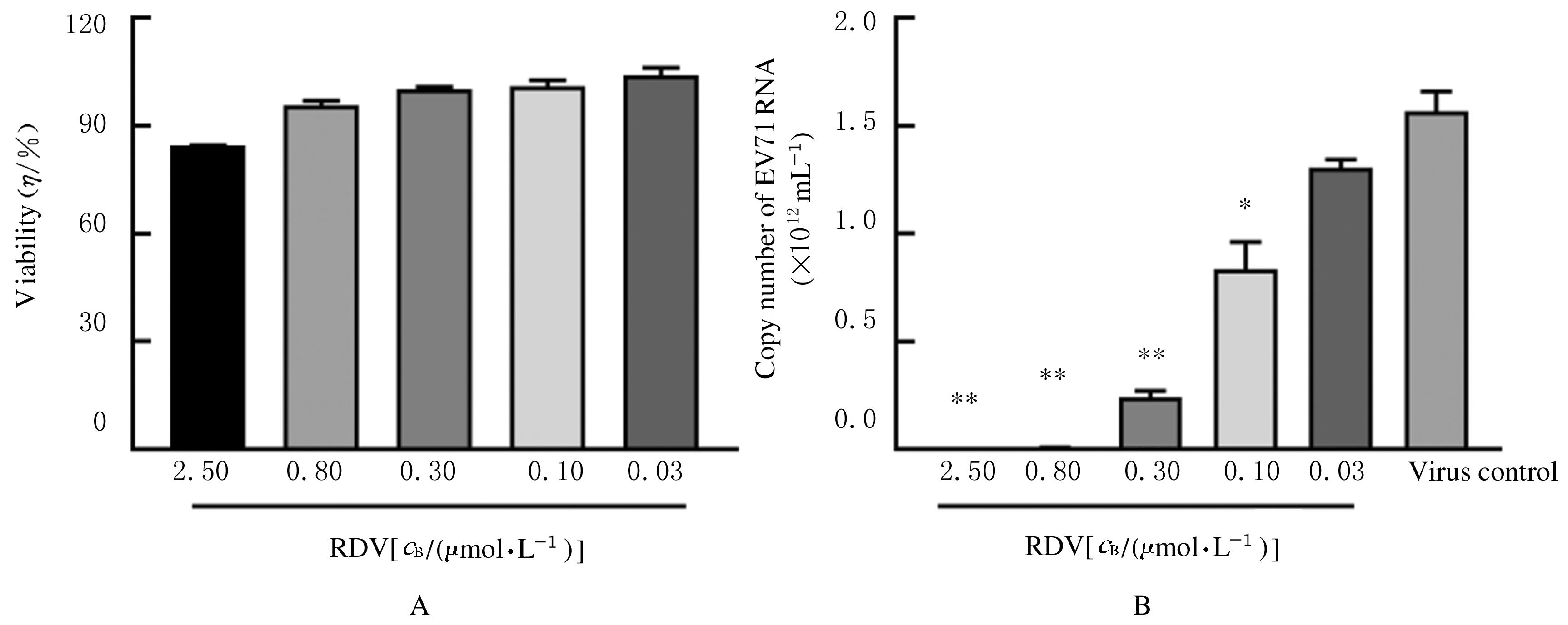
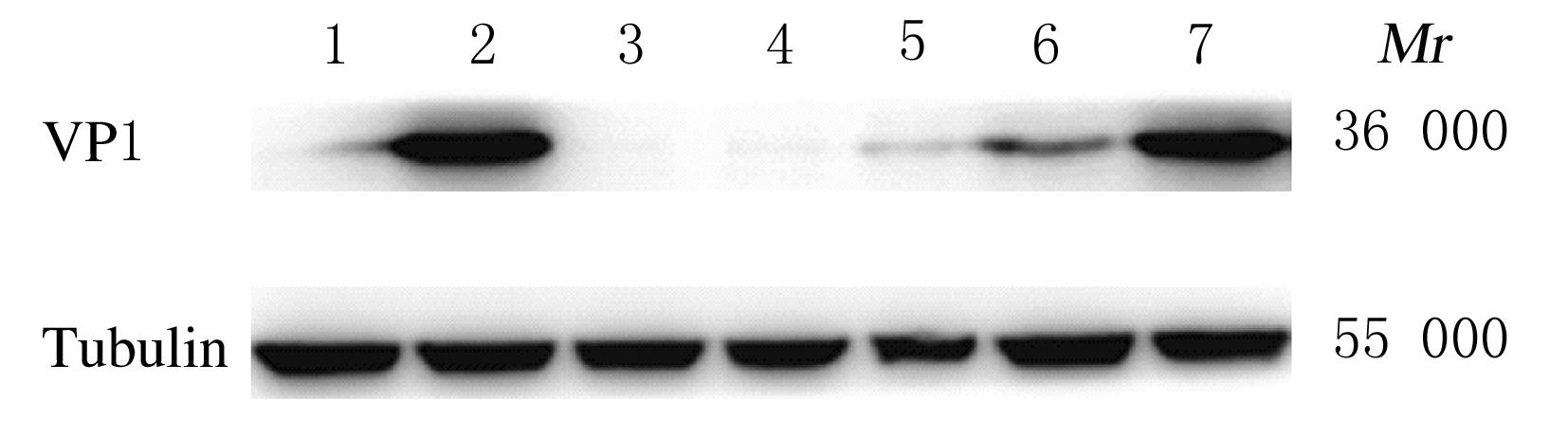
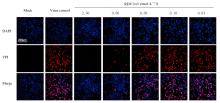
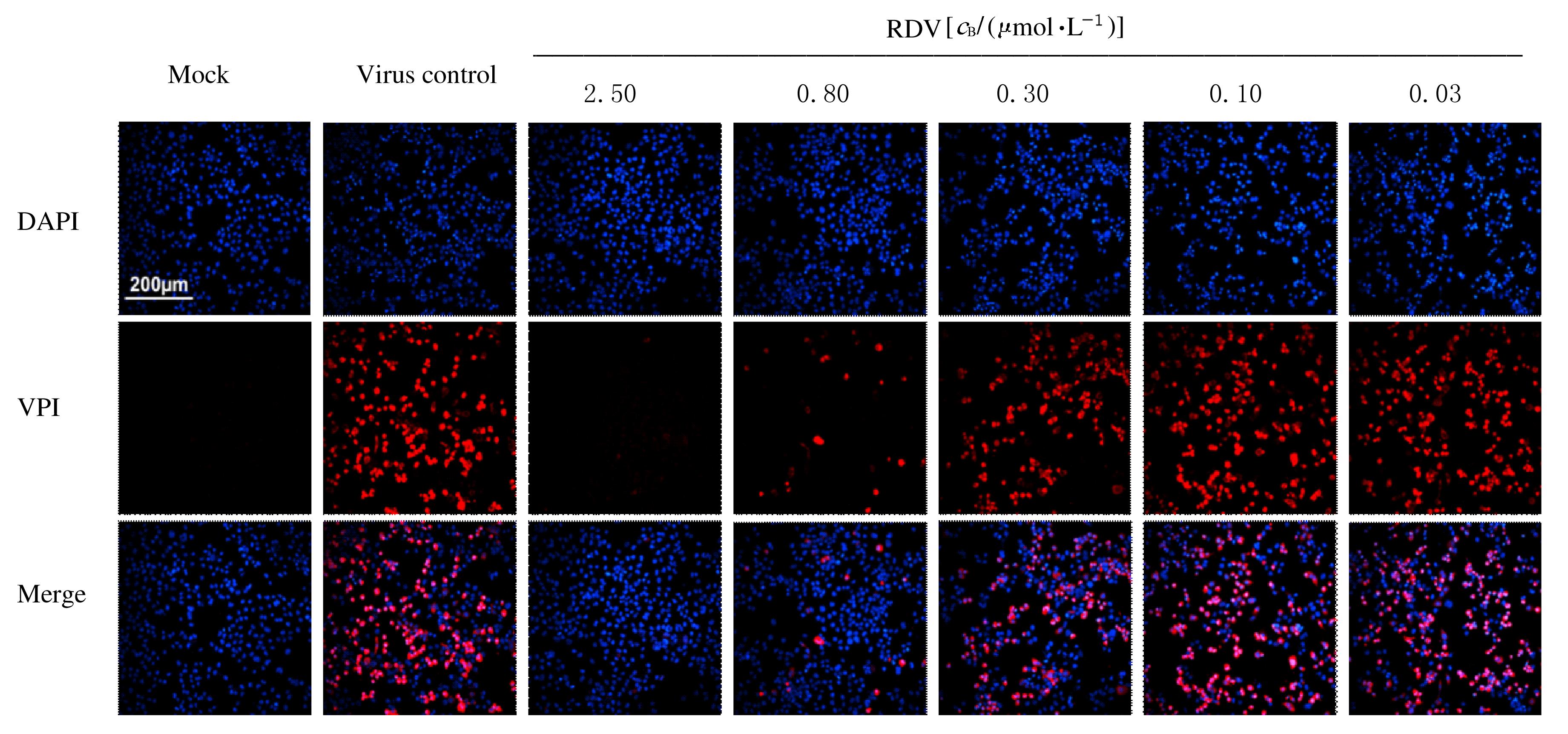
| 1 |
NG Q, HE F, KWANG J. Recent progress towards novel EV71 anti-therapeutics and vaccines[J]. Viruses, 2015, 7(12): 6441-6457.
|
| 2 |
MCMINN P C. Enterovirus vaccines for an emerging cause of brain-stem encephalitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370(9): 792-794.
|
| 3 |
ONG K C, WONG K T. Understanding enterovirus 71 neuropathogenesis and its impact on other neurotropic enteroviruses[J]. Brain Pathol, 2015, 25(5): 614-624.
|
| 4 |
OOI M H, WONG S C, LEWTHWAITE P, et al. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2010, 9(11): 1097-1105.
|
| 5 |
LEE K Y. Enterovirus 71 infection and neurological complications[J]. Korean J Pediatr, 2016, 59(10): 395-401.
|
| 6 |
WARREN T K, JORDAN R, LO M K, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys[J]. Nature, 2016, 531(7594): 381-385.
|
| 7 |
JACOBS M, RODGER A, BELL D J, et al. Late Ebola virus relapse causing meningoencephalitis: a case report[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10043): 498-503.
|
| 8 |
SHEAHAN T P, SIMS A C, GRAHAM R L, et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(396). DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653 .
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653
|
| 9 |
BROWN A J, WON J J, GRAHAM R L, et al. Broad spectrum antiviral remdesivir inhibits human endemic and zoonotic deltacoronaviruses with a highly divergent RNA dependent RNA polymerase[J]. Antiviral Res, 2019, 169: 104541.
|
| 10 |
DE WIT E, FELDMANN F, CRONIN J, et al. Prophylactic and therapeutic remdesivir (GS-5734) treatment in the rhesus macaque model of MERS-CoV infection[J]. PNAS, 2020, 117(12): 6771-6776.
|
| 11 |
WANG M, CAO R, ZHANG L, et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro [J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30(3): 269-271.
|
| 12 |
LAMB Y N. Remdesivir: first approval[J]. Drugs, 2020, 80(13): 1355-1363.
|
| 13 |
LO M K, JORDAN R, ARVEY A, et al. GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 43395.
|
| 14 |
LO M K, FELDMANN F, GARY J M, et al. Remdesivir (GS-5734) protects African green monkeys from Nipah virus challenge[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2019, 11(494). DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.aau9242 .
doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aau9242
|
| 15 |
KONKOLOVA E, DEJMEK M, HŘEBABECKÝ H, et al. Remdesivir triphosphate can efficiently inhibit the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from various flaviviruses[J]. Antiviral Res, 2020, 182: 104899.
|
| 16 |
YIN Z, CHEN Y L, SCHUL W, et al. An adenosine nucleoside inhibitor of dengue virus[J]. PNAS, 2009, 106(48): 20435-20439.
|
| 17 |
SOLOMON T, LEWTHWAITE P, PERERA D, et al. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of enterovirus 71[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2010, 10(11): 778-790.
|
| 18 |
YI E J, SHIN Y J, KIM J H, et al. Enterovirus 71 infection and vaccines[J]. Clin Exp Vaccine Res, 2017, 6(1): 4-14.
|
| 19 |
TCHESNOKOV E, FENG J, PORTER D, et al. Mechanism of inhibition of Ebola virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by remdesivir[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(4): 326.
|
| 20 |
JORDAN P C, LIU C, RAYNAUD P, et al. Initiation, extension, and termination of RNA synthesis by a paramyxovirus polymerase[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2018, 14(2): e1006889.
|
| 21 |
GORDON C J, TCHESNOKOV E P, FENG J Y,et al. The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295(15): 4773-4779.
|
| 22 |
GORDON C J, TCHESNOKOV E P, WOOLNER E, et al. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295(20): 6785-6797.
|
 ),Yonggang LI1(
),Yonggang LI1( )
)